Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mark Schemes: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC Levels
Uploaded by
Victor Barber SanchisOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mark Schemes: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC Levels
Uploaded by
Victor Barber SanchisCopyright:
Available Formats
Mark Schemes
8C
Quick Quiz
Question
Answer
Topic
Marks
Matching End of Unit Test marks
to NC levels
Level
Marks Cumulative
available
total
Suggested
threshold for
achieving level
8Ca
8Cb
8Cc
8Cd
13
13
8Ce
17
17
25
23
End of Unit Test marks
Question
Level Answer
Mark scheme
1 mark for two correct
a spots
1 mark
b5
1 mark
c 38.5 C
1 mark
d a straight line drawn across the graph at 37 C
1 mark
a P = windpipe/trachea, Q = stomach
2 marks 1 mark for each
b i microbes stick to the mucus
1 mark
ii sweep mucus up windpipe
1 mark
grow, reproduce respire, get rid of waste
8
C
2 mark for all four correct
7
7
c acid
1 mark
a the vaccine was introduced
1 mark
b an increase every six years
1 mark
c 1989
1 mark
antiseptic
1 mark
a food poisoning, tuberculosis
1 mark for both correct
b i virus; ii fungus
1 mark for both correct
a room temperature; freezer; fridge
1 mark
b the growth of bacteria in milk is slowed down
1 mark accept bacteria
stops growing but do not
accept kills bacteria
it kills them
1 mark
any two from: water, sex, animals, food, by contact,
injections/contaminated needles
1 mark
a Some remain in the blood to protect against further
infection.
1 mark
b line rises more steeply
1 mark line must start above
0 on the y-axis, no mark if
this is not the case; accept
a line that rises as steeply as
the existing line but reaches a
higher level of antibodies
Exploring Science
M03_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8C.indd 103
edition
103
Pearson Education Limited 2008
28/8/08 11:47:53
8C
Mark Schemes (continued)
Question
Level Answer
Mark scheme
10
a increasing numbers
1 mark
b antibiotic resistance or greater pollution.
1 mark also accept
immigration or poor diet
Answers to Quick Check activities
8
C
Quick
Check
Answers
8Ca
Possible questions for the answers provided are:
1 What phrase can be used to remember the seven life processes?
2 What is the word for a living thing?
3 What is another word for a microbe?
4 What are the three types of microbes?
5 What do you need to do to see microbes?
6 What is the smallest type of microbe?
7 What is an example of a large fungus?
8 What is the name of a microbe that is a one-celled fungus?
9 Why dont scientists classify viruses as living things?
10 What is the singular of bacteria?
8Cb
Made with the help of fungi: beer, Marmite, bread, wine
Made with the help of bacteria: yoghurt
Made with the help of bacteria and fungi: blue cheese, vinegar
Microbes are not used: milk, jam, carrot, chicken, fried egg.
8Cc
1 a Example answers are given in the table below
Disease
Microbe
(e.g. impetigo)
bacteria
(e.g. touch)
How it is spread
cold
viruses
(e.g. air)
(e.g. athletes foot)
fungi
(e.g. touch)
b Any two from the following, which are not in the table: e.g. water, air, sex, touch, food.
2 symptoms
3 a Pupils responses will vary (e.g. colds).
b Pupils responses will vary (e.g. malaria).
8Cd
Pupils own responses.
8Ce
Across
3 antibiotic; 8 air; 10 chlorine; 11 yeast; 13 aerobic; 15 foot; 16 viruses; 19 pasteurisation; 20 measles
Down
1 dioxide; 2 athletes; 4 infected; 5 carbon; 6 bread; 7 microbes; 9 food; 12 poisoning; 14 bacteria;
17 skin; 18 warm
Exploring Science
M03_ES_AB_Y8_5415_U8C.indd 104
edition
104
Pearson Education Limited 2008
28/8/08 11:47:54
You might also like
- Quick Quiz: Number of Yeast CellsDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: Number of Yeast CellsVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- 8g Test Mark Scheme 2008Document2 pages8g Test Mark Scheme 2008Victor Barber Sanchis57% (7)
- 8a Test Mark SchemeDocument3 pages8a Test Mark SchemeAlex Lai55% (11)
- 9c End of Unit TestDocument5 pages9c End of Unit Test박찬우67% (3)
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassHelen50% (2)
- 8gtest PDFDocument4 pages8gtest PDFleelakdd108100% (3)
- Mark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDocument1 pageMark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsSumathi Ganasen100% (1)
- 8E Quick QuizDocument3 pages8E Quick Quizlol_dj70% (10)
- 9 FtestDocument4 pages9 Ftest박찬우100% (2)
- Mark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDocument1 pageMark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsVictor Barber Sanchis20% (5)
- End of Unit Test: Name Class DateDocument6 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name Class DateVictor Barber Sanchis100% (2)
- 8k Light End of Unit TestDocument3 pages8k Light End of Unit TestUsername1833% (12)
- 9c End of Unit TestDocument5 pages9c End of Unit TestEliza Budarz0% (1)
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassSawani100% (1)
- Elements Mixtures and Compounds TestDocument3 pagesElements Mixtures and Compounds Testleelakdd10857% (7)
- 9B Quick QuizDocument2 pages9B Quick Quizameema50% (6)
- 8b TestDocument5 pages8b Testleelakdd108100% (2)
- 8k Light End of Unit Test PDFDocument3 pages8k Light End of Unit Test PDFGurdevBainesNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test (Levels 3-5) : Name - ClassDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test (Levels 3-5) : Name - ClassAmarpreet Kaur100% (1)
- 8I Fluids & 8J Light Progress CheckDocument7 pages8I Fluids & 8J Light Progress CheckL Pedley33% (3)
- 8c Summary SheetsDocument3 pages8c Summary SheetsAreeba Inam Rao80% (5)
- 9C Quick QuizDocument2 pages9C Quick Quizfitrus60% (5)
- 8 CtestDocument4 pages8 Ctestleelakdd108No ratings yet
- KS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersDocument8 pagesKS3 Sci / 8A 8E 8I Test MC AnswersPaul BurgessNo ratings yet
- Revision Quiz For Unit 7JDocument3 pagesRevision Quiz For Unit 7JJohn Osborne100% (2)
- 8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12Document20 pages8F and 8G Homework Booklet Sept & Oct 20 12leelakdd108No ratings yet
- 9 EquizDocument2 pages9 EquizEzra Loganathan Muniandi100% (1)
- 8C Summary SheetDocument2 pages8C Summary Sheet박찬우100% (2)
- End of Unit Test Higher (H) : Give Two ReasonsDocument5 pagesEnd of Unit Test Higher (H) : Give Two Reasonschan myae100% (2)
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Food and Digestion Unit TestDocument4 pagesFood and Digestion Unit Testleelakdd108100% (6)
- 9j Mark SchemeDocument2 pages9j Mark Scheme박찬우50% (4)
- Pressure and Moments Unit TestDocument3 pagesPressure and Moments Unit Test박찬우No ratings yet
- 9e End of Unit Test HigherDocument6 pages9e End of Unit Test HigherZain Ali100% (2)
- 8e Mark SchemeDocument6 pages8e Mark SchemeLamis AhmedNo ratings yet
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesYear 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemerickyNo ratings yet
- Science 9dDocument4 pagesScience 9dno100100% (1)
- 8e CombustionDocument36 pages8e CombustionMohamed HALAWA92% (12)
- 8 EmarkDocument1 page8 Emarkleelakdd108No ratings yet
- Exploring Science Active Book 8Document58 pagesExploring Science Active Book 8Raistlin Chan Ching Kit50% (2)
- 8a End of Unit Test StandardDocument8 pages8a End of Unit Test StandardAaron Joseph100% (1)
- 8F Summary SheetDocument2 pages8F Summary Sheet박찬우100% (1)
- Exploring Science Year 8 Summary Sheets NBNBDocument25 pagesExploring Science Year 8 Summary Sheets NBNBHelen100% (1)
- 8itest PDFDocument4 pages8itest PDFleelakdd10833% (3)
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008shazia imamNo ratings yet
- Year 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark SchemeDocument4 pagesYear 8 - Food and Digestion and Respiration Mark Schemesaffyk780% (5)
- Respiration and microbes documentsDocument5 pagesRespiration and microbes documentsbhumika mehta100% (1)
- End of Unit Test Standard (S) : A Fertilisation B FloweringDocument5 pagesEnd of Unit Test Standard (S) : A Fertilisation B FloweringBeedu Avengers100% (3)
- Fertilisation Seed DispDocument1 pageFertilisation Seed Dispazhar100% (1)
- Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each QuestionDocument2 pagesQuick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Questionameema100% (2)
- 8J Summary SheetDocument2 pages8J Summary Sheet박찬우No ratings yet
- Quick Quiz: © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForDocument3 pagesQuick Quiz: © Pearson Education LTD 2019. Copying Permitted ForBesty Maranatha100% (1)
- End of Unit Test: Name ClassDocument3 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name ClassAFuentesCaballero67% (3)
- Secret FolderDocument6 pagesSecret FolderAnonymous B19kxiYN6SNo ratings yet
- Burning Fuels: I CanDocument5 pagesBurning Fuels: I CanAddy The human100% (1)
- Bacterial Growth Answer SheetDocument3 pagesBacterial Growth Answer SheetKENT BENEDICT PERALESNo ratings yet
- 1.d 2.d 3.a 4.c 5.a 6.c 7.c 8d. 9.d 10. B: Answer Key For MCQ MicrobiologyDocument9 pages1.d 2.d 3.a 4.c 5.a 6.c 7.c 8d. 9.d 10. B: Answer Key For MCQ Microbiologymenah ayyashNo ratings yet
- Scribd Upload A Document Search DocumentsDocument58 pagesScribd Upload A Document Search DocumentsrjleuwolNo ratings yet
- Quiz MicrobiologyDocument66 pagesQuiz MicrobiologySohail ChoudhreyNo ratings yet
- The Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualFrom EverandThe Fundamentals of Scientific Research: An Introductory Laboratory ManualNo ratings yet
- Summary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesDocument2 pagesSummary Sheets: Compounds and MixturesVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Mark Scheme: Science TestsDocument64 pagesMark Scheme: Science TestsVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Mark Schemes: Quick Quiz 1 Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDocument3 pagesMark Schemes: Quick Quiz 1 Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsVictor Barber Sanchis60% (10)
- Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesExploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Es8 Asp G QQ 3Document2 pagesEs8 Asp G QQ 3sureshthevanNo ratings yet
- Mark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsDocument1 pageMark Schem Es: Quick Quiz Matching End of Unit Test Marks To NC LevelsVictor Barber Sanchis20% (5)
- Quick Quiz: Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Document2 pagesQuick Quiz: Exploring Science Edition © Pearson Education Limited 2008Victor Barber Sanchis50% (2)
- Prix Passionnés de Livre: French ReadingchallengeDocument1 pagePrix Passionnés de Livre: French ReadingchallengeVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Prix Passionnés de Livres: Read, Enjoy and Vote!Document4 pagesPrix Passionnés de Livres: Read, Enjoy and Vote!Victor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 8g 2008Document2 pagesQuiz 2 8g 2008Victor Barber Sanchis100% (1)
- CHAPTER 6 y 7 Animal FarmDocument1 pageCHAPTER 6 y 7 Animal FarmVictor Barber SanchisNo ratings yet
- End of Unit Test: Name Class DateDocument6 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name Class DateVictor Barber Sanchis100% (2)
- End of Unit Test: Name Class DateDocument4 pagesEnd of Unit Test: Name Class DateVictor Barber Sanchis100% (1)
- Adult and Paediatric Oral/nasal suction guidelinesDocument13 pagesAdult and Paediatric Oral/nasal suction guidelinesRuby Dela RamaNo ratings yet
- Fowl Pox and Avian Influenza in PoultryDocument17 pagesFowl Pox and Avian Influenza in PoultryUsman KhalidNo ratings yet
- Mechanical Ventilator GuideDocument3 pagesMechanical Ventilator GuideDivine Mercy De JulianNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Sevilla C. Yobueno, Ph.D. SPAMAST Malita Campus I. Cells, Tissues and MembranesDocument5 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Lecture Notes Sevilla C. Yobueno, Ph.D. SPAMAST Malita Campus I. Cells, Tissues and MembranesReuben EscarlanNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument6 pagesRespiratory SystemCraigNo ratings yet
- Respiratory SystemDocument5 pagesRespiratory Systemshahirah77No ratings yet
- KS3 Science Revision WorksheetsDocument104 pagesKS3 Science Revision WorksheetsSofia M Vigo Aguiar100% (5)
- Anatomical and Physiological Differences Between Children and AdultsDocument13 pagesAnatomical and Physiological Differences Between Children and AdultsShubham KathareNo ratings yet
- Practice 1 - m29Document10 pagesPractice 1 - m29khanh duongNo ratings yet
- ATLS Practice Test 3 Answers & ExplanationsDocument10 pagesATLS Practice Test 3 Answers & ExplanationsCarl Sars100% (1)
- 90 TOP THORACIC SURGERY Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF 2018Document28 pages90 TOP THORACIC SURGERY Multiple Choice Questions and Answers PDF 2018Ahmed Kassem0% (1)
- College of Nursing & Allied Health Sciences Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte, PhilippinesDocument68 pagesCollege of Nursing & Allied Health Sciences Tunga-Tunga, Maasin City, Southern Leyte, PhilippinesAgent PimpNo ratings yet
- Ch31 TracheaDocument27 pagesCh31 TracheaLajja Parikh PatelNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemDocument3 pagesAnatomy and Physiology: Human Respiratory SystemVin EighteenthNo ratings yet
- Assisting For Endotracheal IntubationDocument16 pagesAssisting For Endotracheal IntubationSREEDEVI T SURESH100% (1)
- Lung AuscultationDocument62 pagesLung AuscultationOlea CroitorNo ratings yet
- Analgesia and Anesthesia in BirdDocument51 pagesAnalgesia and Anesthesia in BirdCynthia GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Grade 9-Summative AssessmentDocument2 pagesGrade 9-Summative AssessmentMaryjoy Piosca MolaNo ratings yet
- Chapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Document7 pagesChapter10. Class 10th (Page7)Abdus samiNo ratings yet
- Enjoy: Revisf OmDocument263 pagesEnjoy: Revisf OmEtinah ChevureNo ratings yet
- SME - 9 Gas ExchangeDocument22 pagesSME - 9 Gas Exchangekisepe6738No ratings yet
- R v. Kirikiri, (1982) 2 NZLR 648Document4 pagesR v. Kirikiri, (1982) 2 NZLR 64813No ratings yet
- Alterations in OxygenationDocument104 pagesAlterations in OxygenationMelchor Felipe Salvosa100% (1)
- Autologous Tracheal Replacement Surgical Technique 2018 Thoracic Surgery CLDocument9 pagesAutologous Tracheal Replacement Surgical Technique 2018 Thoracic Surgery CLEdgar ForeroNo ratings yet
- Brain Death AANDocument2 pagesBrain Death AANFabián Esteban Maturana Barra100% (1)
- 1st Periodic Test Grade Five W/ TosDocument19 pages1st Periodic Test Grade Five W/ TosReynaldo B. Lapak100% (7)
- Case Study On Status AsthmaticusDocument129 pagesCase Study On Status AsthmaticusLouie MansaNo ratings yet
- The Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AliveDocument14 pagesThe Cells of The Human Body Require A Constant Stream of Oxygen To Stay AlivePeperoniiNo ratings yet
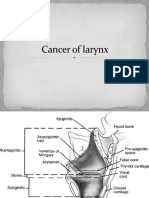
- Cancer of LarynxDocument46 pagesCancer of LarynxVIDYANo ratings yet
- Applied Surgical Anatomy of The Larynx and TracheaDocument24 pagesApplied Surgical Anatomy of The Larynx and TracheaMihaNo ratings yet