Professional Documents
Culture Documents
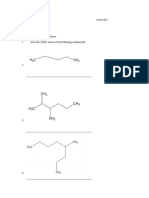
Chapter # 01 Getting Started
Uploaded by
Muhammad Shakaib QureshiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter # 01 Getting Started
Uploaded by
Muhammad Shakaib QureshiCopyright:
Available Formats
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Chapter # 01
Getting Started
Organic chemistry is all around us. All organic compounds contain the element carbon. More
than 10 million organic compounds are known today.
There are two main classes of chemical compounds, inorganic and organic. More than a
century ago all substances then known are classified on the basis of source from which they
were derived. The compounds which were mineral origin were known as Inorganic and
those of vegetable or animals origin were called Organic. For example tablet salt, marble
etc. whereas acetic acid (from vinegar), alcohol (from wine), tartaric acid (from grapes),
citric acid (from lemons) and sucrose (from sugarcane) were organic.
It was assumed that organic compounds could be produced only by living matter, for living
matter was thought to possess a Vital force. As long as this concept prevailed no effort was
made to produce organic compounds in the laboratory, and the Vital force theory long went
unchallenged.
In 1828, the German chemist wholer heat ammonium cynate, derived from inorganic
substances, and obtained the organic compound compound urea.
Definition of Organic Chemistry:
organic chemistry is that branch of chemistry which deals with the study of compounds of
carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbon) and their derivatives
Some features of organic compounds.
1. Peculiar nature of carbon
Carbon forms a large number of compounds. There are millions of organic compounds.
The main reason for such a large number of compounds is its unique property of linking
with other carbon atoms to form long chains or rings. This self linking property of carbon
is called Catenation.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Non-Ionic character of organic compounds
Complexity of organic compounds
They shows isomerism
Slow rate of reaction
_____________________________________________________________________________________
1
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
6. Insoluble in water
Classification of Organic Chemistry
Alkane;
An alkane, or paraffin is a saturated hydrocarbon. Alkanes consist only of
hydrogen and carbon atoms, all bonds are single bonds, and the carbon atoms are not
joined in cyclic structures but instead form an open chain. They have the general chemical
formula CnH2n+2.
Alkene:
An alkene, olefin, or olefine is an unsaturated chemical compound containing
at least one carboncarbon double bond. The simplest acyclic alkenes, with only one double
bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of
hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n
Alkynes:
An alkyne is an unsaturated hydrocarbon which has at least one carbon
carbon triple bond between two carbon atoms. The simplest acyclic alkynes with only one
_____________________________________________________________________________________
2
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
triple bond and no other functional groups form a homologous series with the general
chemical formula CnH2n-2.
Aromatics: The term aromatics compounds stands for the whole series of compounds
which contain one or more benzene rings in their molecule. With the introduction of the
new name of Arenes for all aromatics hydrocarbons (Benzene, naphthalene, Anthracene,
etc) the precise definition of aromatics compounds is Arenes and their derivatives.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
3
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Functional Group
It is defined as a particular atom or a group of atoms which is responsible for the properties
of
compound
where
it
is
present
or
A functional group is an atom or group of atoms in a molecule that gives the molecule its
characteristics chemical properties
_____________________________________________________________________________________
4
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Difference between organic and inorganic properties
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
Organic
Low melting point
Low boiling point
Low solubility in water, high solubility
in non-polar solvent
Flammable
Solutions are non conductors of
electricity
Exhibit covalent bond
Exhibit isomerism
8. Chemical reaction are slow
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
Inorganic
High melting point
High boiling point
High solubility in water, low solubility
in non-polar solvent
Nonflammable
Solutions are conductors of electricity
6. Exhibit ionic bonding
7. Isomers are limited to few exception
(e.g transition elements)
8. Chemical reaction are fast
Source of Organic Compound
Historically, has be mentioned, all organic compounds at one time came from plants or
animals. Many of our most important substances are still derived from these source directly
or indirectly.
1. Plant and animals; Many organic compounds are obtained directly from plant and
animals source by suitable methods of isolation. A few examples are
a. Carbohydrate (cellulose, sugars, starch)
b. Proteins (silk, wool, casein, food protien)
c. Fats and oils (cottonseed, soyabean oils)
d. Vitamins, flavor, resins etc
2. Natural gas and Petroleum; It is the major source of organic compounds, these are
mainly used as a fuel, and also synthetic organic compounds which we use in our
daily life.
3. Coal; Coal is another major source of organic compounds. It yields coke and coal tar
on pyrolysis or destructive distillation. More than 200 organic compounds have been
directly isolated from coal tar.
4. Fermentation;
Fermentation is defined as ythe production of chemicals by the
action of micro organisms. By employing appropriate organisms hosts of useful
substances are produced including alcohols, acids, vitamins and antibodies.
5. Synthesis:
Simple organic compounds derived from petroleum, or coal have been
converted into thousands of useful materials by synthetic methods. Synthetic
materials are dyes, rubber, fibers, plastics, drugs, papers etc.
_____________________________________________________________________________________
5
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
Petroleum Technical Training Institute Khairpur Mirs
Organic Chemistry
[CHT-244]
_____________________________________________________________________________________
Application of Organic compounds
1.Preservatives - citric acid, sodium benzoate are only two of many.
2.Drugs, including antibiotics - aspirin, acetaminophen, prozac, birth control, etc. are ALL
organic
molecules.
3.Plastics - the building blocks that compose plastic are organic molecules, and plastics are
long,
long
chains
of
organic
molecules
linked
together.
4.Flavorings in food - what we taste are the organic compounds interacting with our taste
buds.
5.Scents - perfumes and food - anything we detect with our nose is an organic compound
interacting
with
receptors
in
our
nose
6.Fuel - gasoline for cars and oil for their engines are both organic compounds.
7.Pesticides - most pesticides are organic molecules that have neurotoxic properties to
insects.
8.Food coloring and color - organic molecules are the cause of color in food colorings
9.Vitamins - vitamins are organic molecules. Usually we need them because they help our
body do the chemical reactions it needs to do and contributes to the building blocks that our
cells
and
parts
need
to
stay
healthy.
10.Cosmetics - look at the label of any makeup or nail product - all those compounds are
organic compounds most of the time, mostly (mica and titanium dioxide are examples of
things that are not organic).
_____________________________________________________________________________________
6
Compiled by:
Muhammad Shakaib Qureshi
You might also like
- Organic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsFrom EverandOrganic Chemistry Decoded: Master Orgo with Step-by-Step SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Chapter-5 Coal and Petroleum: Let's LearnDocument3 pagesChapter-5 Coal and Petroleum: Let's LearnNilay SahNo ratings yet
- Basic Science Work Book 1Document64 pagesBasic Science Work Book 1Arezoo ZargollNo ratings yet
- Kami Export - Angelina Lopez - Cellular Respiration Notes 10.20.17Document2 pagesKami Export - Angelina Lopez - Cellular Respiration Notes 10.20.17angelina.lopez248No ratings yet
- 5 0 Biogeochemical CyclingDocument7 pages5 0 Biogeochemical Cyclingapi-222503660No ratings yet
- Biomolecules Packet 2011Document6 pagesBiomolecules Packet 2011Nidhi Sisodia100% (1)
- A Novel and Cost-Effective H2S Removal Technology Using Tire Derived Rubber ParticlesDocument93 pagesA Novel and Cost-Effective H2S Removal Technology Using Tire Derived Rubber Particlesscm996No ratings yet
- Transport and Excretion Worksheet 2Document2 pagesTransport and Excretion Worksheet 2KelslieNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Guide: Episode 601 NameDocument6 pagesNote Taking Guide: Episode 601 NameKaya SNo ratings yet
- Build and Break Down MacromoleculesDocument4 pagesBuild and Break Down MacromoleculesDivineDoctorNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument3 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesJeon JungkookNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pagesAerobic Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- ZOOT 53 Final Examination IdentificationDocument3 pagesZOOT 53 Final Examination IdentificationMyrrh Oliver CasinabeNo ratings yet
- 2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument4 pages2.2.4 Photosynthesis WorksheetHo Thi Phuong Oanh0% (1)
- College Organic Chemistry Semester I: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandCollege Organic Chemistry Semester I: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2: Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesGeneral Biology 2: Biological Moleculesjosh Dez100% (1)
- The Functional Groups: Can You See Me?Document4 pagesThe Functional Groups: Can You See Me?coalie galaxyNo ratings yet
- Bt102 Past PapersDocument69 pagesBt102 Past PapersAlishba khanNo ratings yet
- Sample Biology ExercisesDocument13 pagesSample Biology ExercisesJasmine Bardoles0% (1)
- 2nd Year Chemistry CH # 8Document23 pages2nd Year Chemistry CH # 8Sohail AfzalNo ratings yet
- Afset Abstract Papers ListDocument83 pagesAfset Abstract Papers ListVishal SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Botany - BiomoleculesDocument9 pagesBotany - BiomoleculesP JagadeeswariNo ratings yet
- Chapter 9 Carbon ChemistryDocument6 pagesChapter 9 Carbon Chemistryapi-30718309No ratings yet
- WS 5 IG I Chemistry REACTING MASSES AND CHEMICALDocument4 pagesWS 5 IG I Chemistry REACTING MASSES AND CHEMICALRaj MalkanNo ratings yet
- Nomen CrimDocument4 pagesNomen CrimLeon Antonio VejeranoNo ratings yet
- Bio Molecules WorksheetDocument5 pagesBio Molecules WorksheetAngelica Mianarken DiolataNo ratings yet
- O Level ChemistryDocument4 pagesO Level ChemistryMaryamNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5 PDFDocument3 pagesExperiment 5 PDFJoone Xyron Creencia0% (1)
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheeterikabeltranNo ratings yet
- CH 6-4 NotesDocument2 pagesCH 6-4 Notesapi-342334216No ratings yet
- BiomoleculeworksheetDocument2 pagesBiomoleculeworksheetkatherine corveraNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis WorksheetDocument5 pagesPhotosynthesis Worksheetapi-2428686900% (1)
- Student Exploration: Cell Energy CycleDocument5 pagesStudent Exploration: Cell Energy Cyclevaleli123No ratings yet
- Cape Biology Unit 1Document3 pagesCape Biology Unit 1krypleNo ratings yet
- Cycles WorksheetanswersDocument2 pagesCycles Worksheetanswersah2504525No ratings yet
- Bio Molecule Review WorksheetDocument4 pagesBio Molecule Review WorksheetMa.Janice GarciaNo ratings yet
- A2.1 NotesDocument10 pagesA2.1 NotesteddyenNo ratings yet
- K G K SCH a2VudG9uLmphbnplbkBteXBsYWNlLndjcy5lZHU Copy of 2023 Biology Fall Exam Review ParDocument8 pagesK G K SCH a2VudG9uLmphbnplbkBteXBsYWNlLndjcy5lZHU Copy of 2023 Biology Fall Exam Review Parbrittendaniel13No ratings yet
- Chapter 5 NotesDocument7 pagesChapter 5 NotesshamptonNo ratings yet
- May Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3Document8 pagesMay Pen High School Mid Term Exam: Integrated Science Form 3CHRISTOPHER SCALENo ratings yet
- Waste OilDocument208 pagesWaste OilMasita MohammadNo ratings yet
- 08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesDocument8 pages08 Lion Elephant Energy From MacromoleculesJonghyun (Justin) YangNo ratings yet
- Chapter 40 Notebook QuestionsDocument5 pagesChapter 40 Notebook QuestionsKyle DiseNo ratings yet
- Exam LeakDocument7 pagesExam LeakVenz Lei Collyn Atis EsinNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Cellular LevelDocument6 pagesWeek 2 Cellular LevelDayledaniel SorvetoNo ratings yet
- 2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetDocument7 pages2.2.5 Respiration WorksheetSherisa100% (1)
- ECOLOGY TEST CLASS IVDocument2 pagesECOLOGY TEST CLASS IVNisha SinghNo ratings yet
- Unit I. Biomolecules, Respiration and Metabolism Free Radicals and Oxidative StressDocument11 pagesUnit I. Biomolecules, Respiration and Metabolism Free Radicals and Oxidative StressAngie CaragNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes ExplainedDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Notes ExplainedLelaNo ratings yet
- Energy Fossil Fuels Fracking StudentDocument5 pagesEnergy Fossil Fuels Fracking Studentcnobis85No ratings yet
- Dairy Chapter 1 PDFDocument76 pagesDairy Chapter 1 PDFSteven LiberatoNo ratings yet
- E.Sci9 - Q2 - Week 6Document10 pagesE.Sci9 - Q2 - Week 6HersheyNo ratings yet
- Worksheet Biological MoleculesDocument5 pagesWorksheet Biological MoleculesЕгор БиндерNo ratings yet
- Current Affairs November 2020: VisionDocument95 pagesCurrent Affairs November 2020: VisionAnvin C MathewNo ratings yet
- AP Biology Cellular Energetics Activity #4Document16 pagesAP Biology Cellular Energetics Activity #4cgrossNo ratings yet
- Sterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsFrom EverandSterling Test Prep College Organic Chemistry Practice Questions: Practice Questions with Detailed ExplanationsNo ratings yet
- Cracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionDocument1 pageCracking Hydrocarbons Practice QuestionZhering RodulfoNo ratings yet
- 0807 Model Answers Winter 2015Document23 pages0807 Model Answers Winter 2015mahesh korde100% (1)
- Biogeochemical Cycles ReviewDocument3 pagesBiogeochemical Cycles ReviewwhatdayasayNo ratings yet
- Dual BurnerDocument8 pagesDual Burnergintosaju_792849166No ratings yet
- Your School Name City Name: Chemistry Project FileDocument13 pagesYour School Name City Name: Chemistry Project FileDeepak RawatNo ratings yet
- GP-017A General Permit For Boilers and Heaters Each Less Than 5 MMBTUhDocument38 pagesGP-017A General Permit For Boilers and Heaters Each Less Than 5 MMBTUhC ConleyNo ratings yet
- Stoichiometric CombustionDocument3 pagesStoichiometric CombustionKhairil MunawirNo ratings yet
- Ice 216 175C 1198Document89 pagesIce 216 175C 1198jleonosNo ratings yet
- Refining Crude Oil History, Process and ProductsDocument4 pagesRefining Crude Oil History, Process and ProductsdevifakeNo ratings yet
- Oil Level Sensor - Remove&InstallDocument3 pagesOil Level Sensor - Remove&InstallicoNo ratings yet
- Properties and Characteristics of Liquid FuelsDocument18 pagesProperties and Characteristics of Liquid FuelsTin Aung Kyi100% (2)
- Miller Cycle Engine ExplainedDocument2 pagesMiller Cycle Engine Explaineddzh513No ratings yet
- IOCL ProjectDocument32 pagesIOCL ProjectYuuvraj SinghNo ratings yet
- Nissan Diesel Engine PartsDocument8 pagesNissan Diesel Engine PartsMejia A. Diego25% (4)
- AA Agilent Preinstalation ManualDocument78 pagesAA Agilent Preinstalation ManualAnoba LabNo ratings yet
- Dodge Dakota 2003 Service-Repair-Manual-FREE-PDF-DOWNLOADDocument80 pagesDodge Dakota 2003 Service-Repair-Manual-FREE-PDF-DOWNLOADsen til100% (1)
- PEOC FILTER Wound Pure Precision Wound ElementsDocument2 pagesPEOC FILTER Wound Pure Precision Wound ElementspapashoNo ratings yet
- Study 181 Full Report PDFDocument112 pagesStudy 181 Full Report PDFKarahan YanikNo ratings yet
- Pyrolysis Plants Convert Plastic Waste to FuelsDocument27 pagesPyrolysis Plants Convert Plastic Waste to FuelsPraveen D JadhavNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 SC 54Document5 pagesCHAPTER 1 SC 54David ChangNo ratings yet
- Nota KimiaDocument18 pagesNota KimiaAzmi Bin A Matali100% (1)
- Chapter 5 and 6 AnswersDocument7 pagesChapter 5 and 6 AnswerscbseiscNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Oil RefineryDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Oil Refineryvenkatrangan2003No ratings yet
- Modine InstallDocument24 pagesModine InstallJoseph ShmoeNo ratings yet
- KLM Design SpecificationsDocument12 pagesKLM Design Specificationsijaz fazilNo ratings yet
- Srinivas Institute of Technology: Ranganatha Y H Asst. Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Sub. Code:15ME662Document36 pagesSrinivas Institute of Technology: Ranganatha Y H Asst. Professor Department of Mechanical Engineering Sub. Code:15ME662raghurockramNo ratings yet
- California Proposition 65 WarningDocument45 pagesCalifornia Proposition 65 WarningJORGE ARMANDO CARRASCO TICLLENo ratings yet
- Prioritizing Causes of Fire, Explosion in External Floating Roof TanksDocument15 pagesPrioritizing Causes of Fire, Explosion in External Floating Roof TanksPankaj Singh ChauhanNo ratings yet
- ReciprocatingDocument103 pagesReciprocatingmahesh100% (2)
- Hammer Union PresentationDocument17 pagesHammer Union PresentationDaniel100% (1)
- ST441manual SpecDocument5 pagesST441manual SpecK'atheryne BeelenNo ratings yet
- M09 PDFDocument38 pagesM09 PDFAdrian GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Natural GasDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Natural GasArjunAsjNo ratings yet