Professional Documents
Culture Documents
13.1 WCDMA Channel Structure
Uploaded by
Kamal ChauhanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
13.1 WCDMA Channel Structure
Uploaded by
Kamal ChauhanCopyright:
Available Formats
Version 0 Revision 1
JTO PH II (3G) Ericsson
13. WCDMA CHANNEL STRUCTURE
WCDMA UPLINK AND DOWNLINK CHANNELS
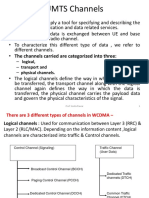
A channel represents the logical connection between the UE and
the Radio Access Network. They are physically represented by a
Chanellisation code used between the RBS and UE. They are
controlled, however, by the RNC along with the rest of the radio
resources. We have three different types of channels, with each
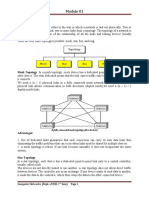
type being mapped into the next as shown in Figure 4-19.
What am I transporting?
User Data or Control Data
To whom am I transporting?
Dedicated or Common
e.g. DCCH,
DTCH, BCCH
Logical
Transport
e.g. BCH, PCH,
FACH, RACH,
HS-DSCH
Physical
One physical channel uses 1 Channelisation code
Figure 4-19: WCDMA Channel Types
LOGICAL CHANNELS
Logical channel types refer to the type of information being transmitted,
and are classified into two groups:
Control channels for the transfer of control information
Traffic channels for the transfer of user information.
A brief description of the logical channels found in the
uplink
and downlink now follows:
The Broadcast Control Channel (BCCH) is a downlink
channel for broadcasting system information.
Paging Control Channel (PCCH) is a downlink channel that
transfers paging information and is used when the UE is in idle
mode.
The Common Control Channel (CCCH) is a bi-directional
channel that transfers control information between the network
BRBRAITT, Jabalpur, Issued in SEPT-2009
-
13-1
and UE. This channel is used by the UE needs to access
the
network.
The Dedicated Control Channel (DCCH) is a point-to-point
bi-directional
channel that transmits dedicated
control information between UE and the network. This
channel is established through a RRC connection setup
procedure.
The Dedicated Traffic Channel (DTCH) is a point-to-point
channel, dedicated to one UE, for transferring user information.
TRANSPORT CHANNELS
A transport channel is defined by how, and with what
characteristics, data is transferred over the air interface. There are
two types of transport channels:
1
Common channels
Dedicated channels.
Common channels are broadcast to everyone in the cell,
whereas
dedicated channels are transmitted and received from one user
only. A brief description of some of the transport channels
now follows:
There is one dedicated transport
Channel (DCH), which is used
uplink. The DCH is set-up for
session, and characterized by the
change and fast power control.
The Broadcast channel (BCH) is a downlink transport channel
that is used to broadcast system and cell specific information,
in System information blocks. The BCH is always transmitted
over the entire cell (to both active and idle UEs) with a
low
fixed bit rate.
The Forward Access Channel (FACH) is a downlink
transport channel that carries control information to UEs when
a random access message has been sent by the UE to the base
station. Its counterpart, the Random Access channel
(RACH) is used in the uplink to send in the random access
message from the UE.
BRBRAITT, Jabalpur, Issued in FEB-2009
channel, the Dedicated
in both downlink and
a voice call of data
possibility of fast rate
13-2
The High Speed Downlink Shared Channel (HS-DSCH) is a
common transport channel shared by all the HSDPA users
in the cell.
It is mapped onto up to 15 physical
channels, depending on the number of codes available for
PHYSICAL CHANNELS
Transport channels are further mapped onto physical channels,
which are defined by channelisation codes, and the Radio
Frequency at which they are broadcast.
Common Downlink Physical Channels:
In this section we take a brief look at the function of the common
downlink physical channels, which are transmitted to all UEs.
The Primary Common Control Physical Channel (PCCPCH): Broadcasts system information.
The
Broadcast
channel is the transport channel that maps onto this physical
channel.
Synchronization Channel (SCH) carries the primary
and secondary Synchronization Codes, which are used for
slot synchronization, frame synchronization and the detection
of the scrambling code group (one out of 64). It is time
multiplexed
(only first 10%) with the P-CCPCH (remaining 90% of
timeslot).
Secondary Common Control Physical Channel (S-CCPCH):
This channel is mapped to by both the Paging Channel (PCH)
and the Forward Access Channel (FACH). Transmits idlemode signaling and control information to UE. Can also
be used for sending short infrequent data.
Common Pilot Channel (CPICH): Sends the scrambling code
of the cell. Provides coherent phase reference for DL channels
and aids channel estimation (handover and cell selection). It is
used in open loop power control to gauge the initial
Common Uplink Physical Channels:
Physical Random Access Channel (PRACH): This channel is
used to carry access requests; control information and short data
bursts. It uses only Open-loop power control and contains therefore
no pilot or TPC bits.
BRBRAITT, Jabalpur, Issued in FEB-2009
13-3
You might also like
- Channel in LTE: Logical ChannelsDocument4 pagesChannel in LTE: Logical Channelskartik sharmaNo ratings yet
- Channel in LTEDocument4 pagesChannel in LTEkartik sharmaNo ratings yet
- 3G LTE Channel TypesDocument3 pages3G LTE Channel TypesAvneesh DubeyNo ratings yet
- LTE ChannelsDocument5 pagesLTE ChannelsBromand TurkmaniNo ratings yet
- 3 ChannleDocument5 pages3 Channlemohammed aliNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Network Physical Layer ProceduresDocument6 pagesWCDMA Network Physical Layer ProceduresAmit BasraNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaaslamsatnaNo ratings yet
- LTE Logical Channels (What Info is TransferredDocument13 pagesLTE Logical Channels (What Info is TransferredAnshul GuptaNo ratings yet
- LTE Protocol Stack Layers ExplainedDocument13 pagesLTE Protocol Stack Layers ExplainedDhyanendra SinghNo ratings yet
- LTE Channels - P-WPS OfficeDocument5 pagesLTE Channels - P-WPS OfficeEsam SamNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackDocument10 pagesTutorial: Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3G/UMTS Protocol StackbyamokeshNo ratings yet
- Wcdmachannels 130219233911 Phpapp02Document19 pagesWcdmachannels 130219233911 Phpapp02Muhammad JunaidNo ratings yet
- LTE Channels Explained: Logical, Transport and Physical ChannelsDocument8 pagesLTE Channels Explained: Logical, Transport and Physical ChannelsFajar Aditya WNo ratings yet
- LTE ChannelDocument11 pagesLTE ChannelNam Song Hau CTONo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Data ChannelsDocument5 pages3G UMTS Data ChannelsJoana FalcãoNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Channel StructuresDocument3 pages3G UMTS Channel StructuresVishalNo ratings yet
- 3G Channel StructuresDocument3 pages3G Channel StructureshamidboulahiaNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channel ConceptDocument18 pagesWcdma Channel Conceptneelachal100% (1)
- UMTS Channels: Logical, Transport and Physical ExplainedDocument4 pagesUMTS Channels: Logical, Transport and Physical ExplainedDiwakar MishraNo ratings yet
- Understanding UMTS/WCDMA ChannelsDocument3 pagesUnderstanding UMTS/WCDMA Channelslimtiongvi100% (1)
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaMostafizaktelNo ratings yet
- Wcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesWcdma Channels: by - Manish SrivastavakikirnNo ratings yet
- WcdmaDocument3 pagesWcdmaSangeen AliNo ratings yet
- MAC in Umts ProtocolsDocument10 pagesMAC in Umts ProtocolsQasim Abbas AlviNo ratings yet
- 05 - LTE FDD and TDD Mode - Radio Channel Types - PPT PDFDocument14 pages05 - LTE FDD and TDD Mode - Radio Channel Types - PPT PDFAhmed GadNo ratings yet
- WCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDocument26 pagesWCDMA Channels & Channel SwitchingDee OyeNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Data Channels: Physical Logical TransportDocument6 pages3G UMTS Data Channels: Physical Logical TransportRoland Nnadi100% (1)
- Umts Wcdma ChannelsDocument3 pagesUmts Wcdma ChannelsCaring PankajNo ratings yet
- By - Manish SrivastavaDocument19 pagesBy - Manish SrivastavaRahul DubeyNo ratings yet
- RRC, Logical Channels, Transport Channels and Physical Channels in WCDMADocument19 pagesRRC, Logical Channels, Transport Channels and Physical Channels in WCDMARitesh RanjanNo ratings yet
- Channel Mapping LTEDocument24 pagesChannel Mapping LTEbadal mishraNo ratings yet
- LTE Logical Channel TypesDocument1 pageLTE Logical Channel TypesAzmat GaadNo ratings yet
- 02 Ra41232en05gla0 Lte ChannelsDocument37 pages02 Ra41232en05gla0 Lte ChannelsMuhammad Ali MalikNo ratings yet
- Day 2 - Wran OperationsDocument32 pagesDay 2 - Wran OperationsAnup SinghNo ratings yet
- Lecture7 RadioInterfaceProtcolsDocument31 pagesLecture7 RadioInterfaceProtcolsRajveer SinghNo ratings yet
- LTE Radio Interface Section 3Document80 pagesLTE Radio Interface Section 3Nikan AminiNo ratings yet
- LTE Technology Works Based On Three Channel Types VizDocument2 pagesLTE Technology Works Based On Three Channel Types VizMuthulingamNo ratings yet
- Lte Communication ChannelsDocument3 pagesLte Communication ChannelsRoderick OchiNo ratings yet
- GSM Channel TypesDocument3 pagesGSM Channel Typessanu81No ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Data ChannelsDocument6 pages3G UMTS Data ChannelsMark EmakhuNo ratings yet
- 3G UMTS Channels - Physical Logical Transport - Radio-Electronics PDFDocument4 pages3G UMTS Channels - Physical Logical Transport - Radio-Electronics PDFanandchoudhary83No ratings yet
- WCDMA Channels: 10th Aug 2007 DeepakDocument40 pagesWCDMA Channels: 10th Aug 2007 DeepakkhurshidNo ratings yet
- LTE Physical, Logical and Transport ChannelsDocument2 pagesLTE Physical, Logical and Transport ChannelsMkathuriNo ratings yet
- Next Generation Networks (The Radio Aspect)Document53 pagesNext Generation Networks (The Radio Aspect)omer449100% (1)
- GSM Physical and Logical ChannelsDocument20 pagesGSM Physical and Logical ChannelsJamshid IbragimovNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument20 pagesGSM Channelsshashikala kotiNo ratings yet
- GSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelDocument20 pagesGSM Channels: Prepared By:-Mohd Nazir ShakeelNguyễn HùngNo ratings yet
- UTRAN Radio Interface ProtocolsDocument31 pagesUTRAN Radio Interface ProtocolsDpkKSinghNo ratings yet
- Wireless LAN (2): HIPERLAN, Bluetooth, 802.11 StandardsDocument74 pagesWireless LAN (2): HIPERLAN, Bluetooth, 802.11 StandardsCynthia PlazaNo ratings yet
- 2139module 4 - L3 - 26.9Document25 pages2139module 4 - L3 - 26.9Chinmoy GhoshNo ratings yet
- LTE Communication Channels ExplainedDocument4 pagesLTE Communication Channels ExplainedVishwaNo ratings yet
- 2G Channels and 3GDocument5 pages2G Channels and 3Gkn09No ratings yet
- Medium Access Control (MAC) in 3GDocument8 pagesMedium Access Control (MAC) in 3Gsamtec32No ratings yet
- LTE NoteDocument45 pagesLTE NoteVarsanNo ratings yet
- GSM ChannelsDocument46 pagesGSM ChannelsAshish KushwahNo ratings yet
- The Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsFrom EverandThe Internet of Things: Key Applications and ProtocolsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Debian HandbookDocument513 pagesDebian HandbookHarey Kosong TojoehNo ratings yet
- BreezeMAX 4000 Si CPE Operator Manual 100324Document149 pagesBreezeMAX 4000 Si CPE Operator Manual 100324Wojciech WójcikNo ratings yet
- Macro Outdoor BTS QIG 101124Document27 pagesMacro Outdoor BTS QIG 101124Kamal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- List of Empanelled Hospitals As On 2nd May 2013Document6 pagesList of Empanelled Hospitals As On 2nd May 2013Kamal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7. ProjVijayDocument9 pagesChapter 7. ProjVijaymanojkumartomar7513No ratings yet
- Environment and BiodiversityDocument61 pagesEnvironment and BiodiversityKamal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Old NCERT World History Class 10 PDF FormatDocument223 pagesOld NCERT World History Class 10 PDF Formatjaykar56100% (4)
- Intro To GMSKDocument12 pagesIntro To GMSKمحسن اشرفNo ratings yet
- 3G Network ArchitectureDocument57 pages3G Network Architecturegurudatt.kulkarniNo ratings yet
- 16 Environmental IssuesDocument17 pages16 Environmental IssuesNarendra JangidNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Circulation Chapter-10Document10 pagesAtmospheric Circulation Chapter-10Kamal ChauhanNo ratings yet
- Network PlanningDocument20 pagesNetwork PlanningFarrukhNo ratings yet
- Cashflow 101 Manual Awaken YourDocument16 pagesCashflow 101 Manual Awaken YourKamal Chauhan100% (11)
- All New Customers 2023-OriginalDocument31 pagesAll New Customers 2023-OriginalcarlosNo ratings yet
- ArrowDevices MIPI UniPro Verification ChecklistDocument833 pagesArrowDevices MIPI UniPro Verification ChecklistSandip BhadaniNo ratings yet
- ASIC For Ethernet Based Real - Time Communication in DCSDocument4 pagesASIC For Ethernet Based Real - Time Communication in DCSm.Ali bzNo ratings yet
- Dual-Band Combiner: 470 - 960 MHZ 1710 - 2700 MHZDocument2 pagesDual-Band Combiner: 470 - 960 MHZ 1710 - 2700 MHZDoc All TelecomNo ratings yet
- CiTRANS 650 U3 Technical PDFDocument128 pagesCiTRANS 650 U3 Technical PDFBagavathy KumarNo ratings yet
- DC 02 CC 0275Document4 pagesDC 02 CC 0275Anonymous uVinWXfo4No ratings yet
- Internet Routing BasicsDocument24 pagesInternet Routing BasicskyawzinmonNo ratings yet
- Multiple BSSID Element: AuthorsDocument16 pagesMultiple BSSID Element: AuthorsNanjil NanbanNo ratings yet
- SS7 Whitepaper Ver 1.41Document19 pagesSS7 Whitepaper Ver 1.41Anonymous Ie0oEXP2eNo ratings yet
- O-001-FD1216S-R1 Datasheet 1.1Document2 pagesO-001-FD1216S-R1 Datasheet 1.1Jaime Orlando Caicedo DiazNo ratings yet
- Mobile Number Portability - WorkshopDocument92 pagesMobile Number Portability - Workshoptamnguyen29842764100% (2)
- 001Document130 pages001Miaik RakNo ratings yet
- PPPoE Technology White PaperDocument11 pagesPPPoE Technology White PaperNaz LunNo ratings yet
- 19mis0018 CN Lab 2Document27 pages19mis0018 CN Lab 2VidhyaNo ratings yet
- Counter Nokia & EricssonDocument4 pagesCounter Nokia & EricssonAbi AnnunNo ratings yet
- CS 4441 - Networks II: Wi-FiDocument22 pagesCS 4441 - Networks II: Wi-FiGemma Ubuhle TsotetsiNo ratings yet
- Vss-Enabled Campus Design: Etherchannel Optimization, Traffic Flow, and VSL Capacity Planning With Vss in The CampusDocument72 pagesVss-Enabled Campus Design: Etherchannel Optimization, Traffic Flow, and VSL Capacity Planning With Vss in The CampusCarlosNo ratings yet
- Module 12: WLAN Concepts: Instructor MaterialsDocument51 pagesModule 12: WLAN Concepts: Instructor MaterialsCurtizagioNo ratings yet
- CCIE Data Center v3 Learning MatrixDocument17 pagesCCIE Data Center v3 Learning MatrixayazNo ratings yet
- LTE - LTE Response Lte Multi Rat IntlDocument12 pagesLTE - LTE Response Lte Multi Rat IntlazzgukNo ratings yet
- LTE Cell Neighbor ListDocument1,253 pagesLTE Cell Neighbor ListLenin Alejandro Ramirez HuaypatinNo ratings yet
- Flowchart - RL FailureDocument1 pageFlowchart - RL FailurefatehmeNo ratings yet
- 6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking WBDocument11 pages6.2.2.5 Lab - Configuring VLANs and Trunking WBShaRonNo ratings yet
- CCNA 1 v5 Pratice Final ExamDocument29 pagesCCNA 1 v5 Pratice Final ExamDago DagoNo ratings yet
- PCRFDocument191 pagesPCRFAnonymous 0riMfln4VZ100% (1)
- Troubleshooting SCTP Path Failure AlarmDocument8 pagesTroubleshooting SCTP Path Failure AlarmBabalu RamNo ratings yet
- Multiplexing and DemultiplexingDocument9 pagesMultiplexing and DemultiplexingNadeem PashaNo ratings yet
- TL Sg2109web DsDocument3 pagesTL Sg2109web DsNguyen Hoang VietNo ratings yet
- Corrigendum No 3 To RFP No Mpsedc/Mpswan/2007-08/01: TH THDocument16 pagesCorrigendum No 3 To RFP No Mpsedc/Mpswan/2007-08/01: TH THharminder ratraNo ratings yet
- CSE3214 Midterm2005 SolutionsDocument14 pagesCSE3214 Midterm2005 Solutionsa1234567asNo ratings yet