Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Globalization and Regionalization
Uploaded by
mimiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Globalization and Regionalization
Uploaded by
mimiCopyright:
Available Formats
Running head: GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
Globalization and Regionalization
Name
Institutional Affiliation
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
2
Globalization and Regionalization
Regionalization is a term normally employed to describe the strategies focusing on a
regional or a local level of scale. Localization strategies focus on monetary, cultural and products
or services. An example is manufacturing and marketing of a specific product aiming at specific
market for instance an expensive private jet for a multimillionaire. Globalization is associated
with notion of strategies at global level. Examples for globalization strategies include free trade
zones, the use of a common currency, free trade zones and many more. Globalization entails
regional boundaries and their products are targeted for the entire world without focusing on
specific regions. An example of globalization for instance, Twitter and Facebook focus on the
entire world without any focus on any geographical region.
Globalization includes combined efforts to tackle the global scale problems such as
global warming. Globalization is a process of interaction among the people governments and
companies of different nations. The process is driven by the international trade and investment in
the world level which is aided by the advancement in information technology. The process has
major effects on the environment, political systems, cultures, prosperity and economic
development. Further, it has an effect towards human physical wellbeing in the societies around
the world. The phenomenon of globalization most of the time contested on empirical and
normative grounds. Regionalization entails dividing an area into smaller regional segments. For
instance regionalization is the division of nation to states and provinces. In business, the process
of regionalization is used as a business management tool as a way of making certain needs in a
particular area is met (Agenor and Pierre-Richard, 2004).
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
3
Globalization is similar to regionalism in that they both are the product of the operation
of both national and international market under the influence of the theories of demand and
supply. Globalization and regionalization may be the center of attention in that they can be
pushed by the wealthier and more industrialized states of the northern countries. The concept of
globalization is mostly contested on empirical and normative grounds ((Agenor and PierreRichard, 2004).
"Globalization" is an extremely late term, just setting up its present importance in the
1970s, which "rose up out of the crossing point of four interrelated arrangements of 'groups of
practice': scholastics, writers, distributers/editors, and administrators". In 2000, the International
Monetary Fund (IMF) recognized four fundamental parts of globalization: exchange and
exchanges, capital and speculation developments, relocation and development of individuals, and
the spread of learning. Further, ecological difficulties, for example, a dangerous atmospheric
deviation, cross-limit water and air contamination, and over-angling of the sea are connected
with globalization. Globalizing forms influence and are influenced by business and work
association, financial matters, socio-social assets, and the regular habitat. Scholarly writing
ordinarily subdivides globalization into three noteworthy areas: financial globalization, social
globalization and political globalization.
Regionalization is the procedure of isolating a range into littler portions called locales.
One of the more evident case of regionalization is the division of a country into states or regions.
Organizations additionally utilize regionalization as an administration instrument and an
approach to verify that requirements novel to specific territories are met. In metropolitan
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
4
territories a few issues can't be fathomed inside city limits, and choices made by one district can
impactsly affect different regions and the earth. While land has customarily been isolated by
political limits, to permit more productive procurement of taxpayer driven organizations and
popularity based representation, this has not loaned itself exceptionally well to compelling
administration of regular assets, urban framework, and other multi-jurisdictional frameworks.
Contamination and wasteful utilization of assets and foundation (land, water, air, living space,
fisheries, streets, utilities and so on.) are case of issues that overflow civil limits.
A notion in the world is that the world may break up to a regional trading blocs and
regionalism instead of globalization and may become a new phenomenon of the world. The
strategies for regionalization differ from globalization. Multinational Corporation develops a
global product for the entire world market and dominates local markets at every corner of the
world. Contrary, the notion fail to note various business activities of large companies takes place
in regional blocs opposed to single global market. Firms around the globe adopt a new slogan
with idea of think regional, and act local and forget global. Statistics after several researches
conducted around the globe shows the immense power for regional markets. All this is evident
where ninety percent of cars registered in Japanese nation are domestically manufactured. The
same is true for the cars sold in America, 85 percent are built in American factories. Strategies
for regionalization differs from globalization in the sense that various companies source
technology, goods, capital and information from around the world but business activities are
centered at specific cities.
Business thrives well when the market for the goods are localized. Localized markets
provide convenience as compared to tough conditions for marketing products on a global
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
5
platform. It is evident that regionalism can take place at the same time as globalization evident in
certain amount of regionalization is likely to be given lower communications and transportation
cost associated with proximity due to geography. The field of political science has a greatest
stress in observing the effort that is extended on the regional economic integration effort as
opposed to global multilateral economic regimes.
Strategies for globalization and regionalization
Primary economic goal of globalization and regionalization aims at reducing available
barriers of trade for the purpose of enrichment of all societies. The two occur as important fields
that impede regulatory barriers between the sovereign entities. They lead to betterment of the
societies through free trade for each and every person provided that one has a freedom to
produce with comparative advantage and the processes of engaging in exchange with others.
Home based strategy Companies start their international expansion first by serving foreign
market from their home base. Companies that have moved to more complex regional strategies
rely on home base strategies. Home based strategies work well for instances where the
economies of concentration outweighs that of dispersion (Chortareas, Georgios, and Theodore
Pelagidis, 2004).
The portfolio strategy involves setting up operation that is out of home region but by the
end report directly to the home base. This is a good strategy for regionalized companies that seek
to establish presence outside the markets they can well serve from home. Portfolio strategy,
being a simple one takes a lot of time to implement especially when the company organically.
The Toyota Company took a lot of time trying to establish their operations in North America. A
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
6
major blow to portfolio strategy for expansion is where the establishing company faces tough
rivals in the non-home country (Doyle, 2004).
Diffusion of technology: the advancement of technology in telecommunication
information technology and complexity in computing leads to diffusion of technology around the
globe. The increased diffusion in technology is an important strategy favoring both regionalism
and globalization. Technology serves the purpose of growing the trends of computer
developments in areas of artificial intelligence and high speed connections which include
wireless applications and integration with biotechnology. These strategies apply to the
globalization and the regionalization (Clott, 2004).
Globalization and regionalization entails threats and opportunities for the creation and
sustaining competitive strategies. Global managers have resolved many strategies to deal with
the globalization and regionalism. The centralization of core operations has been on the rise with
modifications for local adaptation. There is also advancement of transnational strategies for the
purpose of local and international orientation and integration. The managers for globalization and
regionalization needs to make decision which relate to internationalization processes. The
development of innovation in the home market, firms can take products which enter into the
plateau of a mature stage to new international market. These flows moves from developed to the
developing countries.
GLOBALIZATION AND REGIONALIZATION
7
References
Agenor, Pierre-Richard. "Does Globalization Hurt the Poor?" International Economics and
Economic Policy 1, no. 1 (2004): 2151.
Chortareas, Georgios E., and Theodore Pelagidis. "Trade Flows: A Facet of Regionalism or
Globalization?" Cambridge Journal of Economics 28, no. 2 (March 2004): 353271.
Clott, Christopher B. "Perspectives on Global Outsourcing and the Changing Nature of Work."
Business and Society Review 109, no. 2 (2004): 153170.
Doyle, Michael W. "The Challenge of Worldwide Migration." Journal of International Affairs
57, no. 2 (Spring 2004): 15.
You might also like
- Summary Of "What Is Globalization?" By Joachim Hirsch: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESFrom EverandSummary Of "What Is Globalization?" By Joachim Hirsch: UNIVERSITY SUMMARIESNo ratings yet
- Market IntegrationDocument8 pagesMarket IntegrationLyra Joy Calayan100% (2)
- Contemporary World OutlineDocument5 pagesContemporary World OutlineJeffrey CabarrubiasNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Contemporary WorldDocument34 pagesModule 1 Contemporary WorldArdrei Carl Ac Guevarra100% (3)
- Global Interstate SystemDocument18 pagesGlobal Interstate SystemJerico Pilapil Namuco100% (1)
- The Contemporary World: Lesson 1 GlobalizationDocument22 pagesThe Contemporary World: Lesson 1 Globalizationleira bliss100% (2)
- Customer CentricityDocument20 pagesCustomer CentricityKunal GuptaNo ratings yet
- Contemporary WorldDocument91 pagesContemporary WorldMary Rose100% (1)
- CW Midterm ModuleDocument22 pagesCW Midterm ModuleAppoch Kaye RolloqueNo ratings yet
- FASTRACKDocument57 pagesFASTRACKShyam MaariNo ratings yet
- LESSON 1 GCWORLD The Contemporary WordlDocument11 pagesLESSON 1 GCWORLD The Contemporary Wordlshaina juatonNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument111 pagesGlobalizationJeanne100% (2)
- M&S Effective Loyalty Schemes Within Travel and LeisureDocument14 pagesM&S Effective Loyalty Schemes Within Travel and LeisureMarks and Spencer for businessNo ratings yet
- Theories of GlobalizationDocument25 pagesTheories of GlobalizationJosebeth CairoNo ratings yet
- Contemp World Module 3 Topics 1 2Document27 pagesContemp World Module 3 Topics 1 2Miguel Eder100% (1)
- 21st Century Meets The United NationDocument23 pages21st Century Meets The United NationLindsay TudlongNo ratings yet
- POWER School of Technology The Contemporary WorldDocument15 pagesPOWER School of Technology The Contemporary WorldAllan Ometer100% (8)
- Part 1 Overview of Strategic ManagementDocument38 pagesPart 1 Overview of Strategic Managementsmb_146100% (1)
- Origin and History of GlobalizationDocument3 pagesOrigin and History of GlobalizationJomar Buenavista100% (1)
- Relationship Marketing in Banking PDFDocument10 pagesRelationship Marketing in Banking PDFarvind3041990No ratings yet
- A World of Regions-Module 3 in TCWDocument7 pagesA World of Regions-Module 3 in TCWEspinosa Mary Dianne V.100% (2)
- Marketing - Module 8 The Marketing Mix - PLACEDocument10 pagesMarketing - Module 8 The Marketing Mix - PLACEKJ JonesNo ratings yet
- Globalization of Religion - Group 4-ADocument9 pagesGlobalization of Religion - Group 4-Ajeffrey ordinalNo ratings yet
- Globalization DefinitionDocument19 pagesGlobalization DefinitionSharmaine Bernabe67% (3)
- A Comparative Analysis of Global North and Global South Economies (Odeh)Document11 pagesA Comparative Analysis of Global North and Global South Economies (Odeh)wordmazeNo ratings yet
- The Effects of Globalization On World EconomiesDocument55 pagesThe Effects of Globalization On World EconomiesNeptün Oral100% (1)
- TCW Midterms Notes and LEDocument17 pagesTCW Midterms Notes and LEAngel HannahNo ratings yet
- Global Media and Religion-Rey2020Document90 pagesGlobal Media and Religion-Rey2020Gr Macopia100% (1)
- Globalization TheoriesDocument29 pagesGlobalization Theoriesjames adam100% (1)
- Destination Competitiveness - Applying Different ModelsDocument14 pagesDestination Competitiveness - Applying Different ModelsTatiana Silva SantosNo ratings yet
- Regionalism and RegionalizationDocument3 pagesRegionalism and RegionalizationRommel Quivis0% (1)
- Deniell Kahlil Kyro S. Gabon Bsce 2CDocument10 pagesDeniell Kahlil Kyro S. Gabon Bsce 2CDeniell Kahlil Kyro GabonNo ratings yet
- Thecontemporaryworldlessons34 ANSWERSDocument3 pagesThecontemporaryworldlessons34 ANSWERSHannah Beatrice SalesNo ratings yet
- 1.8 Lesson 15 & 16 Contemporary WorldDocument16 pages1.8 Lesson 15 & 16 Contemporary WorldViernes, John Henilon C. - BSED FilipinoNo ratings yet
- TCWD Contemporary Global Governance ActivityDocument1 pageTCWD Contemporary Global Governance ActivityMorticia Vizactyh100% (1)
- Handouts CONTEMPORARYDocument7 pagesHandouts CONTEMPORARYShaina FirmalanNo ratings yet
- 4-The Global Interstate SystemDocument7 pages4-The Global Interstate SystemWynnie RondonNo ratings yet
- Cultural GlobalizationDocument7 pagesCultural GlobalizationChak Mei ChuenNo ratings yet
- Global City 1Document22 pagesGlobal City 1Elvin ManjaresNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Lesson 2 Global Interstate SystemDocument16 pagesUnit 2 Lesson 2 Global Interstate SystemLoiz Santos TrinidadNo ratings yet
- Globalization: The Rise of Information and Communication TechnologyDocument9 pagesGlobalization: The Rise of Information and Communication TechnologyRomana YasmeenNo ratings yet
- 1.why Is Global Governance Multi-Faceted?Document2 pages1.why Is Global Governance Multi-Faceted?Shekinah Faith Requintel100% (1)
- The Contemporary WorldDocument32 pagesThe Contemporary WorldAxel Ngan50% (2)
- Lesson 3 - A History of Global Politics: Creating An International Order (Week 4)Document7 pagesLesson 3 - A History of Global Politics: Creating An International Order (Week 4)Jheza May Bañez100% (1)
- Op-Ed: Globalization Challenged - Reclaiming The Multilateral Cooperation AgendaDocument2 pagesOp-Ed: Globalization Challenged - Reclaiming The Multilateral Cooperation Agendarhiantics_kram11No ratings yet
- Lesson 1 GE3Document8 pagesLesson 1 GE3Maria Lesty BustaleñoNo ratings yet
- Market IntegrationDocument5 pagesMarket IntegrationJanee JaneNo ratings yet
- 3 Ged 104 The Bretton Woods SystemDocument21 pages3 Ged 104 The Bretton Woods Systemjustine reine cornicoNo ratings yet
- Course Outline Ge 3 Contemporary World 2019Document1 pageCourse Outline Ge 3 Contemporary World 2019DarilynNo ratings yet
- TCW Book Chapter 6 To 8 With ExercisesDocument73 pagesTCW Book Chapter 6 To 8 With ExercisesGOTINGA, CHRISTIAN JUDE AVELINONo ratings yet
- My Solution To The Economic Problems of The Philippines!Document2 pagesMy Solution To The Economic Problems of The Philippines!Hazelle Marie Mortel Tacud83% (6)
- Lesson 8 Activity - Ma. Bernadeth LanozaDocument7 pagesLesson 8 Activity - Ma. Bernadeth LanozaEmily Despabiladeras DulpinaNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Globalization (Definition)Document32 pagesModule 1 Globalization (Definition)Mini CabalquintoNo ratings yet
- Gwen Stefani Yahin BS Psychology 2B: 8 Theories of GlobalizationDocument2 pagesGwen Stefani Yahin BS Psychology 2B: 8 Theories of GlobalizationGwen YahinNo ratings yet
- Effects of Globalization - SibalDocument25 pagesEffects of Globalization - SibalTopher AstraquilloNo ratings yet
- Ideologies of GlobalizationDocument13 pagesIdeologies of GlobalizationMa. Angela RosauroNo ratings yet
- Global Interstate SystemDocument34 pagesGlobal Interstate SystemSharmaineMirandaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Globalization and How It Affects Form A National Security PerspectiveDocument13 pagesEffect of Globalization and How It Affects Form A National Security PerspectivejebergNo ratings yet
- 3the Global Interstate System (16-18)Document3 pages3the Global Interstate System (16-18)Tam Gerald Calzado79% (14)
- Global Governance in The 21 CenturyDocument10 pagesGlobal Governance in The 21 CenturyRental SystemNo ratings yet
- TCWD MidtermsDocument20 pagesTCWD MidtermsMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Defining GlobalizationDocument24 pagesDefining GlobalizationdomermacanangNo ratings yet
- The Contemporary World 2Document6 pagesThe Contemporary World 2Nikki Jean HonaNo ratings yet
- Regionalism 101 PPT 2 PDFDocument28 pagesRegionalism 101 PPT 2 PDFlalaine100% (2)
- The Modern World SystemDocument9 pagesThe Modern World SystemShairon PalmaNo ratings yet
- Global Corporate StrategyDocument24 pagesGlobal Corporate StrategyAik Luen LimNo ratings yet
- GlobalizationDocument53 pagesGlobalizationGaurav JainNo ratings yet
- Hba 2301 Deaf Sob December 2016Document3 pagesHba 2301 Deaf Sob December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- Hba 236 Deaf Sob December 2016Document3 pagesHba 236 Deaf Sob December 2016mimi100% (1)
- HBB 2405 Cohes Biochem December 2016Document1 pageHBB 2405 Cohes Biochem December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- HBC 2101Document5 pagesHBC 2101mimiNo ratings yet
- HBB 2401 Cohes Biochem December 2016Document2 pagesHBB 2401 Cohes Biochem December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- HBB 2403 Kakamega December 2016Document2 pagesHBB 2403 Kakamega December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- HBB 2202 Cohes Biochem December 2016Document2 pagesHBB 2202 Cohes Biochem December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S1674927816300727 Main - 2 PDFDocument6 pages1 s2.0 S1674927816300727 Main - 2 PDFmimiNo ratings yet
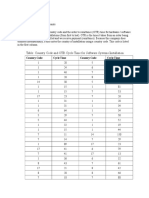
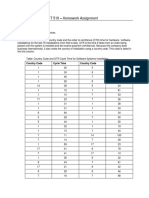
- Table: Country Code and OTR Cycle Time For Software Systems InstallationDocument3 pagesTable: Country Code and OTR Cycle Time For Software Systems InstallationmimiNo ratings yet
- HBB 2400 Cohes Biochem December 2016Document2 pagesHBB 2400 Cohes Biochem December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- Hba 2401Document3 pagesHba 2401mimiNo ratings yet
- HBB 2329 Biochem Cohes December 2016Document2 pagesHBB 2329 Biochem Cohes December 2016mimiNo ratings yet
- DocxDocument4 pagesDocxmimiNo ratings yet
- MAT510 Homework Assignment 5Document4 pagesMAT510 Homework Assignment 5mimiNo ratings yet
- Militarization of Our Nations PoliceDocument8 pagesMilitarization of Our Nations PolicemimiNo ratings yet
- Swot Analysis ExampleDocument4 pagesSwot Analysis ExampleAnna Rachel Abel100% (1)
- Isb PM BrochureDocument12 pagesIsb PM BrochureThrived krishna murthyNo ratings yet
- Final Marketing Strategies For New Market EntriesDocument29 pagesFinal Marketing Strategies For New Market EntriesAmit ShrivastavaNo ratings yet
- MBA 9 Year 1 Strategic Marketing Managament Semester 1Document202 pagesMBA 9 Year 1 Strategic Marketing Managament Semester 1pertuNo ratings yet
- Segmentation:: DemographyDocument4 pagesSegmentation:: DemographyIshtiaq ShushaanNo ratings yet
- 05 Company Bifold Brochure Template DesignDocument8 pages05 Company Bifold Brochure Template DesignEsmulsa Sac TarmaNo ratings yet
- Group Project Topic: The Ethical Movement of A Company According To Stakeholder TheoryDocument21 pagesGroup Project Topic: The Ethical Movement of A Company According To Stakeholder TheoryKamruzzaman HasibNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document10 pagesChapter 2MathiosNo ratings yet
- Kadiyam Gayathri Resume WEDocument1 pageKadiyam Gayathri Resume WEBhavik2002No ratings yet
- Class Schedule Term-4 PGP 2022-24-CirculationDocument3 pagesClass Schedule Term-4 PGP 2022-24-CirculationShanu ShaniaNo ratings yet
- Care365: "Distance Means So Little When Someone Means So Much"Document11 pagesCare365: "Distance Means So Little When Someone Means So Much"Nikhil Gauns DessaiNo ratings yet
- S12 Retail PricingDocument66 pagesS12 Retail PricingVishnuvardhan Ravichandran0% (1)
- Beyond UCPMP 2024Document40 pagesBeyond UCPMP 2024narendra_1983No ratings yet
- Essentials of Contemporary Management 7th Edition Jones Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument53 pagesEssentials of Contemporary Management 7th Edition Jones Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFCaseyBrownaoqn100% (12)
- Supply Chain Unit 3 - CompressedDocument38 pagesSupply Chain Unit 3 - CompressedAmol KareNo ratings yet
- Shoppers Stop - Company Profile: Also ReadDocument4 pagesShoppers Stop - Company Profile: Also ReadSuman KumarNo ratings yet
- What Is CAC and Why Is It A Critical Metric For Digital Marketing Agencies?Document61 pagesWhat Is CAC and Why Is It A Critical Metric For Digital Marketing Agencies?Tecbind UniversityNo ratings yet
- How To Use Google Ads GuideDocument24 pagesHow To Use Google Ads GuideBobanNo ratings yet
- This Is A Business Plan. It Does Not Imply An Offering of SecuritiesDocument40 pagesThis Is A Business Plan. It Does Not Imply An Offering of SecuritiesTinashe RunganoNo ratings yet
- Marketing Communication in Social Media: The Case of Airlines in Central and Eastern EuropeDocument1 pageMarketing Communication in Social Media: The Case of Airlines in Central and Eastern EuropeNeringa VilkaitėNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management A South Asian Perspective 13 EditionDocument15 pagesMarketing Management A South Asian Perspective 13 EditionHasnain Butt100% (1)
- Media in Advertising: Module - 1Document84 pagesMedia in Advertising: Module - 1Cologne AromaNo ratings yet
- 2.JournalofHumanitiesSocialScienceandManagement-Instant Food ProductsDocument13 pages2.JournalofHumanitiesSocialScienceandManagement-Instant Food Productsaarti_ahujaNo ratings yet