Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Test-28 Thermo, KTG WA
Uploaded by
umang dhandhaniaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Test-28 Thermo, KTG WA
Uploaded by
umang dhandhaniaCopyright:
Available Formats
PHYSICS
Target
JEE Advanced 2016
CLASS : CC (ADVANCED)
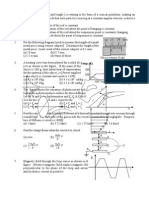
Q.1
Q.2
THERMO & KTG
TEST NO. 28
[SINGLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE]
One mole of a gas expands with temperature according to the relation V = kT2/3. What is the workdone
when the temperature changes by 30C?
3
[3]
(A) 10R
(B) 20R
(C) 30R
(D) 40R
A mercurypallet of length 5 cm is trapped in a horizontal tube of small cross-section area. Length of tube
enclosed bymercury pallet is 20 cm when it is accelerated with a = g/2 in the direction shown. The length
of tube enclosed bypallet if it is accelerated in opposite direction with same acceleration is : (Atmospheric
pressure is 72.5 cm of Hg)
[3]
a
5cm
10cm
(A) 22 cm
Q.3
(B) 22.5 cm
20cm
(C) 21 cm
(D) 21.4 cm
What is fraction of molecule below an altitude h in atmosphere?Assume uniform gravitational field,
isothermal conditions, mass of a molecule m, Boltzman constant k, temperature T.
[3]
(A) f = e(mgh / kT )
(B) f = e ( mgh / kT)
(C) f = 1 e ( mgh / kT) (D) f = 1 e(mgh / kT )
Q.4
CO2 has specific heat capacity of 630 J/kg C at constant volume. If its temperature rises from 20C to
45C. What is the change in its internal energy per unit mass?
[3]
(A) 12.6 kJ/kg
(B) 15.75 kJ/kg
(C) 17.6 kJ/kg
(D) 20.5 kJ/kg
Q.5
A diatomic ideal gas is heated at constant volume until its pressure is doubled. It is again heated at
constant pressure until its volume is doubled. The molar heat capacityfor the whole process is kR where
k is:
[3]
(A) 23/5
(B) 19/5
(C) 19/6
(D) 13/4
Q.6
One mole of a monoatomic ideal gas undergoes the process A B in
the given P-V diagram. The specific heat for this process is [3]
(A) 3R/2
(B) 13R/6
(C) 5R/2
(D) 2R
Q.7
If one mole of monoatomic gas is mixed with one mole of a diatomic gas, the value of for the mixture is
(A) 1.40
(B) 1.50
(C) 1.53
(D) 3.07
[3]
Q.8
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a cycle of process, consisting of two
isochores and two isobars. Temperatures at 1 and 3 equal T1 and T3
respectively. Find the work done by the gas over the cycle, if the point 2
and 4 lie on the same isotherm.
[3]
R (T1 T3 )
2
(A)
(B) R T3 T1
2
2
R
T1 T3
(C)
(D) R T1T3
2
P
2
4
V
PAGE # 1
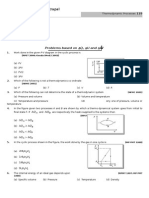
Q.9
On a TP diagram, two moles of ideal gas perform process AB and CD. If the
work done by the gas in the process AB is two times the work done in the
process CD, then what is the value of T1/ T2?
[3]
(A) 1/2
(B) 1
(C) 2
(D) 4
Q.10
Suppose 0.5 mole of an ideal gas undergoes an isothermal expansion as
0.3
energy is added to its as heat Q. Graph shows the final volume vf verses
Q. The temperature of gas is (use ln 3 10 and R = 25/3 J/mol-K) [3]
3
V(m ) 0.2
(A) 360 K
(B) 260 K
(C) 390 K
(D) 490 K
0.1
0
Q.11
One mole of certain diatomic gas is under taken the cyclic process
shown in the diagram . For this cyclic process efficiencyequals : [3]
(A)
6
7
(B)
2
19
(C)
12
19
(D)
P0
10
Q(KJ)
15
2P0
2
9
A
V0
2V0
[PARAGRAPH TYPE]
Paragraph for question nos. 12 to 14
A sample of ideal gas is taken through the cyclic process shown in the figure. The temperature of the gas
at state A is TA = 200 K. At states B and C the temperature of the gas is the same.
p
B
pB
C
pA
A
VA
Q.12
Q.13
Net work done by the gas in the process is
(A) 2PAVA
(B) 4PAVA
[3]
(C) 6PAVA
(D) 8PAVB
Which of the following graphs best represent the cyclic process in T-V diagram.
B
(A)
(B)
A
V
Q.14
3VA
(C)
A
V
(D)
[3]
A
V
What is the greatest temperature of the gas during the cyclic process ?
(A) 600 K
(B) 1200 K
(C) 2400 K
(D) None of these
[3]
PAGE # 2
Q.15
Q.16
[REASONING TYPE]
Statement - 1 : For real gas CpCv > R.
[3]
Statement -2 : In isobaric process, part of heat is spent on doing work during expansion against external
pressure.
(A) Statement-1 is True, Statement-2 is True, Statement-2 is a correct explanation for Statement-1
(B) Statement -1 is True, Statement -2 is True; Statement -2 is NOT a correct explanation for
Statement - 1
(C) Statement - 1 is True, Statement- 2 is False
(D) Statement -1 is False, Statement -2 is True
[MULTIPLE CORRECT CHOICE TYPE]
The density () of an ideal gas varies with temperature T as shown in figure. Then
[4]
A
T
(A) the product of P and V at Ais equal to the product of P and V at B
(B) pressure at B is greater than the pressure at A
(C) work done by the gas during the process AB is negative
(D) the change in internal energy fromAto B is zero.
Q.17
A monoatomic gas undergoes a process given by a (dU) + b(dW) = 0. Now if (dU internal energy
change, dW work done by gas)
[4]
(A)
a
= 1, then the process is isobaric
b
(B) b = 0, then the process is isothermal
(C)
a
= 1, then the process is adiabatic
b
(D)
a
2
= , then the process is isobaric
b
3
Q.18
Figure shows an indicator diagram. During path 1-2-3, 100 cal are
given to the system and 40 cal work is done. During path 1-4-3, the
work done is 10 cal.
[4]
(A) Heat given to the system during path 1-4-3 is 70 cal
(B) If the system is brought from 3 to 1 along straight line path 3-1, work done is 25 cal
(C) Along straight line path 3-1, the heat ejected by the system is 85 cal
(D) The internal energy of the system in state 3 is 140 cal above that in state 1.
Q.19
A fixed quantity of an ideal gas can be expanded from an initial state to a certain volume through two
different processes
(i) PV2 = constant and (ii) P = KV2 where K is a constant. Then
[4]
(A) Final temperature in (i) will be greater than that in (ii)
(B) Final temperature in (ii) will be greater than that in (i)
(C) Heat is given to the gas in (i) & rejected by the gas in (ii)
(D) Heat is given to the gas in (ii) & rejected by the gas in (i)
PAGE # 3
Pressure
Q.20
[MATRIX TYPE]
When a sample of a gas is taken from state i to state f along path iaf , heat supplied to the gas is 50 cal
and work done by the gas is 20 cal. If it is taken by path ibf, then heat supplied is 36 cal.
[6]
a
b
Volume
Q.21
(A)
Work done by the gas along path ibf is
(P) 6 cal
(B)
If work done upon the gas is 13 cal for the return
path fi, then heat rejected by the gas along path fi is
(Q) 18 cal
(C)
If internal energy of the gas at state i is 10 cal, then
internal energy at state f is
(R) 40 cal.
(D)
If internal energy at state b is 22 cal and at i is 10 cal
then heat supplied to the gas along path ib is
(S) 43 cal
An ideal gas is taken along the reversible processes as represented by the adjoining diagram.
[6]
p(N/m )
2
15
10
5
A
2
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Column-I
For process B C
For process A B
For cycle A B C A
For process C A
V(m3)
(P)
(Q)
(R)
(S)
(T)
Column-II
Q > 0
W > 0
U > 0
W = 0
Q < 0
[SUBJECTIVE TYPE]
Q.22
Figure shows the VT diagram for helium gas in a cyclic process. Find 2V
the ratio of maximum and minimum pressure.
[5]
VT = const.
TV = const.
Q.23
0.5 mole of an ideal gas is kept inside an adiabatic cylinder
of length L and cross-sectional area A closed by
massless adiabatic piston. The cylinder is attached with a
1 2
conducting rod of length L, cross-sectional area
m
900
and thermal conductivity 415.5 W/m-K, whose other end is
maintained at 0C. The piston is moved such that the
temperature of the gas remains constant at 27C. Find the
velocity (in mm/sec) of piston when it is at height L/2 from L
the bottom of cylinder. Rod is well lagged and has negligible
heat capacity. R = 8.31 J/mol-K.
[5]
2T
4T
27C
A
0C
PAGE # 4
You might also like
- Advanced Fiitjee PaperDocument8 pagesAdvanced Fiitjee PaperKratosNo ratings yet
- Chemical Equlibrium and Ionic EqilibriumDocument13 pagesChemical Equlibrium and Ionic EqilibriumsantoshguptaaNo ratings yet
- Classnote 573598c38d689Document14 pagesClassnote 573598c38d689HarshitShuklaNo ratings yet
- IIT2014-MID-PHASE TEST SolutionsDocument4 pagesIIT2014-MID-PHASE TEST SolutionsAkashdeep RamnaneyNo ratings yet
- JEE Physics Waves Practice TestDocument4 pagesJEE Physics Waves Practice Testumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- Fitjee Test Paper of MathDocument11 pagesFitjee Test Paper of Mathsudhir_kumar_33No ratings yet
- Phy Kvpy Archive XiiDocument99 pagesPhy Kvpy Archive XiiSudipta SarkarNo ratings yet
- Ionic EquilibriumDocument10 pagesIonic EquilibriumPranav MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Revision NotesDocument11 pagesRevision NotesRosellaNo ratings yet
- Kvpy 2016 SB - SX Stream PCMDocument43 pagesKvpy 2016 SB - SX Stream PCMKrishna KeerthanNo ratings yet
- Ionic Equlibrium QuestionsDocument19 pagesIonic Equlibrium Questionskishangopi123No ratings yet
- Org Nic Lecture Notes: Topic: IsomerismDocument51 pagesOrg Nic Lecture Notes: Topic: IsomerismRaviNo ratings yet
- Quadratic Equations MC SIR DPP 3Document4 pagesQuadratic Equations MC SIR DPP 3ChessNo ratings yet
- Ntse Stage II Paper Analysis 2019 PDFDocument7 pagesNtse Stage II Paper Analysis 2019 PDFJeetu RaoNo ratings yet
- Kvpy Mock Test - 2: Classroom Contact ProgrammeDocument15 pagesKvpy Mock Test - 2: Classroom Contact Programmetan jigNo ratings yet
- CPP (Chemical Bonding) CNG P-IDocument1 pageCPP (Chemical Bonding) CNG P-Ipankaj16fbNo ratings yet
- KVPY SB 2 SX StreamDocument117 pagesKVPY SB 2 SX StreamashutoshNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE CPPs Atomic StructurDocument8 pagesFIITJEE CPPs Atomic StructurrahulNo ratings yet
- IIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestDocument15 pagesIIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestPRAKHAR GUPTANo ratings yet
- Concept Recapitulation Test II/Advanced/PAPER-1/Question/QuestionDocument25 pagesConcept Recapitulation Test II/Advanced/PAPER-1/Question/Questionullasagw100% (1)
- Electrostatics Problems SetDocument10 pagesElectrostatics Problems SetRatan Kumar ThakurNo ratings yet
- 24 T WKBG Oi Y2 Ucv 3 U IUnrDocument21 pages24 T WKBG Oi Y2 Ucv 3 U IUnrSachinNo ratings yet
- DPP Volumetric Analysis JH Sir-3593Document11 pagesDPP Volumetric Analysis JH Sir-3593Shivam Kumar100% (1)
- Alkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 2Document3 pagesAlkanes - Alkenes - Alkynes - DPP 2Vishal_93No ratings yet
- JEE ADVANCED 2016 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEET-31Document3 pagesJEE ADVANCED 2016 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEET-31umang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- Jee Advanced Paper 1 Model PaperDocument12 pagesJee Advanced Paper 1 Model PaperLakkaraju PrasannaNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee) : Common Test (Phase - IDocument13 pagesFiitjee) : Common Test (Phase - IRahul SoodNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Periodic Table JH Sir-3576 PDFDocument5 pagesDPP 01 Periodic Table JH Sir-3576 PDFChessNo ratings yet
- DPP 01 Gaseous State JH Sir-3583Document11 pagesDPP 01 Gaseous State JH Sir-3583Shivam Kumar75% (4)
- Ionic Equilibrium Practice Problems SolutionsDocument2 pagesIonic Equilibrium Practice Problems SolutionsObama binladenNo ratings yet
- Fiitjee Rit 2Document11 pagesFiitjee Rit 2Baljeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Fiitjee CPPDocument1 pageChemistry Fiitjee CPPAkshit SharmaNo ratings yet
- Esankalp 022 W1-3 - Ph-2 - Paper-2Document14 pagesEsankalp 022 W1-3 - Ph-2 - Paper-2Ayush ChouhanNo ratings yet
- Aits 2122 CRT IV Jeea LD Paper 2 PDFDocument15 pagesAits 2122 CRT IV Jeea LD Paper 2 PDFSantanu SahaNo ratings yet
- Study Material & Test Papers for Logarithmic InequalitiesDocument3 pagesStudy Material & Test Papers for Logarithmic InequalitiesChessNo ratings yet
- Kvpy SB Solutions PDFDocument34 pagesKvpy SB Solutions PDFSharad SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry, Mathematics & Physics Internal Test Series: InstructionsDocument16 pagesChemistry, Mathematics & Physics Internal Test Series: InstructionsgauravNo ratings yet
- Grand Test-P-IIDocument18 pagesGrand Test-P-IIHardik Rajpal50% (2)
- Question PaperDocument15 pagesQuestion PaperSidNo ratings yet
- CPP: Ellipse: X y A B yDocument3 pagesCPP: Ellipse: X y A B ySamridh GuptaNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE Concept Recapitulation Test Paper 1 PCM Physics Chemistry MathematicsDocument21 pagesFIITJEE Concept Recapitulation Test Paper 1 PCM Physics Chemistry MathematicsMeenakshi Gupta100% (2)
- 08 Indefinite & Definite IntegrationDocument6 pages08 Indefinite & Definite IntegrationSrinidhi RajendranNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Problems SolvedDocument19 pagesCurrent Electricity Problems SolvedChess33% (3)
- Fiitjee 38Document5 pagesFiitjee 38BHAAJI0001100% (1)
- Resonance DPPDocument6 pagesResonance DPPshambhavi26100% (2)
- DPP 02 Periodic Table JH Sir-3579Document8 pagesDPP 02 Periodic Table JH Sir-3579AmitSharmaNo ratings yet
- Test, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFDocument18 pagesTest, Bansal Chemicalequilibrium PDFTarun Gupta0% (2)
- Wave Optics PDFDocument12 pagesWave Optics PDFJatin BhasinNo ratings yet
- CTY-2022 - PT1 - JEE (Main)Document49 pagesCTY-2022 - PT1 - JEE (Main)Gamingsone ZoneNo ratings yet
- IIT-1337/29(28/11/09) HYD-HG/SR IIT SPARK/PAPER-2Document14 pagesIIT-1337/29(28/11/09) HYD-HG/SR IIT SPARK/PAPER-2Hardik RajpalNo ratings yet
- Mock Test 3 With Solutions PDFDocument13 pagesMock Test 3 With Solutions PDFGamerizoneNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE - JEE (Main) 1Document14 pagesFIITJEE - JEE (Main) 1Aditya Jain100% (1)
- Question Bank MOD and Indefinite IntegrationDocument15 pagesQuestion Bank MOD and Indefinite IntegrationRAKTIM ROUTHNo ratings yet
- 1457156375-Inorganic Chemistry Revision Book JEE Main-2016.PmdDocument49 pages1457156375-Inorganic Chemistry Revision Book JEE Main-2016.PmdSummer GreenNo ratings yet
- 29 QusDocument16 pages29 QusAsafAhmadNo ratings yet
- JEE MAIN - PART TEST-2 - 24-09-2018 - PAPER-2 - Phase-1+ROTATIONAL MOTION - PASDocument31 pagesJEE MAIN - PART TEST-2 - 24-09-2018 - PAPER-2 - Phase-1+ROTATIONAL MOTION - PASVinod AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Physics CPP FIITJEE PDFDocument24 pagesPhysics CPP FIITJEE PDFAshish RanjanNo ratings yet
- FIITJEE ALL INDIA TEST SERIES PART TEST – I PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY AND MATHEMATICSDocument20 pagesFIITJEE ALL INDIA TEST SERIES PART TEST – I PHYSICS, CHEMISTRY AND MATHEMATICSKratosNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Processes ExplainedDocument8 pagesThermodynamic Processes ExplainedAman BhuttaNo ratings yet
- 13th HA - Practice Test-1 To 4 - EDocument19 pages13th HA - Practice Test-1 To 4 - Eumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- Permutation & CombinationDocument21 pagesPermutation & Combinationumang dhandhania100% (1)
- JEE ADVANCED 2016 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEET-31Document3 pagesJEE ADVANCED 2016 MATHEMATICS WORKSHEET-31umang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- XII (A) CODE REVIEW PAPER-IDocument16 pagesXII (A) CODE REVIEW PAPER-Iumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- JEE Main Code-A ReviewDocument16 pagesJEE Main Code-A Reviewumang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- PCM-22-09-2013 - RT-5 - Ans - Key - 12th (A)Document1 pagePCM-22-09-2013 - RT-5 - Ans - Key - 12th (A)umang dhandhaniaNo ratings yet
- Different I AbilityDocument21 pagesDifferent I Abilityumang dhandhania50% (2)
- For More Study Material & Test Papers Visit: www.mathsiit.comDocument18 pagesFor More Study Material & Test Papers Visit: www.mathsiit.comUmang Dhandhania100% (1)
- Applied Hydraulic Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersDocument5 pagesApplied Hydraulic Engineering - Lecture Notes, Study Material and Important Questions, AnswersM.V. TVNo ratings yet
- GCSE Physics Paper 2 Model Answer BookletDocument93 pagesGCSE Physics Paper 2 Model Answer BookletIntisharNo ratings yet
- SteamWhirl PhenomenaDocument6 pagesSteamWhirl PhenomenaAle MilicNo ratings yet
- Typical Vibration Signatures AnalysisDocument8 pagesTypical Vibration Signatures Analysisdfz138100% (1)
- Competitor Comparison Variable Speed Drives in PumpingDocument132 pagesCompetitor Comparison Variable Speed Drives in PumpingYuriy KarpusNo ratings yet
- Physics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduDocument38 pagesPhysics 3232 Optics I: Introduction: Prof. Rick Trebino, Georgia Tech WWW - Frog.gatech - EduTriaNo ratings yet
- WKB ApproxDocument21 pagesWKB ApproxdevendrakphyNo ratings yet
- All ComDocument47 pagesAll Comkushagrajoshi69No ratings yet
- Bridge-Design of Shallow FoundationsDocument35 pagesBridge-Design of Shallow FoundationshassscribedNo ratings yet
- P-Delta Analysis Column ForcesDocument9 pagesP-Delta Analysis Column ForcesMauricio CatunaNo ratings yet
- Asian CatalougeDocument15 pagesAsian CatalougearunscholarNo ratings yet
- NewLecture8 Centrifugal CompressorsDocument126 pagesNewLecture8 Centrifugal CompressorsKhalid Mahmood100% (1)
- Perfiles Pesos y NomenglaturasDocument32 pagesPerfiles Pesos y NomenglaturasErick Ccari TapiaNo ratings yet
- Science Daily Lesson LogrDocument1 pageScience Daily Lesson LogrAudie Nocedo MontecastroNo ratings yet
- IB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)Document3 pagesIB Lab - 09 Projectile Motion (DCP CE)ringo_tigerNo ratings yet
- SDOF Damped Forced Vibration - NewmarkDocument5 pagesSDOF Damped Forced Vibration - NewmarkAbu Hadiyd Al-IkhwanNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete SectionsDocument30 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Sectionsjeovan100% (1)
- TOS GRADE 7 3rd GRADINGDocument1 pageTOS GRADE 7 3rd GRADINGMELISSA MORENONo ratings yet
- Problems Involving Rate of ChangeDocument5 pagesProblems Involving Rate of ChangePaolo NaguitNo ratings yet
- Slab DesignDocument88 pagesSlab DesignNOORFARAH HUSNA BINTI INTAZALI100% (1)
- General Theory of Aerodynamic Instability and The Mechanism of Flutter - TheodorsenDocument26 pagesGeneral Theory of Aerodynamic Instability and The Mechanism of Flutter - TheodorsenAbdul Aziz Abdul MajidNo ratings yet
- Kramer Steven PDFDocument32 pagesKramer Steven PDFFurkan YılmazNo ratings yet
- Flexibility Of, and Load Distribution In, Multi-Bolt Lap Joints Subject To In-Plane Axial LoadsDocument50 pagesFlexibility Of, and Load Distribution In, Multi-Bolt Lap Joints Subject To In-Plane Axial LoadsErico Antonio TeixeiraNo ratings yet
- TWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2Document4 pagesTWI Ultrasonic Inspection Coursework 2HassanSobohNo ratings yet
- 02Document8 pages02Nghiem QuocNo ratings yet
- Slab reinforcement design calculationsDocument34 pagesSlab reinforcement design calculationsGayan IndunilNo ratings yet
- Monthly Test 1 ON M1: Engr. Md. NadimDocument2 pagesMonthly Test 1 ON M1: Engr. Md. NadimsaadNo ratings yet
- 1PHYSICS I - FORCES AND EQUILIBRIUM - STUDENTS - 2020 (3) (Autosaved)Document16 pages1PHYSICS I - FORCES AND EQUILIBRIUM - STUDENTS - 2020 (3) (Autosaved)Aser SerNo ratings yet
- Ugural - Advanced Strength PDFDocument435 pagesUgural - Advanced Strength PDFA Chilik50% (2)
- Einstein-Rosen Bridge Revisited and Lightlike ThinDocument15 pagesEinstein-Rosen Bridge Revisited and Lightlike ThinSomanshu KumarNo ratings yet
- Quantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowFrom EverandQuantum Physics: What Everyone Needs to KnowRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (48)
- Quantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessFrom EverandQuantum Spirituality: Science, Gnostic Mysticism, and Connecting with Source ConsciousnessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Quantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishFrom EverandQuantum Physics for Beginners Who Flunked Math And Science: Quantum Mechanics And Physics Made Easy Guide In Plain Simple EnglishRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- Too Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldFrom EverandToo Big for a Single Mind: How the Greatest Generation of Physicists Uncovered the Quantum WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (8)
- Summary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingFrom EverandSummary and Interpretation of Reality TransurfingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismFrom EverandThe Tao of Physics: An Exploration of the Parallels between Modern Physics and Eastern MysticismRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (500)
- Midnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterFrom EverandMidnight in Chernobyl: The Story of the World's Greatest Nuclear DisasterRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (409)
- A Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesFrom EverandA Brief History of Time: From the Big Bang to Black HolesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (2193)
- The Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceFrom EverandThe Physics of God: How the Deepest Theories of Science Explain Religion and How the Deepest Truths of Religion Explain ScienceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (23)
- Packing for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidFrom EverandPacking for Mars: The Curious Science of Life in the VoidRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1395)
- The End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)From EverandThe End of Everything: (Astrophysically Speaking)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (155)
- Bedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceFrom EverandBedeviled: A Shadow History of Demons in ScienceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Lost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayFrom EverandLost in Math: How Beauty Leads Physics AstrayRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (125)
- The Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeFrom EverandThe Magick of Physics: Uncovering the Fantastical Phenomena in Everyday LifeNo ratings yet
- Strange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsFrom EverandStrange Angel: The Otherworldly Life of Rocket Scientist John Whiteside ParsonsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (94)
- The Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityFrom EverandThe Holographic Universe: The Revolutionary Theory of RealityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (75)
- What is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesFrom EverandWhat is Life?: With Mind and Matter and Autobiographical SketchesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (139)
- The Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldFrom EverandThe Beginning of Infinity: Explanations That Transform the WorldRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (60)
- Starry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationFrom EverandStarry Messenger: Cosmic Perspectives on CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (158)
- Black Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseFrom EverandBlack Holes: The Key to Understanding the UniverseRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- The Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsFrom EverandThe Sounds of Life: How Digital Technology Is Bringing Us Closer to the Worlds of Animals and PlantsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- The Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldFrom EverandThe Power of Eight: Harnessing the Miraculous Energies of a Small Group to Heal Others, Your Life, and the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (53)