Professional Documents
Culture Documents
EE 287 Circuit Theory Marking Scheame: Solution
Uploaded by
Eric Leo AsiamahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
EE 287 Circuit Theory Marking Scheame: Solution
Uploaded by
Eric Leo AsiamahCopyright:
Available Formats
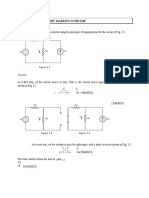
EE 287: CIRCUIT THEORY MARKING SCHEAME
Q1. Find the current in the 6 resistor using the principle of superposition for the circuit of Fig. 3.1.
Figure 3.1
Solution:
As a first step, set the current source to zero. That is, the current source appears as an open circuit as
shown in Fig. 3.2.
1
A (3MARKS)
(2MARKS)
Figure 3.2
Figure 3.3
As a next step, set the voltage to zero by replacing it with a short circuit as shown in Fig. 3.3.
I=
The total current is then the sum of 1 and 2
(2MARKS)
=
=
A(3MARKS)
Q2.
Solution:
(2marks)
Since we are interested in the current
through , the resistor
is identified as circuit B and the
remainder as circuit A. After removing the circuit B, circuit A is as shown in Fig. 3.35.
(2marks)
Figure 3.35
To find , we have to deactivate the independent voltage source. Accordingly, we get the circuit in Fig.
3.36.
= (5 20 ) + 4
Figure 3.36
+ 4 = 8 (2marks)
Referring to Fig. 3.35,
50 + 25 = 0
Hence
= 2A
= = 20( ) = 40V (2marks)
Thus, we get the Thevenins equivalent circuit which is as shown in Fig.3.37.
Figure 3.37
Figure 3.38
Reconnecting the circuit B to the Thevenins equivalent circuit as shown in Fig. 3.38, we get
=
= 4A (2marks)
Q3. Briefly explain the following terms:
a. Graph (or linear graph)
b. Branch
c. Node
d. Path
e. Loop
f. Mesh
Graph (or linear graph): A network graph is a network in which all nodes and loops are retained but its
branches are represented by lines. The voltage sources are replaced by short circuits and current sources
are replaced by open circuits.(2marks)
Branch: A line segment replacing one or more network elements that are connected in series or parallel.
(2marks)
Node: Interconnection of two or more branches. It is a terminal of a branch. Usually interconnections of
three or more branches are nodes.(2marks)
Path: A set of branches that may be traversed in an order without passing through the same node more
than once.(2marks)
Loop: Any closed contour selected in a graph.(2marks)
Mesh: A loop which does not contain any other loop within it.(2marks)
Q4. The systematic manner in which we can calculate all currents and voltages in
circuits that contain multiple nodes and loops are nodal analysis and loop analysis.
Briefly explain loop and node analysis.
Nodal Analysis An analysis technique in which one node in an N-node network is selected as the
reference node and Kirchhoffs current law is applied at the remaining N-1 non reference nodes. The
resulting N-1 linearly independent simultaneous equations are written in terms of the N-1 unknown node
voltages. In a nodal analysis we employ KCL to determine the node voltages.(5marks)
Loop Analysis An analysis technique in which Kirchhoffs voltage law is applied to a network containing
N independent loops. A loop current is assigned to each independent loop, and the application of KVL to
each loop yields a set of N independent simultaneous equations in the N unknown loop currents. a loop
analysis we use KVL to determine the loop currents.(5marks)
Q5. Briefly explain how you understand by the terms, port and the parameters of a two-port network.
A pair of terminals through which a current may enter or leave a network is known
as a port. A port is an access to the network and consists of a pair of terminals; the
current entering one terminal leaves through the other terminal so that the net
current entering the port equals zero.(3marks)
The parameters of a two-port network completely describes its behavior in
terms of the voltage and current at each port.
(3marks)
4marks for suitable examples
Q6. Answer the following questions briefly:
a. What is a graph of network?
b. What is tree of a network?
c. Give the properties of tree in a graph
d. What is a node?
e. What is a super node?
What is a graph of network?
When all elements in a network are replaced by lines with circles of dos at both ends. (2marks)
2
What is tree of a network?
It is an interconnected open set of branches which include all the nodes of the given graph. (2marks)
Give the properties of tree in a graph. It consists of all the nodes of the graph
If the graph has N no of nodes the tree will have N-I branches There will be
no closed path in the tree
There can be many possible different trees for a given graph depending on the no of nodes and
branches. (2marks)
What is a node?
A node is a point in a network in which two or more elements have a common connection. (2marks)
What is a super node?
The region surrounding a voltage source which connects the two nodes directly called super
node. (2marks)
You might also like
- EE 287 Circuit Theory Marking Scheame: SolutionDocument5 pagesEE 287 Circuit Theory Marking Scheame: SolutionEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Symbolic Circuit Modeling and Simulation Using A Sparse Matrix: An IntroductionDocument6 pagesSymbolic Circuit Modeling and Simulation Using A Sparse Matrix: An IntroductionmfqcNo ratings yet
- Series and Parallel Circuits ExplainedDocument26 pagesSeries and Parallel Circuits ExplainedAlejandro Ca MaNo ratings yet
- CIRCUIT ANALYSIS TECHNIQUESDocument118 pagesCIRCUIT ANALYSIS TECHNIQUESMahasan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Resistive Circuit Analysis Using Node MethodDocument68 pagesResistive Circuit Analysis Using Node MethodAli AsherNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 5 Study of Mesh Analysis and Nodal AnalysisDocument10 pagesDC Lab Exp 5 Study of Mesh Analysis and Nodal Analysisbirhosen92No ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes Mesh AnalysisSwaroop RamaswamyNo ratings yet
- Day 6 Notes MESH ANALYSISDocument11 pagesDay 6 Notes MESH ANALYSISturzo_eeeNo ratings yet
- Mason IRE 1953Document13 pagesMason IRE 1953meifiusNo ratings yet
- DC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, KharagpurDocument30 pagesDC Circuit: Version 2 EE IIT, Kharagpurupt vadodaraNo ratings yet
- DC and Ac NetworksDocument12 pagesDC and Ac NetworksEzekiel JamesNo ratings yet
- 04 Basic Electrical, Electronics and Measurement EngineeringDocument82 pages04 Basic Electrical, Electronics and Measurement EngineeringkrishnandrkNo ratings yet
- Unit2 KCVDocument47 pagesUnit2 KCVsanoopmkNo ratings yet
- Superposition Theorem States ThatDocument7 pagesSuperposition Theorem States ThatHaj AliNo ratings yet
- Basics of Electrical Circuits Objective QuestionsDocument8 pagesBasics of Electrical Circuits Objective QuestionsSweetlineSoniaNo ratings yet
- Circuit and System Analysis EHB 232E: Example: Find The Node Voltages of Following Circuits in JW Domain by UsingDocument25 pagesCircuit and System Analysis EHB 232E: Example: Find The Node Voltages of Following Circuits in JW Domain by UsingBatuhan ÇolaklarNo ratings yet
- DC Lab Exp 5Document15 pagesDC Lab Exp 5Sagor Saha100% (3)
- FCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)Document11 pagesFCS+Chapter+3 (3 1-3 3)kujong agacerNo ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Thevenin's and Norton TheoremDocument132 pagesNodal Analysis Mesh Analysis Superposition Thevenin's and Norton Theoremkarra veera venkata prasadNo ratings yet
- Loop Analysis of DC CKTDocument10 pagesLoop Analysis of DC CKTDev SwainNo ratings yet
- RealAnalog Circuits1 Chapter3Document36 pagesRealAnalog Circuits1 Chapter3Raghu TejaNo ratings yet
- Mesh Current AnalysisDocument4 pagesMesh Current AnalysisMohammad Sohaib MurtadhaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Power System Analysis 3. The Admittance Model and NetworkDocument41 pagesElectrical Power System Analysis 3. The Admittance Model and Networkbuggs1152100% (6)
- TransformerDocument9 pagesTransformerUtkarsh SengarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 DC CircuitsDocument22 pagesChapter 2 DC CircuitsSolomon AsefaNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - NewDocument64 pagesUnit2 - NewHarsha AnantwarNo ratings yet
- Capacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Document6 pagesCapacitive Reactance Experiment - LAB 7Mr_asad_20No ratings yet
- Experiment 6 and Experiment 7Document5 pagesExperiment 6 and Experiment 7Gebre TensayNo ratings yet
- Radio Frequency and Microwave Circuits:: Ananthv@iisermohali - Ac.inDocument3 pagesRadio Frequency and Microwave Circuits:: Ananthv@iisermohali - Ac.inElectronic BoyNo ratings yet
- Delta-Star and Star-Delta Network TransformationsDocument32 pagesDelta-Star and Star-Delta Network TransformationsRamesh DongaraNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With AnswersDocument0 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank, 2 Marks With Answersaishuvc1822No ratings yet
- An Autonomous Institute Under The Aegis of Ministry of Education, Govt. of IndiaDocument52 pagesAn Autonomous Institute Under The Aegis of Ministry of Education, Govt. of IndiaRahul MeenaNo ratings yet
- University of ZimbabweDocument6 pagesUniversity of ZimbabweTatenda BizureNo ratings yet
- Network TheromsDocument118 pagesNetwork TheromsNaim Maktumbi NesaragiNo ratings yet
- Network TopologyDocument47 pagesNetwork TopologySagar S Poojary50% (2)
- Dept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Sem / Year: Ii / IDocument41 pagesDept. of Electronics and Communication Engineering: Sem / Year: Ii / Ivalan_carl07No ratings yet
- Arc ModelDocument5 pagesArc Modelbinoy_ju07No ratings yet
- Equivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4Document12 pagesEquivalent Resistance Delta - Wye Transformation: Experiment # 4John Phillip Lopez MasagcaNo ratings yet
- Microwave Note 11Document94 pagesMicrowave Note 11Rayan NezarNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis and Synthesis Class NotesDocument61 pagesNetwork Analysis and Synthesis Class NotesSandeep Kumar50% (2)
- CH 2.2networkDocument22 pagesCH 2.2networkTeshale AlemieNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionDocument33 pagesCircuit Theory Question Bank - CIT EditionMichael FosterNo ratings yet
- EE201 Matrix AnalysisDocument18 pagesEE201 Matrix AnalysisAeshwrya PandaNo ratings yet
- Ee6201 Circuit Question BankDocument33 pagesEe6201 Circuit Question BankBanu ChandarNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3B Methods of Analysis MeshDocument11 pagesChapter 3B Methods of Analysis MeshChristian MuliNo ratings yet
- Solving Transient Events in Electrical Circuits Using Differential EquationsDocument7 pagesSolving Transient Events in Electrical Circuits Using Differential EquationsShernan Paul ClaveriaNo ratings yet
- CH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Document30 pagesCH 2meshandnodeanalysis-Jameel23oct23Gorin GorinNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 2marks QuestionsDocument8 pagesUnit - 1 2marks QuestionsVinoth KaladheepanNo ratings yet
- Circuit TheoryDocument33 pagesCircuit Theoryavi713331No ratings yet
- EE201 Electric Circuit Analysis Question BankDocument14 pagesEE201 Electric Circuit Analysis Question BankFLOWERNo ratings yet
- BEE Mesh Analysis PresentationDocument8 pagesBEE Mesh Analysis Presentation230301120111No ratings yet
- Model Multiwinding TransformDocument8 pagesModel Multiwinding Transformearla1005No ratings yet
- 1 - ELC ALL Unit MCQDocument84 pages1 - ELC ALL Unit MCQmandar.linkedinNo ratings yet
- EEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalDocument29 pagesEEC 115 Electrical Engg Science 1 PracticalNwafor Timothy100% (9)
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- Resistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisFrom EverandResistivity Modeling: Propagation, Laterolog and Micro-Pad AnalysisNo ratings yet
- Feynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterFrom EverandFeynman Lectures Simplified 2C: Electromagnetism: in Relativity & in Dense MatterNo ratings yet
- Lesson Ten: Introduction To ProgrammingDocument75 pagesLesson Ten: Introduction To ProgrammingEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Introduction To The Computer 1Document10 pagesIntroduction To The Computer 1Eric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Physical V Chemical ChangeDocument8 pagesPhysical V Chemical ChangeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Bece Past Questions Answers 2010 Maths Part1 QustionsDocument8 pagesBece Past Questions Answers 2010 Maths Part1 QustionsEric Leo Asiamah100% (1)
- Data Structure 2 As CHDocument6 pagesData Structure 2 As CHEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- DBMS Lab ManualDocument39 pagesDBMS Lab ManualVivek Sharma21% (14)
- COE381 Microprocessors Marking Scheame: Q1 (A) - Write Explanatory Note On General-Purpose ComputersDocument6 pagesCOE381 Microprocessors Marking Scheame: Q1 (A) - Write Explanatory Note On General-Purpose ComputersEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 (Ictelective)Document40 pagesLesson 1 (Ictelective)Eric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Inf 370 - Information Security: Lab 1: Internet Footprinting Using LINUX and WINDOWSDocument5 pagesInf 370 - Information Security: Lab 1: Internet Footprinting Using LINUX and WINDOWSEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Basic Computer StructureDocument15 pagesBasic Computer StructureRhea AdaniNo ratings yet
- Data Structure 2 B SCHDocument7 pagesData Structure 2 B SCHEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Data Communication BSC He A MeDocument7 pagesData Communication BSC He A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Bmfi (School of Engineering) : Examination PaperDocument2 pagesBmfi (School of Engineering) : Examination PaperEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Web Based TechascheameDocument4 pagesWeb Based TechascheameEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Networking 1 BSC He A MeDocument4 pagesNetworking 1 BSC He A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Asche A MeDocument7 pagesData Communication Asche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Database Concept and Tech 1 Asche A MeDocument5 pagesDatabase Concept and Tech 1 Asche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Database Concept and Tech 1 BSC He A MeDocument5 pagesDatabase Concept and Tech 1 BSC He A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Database Concept and Tech 1 BSC He A MeDocument5 pagesDatabase Concept and Tech 1 BSC He A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Intro To Computer Arch It U Rebs Che A MeDocument7 pagesIntro To Computer Arch It U Rebs Che A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Classical Control 2 Sche A MeDocument6 pagesClassical Control 2 Sche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Classical Control 1 Sche A MeDocument7 pagesClassical Control 1 Sche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Asche A MeDocument7 pagesData Communication Asche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- End of Semester Examination: Web Technologies Marking ScheamDocument7 pagesEnd of Semester Examination: Web Technologies Marking ScheamEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Database Concept and Tech 1 Asche A MeDocument5 pagesDatabase Concept and Tech 1 Asche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Data Structure 2 B SCHDocument7 pagesData Structure 2 B SCHEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Open Source Opers Ys Asche A MeDocument3 pagesOpen Source Opers Ys Asche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Networking 1 BSC He A MeDocument4 pagesNetworking 1 BSC He A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- Classical Control 2 Sche A MeDocument6 pagesClassical Control 2 Sche A MeEric Leo AsiamahNo ratings yet
- 31 Mesh-Current and Nodal AnalysisDocument17 pages31 Mesh-Current and Nodal AnalysisSandipan DasNo ratings yet
- Verification of Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument2 pagesVerification of Circuit Using Mesh and Nodal AnalysisAbhishek RajNo ratings yet
- Class 5 - Node Voltage AnalysisDocument22 pagesClass 5 - Node Voltage AnalysisSwayam Tejas PadhyNo ratings yet
- Electrotechnics 1B Outcome A Tutorial 1 2022 PDFDocument6 pagesElectrotechnics 1B Outcome A Tutorial 1 2022 PDFMakobela MmakwenaNo ratings yet
- Nodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanDocument16 pagesNodal's and Maxwell's Theorem Anore, James IvanMeiko AbrinaNo ratings yet
- Final Report Iec-10Document10 pagesFinal Report Iec-10protikbiswas2088No ratings yet
- EEE 205 Quiz 1-A-SolutionDocument1 pageEEE 205 Quiz 1-A-SolutionengshimaaNo ratings yet
- Nodal Analysis Circuit Voltage SolutionDocument6 pagesNodal Analysis Circuit Voltage Solutionalain allitz JimeneaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1 Circuit Analysis Due Date: 26 Feb Assignment 1: S.No Answers 1Document21 pagesAssignment 1 Circuit Analysis Due Date: 26 Feb Assignment 1: S.No Answers 1Jibran ShahidNo ratings yet
- Pspice NotesDocument123 pagesPspice NotesKeane Foo100% (1)
- Node Analysis & Graph Theory PDFDocument59 pagesNode Analysis & Graph Theory PDFpurushg62No ratings yet
- Network Theory GateDocument273 pagesNetwork Theory GateGangireddy Sanjeev100% (1)
- Nodal Analysis of Electric CircuitsDocument5 pagesNodal Analysis of Electric Circuitsapi-26587237100% (3)
- Solucionario. Análisis Nodal y de MallasDocument70 pagesSolucionario. Análisis Nodal y de Mallasßräyän Nðnð FichüNo ratings yet
- ESc201 Introduction to Electronics Circuit AnalysisDocument33 pagesESc201 Introduction to Electronics Circuit AnalysisPrakhar chhalotreNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Part 1: Nodal & Mesh AnalysisDocument68 pagesChapter Three: Sinusoidal Steady-State Analysis Part 1: Nodal & Mesh Analysis01 PrOdUcTiOnNo ratings yet
- DC Circuits:: DET 101/3 Basic Electrical Circuit 1Document150 pagesDC Circuits:: DET 101/3 Basic Electrical Circuit 1guna6986No ratings yet
- Network Analysis & Synthesis (Book)Document218 pagesNetwork Analysis & Synthesis (Book)hayatNo ratings yet
- Lecture No.2Document22 pagesLecture No.2Mohammed Dyhia AliNo ratings yet
- Ee16 ElectronicsDocument114 pagesEe16 ElectronicsAndrew KimNo ratings yet
- Black Box Transformer ModelingDocument5 pagesBlack Box Transformer ModelingdankorankoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsDocument125 pagesChapter 3 - Methods of Circuit Analysis and Circuit TheoremsNaim NizamNo ratings yet
- Det10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremDocument87 pagesDet10013 & Electrical Technology: DC Equivalent Circuit & Network TheoremF1090 ALIF IKHWANNo ratings yet
- EE 211/212 SP15 HW #04 SolutionsDocument16 pagesEE 211/212 SP15 HW #04 SolutionsAyaz AhmadNo ratings yet
- EE Lab Analyzes Circuit VoltagesDocument7 pagesEE Lab Analyzes Circuit VoltagesRoss LevineNo ratings yet
- Electric Circuit and Electronics NoteDocument34 pagesElectric Circuit and Electronics NoteEzekiel JamesNo ratings yet
- Unit-III (Fundamentals of Electrical Engg.) PDFDocument32 pagesUnit-III (Fundamentals of Electrical Engg.) PDFpramana_gmritNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mesh and Nodal AnalysisDocument27 pagesChapter 3 Mesh and Nodal Analysisthines raveentraanNo ratings yet
- LAB2Document7 pagesLAB2Møhâmmåd ÑäfãíNo ratings yet
- UAE University Electric Circuits Chapter SummaryDocument362 pagesUAE University Electric Circuits Chapter SummaryPattem KedarnathNo ratings yet