Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Module2 Dopamine ReplacementDrugs Levodopa
Uploaded by
Ale GastelumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Module2 Dopamine ReplacementDrugs Levodopa
Uploaded by
Ale GastelumCopyright:
Available Formats
Drug Information Table
Dopamine-replacement Drugs levodopa/carbidopa (Sinemet)
Therapeutic Use
Administration
Relieves symptoms of
Parkinsons disease
Addition of carbidopa (at least
75 mg/day) allows for reduced
dose of levodopa and prevents
some adverse effects
Begin administration with low
doses to reduce side effects
of levodopa (daily doses of
levodopa greater than 1,000
mg have increased side effects)
Advise patient that it can take
up to 6 months for full response
to levodopa/carbidopa to occur
Monitor for loss of drug effect
and on-off episodes and
report these to provider
Immediate-release tablets
begin working within 30 min,
then begin to wear off
Extended-release tablets work
over 4 to 6 hr but can take up
to 2 hr to begin working in the
morning
Side/Adverse Effects
Interventions
Patient Instructions
Nausea, vomiting
Addition of carbidopa (at
least 75 mg/day) relieves GI
symptoms
Advise patient to take drug
with food if necessary but to
avoid high-protein foods, which
decrease absorption
Darkening of urine and sweat
Observe patient's urine and
sweat for a change in color
Warn patient that darkening of
urine and sweat can occur
Orthostatic (postural)
hypotension
Monitor patient for this effect
and prevent falling
Instruct patient to move slowly
to sitting/standing position
Dyskinesias, tremors, twitching,
and other movements
Administer amantadine
(Symmetrel) as ordered to
decrease dyskinesias
Lower dose of levodopa for
dyskinesia
Increase bedtime dose of
levodopa for dystonia in
morning
Give dose four times (instead of
three times) daily if symptoms
present a couple hours before
next dose
Instruct patient to inform
provider if dyskinesias develop
Avoid high-protein foods, which
decrease absorption
Symptoms of psychosis;
hallucinations, paranoia
Decrease levodopa/carbidopa
dosage
Administer 2nd generation
antipsychotics, such as
quetiapine (Seroquel) to relieve
symptoms
Instruct patient to notify
provider if these symptoms
occur
On-off episodes (random
times throughout day where
Parkinsons disease symptoms
potentiate )
Use controlled release Sinemet
(if previously using immediaterelease tablets)
Administer dopamine agonist
(e.g., pramipexole [Mirapex])
Administer COMT inhibitor
(e.g., entacapone [Comtan])
Administer MAO-B inhibitor
(e.g., selegiline [Eldepryl])
Instruct patient to notify
provider if these symptoms
occur
Avoid high protein foods which
decrease absorption
Contraindications
Precautions
Narrow-angle glaucoma
History of melanoma
Psychosis, suicidal thoughts
Older adults
Existing renal, hepatic,
respiratory, or endocrine
disorders
Wide angle glaucoma
Peptic ulcer disease
Depression, bipolar disorder
Interactions
Traditional (1st generation)
antipsychotics and preparations
with vitamin B6 decrease
levodopa/carbidopa action
MAOI antidepressants within 2
weeks can cause hypertensive
crisis
High protein meals decrease
levodopa/carbidopa action
Anticholinergic drugs increase
response to levodopa/
carbidopa
You might also like
- CMSRN Exam GuideDocument12 pagesCMSRN Exam GuideAle Gastelum100% (1)
- Contoh Format Apa StyleDocument8 pagesContoh Format Apa StyleFutri F. FauziahNo ratings yet
- Patient safety medical device connectionsDocument1 pagePatient safety medical device connectionsAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- New Drug CardsDocument2 pagesNew Drug CardsAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- Order of Lab Value Draws: Additives by Tube Color # of Times To Invert TubeDocument1 pageOrder of Lab Value Draws: Additives by Tube Color # of Times To Invert TubeGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Tubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesDocument38 pagesTubing Misconnections Self Assessment For Healthcare FacilitiesAle Gastelum100% (1)
- QuestionsDocument46 pagesQuestionsAle GastelumNo ratings yet
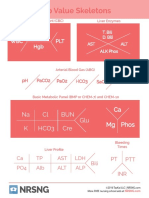
- Lab Value Skeletons: Ca MG Phos Na CL BUN K Hco3 Cre GluDocument1 pageLab Value Skeletons: Ca MG Phos Na CL BUN K Hco3 Cre GluGloryJaneNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Drug Packet PDFDocument30 pagesCardiac Drug Packet PDFAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- IV Solutions CheatsheetDocument1 pageIV Solutions CheatsheetRosemaryCastroNo ratings yet
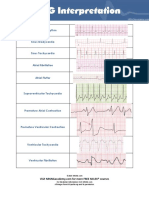
- 10 Common EKG Heart Rhythms PDFDocument1 page10 Common EKG Heart Rhythms PDFAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- 50 Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsDocument2 pages50 Most Commonly Prescribed MedicationsGloryJane67% (3)
- Module2 Dopamine ReplacementDrugs LevodopaDocument1 pageModule2 Dopamine ReplacementDrugs LevodopaAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- Module1 ExamplesOfDrug FoodInteractionsDocument1 pageModule1 ExamplesOfDrug FoodInteractionsAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- Module2 General AnesthesiaBarbiturate ThiopentalDocument1 pageModule2 General AnesthesiaBarbiturate ThiopentalAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- Module2 Direct ActingDopamineReceptorAgonistsPramipexoleDocument1 pageModule2 Direct ActingDopamineReceptorAgonistsPramipexoleAle GastelumNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5783)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)