Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Metabolic Syndrome
Uploaded by
GerardLumCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Metabolic Syndrome
Uploaded by
GerardLumCopyright:
Available Formats
jslum.
com | Medicine
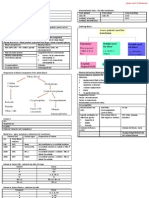
Metabolic Syndrome
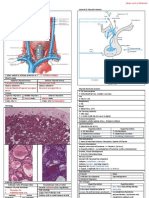
Definition Acanthosis Nigricans
Metabolic Syndrome X Brown → Black
Syndrome X Poorly Defined
Insulin Resistance Syndrome Velvety Hyperpigmentation of Skin
Reaven’s Syndrome Found in Body Folds
CHAOS (in Australia) (posterior, lateral folds of neck, axilla, groin, umbilicus, forehead)
• Coronary Artery Disease Age < 40 y/o
• High Blood Pressure May be Genetically Inherited
• Adult onset Diabetes Associated with Obesity, Endocrinopathies
• Obesity Caused by
• Stroke Insulin Resistance (↑ circulating insulin levels)
Combination of medical disorders Insulin spillover into skin
Aggregate of certain symptoms, signs Results in abnormal ↑ in growth (hyperplasia of skin)
↑ Risk
Coronary Heart Disease
Diseases related to Plaque Buildups in Artery Walls
(Stroke, Peripheral Vascular Disease)
Type 2 Diabetes
Symptoms, Features
Abdominal Obesity Xanthelasmata, Xanthoma
Excessive fat tissue in, around abdomen Signs of Dyslipidaemia
Atherogenic Dyslipidemia Not usually present in Metabolic Syndrome
↑ TG, ↓ HDL, ↑ LDL
Foster Plaque build-ups in Artery walls
↑ Blood Pre ssure
Insulin Resistance, Glucose I ntolerance
Prothrombin state
↑ Fibrinogen, Plasminogen AcƟvator Inhibitor-1 in Blood
Proinflammatory state
↑ C-Reactive Protein in Blood
Hyperuricaemia
Fatty Liver
Especially in concurrent obesity
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Women
Acanthosis Nigricans Non-Alcoholi c Fatty Liver
Consistently associated with Insulin Resistance
Abdominal (Central) Obesity Other associated variables
Visceral Type 2 DM
Male pattern Obesity
Apple-shaped adiposity Dyslipidaemia
Overweight with fat deposits around Insulin Resistance ca use Fat Accumulation in 3 mechanisms
waist Impaired in Oxidation of Fatty Acids
↑ Synthesis, Uptake of Fatty Acids
↓ Hepatic secretion of VLD Lipoprotein Cholesterol
Glucose Int olerance (Impaired Glucose Tolerance)
WHO, ADA
Intermediately ↑ Blood Glucose level 2 hours after glucose given
But less than would qualify for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome
Glucose levels – 7.8 – 11.0 mmol/L (75g oral glucose tolerance test)
Multiple cystic follicles in Ovary
Fasting Glucose
Affect approximately 5-15% of women of reproductive age (12-45 y/o)
• Normal
Principal Features
• Mildly ↑ Obesity
Often associated with Insulin Resistance
Anovulation (results in irregular menstruation)
↑ Risk of Cardiovascular pathology
Acne
May precede Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus by many years Excessive amounts, Effe cts of Androgenic hor mones (musculinizing)
Causes (Unkn own)
Insulin Resistance Insulin Resistance
Caused by Diabetes
Specific Genes Obesity
Excess Weight
Lack of Physical Activity
Muscle, Fat, Liver cells do not respond properly to Insulin
(glucose uptake, metabolism, storage)
As a result, ↑ Insulin is required (Pancreas ↑ Production, eventually Fail)
Hyperglycaemia, Hyperinsulinaemia
Metabolic Syndrome
Type 2 Diabetes
jslum.com | Medicine
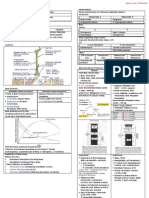
Diagnosis (Guidelines ) Risk Factors
WHO Stress
World Health Organization Criteria (1999) Upset Hormonal Balance (HPA-Axis )
NCEP-ATP III ↑ Cortisol Levels
US National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III ↑ Glucose, Insulin
IDF Insulin-mediated effects on Adipose Tissue
International Diabetes Federation concensu s worldwide definition of metabolic Promote
syndrome (2006) • Visceral Adiposity
WHO ATP III IDF • Insulin Resistance
Central Obesity √ √ √ • Dyslipidaemia
↑ BP √ √ √ • Hypertension
↑ TG √ √ √ Overweight, Obesity
↓ HDL √ √ √ Central adiposity
↑ FPG (Fasting Plasma Glucose) √ √ Sedentary Lifestyle
Microalbuminuria √ ↑ Adipose Tissue (central)
Criterias for Diagnosis Presence of Any 3 Cr iterias Central Obe sity ↓ HDL Cholesterol
DM, Glucose AND ↑ TG
Intolerance, Any 2 Cr iterias
Insulin Resi stance ↑ BP
AND ↑ Glucose
Any 2 Cr iterias Aging
Diabetes Mellitus
Epidemiology Type 2 Diabetes
3rd National Health & Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANLS III) Criteria Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT)
47 million people have Metabolic Syndrome Coronary Heart Disease
Including 44% of those in > 50 y/o group Lipodystrophy
Metabolic Syndrome present in Genetic
10% Women, 15% Men with Normal Glucose Tolerance Acquired
42% Women, 64% Men with Impaired Fasting Glucose
78% Women, 74% Men with Type 2 Diabetes Metabolic Syndrome ↑ Risk for CVS Disease
Most Patients (>80%) with Type 2 Diabetes have Metabolic Syndrome Caused by
(converse in not necessarily true) Hypertension
Affects 1 in 5 people Dyslipidaemia
Prevalence ↑ with Age Hyperglycaemia
Hypertension
Etiology ↙ ↘
Weight (Obese) Vascular Damage, Endothelium Injury ↑ Peripheral Resistance
Genetics ↓ ↓
Atherosclerosis ↑ Heart Workload
Aging ↓ ↓
Sedentary Lifestyle (↓ Physical activity, ↑ Caloric Intake) Aneurysms Cardiac Muscles Hypertrophy
Insulin Resistance Thrombosis ↓
Stress Embolism Heart Failure
Stenosis
Adipose Tissue ↓
Myocardial Infarction
Storage depot of Fat Stroke
Secretes Cytokines Renal Artery S tenosis
When there is Obesity (Marked ↑ in Adipose Tissue) Dyslipidaemia
↑ Systemic Inflammation markers ↙ ↘
↑ C-Reactive Protein Accumulation of Lipoproteins in Impair Endothelial cell function by
↑ Fibrinogen Vessel Wall, Macrophages ↑ ROS local production
↘ ↙
↑ IL-6 Atherosclerosis
↑ TNF-α ↓
Aneurysm
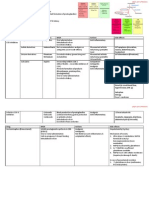
Pathophysiol ogy (Insulin Resistance in Metabolic Syndrome) Thrombosis
Lack of Exercise Embolism
Uncontrolled Diet Stenosis
↓
↓
Myocardial Infarction
Obesity Stroke
↙ ↘ Renal Artery S tenosis
Excess circulating FFA deposited in Adipose Tissue release Hyperglyc aemia
Muscle, Liver Tissues Adipocytokines ↙ ↓ ↘
Intracellular TG ↑ markedly (Leptin, Adiponectin, Resistin) Non-Enzymatic Activation of Intracellular
↓ ↓ Glycosylation Protein Kinase C Hyperglyc aemia with
↓ ↓ distrubances in
Potent Inhibitors In Obesity state
AGE Formation Include production of Polyol Pathway
(Insulin Signalling) ↓ Adiponectin Accumulate at Vessel Wall Proangiogenic, ↓
Intracellular TG ↑ Resistin ↓ Profibrinogenic molecules Intracellular accumulation
Products of Fatty Acid Metabolism ↓ Enhance Lipoproteins ↓ of metabolism of Sorbitol
Adiponectin (Insulin Sensitivity) Deposition ↑ Deposition of ECM, BM ↓
Resistin (Insulin Resistance ) Material ↑ Intracellular Osmolality
↙ ↑ H2O Influx
Insulin Resistance ↓ Intracellular
Antioxidant Reserves
↓
Endothelial Cell Injury
↙
Diabetic Macrovascular Disease
Diabetic Microangiopathy
Diabetic Complications
jslum.com | Medicine
Prevention
Exercise
Start slowly
Gradually step up to exercising on most days of the week (30-60 mins)
Lose Weight
If Overweight
Healthy Diet
↑ Fruits, Vegetables
↓ Saturated Fats, Trans Fat, Cholesterol, Salt
Quit Smoking
Treatment
Change of Lifestyle
Caloric restriction
Physical activity
Drug
Hypertension – Diuretics, ACE Inhibitors
↓LDL, ↓TG, ↑HDL – Cholesterol Drugs
↓ Insulin Resistance – Metformin, Thiazolidinediones
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (894)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Pituitary Gland PathologyDocument4 pagesPituitary Gland PathologyGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Soft Tissue InfectionsDocument3 pagesSoft Tissue InfectionsGerardLum100% (1)
- Principles of Blood TransfusionDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Blood TransfusionGerardLum100% (3)
- Hypothyroid Newsletter 01.20.09Document24 pagesHypothyroid Newsletter 01.20.09Powerbug777100% (8)
- Effects of ObesityDocument48 pagesEffects of ObesityFairuz KangNo ratings yet
- Case Study CVDDocument7 pagesCase Study CVDapi-280549915No ratings yet
- Urinary Tract InfectionDocument4 pagesUrinary Tract InfectionGerardLum100% (2)
- Posterior Pituitary SyndromeDocument1 pagePosterior Pituitary SyndromeGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Vesico Ureteral RefluxDocument1 pageVesico Ureteral RefluxGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument1 pageUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Sexually Transmitted DiseasesDocument6 pagesSexually Transmitted DiseasesGerardLum100% (3)
- ThalassaemiaDocument4 pagesThalassaemiaGerardLum100% (4)
- Thyroid PhysiologyDocument2 pagesThyroid PhysiologyGerardLum100% (2)
- ThrombophiliaDocument3 pagesThrombophiliaGerardLum100% (1)
- Renal Function in Disease StateDocument2 pagesRenal Function in Disease Statedamai140390No ratings yet
- Pituitary DysfunctionDocument2 pagesPituitary DysfunctionGerardLum0% (1)
- Soft Tissue TumoursDocument8 pagesSoft Tissue TumoursGerardLum100% (2)
- Skeletal Muscle RelaxantsDocument1 pageSkeletal Muscle RelaxantsGerardLum100% (2)
- Renal Excretion of DrugsDocument3 pagesRenal Excretion of DrugsGerardLum100% (3)
- Prostate GlandsDocument3 pagesProstate GlandsDragan PetrovicNo ratings yet
- Pathology of TestesDocument4 pagesPathology of TestesGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology GlomerulonephritisDocument4 pagesPathology GlomerulonephritisGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathology of DiabetesDocument4 pagesPathology of DiabetesGerardLum100% (4)
- Pathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Calcium, Phosphate HomeostasisGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Nerve InjuryDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Nerve InjuryGerardLum100% (1)
- Pathology of Thyroid DiseasesDocument5 pagesPathology of Thyroid DiseasesGerardLum100% (2)
- Pathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesDocument5 pagesPathogenesis Chronic Complications DiabetesGerardLum100% (1)
- Paediatrics OrthopaedicsDocument5 pagesPaediatrics OrthopaedicsGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Pathogenesis Bleeding DisordersDocument4 pagesPathogenesis Bleeding DisordersGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Overview of AnaemiaDocument2 pagesOverview of AnaemiaGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Nsaids DrugsDocument2 pagesNsaids DrugsIrene Zae MwandotoNo ratings yet
- Obstructive UropathyDocument3 pagesObstructive UropathyGerardLum100% (1)
- Nocturnal EnuresisDocument1 pageNocturnal EnuresisGerardLumNo ratings yet
- Stephen Holt MD-Anti Aging and Aesthetic MedicineDocument48 pagesStephen Holt MD-Anti Aging and Aesthetic MedicineStephen Holt MDNo ratings yet
- Unmet Needs in Hispanic/Latino Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusDocument8 pagesUnmet Needs in Hispanic/Latino Patients With Type 2 Diabetes MellitusChris WilliamsNo ratings yet
- Scientific names and uses of areca nutDocument15 pagesScientific names and uses of areca nutK AnjaliNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4api-307989771No ratings yet
- PRESCRIBING AND DOSAGE GUIDE FOR HERBAL FORMULAEDocument17 pagesPRESCRIBING AND DOSAGE GUIDE FOR HERBAL FORMULAEInfohoggNo ratings yet
- (Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology) Stanley J. Ulijaszek, Neil Mann, Sarah Elton - Evolving Human Nutrition_ Implications for Public Health-Cambridge University Press (2012Document416 pages(Cambridge Studies in Biological and Evolutionary Anthropology) Stanley J. Ulijaszek, Neil Mann, Sarah Elton - Evolving Human Nutrition_ Implications for Public Health-Cambridge University Press (2012sayed makandarNo ratings yet
- 1828 FullDocument6 pages1828 FullChikezie OnwukweNo ratings yet
- Cobas b101 PDFDocument6 pagesCobas b101 PDFGolden Flower ATLMNo ratings yet
- Ayuno Intermitente Test 2Document16 pagesAyuno Intermitente Test 2Denisse San MartínNo ratings yet
- Fact Sheeton Canola OilDocument15 pagesFact Sheeton Canola OilMonika ThadeaNo ratings yet
- 07 MJN 24 (3) Nopphanath Et Al.Document10 pages07 MJN 24 (3) Nopphanath Et Al.Egy SunandaNo ratings yet
- Causes of ObesityDocument3 pagesCauses of ObesityKaren Chambre100% (1)
- Liu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityDocument17 pagesLiu 2017-Herbal Medicine For The Treatment of ObesityMas NuriNo ratings yet
- Nutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansDocument26 pagesNutrients: Obesity and Dyslipidemia in South AsiansFitriNo ratings yet
- Does Family History of Obesity, Cardiovascular, and Metabolic Diseases Influence Onset and Severity of Childhood ObesityDocument6 pagesDoes Family History of Obesity, Cardiovascular, and Metabolic Diseases Influence Onset and Severity of Childhood ObesityTony Miguel Saba SabaNo ratings yet
- ACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 14 Exercise GuidelinesDocument57 pagesACE Personal Trainer Manual Chapter 14 Exercise GuidelinesĐạt NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Heart Failure in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome XDocument12 pagesHeart Failure in Patients With Metabolic Syndrome XErwin SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Atherosclerosis and Ischemic Heart Disease: UtlineDocument8 pagesAtherosclerosis and Ischemic Heart Disease: UtlinevmdcabanillaNo ratings yet
- NOCN ESOL International Reading Level C2 Proficient Paper AA Sample Examination Task SheetDocument12 pagesNOCN ESOL International Reading Level C2 Proficient Paper AA Sample Examination Task SheetRania NerNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Management ATIDocument15 pagesDiabetes Management ATIJessica ChirinoNo ratings yet
- Haramaya University College of Health and Medical ScienceDocument39 pagesHaramaya University College of Health and Medical Scienceani gadaNo ratings yet
- Managing Prameha According to Ayurvedic PrinciplesDocument12 pagesManaging Prameha According to Ayurvedic PrinciplesKrishan KumarNo ratings yet
- Metabolic Syndrome Guidelines SummaryDocument3 pagesMetabolic Syndrome Guidelines SummaryCrhistian Celis OlaveNo ratings yet
- Biological Activities of Stilbenoids: Molecular SciencesDocument25 pagesBiological Activities of Stilbenoids: Molecular SciencesAna PaulaNo ratings yet
- Defeat Diabetes With A Vegan DietDocument48 pagesDefeat Diabetes With A Vegan DietLigia DeborahNo ratings yet
- 11 Foods For Amazing Sex M16Document39 pages11 Foods For Amazing Sex M16Massimiliano SabatoNo ratings yet
- Andropause: Current Concepts: Keywords: Androgen Deficiency in Ageing Male, Late Onset Hypogonadism, TestosteroneDocument14 pagesAndropause: Current Concepts: Keywords: Androgen Deficiency in Ageing Male, Late Onset Hypogonadism, TestosteroneYariCárdenasNo ratings yet