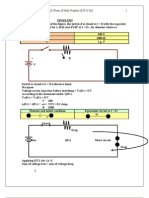
Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Syllabus
Uploaded by
Ruchi Sharma0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesefef
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentefef
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSyllabus
Uploaded by
Ruchi Sharmaefef
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as TXT, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
PRINCIPLES OF ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING
1.Circuit components; network graphs.
2.KCL, KVL; circuit analysis methods.
3.Nodal analysis, mesh analysis.
4.Thevenin s, Norton s, Superposition and Maximum Power Transfer theorems.
5.Transient response of DC and AC networks.
6.Three phase circuits; Balanced three phase circuits.
7.Magnetically coupled circuits.
SIGNALS AND SYSTEMS
1.Representation of continuous time and discrete-time signals & systems.
2.LTI systems.
3.Convolution; impulse response.
4.Time-domain analysis of LTI systems based on convolution and differential/diff
erence equations.
5.Fourier transform.
6.Laplace transform, Z-transform.
7.Transfer function.
8.Sampling and recovery of signals.
9.DFT, FFT Processing of analog signals through discrete-time systems.
10.Linear convolution, discrete cosine transform, FIR filter, IIR filter, biline
ar transformation.
ELECTROMAGNETIC THEORY
1.Maxwell s equations.
2.Wave propagation in bounded media.
3.Boundary conditions.
4.Reflection and refraction of plane waves.
5.Transmission lines.
6.Travelling and standing waves.
7.Impedance matching, Smith chart.
8.Gauss Theorem.
9.Electric field and potential due to point, line, plane and spherical charge di
stributions.
10.Ampere s and Biot-Savart s laws; inductance, dielectrics, capacitance.
ANALOG ELECTRONICS
1.Characteristics and equivalent circuits (large and small-signal) of Diode.
2.BJT, JFET and MOSFET.
3.Diode circuits: clipping, clamping, rectifier.
4.Biasing and bias stability.
5.FET amplifiers. Current mirror.
6.Amplifiers: single and multi-stage, differential, operational, feedback and po
wer.
7.Analysis of amplifiers; frequency response of amplifiers.
8.OPAMP circuits.
9.Filters:basics of filter circuits and applications, simple active filters.
10.sinusoidal oscillators: criterion for oscillation.
11.Single-transistor and OPAMP configurations.
12.Function generators and wave-shaping circuits.
13.Linear and switching power supplies.
DIGITAL ELECTRONICS
1.Boolean algebra; minimization of Boolean functions; logic gates.
2.Digital IC families (DTL, TTL, ECL, MOS, CMOS).
3.Combinational circuits: arithmetic circuits, code converters, multiplexers and
decoders.
4.Sequential circuits: latches and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers.
5.Comparators, timers, multivibrators.
6.Sample and hold circuits, ADCs and DACs. Semiconductor memories.
7.Logic implementation using programmable devices (ROM, PLA, FPGA).
ELECTRICAL MACHINES
1.Single phase transformers, three phase transformers - connections, parallel op
eration, auto-transformer.
2.Energy conversion principles.
3.DC machines - types, windings, generator characteristics, armature reaction an
d commutation.
4.Starting and speed control of motors.
5.Induction motors(including 3 phase) - principles, types, performance character
istics, starting and speed control.
6.Synchronous machines - performance, regulation, parallel operation of generato
rs.
7.Motor starting, characteristics and applications.
8.Servo and stepper motors.
ANALOG COMMUNICATION
1.Random variables: continuous, discrete.
2.Probability, probability functions.
3.Statistical averages; probability models.
4.Random signals and noise: white noise,noise equivalent bandwidth; signal trans
mission with noise; signal to noise ratio.
5.Linear CW modulation: Amplitude modulation.
6.DSB, DSB-SC and SSB.
7.Modulators and Demodulators; Phase and Frequency modulation: PM & FM signals;
narrowband FM; generation & detection of FM and PM.
8.Deemphasis,Preemphasis. CW modulation system.
9.Superhetrodyne receivers, AM receivers, communication receivers, FM receivers.
10.phase locked loop, SSB receiver Signal to noise ratio calculation for AM and
FM receivers.
DIGITAL COMMUNICATION
1.Pulse code modulation (PCM), differential pulse code modulation (DPCM), deltam
odulation (DM).
2.Digital modulation and demodulation schemes: amplitude, phase and frequency ke
ying schemes.
3.Sampling, quantizing, coding, frequency and time domain multiplexing.
4.(ASK, PSK, FSK). Error control coding: error detection and correction, linear
block codes, convolution codes.
5.Information measure and source coding.
6.Data networks, 7-layer architecture.
7.Power line carrier communication systems.
You might also like
- Windows Codecs RawDocument1 pageWindows Codecs Rawsidfrid00No ratings yet
- WM Capture 8 Setup LogDocument19 pagesWM Capture 8 Setup LogRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Windows Repair Setup LogDocument50 pagesWindows Repair Setup LogRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Miflash@2018427Document1 pageMiflash@2018427Ruchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Table Text Service AmharicDocument9 pagesTable Text Service AmharicRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Third Party NoticesDocument4 pagesThird Party NoticesAline França FernandesNo ratings yet
- Launch UrlDocument1 pageLaunch UrlRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- PrimoPDF Setup LogDocument1 pagePrimoPDF Setup LogRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- About Should - HelpDocument3 pagesAbout Should - HelpEzlan HarithNo ratings yet
- Default HelpDocument2 pagesDefault HelpDj ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Miflash@201865Document1 pageMiflash@201865Ruchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- About TestDrive - HelpDocument1 pageAbout TestDrive - HelpSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- GmreadmeDocument1 pageGmreadmeAccap Aninam DimaraNo ratings yet
- Out LogDocument1 pageOut Logrodrigo_meneguettiNo ratings yet
- About Pester - HelpDocument3 pagesAbout Pester - HelpSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- About Mocking - HelpDocument4 pagesAbout Mocking - HelpSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Table Text Service AmharicDocument9 pagesTable Text Service Amharicscottyburger0% (1)
- Default HelpDocument2 pagesDefault HelpDj ChandlerNo ratings yet
- Cert OverrideDocument1 pageCert OverrideviquezejinNo ratings yet
- Site Security Service StateDocument1 pageSite Security Service StatehjhjNo ratings yet
- About BeforeEach AfterEach - HelpDocument2 pagesAbout BeforeEach AfterEach - HelpRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Windows Codecs RawDocument1 pageWindows Codecs Rawsidfrid00No ratings yet
- Table Text Service YiDocument30 pagesTable Text Service YidjjazrielNo ratings yet
- About BeforeEach AfterEach - HelpDocument2 pagesAbout BeforeEach AfterEach - HelpRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Revocation SDocument10 pagesRevocation SRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- Network Analysis by Van Valkenburg Chap 5 Solution ManualDocument70 pagesNetwork Analysis by Van Valkenburg Chap 5 Solution ManualBilal Mobeen85% (96)
- PrimoPDF Setup LogDocument1 pagePrimoPDF Setup LogRuchi SharmaNo ratings yet
- About TestDrive - HelpDocument1 pageAbout TestDrive - HelpSatish Kumar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Table Text Service TigrinyaDocument9 pagesTable Text Service TigrinyaMuhammad Farid ZakiNo ratings yet
- GmreadmeDocument1 pageGmreadmeAccap Aninam DimaraNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Step Down PSIMDocument6 pagesStep Down PSIMAnonymous W44hzJ9roNo ratings yet
- MNIT Internship Report PDFDocument35 pagesMNIT Internship Report PDFANIL JAKHAR0% (1)
- MVDT2002 Service ManualDocument200 pagesMVDT2002 Service ManualJuan Carlos PerdomoNo ratings yet
- Sedra Smith Instructors Solutions Manual XXDocument500 pagesSedra Smith Instructors Solutions Manual XXsavaş sertkaya100% (1)
- DSAEDA00045755Document16 pagesDSAEDA00045755Rafael OlaveNo ratings yet
- Analog Circuits DesignDocument8 pagesAnalog Circuits DesigngiribabukandeNo ratings yet
- 32V-300A60kHz Edge Resonant Soft-Switching PWM DCDC Converter With DC Rail Series Switch-Parallel Capacitor Snubber Assisted by High-Frequency Transformer Parasitic Components PDFDocument7 pages32V-300A60kHz Edge Resonant Soft-Switching PWM DCDC Converter With DC Rail Series Switch-Parallel Capacitor Snubber Assisted by High-Frequency Transformer Parasitic Components PDFKapil AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Cooling Methods for Electronic EquipmentDocument31 pagesCooling Methods for Electronic EquipmentShashank PansariNo ratings yet
- PSD1Document39 pagesPSD1Swati DevNo ratings yet
- C1815, NPN TransistorDocument2 pagesC1815, NPN Transistorabcx769No ratings yet
- RF Voice TransmitterDocument82 pagesRF Voice TransmittergumankhanNo ratings yet
- Datasheet PDFDocument11 pagesDatasheet PDFLOLONo ratings yet
- MTech (ECE) - Odd Sem-Aug-Dec-2022Document4 pagesMTech (ECE) - Odd Sem-Aug-Dec-2022AshuNo ratings yet
- Optical Current Transformer: Applications and AdvantagesDocument20 pagesOptical Current Transformer: Applications and Advantagesshubham jaiswalNo ratings yet
- 72 Cells DatasheetDocument2 pages72 Cells DatasheetSemih HürmeydanNo ratings yet
- AN3396 MaximDocument11 pagesAN3396 MaximFlavioHernanNo ratings yet
- Calculate power needs for an EX8208 switchDocument5 pagesCalculate power needs for an EX8208 switchbrightanvilNo ratings yet
- DC Reactor Type Transformer Inrush Current Limiter PDFDocument7 pagesDC Reactor Type Transformer Inrush Current Limiter PDFalex696No ratings yet
- AnIntroductionToPiezoelectricMaterialsAndApplicatioIntroPages PDFDocument17 pagesAnIntroductionToPiezoelectricMaterialsAndApplicatioIntroPages PDFCak AntoNo ratings yet
- PLEDDocument16 pagesPLEDRiya PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- Line ProtectionDocument91 pagesLine Protectionhafiz_hazreen100% (1)
- Atlas DCA Pro (Model DCA75) Software Package Revisions: Latest Version at The TopDocument2 pagesAtlas DCA Pro (Model DCA75) Software Package Revisions: Latest Version at The TopAirkid Discomovil JesusNo ratings yet
- Scattering Mechanisms in Β-Ga2O3 Junctionless SOI MOSFET - Investigation of Electron Mobility and Short Channel EffectsDocument6 pagesScattering Mechanisms in Β-Ga2O3 Junctionless SOI MOSFET - Investigation of Electron Mobility and Short Channel Effects刘锦成No ratings yet
- TPS61042 Constant Current LED Driver: 1 Features 3 DescriptionDocument31 pagesTPS61042 Constant Current LED Driver: 1 Features 3 DescriptiontcmNo ratings yet
- X28C256P 25Document24 pagesX28C256P 25malca53328No ratings yet
- 2011 0079 Jobbagy BiomedicalDocument257 pages2011 0079 Jobbagy BiomedicalTan Huynh50% (2)
- 169 T562 PDFDocument5 pages169 T562 PDFYulian Deni AdhitamaNo ratings yet
- MB3773Document28 pagesMB3773Morteza BaratzadehNo ratings yet
- RESISTOR COLORDocument29 pagesRESISTOR COLORJomer JuanNo ratings yet
- Presented By: RUCHI SHARMA:14105A0007 RUTUJA SOLKAR:14105A0008Document13 pagesPresented By: RUCHI SHARMA:14105A0007 RUTUJA SOLKAR:14105A0008PRABAKAR PONNUSAMYNo ratings yet