Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Field Training Report Format22-07c
Uploaded by
dhiraj patilCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Field Training Report Format22-07c
Uploaded by
dhiraj patilCopyright:
Available Formats
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Chapter 1
INTRODUCTION
1.1) General:
Structural designing is basically a combination of knowledge and experience. The
knowledge component includes knowing basics of mechanics, material properties, tool of
analysis, design methodology and code provisions for structural designing mention in relevant IS
Codes such as IS 456, IS 1893, IS 800,etc.
In the theory subjects we learn the design of RCC structures and all the theory part cannot
be applied directly in the field or construction site. So the ultimate aim of field training is to get
knowledge of practical design of RCC buildings. There is a some difference in the theoretical
designing of structures, we strictly follows the IS code provisions but in practical point of view
there is some changes as per convenience of the designer and as per general formwork sizes used
on the sites. In practice we first assume the sizes of the components of the structure and then
checks are taken for those sizes.
Field training is being carried out in a consulting firm of Mr. Jaysinh Deshmukh who
completed his post graduate in structure and he started its own business as structural consultant.
Office is situated in Sayville Ingale Nager, Kolhapur. He is good structural engineering and he
was design apartments, bungalows etc in his career.
1.2)
Project details:
Name of the project
:-
Bungalow Design
Client
:-
Mr. Nadeem Mujawar
Contractor
:-
Consultant
:-
Jaysinh Deshmukh
Built-up area
:-
1284 square ft
Estimated Cost
:-
15, 40,000
Duration of Project
:-
6 month
Work schedule
:-
work will be start in next month
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Chapter 2
ABSTRACT OF WORK DONE
Trainee Name: - Dhiraj K Patil
Name of Industry: - Jaysinh Deshmukh
Training period from date 12 June 2015 to date 4 July 2015
Table 2.1 Works done
Sr.
No.
Day &
Date
Abstract of Work done
June 12
Study of various Structural Drawings
Skill exposure
(Technical/practical/Mana
gement/communication/te
am work/contemporary
issues/ society
expectations)
Practical
June 13
June 15
June 16
June 14
June 18
June 19
June 20
June 22
Site visit
Make center line plan and position of column
Crate model on staad pro
Calculate load then apply on model and analyze
According to result from staad pro crate group
Design of column
Design of foundation
Design of foundation
Practical
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
10
June 23
11
June 24
12
June 25
13
June 26
Drawing of foundation and column
Design of slab
Design of slab
Drawing of slab
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
14
June 27
15
June 29
16
June 30
Design of beam
Design of beam
Design of beam
Technical
Technical
Technical
17
July 1
18
July 2
19
July 3
20
July 4
Design of beam
Drawing of beam
Drawing of beam
Drawing of beam
Technical
Technical
Technical
Technical
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Chapter 3
DETAILS OF WORK DONE
3.1) General
On the initial stage of field training, sir gave information about the design of various
structural members & their functional requirement in building. Also sir gave us standard values
of various loads like live load, dead load and floor finish load for different types of building and
load calculation for various types of structural members. He told some basic things regarding the
practical design of RCC members. The limit state method is used for the design. At the initial
stage I learned the designing the structural members using their thumb rules. Then they told
minimum and maximum provision of steel in structural members. They had checked the designs
and told if any wrong things done or any changes in the design.
After this we done design using software STAAD-Pro then they checked and they gave
suggestion about design.
Fig 3.1 Ground floor plan
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Fig 3.2 First floor plan
Fig 3.3 Center line plan
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
3.1.1) Staad pro modeling
From centerline plan crate model of building in staad pro software and apply calculated
load on model and analyze model with different load combination. Following figure show model
in staad pro.
Fig 3.4 3D model
Fig 3.5 Model different load combination
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
3.2) Design
After analyze model in staad pro make group according load for designing column and
footing.
Table 3.1 Grouping
Group
Node No
Axial load in kN
510.485
17 18 20 21 23 25
19
24
348.646
16, 22
348.646
348.646
3.2.1) Column design
Column design for group A
General Design Parameters:
Column size, (B x D) = 300 x 375 mm
Column height, (L) = 3000 mm
From analysis results, load on column
Axial load = 510.485 KN
Fck = 20.00 N/mm
Fy = 415 N/mm
Design procedure:
Slenderness ratio = 3000/300 = 10 < 12
Thus design the column as a short column.
Calculation of area of steel:
Assume 1% steel
P = (0.4fck X 0.99Ag) + (0.76fy X 0.01Ag)
510.485 x 103 x 1.5 = (0.4 X 20 X 0.992Ag) + (0.67 X 415 X 0.01Ag)
Ag = 71559.83
Since one dimension of column in 230mm
Other dimension of column = 71559.83/230=311.2
Provide = 375 mm
Check for minimum eccentricity
For longer span
e min = (leff / 500)+(D/30)= (3000/ 500)+(375/30)=18.5<20 Hence ok
For shorter span
e min = (leff / 500)+(D/30)= (3000/ 500)+230/30)=11.5<20 Hence ok
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Ties Details:
Calculation of diameter of ties:
As per IS 456: 2000 Clause 26.5.3.2 (c), the diameter of the polygonal links or lateral ties
shall be not less than the following
i) one-fourth the diameter of the largest longitudinal bar = 16/4 = 4 mm
ii) In no case less than = 6 mm
Required diameter = maximum of (3, 6) = 6 mm
Provide 6 mm diameter for ties.
Calculation of spacing of ties:
As per IS 456: 2000 Clause 26.5.3.2 (c), the pitch of transverse reinforcement shall be not
more than the least of the following distances:
i ) The least lateral dimension of the compression member = 230 mm
ii) Sixteen times the smallest diameter of the longitudinal reinforcement bar to be tied
= 16 x 16 = 256 mm
iii) 300 mm
Required spacing = minimum of (230, 256, 300) = 200 mm #
Provide ties 6 mm dia @ 200 mm c/c
Summary:
Provide
Provide
Provide
Provide
Provide
rectangular section: 230 x 380 mm
#16 - 4 nos.
#12 - 2 nos.
ties 6 mm dia @ 200 mm c/c
2 legged ties along width and 2 legged ties along depth
Fig 3.6 Details reinforcement in column
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
3.2.2) Footing design
Footing design for group A
Foundation Design: (Design by Limit State Method as per IS 456: 2000)
Size of column, (b x l) = 0.300 x 0.375 m
SBC of soil = 300 kN/m
Fck = 20.00 N/mm
Fy = 415.00 N/mm
Loads on Footing
Factored axial load on column,(P) = 510.485 kN
Self Weight of footing assumed (Sw) = 10.00 % of Pw = 51.043 kN
Total Ultimate load,(Pu1 ) = 561.5335 kN
Footing Area
Area of footing, (Af) = P1 /SBC = 561.5335 / 300.00 = 1.871m
Required length of footing = Lf= 1450mm
Therefore breath of footing =Bf= 1310
Adopt area of footing = 1.45x1.31=1.89>1.871 OK
SBC Check:
Upward pressure due to axial load,(P r1w) = P1 / (L x B) = 445.66 kN/m
Depth Calculations:
Depth required for punching shear:
Depth required from bending moment considerations:
Mux = P shaded area perpendicular distance
= 445.66 1.31 (0.538/2) = 84.49 kNm
Width of the footing at top =b1=230+2x50=330mm
Required eff. Depth from bending about x axis=304.57mm
Muy = P shaded area perpendicular distance
= 445.66 1.45 (0.538/2) =93.52 kNm
d req = 267.08 mm
Provide total depth of 400 mm and max thick at the end equal to 200mm
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Area of steel required:
Ast x =530.1mm2
Provide 10 mm dia bar
No of bar = 7
Ast y =591.97.14mm2
Provide 10 mm dia bar
No of bar = 8
Summary:
Details of slopped footing are as follows
Size=1450x1310 mm at bottom and 575 x 430 mm at top
Depth of footing = 400 mm
Thickness at the edge =200mm
Reinforcement for bending
X axis =7 Nos # 10 mm bar parallel to length
Y axis= 8 Nos # 10 mm bar perpendicular to length
Fig 3.7 Details reinforcement in footing
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
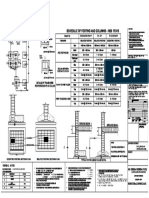
Table3.2 Schedule of footing and columns -: M20 & Fe415
3.1.3) Design of Slab
Slab Name: S1
Slab Type: Two-way Slab
Grade of Concrete: M20
Grade of Steel: Fe415
Dimensions: Lx = 3.99 m, Ly = 3.18 m ,
Span Ratio: Longer/Shorter = 1.25<2
Assume 0.2% of steel
Modification factor=1.68
Load calculation
Self wt= 0.15 x25=3.2kN/m2
Floor finish=0.75 kN/m2
Imposed=2 kN/m2
Total load=6.5 kN/m2
Factor load=9.75 kN/m2
Moment and Steel Calculations:
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
10
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Coefficients (x and y ) are computed as per clause D-1.1and 24.4.1 of IS 456:2000:
Mx = x x W x Lx x Lx :-0.07555 x 3.305 x 9.75=8.04 kNm
My = y x W x Lx x Lx :-0.056 x 3.305 x 9.75 = 5.96 kNm
Check for depth
d= 4115 / 20 x 2=102.67 <118mm
safe
Main steel
Ast = (0.5 x Fck/ Fy)(1-(1-(4.6 x Mu/Fck x b x d2 ))1/2 ) x b x d =151.71 mm2
Use 8 mm dia bar
Spacing = 1000 x 50/ 151.71= 329.56mm
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c
Bend alternate bar at 0.15 x 4.115 = 600mm from the center of support
Distributed steel
Ast = (0.5 x Fck/ Fy)(1-(1-(4.6 x Mu/Fck x b x d2 ))1/2 ) x b x d =111.83 mm2
Use 8 mm dia bar
Spacing = 1000 x 50/ 11.83= 329.56mm
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c in middle strip =0.75 Fy=3.086
Edge strip = 4115/8= 514.37
Torsion steel
Required steel=0.75 x Ast=124.39 mm2
Using 8mm dia bar = spacing = 100 x 50/124.39 =401.96
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c
Summery
Total depth
150 mm
Main steel
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c
Distributed steel
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c
Torsion steel
Provide #8 mm@300 mm c/c
Table3.3 Schedule of first floor slab
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
11
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Table3.4 Schedule of terrace floor slab
3.1.4) Design of beam
First floor beam design B24
Width= 230mm Depth = 375 mm
Fck= M20 Fy =Fe415
Span moment = 61.278 kN m
Left end moment= 58.447 kN m
Right end moment = 87.034 kN m
Fig 3.8 bending moment dig for beam B24
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
12
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Beam design for span moment
Beam design as flange beam
Lf= K ((lo /6) + 6Df) + bw
=0.5((5.4/6) +6 x0.15) + 0.23=1.13
Df= 150mm bw = 230mm D= 375 mm d=40mm
d= 375-40=335mm
bf = bw = 1.13-0.23=0.9m
Mu= 61.278 kNm
Xu= Df
Mu = 0.36 x 20 x 0.9 x150 (325-0.42 x 150) =254.664kNm>61.278 kNm
Beam under reinforced
Ast=543.43mm2
Provide 16 mm dia bar
No of bar=3 no
Ast pro=603.18mm2
Beam design for left end moment
Moment = 58.447 kNm
Beam design as rectangular beam
Xumax= 155.675
Mumax=66.92 kNm>58.447kNm
Beam is under reinforced section
Ast=574.006
Provide 16 mm dia bar
No of bar= 3
Beam design for right end moment
Moment = 87.034 kNm
Beam design as rectangular beam
Mumax=66.92 kNm<87.034kNm
Beam for over reinforced section
Ast1=Mumax /(0.87 x Fy x (d-0.42 x Xumax)) =713.93 mm2
Ast2= (Mu-Mumax)/ (0.87 x 415 x (d-40)
=195.47 mm2
Ast =713.93 + 195.47=909.4mm2
Provide 2 No of 16mm dia bar and 2 No of 20mm dia bar
Asc = (0.87 x Fy x Ast2)/217.5=324.48mm
Provide 16 mm dia bar
No of bar =2
Shear reinforcement
Tu= (Vu/b x d) =115.359 x103 /230 x 325=1.53 N/mm2
Pt=0.5%
Tc=0.48N/mm2
Tcmax =2.8 N/mm2
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
13
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Since Tcmax >Tv>Tc
Shear reinforcement req
Vus=115.359 x 103 0.48 x 230 x 325
=79.479 kN
Assume 8mm dia two legged stirrups
Spacing = (0.87x415x2x 0.7854 x 8x 8x325)/79479
=148mm
Check for spacing
i)
0.75 d= 0.75 x 325= 24375 mm
ii)
300mm
iii)
Min spacing =(Asv x 0.87 x 415 /(0.4x 230))
=394.53mm
Provide 8mm dia two lagged vertical stirrups at 140mm c/c throughout the beam
Table3.5 Schedule of ground beam
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
14
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Table3.6 Schedule of first beam
Table3.7 Schedule of terrace beam
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
15
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
Chapter 4
CONCLUSION
The RCC design of building has to be done on safer side in actual practice because of
lack of accuracy and unskilled labour.
Concrete of M20 grade and steel Fe 415 is used. Water cement ratio 0.45 and machine
mixing method is used for concrete.
Bar bending length are changes as boundary condition of slab is changes. (E.g. for
discontinuous end 1/6th span , for continues end 1/4th span)
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
16
FIELD TRAINING REPORT
REFERENCES
1) IS 875.
2) IS 456-2000, Code for Plain and Reinforced Concrete.
3) SP-16, Design Aids for Reinforced Concrete.
4) R.C.C. Designs (Reinforced Concrete Structures) by B. C. Punmia, Ashok Kr. Jain, Arun Kr.
Jain.
Rajarambapu Institute of Technology, Rajaramnagar
17
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- Guidelines Bridge DesignDocument208 pagesGuidelines Bridge Designaa19100% (13)
- Ricoh mpc307 407 Parts ManualDocument244 pagesRicoh mpc307 407 Parts Manualmark adams50% (2)
- Field Training Report Format22-07Document19 pagesField Training Report Format22-07dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- First Floor Beam and SlabDocument1 pageFirst Floor Beam and Slabdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 7Document39 pagesLab Report 7Fatinnnnnn100% (2)
- Sdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Document68 pagesSdoquezon Adm SHS12 Stem GP1 Q1M4 1 68Zeicel Allijah De Los SantosNo ratings yet
- Schedule of Beam and Slab For Ground Floor Top-ModelDocument1 pageSchedule of Beam and Slab For Ground Floor Top-Modeldhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Name of Work: Improvement of Water Storage Capacity of Well and Beautification of WellDocument1 pageName of Work: Improvement of Water Storage Capacity of Well and Beautification of Welldhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Gokul Shirgaon 1Document10 pagesGokul Shirgaon 1dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- B Series Lubrication System Flow SchematicDocument7 pagesB Series Lubrication System Flow Schematicdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- First Floor BeamDocument3 pagesFirst Floor Beamdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Mahadiscom - 1Document2 pagesMahadiscom - 1dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Estimate For Consultancy ChargesDocument8 pagesEstimate For Consultancy Chargesdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Drawing1 ModelDocument1 pageDrawing1 Modeldhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- MahadiscomDocument2 pagesMahadiscomdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument39 pagesThesis PDFdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Review PaperDocument6 pagesReview Paperdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- I J 50707025Document8 pagesI J 50707025dhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Applications of Remote Sensing and G.I.S. in Civil EngineeringDocument36 pagesApplications of Remote Sensing and G.I.S. in Civil Engineeringdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Thesis PDFDocument39 pagesThesis PDFdhiraj patilNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Folio Soap and DetergentDocument13 pagesChemistry Folio Soap and DetergentMarinda YieNo ratings yet
- (Doi 10.1002/9781119013228.Ch1) Kassapoglou, Christos - Modeling the Effect of Damage in Composite Structures (Simplified Approaches) Damage in Composite Structures- Notch SensitiDocument7 pages(Doi 10.1002/9781119013228.Ch1) Kassapoglou, Christos - Modeling the Effect of Damage in Composite Structures (Simplified Approaches) Damage in Composite Structures- Notch SensitiAdimasu AyeleNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow GraphDocument38 pagesSignal Flow Graphgaurav_juneja_4No ratings yet
- 5 V, 12-Bit, Serial 3.8 ADC in 8-Pin Package: Ms Conversion TimeDocument13 pages5 V, 12-Bit, Serial 3.8 ADC in 8-Pin Package: Ms Conversion TimeHrushi KesanNo ratings yet
- Power Generation by Using Piezoelectric Transducer With Bending Mechanism SupportDocument6 pagesPower Generation by Using Piezoelectric Transducer With Bending Mechanism SupportIAES IJPEDSNo ratings yet
- 17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsDocument12 pages17 Capacitors and Inductors in AC CircuitsAbhijit PattnaikNo ratings yet
- Bearings Exam Question HomeworkDocument3 pagesBearings Exam Question Homeworkabbey4623No ratings yet
- A Facile Synthesis, Characterization of N-Substituted 7-Methoxy 3-Phenyl 4 (3-Piperzin - 1-Yl-Propoxy) Chromen-2-OneDocument21 pagesA Facile Synthesis, Characterization of N-Substituted 7-Methoxy 3-Phenyl 4 (3-Piperzin - 1-Yl-Propoxy) Chromen-2-OneNalla Umapathi ReddyNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 - ComplexationDocument48 pagesTopic 2 - ComplexationLokesh JaiswalNo ratings yet
- States of Matter Lesson PlanDocument8 pagesStates of Matter Lesson Planapi-383721875No ratings yet
- Car Plate Recognition by Neural Networks and Image Processing Using Integration of WaveletsDocument5 pagesCar Plate Recognition by Neural Networks and Image Processing Using Integration of Waveletsjamal fathiNo ratings yet
- FuelDocument172 pagesFuelImtiaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Valv MarwinDocument15 pagesValv MarwinNestor OliNo ratings yet
- Appendix 27 Alternative Requirements For Glass-Lined VesselsDocument2 pagesAppendix 27 Alternative Requirements For Glass-Lined VesselsBinay K SrivastawaNo ratings yet
- Sigma Modeling PDFDocument215 pagesSigma Modeling PDFYuri Gutierrez PerezNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Multiphase Fluid Dynamics: 1.1. Scope of The BookDocument40 pagesIntroduction To Multiphase Fluid Dynamics: 1.1. Scope of The Bookdanijelkr88No ratings yet
- Old-Examination-Questions-Ch.#17 (Dr. Gondal - Phys102) : at One End, Are Approximately: (Ans: 170 and 510 HZ)Document5 pagesOld-Examination-Questions-Ch.#17 (Dr. Gondal - Phys102) : at One End, Are Approximately: (Ans: 170 and 510 HZ)Alexandro Andra PizzaroNo ratings yet
- Report 2012 - DPT - Chemical - Engineering - USC PDFDocument57 pagesReport 2012 - DPT - Chemical - Engineering - USC PDFJuberthArmandoBuitragoNo ratings yet
- DLL Week 2 G7 Science 22-23 Q2Document28 pagesDLL Week 2 G7 Science 22-23 Q2Lady MayugaNo ratings yet
- Chem 11 - Lab 1 - How Thick Is Aluminum FoilDocument1 pageChem 11 - Lab 1 - How Thick Is Aluminum FoilabmacphailNo ratings yet
- Application of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackDocument8 pagesApplication of FRC in Construction of The Underground Railway TrackClaudio PazNo ratings yet
- 750 Multilin Feeder Management Relay ManualDocument446 pages750 Multilin Feeder Management Relay ManualFerdinandja100% (1)
- Electric Power Steering - An Overview of Dynamics Equation and How It - S Developed For Large VehicleDocument8 pagesElectric Power Steering - An Overview of Dynamics Equation and How It - S Developed For Large VehiclecieloNo ratings yet
- History of MaichewDocument2 pagesHistory of MaichewSehabom Geberhiwot100% (1)
- Bio Analytical SopDocument17 pagesBio Analytical SopalexpharmNo ratings yet
- 000 ProntoSIL CatalogDocument12 pages000 ProntoSIL CatalogAbhijeet SangwanNo ratings yet
- Reliability and Performance Indices of Power Generating Units in PolandDocument7 pagesReliability and Performance Indices of Power Generating Units in Polandwoldemariam workuNo ratings yet