Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Keys To Student Success (1 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P1-5
Uploaded by
kayak001Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Keys To Student Success (1 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P1-5
Uploaded by
kayak001Copyright:
Available Formats
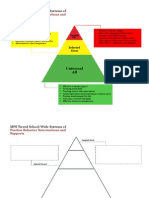
Key to Student Success
Creating a School-Wide Positive Behavior Plan
Student
Achievement
Rigorous Behavior
Instruction Management
v Increasing Staff Competency and Capacity
v Investing in Outcomes, Data, Practices and Systems
Key to Student Success:
Creating A School-Wide Behavior Plan
October 2007
Principals and School Leaders:
Our vision is that Minneapolis Public Schools will be safe, orderly learning
environments where students, staff and families share high expectations for
academic achievement and personal behavior. However, we cannot fulfill this
vision on our own. We also envision a community in which everyone helps to
create a mutually respectful, fair and caring environment where diversity is
valued.
This guide will help your school create a preventive, proactive and positive
school-wide behavior plan. Its content is based upon research from around the
nation and around our own school district. These strategies, supported by a
federal Safe Schools Healthy Students grant and by the Minnesota
Department of Education, have proven effective in several Minneapolis
schools and can work in yours.
This is not another new initiative, but a framework to help your school align
the work of teaching academics with the work of teaching behavior.
Simply put, teaching behavior is teaching. By developing a climate where
everyone can learn, we are increasing the chances for all students to succeed.
Eleanor T.Coleman
Chief of Student Support, Family and Community Engagement
October 10, 2007 | Key to Student Success 2
Developing Positive Behavior
Components of a District-Wide System Promoting
Excellent Attendance, Positive Behavior and Healthy Student Development
v System is organized, consistent, cohesive
Community & District v District policies and procedures support system
v Families engaged early in positive ways
Family Level v District articulates clear behavior and attendance expectations
v Public policy supports v Systems in place for adult leadership and skill development (HR, MFT, unions)
developing positive v Cultural competence increased through training and skill development
behavior v Resources consistent and aligned to support development of positive behavior
v Knows and supports MPS v Responsibility, accountability, monitoring assured (ELL, Sp Ed, C&I)
behavior and attendance
expectations Principals/ Teachers All Staff Students
v Parent forums offer School Administrators v Have skills to connect v Have skills to v Understand
opportunities for v Responsible for ensuring with students connect with behavior and
engagement with families Level v Are culturally competent students attendance
building-wide
on academics and support approaches to behavior v Have classroom v Are culturally expectations
parent input and attendance management skills competent v Develop the skills to
v Communication consistent v Clear behavior and v Have skills to teach and v Are able to teach and be responsible for
and ongoing attendance expectations reinforce behavior and reinforce behavior own behavior
v Early childhood programs posted and taught attendance expectations and attendance v Help students gain
high quality and aligned v Connect with students v Resources in place to expectations age-appropriate
with best practices of and families in culturally support positive v Know how to deal skills to create and
academic and child respectful ways behavior instruction with inappropriate maintain a safe and
development v Ensure staff training in behavior learning-focused
v Partnerships offer targeted effective teaching skills, v Use problem solving environment
support resources at: including cultural teams (CTARS, SST, v Have input on
School level competence etc.) to intervene building wide
Groups level v Ensure fair, equitable, with at risk students behavior plan
Individual level consistent treatment v Represented on
v Student Attendance building-wide
Review Board (SARB) behavior teams
supports student Student v Receive targeted,
attendance individualized help to Data Systems
v Youth leadership is Level develop positive behavior v Aligned v User friendly
recognized and nurtured v Interventions focused on v Data accurate and easily accessible
redirecting toward v Staff have skills to access and interpret data (T.A.)
learning and developing v Process for data collection and monitoring standardized
positive social skills
Accountability v Aligned with data v Lines of accountability clear v Expectations are clear
Systems v Monitoring frequent v Focus on learning and improving adult and student performance
October 10, 2007 | Key to Student Success 3
School-Wide Positive Behavior Plan
Table of Contents
Page 5 Components of a School-Wide Positive Behavior Plan
Page 6 3-Tiered District-Wide Support Services for Students
MPS Tiered School-Wide Systems of PBIS
Mapping Tool for School Supports
Page 10 Progressive Phases of Implementation
Phases 1-3
Page 15 Prevention Intervention Program Systems Checklist
Page 18 Positive Behavior Plan Details Sample
Page 21 Positive Behavior Plan Details Worksheet
Tabbed Resources and Samples
Section Online Resources, p24
Steps to Access PBIS Big 5 Graphs, p25
A Walk-Through Tool for Examining Your Positive Behavior Plan, p27
Sample Matrix of Expectations and Worksheet, p28-30
Active Response Flow Chart, p31
Discovery Discipline Codes and Definitions, p32
Behavior Incident Report Form, p35
School Board Policy for School-Wide Behavior Plans, p37
Effect of PBIS at Sullivan, p39
Page 40 Indicators of PBIS / Best Practices
October 10, 2007 | Key to Student Success 4
Components of a School-Wide Positive Behavior Plan
There are fundamental components for a school-wide positive behavior plan to be effective. While each school will have its
own individual characteristics for how these components appear and operate, all are essential for success.
1. A positive behavior team that is representative of 5. Clear distinctions between which behaviors are
the entire school community and meets at least handled in the classroom and which behaviors are
monthly to review and analyze data, write action plans handled outside of the classroom. The distinctions are
and train other members of the staff and school communicated and understood by all staff.
community. 6. A systematic approach for responding to behavior
2. Three to five positively stated expectations violations and for dealing with dangerous situations
with a system for teaching, practicing and positively and crisis management. The approach is
reinforcing throughout the school year. communicated and understood by all staff.
3. An educational approach to teaching 7. Data based decision making with a system for
expectations, including direct teaching of routines, collecting, analyzing and making decisions based on
transitions and social skills. Emphasis is placed on data from multiple resources.
prevention. 8. Families know and support behavior and
4. Positive acknowledgement for staff and students attendance expectations.
who demonstrate understanding of these Reference:
Sugai & Horner, 2007, www.pbis.org
expectations, as well as a system for delivering
positive acknowledgement.
October 10, 2007 | Key to Student Success 5
You might also like
- Budget Discussions Acceleration 2020 One-PageDocument2 pagesBudget Discussions Acceleration 2020 One-Pageapi-393900181No ratings yet
- Edited ResumeDocument4 pagesEdited Resumeapi-736829863No ratings yet
- Kelly G ResumeDocument3 pagesKelly G Resumeapi-402337694No ratings yet
- 2022-2024 Curriculum Management PlanDocument37 pages2022-2024 Curriculum Management Plansalma ahmedNo ratings yet
- 10 Principles For BuildingDocument19 pages10 Principles For BuildingREGINA MAE JUNIONo ratings yet
- Jduax ResumeDocument2 pagesJduax Resumeapi-486318866No ratings yet
- Self-Assessment and Reflection Final PDFDocument9 pagesSelf-Assessment and Reflection Final PDFJuan Carlos Ruiz MalásquezNo ratings yet
- Assignment-Self AsessmentDocument9 pagesAssignment-Self Asessmentapi-659774512No ratings yet
- Ead 520 Benchmark Character ProposalDocument16 pagesEad 520 Benchmark Character Proposalapi-662585020No ratings yet
- Updated ResumeDocument2 pagesUpdated Resumeapi-606262033No ratings yet
- Jenna Fawcett 2024Document2 pagesJenna Fawcett 2024api-544757782No ratings yet
- As Resume Allen Elementary FinalDocument2 pagesAs Resume Allen Elementary Finalapi-410748670No ratings yet
- Petteyvictoriaresume 2023Document3 pagesPetteyvictoriaresume 2023api-643520743No ratings yet
- School Excellence FrameworkDocument15 pagesSchool Excellence FrameworkGREG.THWAITESNo ratings yet
- Nada Zaki CV 21Document2 pagesNada Zaki CV 21api-374316401No ratings yet
- Aces Slides Casl 2Document28 pagesAces Slides Casl 2api-401672390No ratings yet
- New ResumeDocument2 pagesNew Resumeapi-484699463No ratings yet
- AOP Feb. To June 2022 FinalDocument9 pagesAOP Feb. To June 2022 FinalSt.William's MagsingalNo ratings yet
- BrochureDocument2 pagesBrochureapi-357520640No ratings yet
- Loan Officer ResumeDocument3 pagesLoan Officer ResumeDEMUREX BUSInESS COnCEPTNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Curriculum, Assessment, and Program EvaluationDocument5 pagesEarly Childhood Curriculum, Assessment, and Program EvaluationAivee ManahanNo ratings yet
- Main Scale Teacher Job DescriptionDocument3 pagesMain Scale Teacher Job DescriptionMarta VartolomeiNo ratings yet
- Business Plan: An Independent Public SchoolDocument6 pagesBusiness Plan: An Independent Public SchoolLewiNo ratings yet
- Celeste Long PGP Template-TransitionDocument6 pagesCeleste Long PGP Template-Transitionapi-404096250No ratings yet
- Alberta Leadership Quality Standards LqsDocument8 pagesAlberta Leadership Quality Standards Lqsapi-544038337No ratings yet
- GPE Sstatrtegic Planningtategic Plan 2012-2015 EnglishDocument43 pagesGPE Sstatrtegic Planningtategic Plan 2012-2015 EnglishShah ZazaiNo ratings yet
- Concord School 5027 2019 2022 School Strategic PlanDocument8 pagesConcord School 5027 2019 2022 School Strategic PlanHiếu ĐỗNo ratings yet
- Equitable Environment Board Presentation - October 24, 2022Document34 pagesEquitable Environment Board Presentation - October 24, 2022Jay BradleyNo ratings yet
- Equitable Environment Board Presentation - October 24, 2022Document34 pagesEquitable Environment Board Presentation - October 24, 2022Jay BradleyNo ratings yet
- Medina PS Plan 2021 - 2023Document8 pagesMedina PS Plan 2021 - 2023tamNo ratings yet
- Jeanette JacobsDocument3 pagesJeanette Jacobsapi-448653608No ratings yet
- PBIS Trifold BrochureDocument2 pagesPBIS Trifold BrochureparkerpondNo ratings yet
- SEL Toolkit 2021Document23 pagesSEL Toolkit 2021Maria CequenaNo ratings yet
- DownloadedDocument2 pagesDownloadedapi-363229766No ratings yet
- Traci Copeland: Education Professional ExperienceDocument3 pagesTraci Copeland: Education Professional Experienceapi-680633492No ratings yet
- 7th Grade Orientation MaltzDocument15 pages7th Grade Orientation Maltzapi-371823870No ratings yet
- School Counselor Evaluation RubricDocument17 pagesSchool Counselor Evaluation Rubricapi-335168016No ratings yet
- genesis romero resumeDocument3 pagesgenesis romero resumeapi-737299388No ratings yet
- Sao MR JDocument2 pagesSao MR Japi-376826833No ratings yet
- Pbis Tri Fold BrochureDocument2 pagesPbis Tri Fold BrochureparkerpondNo ratings yet
- Maximizing Instruction Through Professional Development: Juan Salgado 5/20/2020Document16 pagesMaximizing Instruction Through Professional Development: Juan Salgado 5/20/2020api-484995893No ratings yet
- Overview of Gep3: Saka Adebayo Ibraheem Education Officer, Kano FODocument18 pagesOverview of Gep3: Saka Adebayo Ibraheem Education Officer, Kano FOHafsat SadiqNo ratings yet
- RIDE Strategic Plan 2021-2025Document19 pagesRIDE Strategic Plan 2021-2025WJAR NBC 10No ratings yet
- School Counselor Evaluation Rubric - Self AssessmentDocument17 pagesSchool Counselor Evaluation Rubric - Self Assessmentapi-396518120No ratings yet
- Jps Strategic PlanDocument16 pagesJps Strategic Planthe kingfish100% (1)
- Emily Lane ResumeDocument3 pagesEmily Lane Resumeapi-470919717No ratings yet
- Martha Naranjo ResumeDocument3 pagesMartha Naranjo Resumeapi-524058157No ratings yet
- WHC Parent Handbook 2021Document24 pagesWHC Parent Handbook 2021Simon ChownNo ratings yet
- Morgan Schoenrock Resume 1Document3 pagesMorgan Schoenrock Resume 1api-539763985No ratings yet
- 13 Poniente Cid Erick R. SNED 27 FinalDocument11 pages13 Poniente Cid Erick R. SNED 27 FinalCid PonienteNo ratings yet
- Mariah Irizarry: CertificationsDocument3 pagesMariah Irizarry: Certificationsapi-578472382No ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas for Excelsior School Providing Quality EducationDocument19 pagesBusiness Model Canvas for Excelsior School Providing Quality EducationRajkishor YadavNo ratings yet
- I. School Counseling Department Counselling Core BeliefsDocument8 pagesI. School Counseling Department Counselling Core BeliefsAnnie MallariNo ratings yet
- Parthenia Wynn Resume 1Document2 pagesParthenia Wynn Resume 1api-628934716No ratings yet
- School Counselor Self EvaluationDocument17 pagesSchool Counselor Self Evaluationapi-365742399No ratings yet
- CV Tazmeen TeachDocument2 pagesCV Tazmeen Teachmuhammad.dawood23220No ratings yet
- Ed Teaching Quality Standard EnglishDocument8 pagesEd Teaching Quality Standard Englishapi-380548110No ratings yet
- Amelia Davis-Resume 2022Document2 pagesAmelia Davis-Resume 2022api-541685795No ratings yet
- Create a Growth Mindset School: An Administrator's Guide to Leading a Growth Mindset CommunityFrom EverandCreate a Growth Mindset School: An Administrator's Guide to Leading a Growth Mindset CommunityRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (13)
- Civic TechnologyDocument35 pagesCivic Technologykayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (7 of 7) School-Wide Positive BehaviorP37-41Document5 pagesKeys To Student Success (7 of 7) School-Wide Positive BehaviorP37-41kayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (6 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P35-36Document2 pagesKeys To Student Success (6 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P35-36kayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (4 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P11-26Document16 pagesKeys To Student Success (4 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P11-26kayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (5 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P27-34Document8 pagesKeys To Student Success (5 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P27-34kayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (3 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P8-10Document3 pagesKeys To Student Success (3 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P8-10kayak001No ratings yet
- Keys To Student Success (2 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P6-7Document2 pagesKeys To Student Success (2 of 7) School-Wide Positive Behavior P6-7kayak001No ratings yet
- CV Program Coordinator NigeriaDocument8 pagesCV Program Coordinator NigeriaCV Program CoordinatorNo ratings yet
- Presentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Document28 pagesPresentacion ISA Graphic Febrero 2015Ileana ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Student Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Document32 pagesStudent Name Student Number Assessment Title Module Title Module Code Module Coordinator Tutor (If Applicable)Exelligent Academic SolutionsNo ratings yet
- Antigua and Barbuda, Build Free Back LinksDocument7 pagesAntigua and Barbuda, Build Free Back LinkswaNo ratings yet
- Spjc/Lim Lima-Callao, Peru: .Radar - Minimum.AltitudesDocument41 pagesSpjc/Lim Lima-Callao, Peru: .Radar - Minimum.AltitudesVicente PortocarreroNo ratings yet
- Pe 1997 01Document108 pagesPe 1997 01franciscocampoverde8224No ratings yet
- Essay 5 Practice Activities - DBS IntroductionsDocument6 pagesEssay 5 Practice Activities - DBS IntroductionsLeyla IsayevaNo ratings yet
- Emergency Incidents AssignmentDocument4 pagesEmergency Incidents Assignmentnickoh28No ratings yet
- Damayan Benefit PolicyDocument2 pagesDamayan Benefit PolicyMSWDO STA. MAGDALENANo ratings yet
- Intangible Capital: Key Factor of Sustainable Development in MoroccoDocument8 pagesIntangible Capital: Key Factor of Sustainable Development in MoroccojournalNo ratings yet
- Marie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th GradeDocument50 pagesMarie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th Gradeluiz carvalhoNo ratings yet
- 3 Axis AccelerometerDocument9 pages3 Axis AccelerometerResearchDesignLabNo ratings yet
- AirROC T35 D45 D50 Tech SpecDocument4 pagesAirROC T35 D45 D50 Tech SpecmdelvallevNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 Empowerment MidtermDocument5 pagesLesson 2 Empowerment Midtermaronfranco223No ratings yet
- Digital Payments in IndiaDocument6 pagesDigital Payments in IndiaInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Basics of Directional-Control ValvesDocument11 pagesBasics of Directional-Control ValvesJosh LeBlancNo ratings yet
- The Power Elite and The Secret Nazi PlanDocument80 pagesThe Power Elite and The Secret Nazi Planpfoxworth67% (3)
- 4563Document58 pages4563nikosNo ratings yet
- Kribhco Summer Trainning ReportDocument106 pagesKribhco Summer Trainning ReportMihir Patel0% (1)
- FFT FundamentalsDocument27 pagesFFT FundamentalsVivien VilladelreyNo ratings yet
- 325W Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass ModuleDocument2 pages325W Bifacial Mono PERC Double Glass ModuleJosue Enriquez EguigurenNo ratings yet
- Pearce v. FBI Agent Doe 5th Circuit Unpublished DecisionDocument6 pagesPearce v. FBI Agent Doe 5th Circuit Unpublished DecisionWashington Free BeaconNo ratings yet
- Gram-Charlier para Aproximar DensidadesDocument10 pagesGram-Charlier para Aproximar DensidadesAlejandro LopezNo ratings yet
- Προσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςDocument20 pagesΠροσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςARISTEIDIS VIKETOSNo ratings yet
- Techniques For Optimal Placement of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations A ReviewDocument5 pagesTechniques For Optimal Placement of Electric Vehicle Charging Stations A Reviewkumar_ranjit6555No ratings yet
- SMB GistDocument7 pagesSMB GistN. R. BhartiNo ratings yet
- Section E Self Assessment Checklist For Metal Control StandardsDocument2 pagesSection E Self Assessment Checklist For Metal Control StandardsMohammed Ishak100% (1)
- Detection of Phising Websites Using Machine Learning ApproachesDocument9 pagesDetection of Phising Websites Using Machine Learning Approachesshresthabishal721No ratings yet
- PMUY supplementary document titleDocument1 pagePMUY supplementary document titleChandan Kumar Jha69% (67)
- Introduction To Circuit LabDocument8 pagesIntroduction To Circuit LabDaudKhanNo ratings yet