Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Dyn
Uploaded by
Ryan LumOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Dyn
Uploaded by
Ryan LumCopyright:
Available Formats
Temasek Junior College IP Physics
Name:
Class:
Date:
IP4 Revision Worksheet
Dynamics
Multiple Choice questions:
1
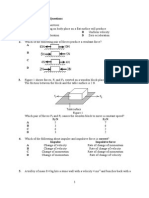
The figure shows an object at position O which is acted upon by two forces, P and Q.
P
O
Which of the following diagrams correctly represents the resultant force, R, of P and Q?
A
B
P
P
R
R
Q
P
R
P
(
Which of the following cannot be the resultant force on an object when 2 N, 3 N, and 10 N
forces act on it?
A 3N
C 7N
B
D
5N
10 N
(
A force of 54 N pushes two touching blocks of mass 6.0 kg and 2.0 kg along a flat surface.
The frictional force between the blocks and the surface is 6.0 N.
54 N
6.0 kg
6.0 N
2.0 kg
What is the magnitude of the resultant force on the 6.0 kg mass?
A 12 N
C 45 N
B
D
36 N
48 N
(
A skydiver jumps from an aircraft. The Earth exerts a downward force FE on the skydiver who
also exerts an upward force Fs on the Earth.
skydiver
diagram not drawn to scale
FE
FS
Earth
Which statement is correct?
A
B
C
D
the magnitude of FE > the magnitude of FS
the magnitude of FE < the magnitude of FS
the magnitude of FE = the magnitude of FS and they cancel each other out
the magnitude of FE = the magnitude of FS and they do not cancel each other out
The figure shows a 5.0 kg mass suspended at a point O by two light, inextensible strings, OP
and OQ. Take g = 10 m s-2.
30
What of the following correctly shows the tensions in the strings?
A
B
C
D
Tension in OP / N
0.0
5.0
50
87
Tension in OQ / N
25
4.3
50
100
(
The figure shows a constant force of 12.0 N pulling a 5.00 kg copper block along a straight
horizontal track. A frictional force of 2.00 N is acting against the direction of motion of the
block.
copper
block
12.0 N
2.00 N
Given that the initial velocity of the copper block is 1.00 m s-1, what is the distance covered by
the block in 3.00 s?
A 5.00 m
C 13.8 m
B
D
12.0 m
15.6 m
(
Short Structured Questions:
1
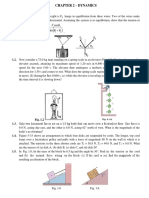
A 70. 0 kg high-jumper must exert a force on the ground to produce an upward acceleration of
4.00 times the acceleration due to gravity.
(a)
State Newtons Third Law of Motion.
[2]
(b)
(c)
Draw a free-body diagram to show all the forces acting on the high-jumper at the
moment when he just leaves the ground in the space provided below.
[2]
Calculate the net force on the high-jumper at the moment when he just leaves the
ground.
net force =
N [3]
Total: 7 marks
Fig. 2.1 shows the horizontal forces as a cyclist travels forwards.
Fig. 2.1
The cyclist produces the driving force that acts on the back wheel.
In this question, you may ignore any frictional force acting on the front wheel.
(a)
The bicycle accelerates until a constant speed is reached.
(i)
Describe how the size of the air resistance changes during this time.
[2]
(ii)
Compare the sizes of the two horizontal forces when the bicycle is accelerating.
[1]
(b)
The total mass of the bicycle and the cyclist is 75 kg. At one instant, the speed of the
bicycle is 4.0 m / s, the driving force is 30 N and the air resistance is 20 N.
Calculate
(i)
the total kinetic energy of the bicycle and the cyclist,
total kinetic energy =
[3]
(ii)
the acceleration of the bicycle and the cyclist.
acceleration =
[2]
Total: 8 marks
A window cleaner of mass 65 kg cleans windows of a high-rise building from an external lift.
The lift is suspended from the roof by two cables. The mass of the lift is 550 kg.
Take g = 10 m s-2.
(a)
Calculate the total tension T in the cables when the lift hangs at rest at the sixth floor.
T=
(b)
[2]
The total tension in the cables increased to T1 when the lift moves at a constant
acceleration of 0.20 m s-2 for 10 s.
(i)
State the direction of the acceleration.
[1]
(ii)
Calculate the total distance travelled by the lift during this 10 s.
distance =
[3]
(iii)
Calculate the force exerted by the cleaner on the bottom of the lift when the lift is
accelerating at 0.20 m s-2.
force =
[3]
Total: 9 marks
You might also like
- STPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsDocument9 pagesSTPM 2015 Term 1 Trial SMK Sultan Abdul Hamid QuestionsSouseiseki ChromeNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetDocument12 pagesWork Energy Power and Efficiency IB WorksheetAnonymous LZmFaXc100% (2)
- Trialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionDocument6 pagesTrialstpm 2023 YUHUApaper 1 QuestionMathew Cheng Yu HaoNo ratings yet
- STPM 2014 Physics Trial 2Document17 pagesSTPM 2014 Physics Trial 2choichiang100% (1)
- Tutorial 4Document5 pagesTutorial 4Winni TanNo ratings yet
- Phys 699Document25 pagesPhys 699joseftrihandokoNo ratings yet
- Phys 698Document21 pagesPhys 698joseftrihandokoNo ratings yet
- All Answers - Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Physics DocumentDocument22 pagesAll Answers - Concise SEO-Optimized Title for Physics DocumentNadiatul JannahNo ratings yet
- Physics Paper PDFDocument18 pagesPhysics Paper PDFRana IrfanNo ratings yet
- سكند فصل اول 2015-2016 PDFDocument2 pagesسكند فصل اول 2015-2016 PDFمعاذ امجد ابو يحيىNo ratings yet
- Physics Section A QuestionsDocument8 pagesPhysics Section A QuestionsFakhriHaziqNo ratings yet
- 2.2 ForceDocument16 pages2.2 ForcecetinNo ratings yet
- Physics1 MT2 KeyDocument6 pagesPhysics1 MT2 KeyMuyad AmirNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument5 pagesPhysicsBacillus SubtilisNo ratings yet
- R7100306 Classical MechanicsDocument2 pagesR7100306 Classical MechanicssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- STPM 2004 p2 AnswerDocument20 pagesSTPM 2004 p2 AnswersuhailieliasNo ratings yet
- WORK DONE BY FORCESDocument19 pagesWORK DONE BY FORCESMohammed Aftab Ahmed100% (1)
- Paper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Document15 pagesPaper 1 Fizik PAT 2016Junaidah Mohamad RamliNo ratings yet
- Physics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerDocument4 pagesPhysics Worksheet on Work, Energy and PowerGaming baseNo ratings yet
- Tutorial - Newton's Law of MotionDocument12 pagesTutorial - Newton's Law of MotionNURUL NAJIHAH KHAIRUDDINNo ratings yet
- Class: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Document7 pagesClass: XI Second Term Examination 2014-15 Subject: Physics Set B1 Time Allowed: 3 Hours Maximum Marks: 70Aryan SinghNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document4 pagesTutorial 4Cheryl LowNo ratings yet
- Newton's Laws of Motion ExplainedDocument101 pagesNewton's Laws of Motion Explainedsanits59196% (23)
- Assignment 2.2 ForcesDocument4 pagesAssignment 2.2 Forcespanghua tanNo ratings yet
- Work Power and Energy MCQs TestDocument26 pagesWork Power and Energy MCQs Testrizal123100% (1)
- Vectors and Scalars in MechanicsDocument18 pagesVectors and Scalars in Mechanicsmardel11No ratings yet
- Mechanics SummaryDocument27 pagesMechanics Summaryuse otherNo ratings yet
- Test 1: Bus velocity and projectile motion problemsDocument7 pagesTest 1: Bus velocity and projectile motion problemstaekim btsNo ratings yet
- Ce2 Sample2Document5 pagesCe2 Sample2ParZiValNo ratings yet
- Physics I Problems PDFDocument1 pagePhysics I Problems PDFbosschellenNo ratings yet
- Resonance Test SeriesDocument19 pagesResonance Test SeriesAman Shrivastava0% (1)
- A2 RevisionDocument10 pagesA2 Revisiongaya8404No ratings yet
- KCT MODEL EXAM ENGINEERING MECHANICSDocument4 pagesKCT MODEL EXAM ENGINEERING MECHANICSArunGopal PonnusamyNo ratings yet
- PHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFDocument9 pagesPHY5113 TUTORIAL N0 3 Questions PDFAlbertNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise SolutionsDocument2 pagesChapter 4 Forces and Newton's Laws of Motion Exercise SolutionsLorenzo YapNo ratings yet
- Resonance Test PaperDocument51 pagesResonance Test PaperSrijan Agrawal100% (1)
- Impo. WpeDocument24 pagesImpo. WpeChirayu SharmaNo ratings yet
- Force and MotionDocument7 pagesForce and MotionDavidHutasoit100% (2)
- 2015 - Practice Second Exam 211 CH 7-11Document27 pages2015 - Practice Second Exam 211 CH 7-11Qassem MohaidatNo ratings yet
- 2a-Dynamics MC Practice ProblemsDocument26 pages2a-Dynamics MC Practice Problemsruuki25No ratings yet
- DPP 15-17 PDFDocument5 pagesDPP 15-17 PDFAnkur GoyalNo ratings yet
- Physics Old Exam With Solutions 051Document11 pagesPhysics Old Exam With Solutions 051poker100% (1)
- CAPE Physics Unit I MarathonDocument26 pagesCAPE Physics Unit I MarathonLeighton ThompsonNo ratings yet
- UPK1 PhysicsDocument11 pagesUPK1 PhysicsErmie DharlyaNo ratings yet
- USTH B1 Exercise Part3 QuestionDocument7 pagesUSTH B1 Exercise Part3 Questionbình minh trầnNo ratings yet
- SECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DDocument17 pagesSECTION A: Objective Questions Instruction: Answer All Questions. 1. A B C D 2. A B C DNurlailie Md JamilNo ratings yet
- STPM Physics QuestionDocument10 pagesSTPM Physics Questionmuhdsabri510% (1)
- Chapter 2 - DynamicsDocument8 pagesChapter 2 - DynamicsTHIÊN LÊ TRẦN THUẬNNo ratings yet
- Examples MomentumDocument9 pagesExamples Momentumettypasewang0% (1)
- JR Iit StarDocument18 pagesJR Iit Star2pwxanqt8aNo ratings yet
- Physics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Document12 pagesPhysics 712 ND LE1 Stsem 20112012Alexis Julia CanariaNo ratings yet
- General Physics Worksheet for Freshman Unity (1)Document3 pagesGeneral Physics Worksheet for Freshman Unity (1)Ziyad MohammedNo ratings yet
- PHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2Document12 pagesPHN001_Unit1st_Assisgnment1st_2022 2harshitaNo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalDocument2 pagesWork Energy Power DPP Iitians Tapasya Akash GoyalAkash Goyal100% (1)
- GP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsDocument14 pagesGP1 S 14 Chap 5 ProblemsUmbina Gescery100% (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- GahhDocument6 pagesGahhRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Project Duration, Costs, and Standard Deviation AnalysisDocument3 pagesProject Duration, Costs, and Standard Deviation AnalysisRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Organizational Chart: Project ManagerDocument1 pageOrganizational Chart: Project ManagerRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Example of Project Charter, WBS and WBS Dictionaries Apr 16Document12 pagesExample of Project Charter, WBS and WBS Dictionaries Apr 16Ryan Lum100% (1)
- WBS DictionaryDocument6 pagesWBS DictionaryRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 5 & 6 Discussion and Computation QuestionsDocument3 pagesTutorial 5 & 6 Discussion and Computation QuestionsRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Love Dance Plot DetailsDocument1 pageLove Dance Plot DetailsRyan LumNo ratings yet
- Examination Data Sheet For The Physical Sciences (Physics) Table 1 Physical Constants Name Symbol ValueDocument2 pagesExamination Data Sheet For The Physical Sciences (Physics) Table 1 Physical Constants Name Symbol ValueMnjonero BaloyiNo ratings yet
- AP PhysicsDocument27 pagesAP PhysicsJoao Figueiredo100% (1)
- O Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Document2 pagesO Level Physics Formula Sheet 2Taha Maroof100% (1)
- Magnetostatics NotesDocument19 pagesMagnetostatics Notespraveen3.rkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEDocument44 pagesChapter 2 Force and Motion STUDENTS MODULEMohd Khairul Anuar100% (4)
- L16 FrictionDocument7 pagesL16 Frictioni5piritiNo ratings yet
- s24 Nuclear ChemistryDocument115 pagess24 Nuclear ChemistryRushikesh KhoreNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Review Package Conceptual QuestionsDocument10 pagesUnit 1 Review Package Conceptual QuestionsasmipinkiNo ratings yet
- Physics Notes PDF For Class 9Document3 pagesPhysics Notes PDF For Class 9Mithilesh Kr Prem100% (1)
- (1217) Test Papers 24 04 16 CT 3 (P 1 P 2) BDocument31 pages(1217) Test Papers 24 04 16 CT 3 (P 1 P 2) BBhagwat Singh UdawatNo ratings yet
- Unit TestDocument9 pagesUnit Testlea jalopNo ratings yet
- Derivatives and Physics Problems With SolutionsDocument3 pagesDerivatives and Physics Problems With SolutionsMaria AnderlucciNo ratings yet
- Equilibrium of A Particle in Space.: Lab Report # 2Document4 pagesEquilibrium of A Particle in Space.: Lab Report # 2HasanNo ratings yet
- 12th Physics 3 Mark Questions - Volume - 1Document2 pages12th Physics 3 Mark Questions - Volume - 1jesusjustinNo ratings yet
- SVKM J.V. Parekh International School Grade: VI Div: Subject: Physics Topic: Gravity Name of The Student: Roll NoDocument9 pagesSVKM J.V. Parekh International School Grade: VI Div: Subject: Physics Topic: Gravity Name of The Student: Roll NoWere WolfNo ratings yet
- PC1431 MasteringPhysics Assignment 6Document16 pagesPC1431 MasteringPhysics Assignment 6stpmoment33% (3)
- Motion in Two and Three DimensionsDocument16 pagesMotion in Two and Three DimensionsBrandy Swanburg SchauppnerNo ratings yet
- OscillationsDocument29 pagesOscillationsTetsuya OkazakiNo ratings yet
- Velocity, acceleration, and motion problems involving blocks, trains, races, and ballisticsDocument1 pageVelocity, acceleration, and motion problems involving blocks, trains, races, and ballisticsRoxanne de RoxasNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Linear Motion AnswerDocument11 pages2.1 Linear Motion AnswerEMELDA GRACE A/P H. DEVARAJ ASIR MoeNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2Document98 pagesGeneral Physics 2Jessica May Reyes100% (1)
- Electric Forces and Electric Fields-Final Report in Physics For TeachersDocument46 pagesElectric Forces and Electric Fields-Final Report in Physics For TeachersMaria Cristina DelmoNo ratings yet
- SAT II Physics Practice Test 2Document7 pagesSAT II Physics Practice Test 2td2012No ratings yet
- SHM experiment and graphing spring constantDocument8 pagesSHM experiment and graphing spring constantNurul ShaiedahNo ratings yet
- Paramahamsa Tewari - On Planetary Motion Caused by Solar Space VortexDocument9 pagesParamahamsa Tewari - On Planetary Motion Caused by Solar Space VortexKluff5878No ratings yet
- Electric Charge & Coulomb Force-Solution PDFDocument8 pagesElectric Charge & Coulomb Force-Solution PDFVishal AroraNo ratings yet
- Physics! Unit 04 BFPM Packet 2013Document20 pagesPhysics! Unit 04 BFPM Packet 2013Kelly O'SheaNo ratings yet
- General Physics 1: Learning Activity Sheets TorqueDocument66 pagesGeneral Physics 1: Learning Activity Sheets TorqueUser IhmnidaNo ratings yet
- Comparing Aristotle and Galileo's Concepts of MotionDocument3 pagesComparing Aristotle and Galileo's Concepts of MotionLjae NatinoNo ratings yet
- Radio PharmacyDocument44 pagesRadio PharmacyIndah PrihandiniNo ratings yet