Professional Documents
Culture Documents
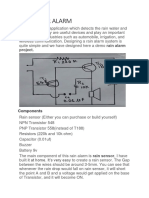
Rain Alarm
Uploaded by
Sebastin AshokCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Rain Alarm
Uploaded by
Sebastin AshokCopyright:
Available Formats
Rain Alarm
Working: Water is a conductor of electricity. When water is in contact with the probe then
there is a flow of current toward the base of NPN transistor (BC548), which conducts. With the
conduction of NPN transistor, electron reaches to Q2, which is a PNP transistor . PNP transistor
(BC558) also conducts and current flows through the speaker. In a speaker there is inductive
coil which causes motion in one direction and after that produces induce current, which is in
opposite direction to the flow of current this induced current in the form of pulse, flows through a
capacitor, resistance and makes 1st transistor BC548 off for an inter-well and after-that it
relaxes to previous state. This process repeats again and again till probe is in contact with water
and an oscillation is created in the circuit. Speaker diaphragm vibrates and gives a tone.
Frequency of the circuit depends on the value of Coil impendence, Capacitor and Resistance
Value.
Circuit Diagram of Rain Alarm
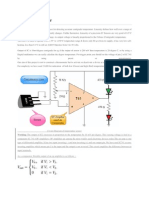
2 Temperature sensing system
This project uses IC LM35 as a sensor for detecting accurate centigrade
temperature. Linearity defines how well over a range of temperature a sensors
output consistently changes. Unlike thermistor, Linearity of a precision IC Sensors
are very good of 0.5C accuracy and has wide temperature range. its output voltage
is linearly proportional to the Celsius (Centigrade) temperature.
The LM35 is rated to operate over a -55 to +150C temperature range.It draws
only 60 A from its supply, it has very low self-heating, less than 0.1C in still air.
LM35 Operates from 4 to 30 volts.
Output of IC is 10mv/degree centigrade for eg if the output of sensor is 280 mV then
temperature is 28 degree C. so by using a Digital multimeter we can easily calculate
the degree temperature. For trigger point you should set the voltage of pin 2 of IC
741
by
using
preset
or
potentiometer.
Our aim of this project is not to construct a thermometer but to activate or
deactivate a device at a particular margin temperature. For simplicity we have used
2 LED for indication of both low (Green) and high (Red) temperature.
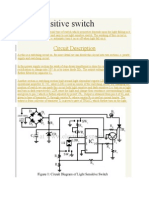
Battery charger circuit using SCR.
Description.
A simple battery charger based on SCR is shown here.Here the SCR rectifies the AC mains
voltage to charge the battery.When the battery connected to the charger gets discharged the
battery voltage gets dropped.This inhibits the forward biasing voltage from reaching the
base of the transistor Q1 through R4 and D2.This switches off the transistor.When the
transistor is turned OFF,the gate of SCR (H1) gets the triggering voltage via R1 & D3.This
makes the SCR to conduct and it starts to rectify the AC input voltage.The rectified voltage is
given to the battery through the resistor R6(5W).This starts charging of the battery.
When the battery is completely charged the base of Q1 gets the forward bias signal through
the voltage divider circuit made of R3,R4,R5 and D2.This turns the transistor ON.When the
Q1 is turned ON the trigger voltage at the gate of SCR is cut off and the SCR is turned
OFF.In this condition a very small amount of charge reaches the battery via R2 and D4 for
trickle charging.Since the charging voltage is only half wave rectified ,this type of charger is
suitable only for slow charging.For fast charging full wave rectified charging voltage is
needed.
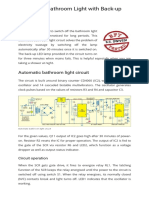
Street light circuit.
Description.
The circuit diagram present here is that of a street light that automatically switches ON
when the night falls and turns OFF when the sun rises. In fact you can this circuit for
implementing any type of automatic night light.
The circuit uses a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) to sense the light .When there is
light the resistance of LDR will be low. So the voltage drop across POT R2 will be high.This
keeps the transistor Q1 ON. The collector of Q1(BC107) is coupled to base of Q2(SL100). So
Q2 will be OFF and so do the relay. The bulb will remain OFF.
When night falls the resistance of LDR increases to make the voltage across the POT R2 to
decrease below 0.6V. This makes transistor Q1 OFF which in turn makes Q2 ON. The relay
will be energized and the bulb will glow.
You might also like
- LM35 Temperature Sensor Circuit Activates LEDs at ThresholdsDocument5 pagesLM35 Temperature Sensor Circuit Activates LEDs at ThresholdsAbhinav Madheshiya100% (1)
- SCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsDocument5 pagesSCR Power Control Circuit: SCS: Motor Start/stop Circuit, An Equivalent Circuit With Two TransistorsMark Kenneth Apuyan100% (1)
- Automatic Street Light Control Using LDRDocument18 pagesAutomatic Street Light Control Using LDRkrimouneeshNo ratings yet
- 10 Different Electronic ProjectsDocument16 pages10 Different Electronic ProjectsNestor Arnad jr.No ratings yet
- Light Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547Document3 pagesLight Dependent Resistor LM339 Automatic Lightdark Indicator BC 547yeateshwarriorNo ratings yet
- Varius and Explanation PDFDocument7 pagesVarius and Explanation PDFnormangNo ratings yet
- IC 555 ProjectsDocument14 pagesIC 555 ProjectsParth Lad100% (1)
- Laser Door Alarm Detects IntrudersDocument9 pagesLaser Door Alarm Detects IntrudersPooja PanhalekarNo ratings yet
- "Clap Switch": Submitted byDocument10 pages"Clap Switch": Submitted byKrishna Kumar SinghNo ratings yet
- Electronics Hobby CircuitsDocument183 pagesElectronics Hobby Circuitsbeckam88100% (3)
- Thyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Document28 pagesThyristor Application & Photosensitive Control Circuits: Chapter No.5Kim ManaloNo ratings yet
- Chapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitDocument11 pagesChapter Three System Driver 3.1 MOSFET Control CircuitAlhussain EmbarkNo ratings yet
- Clap SwitchDocument10 pagesClap SwitchKrishna Kumar Singh100% (2)
- Project in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRDocument9 pagesProject in Industrial Electronics: Prepared By: Norvel Hez P. Chiu Adham Jay C. Taborada Jaime A. Tracarol JRRyan CireraNo ratings yet
- Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleDocument24 pagesSilicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrinciplesixfacerajNo ratings yet
- Remote Control For Home AppliancesDocument2 pagesRemote Control For Home AppliancesMushtaq AhmadNo ratings yet
- Design Ideas PDFDocument5 pagesDesign Ideas PDFJohn Abrahim100% (1)
- Thyristor Turn-On Methods and Firing CircuitsDocument33 pagesThyristor Turn-On Methods and Firing CircuitsOmkar GuravNo ratings yet
- Industrial Electronics: Understanding Thyristors and SCR OperationDocument4 pagesIndustrial Electronics: Understanding Thyristors and SCR Operationtinonoy KulitlitNo ratings yet
- MultivibratorsDocument14 pagesMultivibratorsMuhammadSajidNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesDocument9 pagesChapter 8 Power Semiconductor DevicesJibril JundiNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics ProjectsDocument5 pagesPower Electronics ProjectsEngr FN ANo ratings yet
- Automatic Night Light Circuit Using SCR: Semester ProjectDocument10 pagesAutomatic Night Light Circuit Using SCR: Semester ProjectNasheed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Thyristors: Controlled Rectifier, or SCR, But The Usual Device For AC Control Is The Triac. in Spite of The GreatDocument4 pagesThyristors: Controlled Rectifier, or SCR, But The Usual Device For AC Control Is The Triac. in Spite of The GreathardmanpersonNo ratings yet
- ProjectDocument5 pagesProjectLokesh PatelNo ratings yet
- Module 1 NotesDocument30 pagesModule 1 NotesSoxamNo ratings yet
- Dancing LightDocument10 pagesDancing LightSurajj KumarNo ratings yet
- Automatic Bathroom Light With Back-Up Lamp - Full Project AvailableDocument2 pagesAutomatic Bathroom Light With Back-Up Lamp - Full Project AvailableragupaNo ratings yet
- Automatic gate light and call bell systemDocument2 pagesAutomatic gate light and call bell systemPrabhu BharaniNo ratings yet
- Mini Project ReportDocument11 pagesMini Project ReportNurulAnisAhmad100% (1)
- SMPS CKTDocument5 pagesSMPS CKTdkjena1No ratings yet
- Pyroelectric fire sensor circuitDocument2 pagesPyroelectric fire sensor circuitUma ShankarNo ratings yet
- 12V 4A Solar ChargerDocument2 pages12V 4A Solar Chargerdoraemon007No ratings yet
- Light sensitive switch circuit turns on light automaticallyDocument3 pagesLight sensitive switch circuit turns on light automaticallyKunal ThakkarNo ratings yet
- Breadboard ActivitiesDocument3 pagesBreadboard Activitiesfrancis kenn garciaNo ratings yet
- Rain AlarmDocument15 pagesRain AlarmTARIT DAS100% (4)
- Accurate 1 Second Time Base From Crystal OscillatorDocument4 pagesAccurate 1 Second Time Base From Crystal OscillatorOliverQueen773sNo ratings yet
- LED (Light-Emitting Diode) : ApplicationsDocument17 pagesLED (Light-Emitting Diode) : Applicationsvidya naveenNo ratings yet
- Automatic Speed LimiterDocument28 pagesAutomatic Speed LimiterDinesh RajeshNo ratings yet
- Abad Dominguez Practica06Document22 pagesAbad Dominguez Practica06erick alavaNo ratings yet
- Fire AlarmDocument3 pagesFire AlarmBarathi Raja Engira SathishNo ratings yet
- Auto Turn Off Battery ChargerDocument1 pageAuto Turn Off Battery ChargerH3liax100% (7)
- Industrial Electronics 1st ExamDocument34 pagesIndustrial Electronics 1st ExamJomar Bonje100% (1)
- Supplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalDocument21 pagesSupplementary Components and System: Engr - Kashif IqbalHassan Bin QasimNo ratings yet
- Hack Into A Stopwatch To Make A Phototimer PDFDocument5 pagesHack Into A Stopwatch To Make A Phototimer PDFPravin MevadaNo ratings yet
- Best of Design Ideas - Volume 2Document18 pagesBest of Design Ideas - Volume 2ableseaman100% (3)
- Characteristics of Thyristor: Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleDocument25 pagesCharacteristics of Thyristor: Silicon Controlled Rectifier SCR - Two Transistor Model - Operating PrincipleHayder AliNo ratings yet
- Laser Basic DetailDocument1 pageLaser Basic DetailMallieswaran SubbaiyanNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and PLC: SCHEME/YEAR:C-16/3 YEAR/5 SEM Subject Code: Ee-504Document76 pagesPower Electronics and PLC: SCHEME/YEAR:C-16/3 YEAR/5 SEM Subject Code: Ee-504rathina4careerNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document9 pagesExperiment 1John Wilfredd CurimoNo ratings yet
- Pplication OTE: Low Voltage DC Supply Dimmable Ballast For 1 X 36W T8 LampDocument13 pagesPplication OTE: Low Voltage DC Supply Dimmable Ballast For 1 X 36W T8 LampBravo MacNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- STEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10From EverandSTEM: Science, Technology, Engineering and Maths Principles Teachers Pack V10No ratings yet
- TVDocument69 pagesTVSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- WPTDocument58 pagesWPTSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- SRM Two Project AbstractDocument1 pageSRM Two Project AbstractSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Motivation: 2250 2200 2150 2100 2050 2000 Uranium Natural Gas OilDocument32 pagesMotivation: 2250 2200 2150 2100 2050 2000 Uranium Natural Gas OilSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Sensor InformationDocument8 pagesSensor InformationSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Sensor InformationDocument8 pagesSensor InformationSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Adaptive Self Healing Algorithm For Border Coverage Area Problem in Wireless Sensor NetworkDocument1 pageAdaptive Self Healing Algorithm For Border Coverage Area Problem in Wireless Sensor NetworkSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Fall Detection by Helmet Orientation and Acceleration During Bike RidingDocument6 pagesFall Detection by Helmet Orientation and Acceleration During Bike RidingSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Binary Partition Trees Represent Hyper Spectral ImagesDocument5 pagesBinary Partition Trees Represent Hyper Spectral ImagesSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Database Management System Document NotesDocument14 pagesDatabase Management System Document NotesSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Sensor InformationDocument8 pagesSensor InformationSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- 12345678Document9 pages12345678Sebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- 1Document4 pages1Sebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Burglar Alarm System Term PaperDocument12 pagesBurglar Alarm System Term PaperSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Frequency SelectionDocument12 pagesFrequency SelectionSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Barcode Scanner Project for XScale DeviceDocument5 pagesBarcode Scanner Project for XScale DevicekaxkusNo ratings yet
- Automatic Railway Gate Control by Using Microcontroller - 24 PagesDocument44 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate Control by Using Microcontroller - 24 PagesSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- ADC0808/ADC0809: General DescriptionDocument7 pagesADC0808/ADC0809: General DescriptionSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- 1 Block Based Robust Blind Image WatermarkingDocument4 pages1 Block Based Robust Blind Image WatermarkingSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Temperature SensorDocument6 pagesTemperature SensorSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Abondand Object DetctionDocument13 pagesAbondand Object DetctionRajasekar PanneerselvamNo ratings yet
- Apr 9600Document17 pagesApr 9600Andres GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Winnowing MechanismpDocument3 pagesAutomatic Winnowing MechanismpSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- 06786371Document12 pages06786371Sebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Industrial Battery Charger by Thyristor Firing Angle ControlDocument2 pagesIndustrial Battery Charger by Thyristor Firing Angle Controldebashish1135No ratings yet
- C280, Computer Vision: Prof. Trevor DarrellDocument84 pagesC280, Computer Vision: Prof. Trevor DarrellSebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- Bridge 2Document23 pagesBridge 2Sebastin AshokNo ratings yet
- A.8 Automatic ParkingDocument30 pagesA.8 Automatic ParkingMusthafa KadershaNo ratings yet
- Automatic Railway Gate ControllerDocument19 pagesAutomatic Railway Gate ControllerVarun KumarNo ratings yet
- ThermsDocument2 pagesThermsRyle ArbonNo ratings yet
- MeghanaDocument17 pagesMeghanaSravya BodduNo ratings yet
- 8086 Masm ProgramsDocument46 pages8086 Masm ProgramsVeera Ragavan50% (8)
- Temperature of Freshly Mixed Hydraulic-Cement Concrete: Standard Test Method ForDocument3 pagesTemperature of Freshly Mixed Hydraulic-Cement Concrete: Standard Test Method ForMario UzuriagaNo ratings yet
- Practical Boiler Operation Engineering (Amiya Ranjan Mallick) (Z-Library)Document618 pagesPractical Boiler Operation Engineering (Amiya Ranjan Mallick) (Z-Library)Tùng Lâm PhạmNo ratings yet
- Lab No 2Document3 pagesLab No 2Sohira QaziNo ratings yet
- Manual de ViscosimetroDocument14 pagesManual de ViscosimetroJoséNo ratings yet
- My e Book For Statistics For FreeDocument83 pagesMy e Book For Statistics For FreeAnthony Joshua100% (1)
- Cups To Grams Weight Converter - GoodtoKnowDocument2 pagesCups To Grams Weight Converter - GoodtoKnowgerryNo ratings yet
- 1 - The Manual-roll to Roll Heat Press 中性说明书Document28 pages1 - The Manual-roll to Roll Heat Press 中性说明书VMLP OrMdo SecGenNo ratings yet
- OvenDocument54 pagesOvenIsmail Hasan SaputraNo ratings yet
- Figure 2. Connection Sleeve For ThermoelementsDocument5 pagesFigure 2. Connection Sleeve For ThermoelementsNicolás VargasNo ratings yet
- ThermodynamicsDocument248 pagesThermodynamicssnehaeslate100% (1)
- Applying ISO Guide To Uncertainty of Temperature MeasurementDocument28 pagesApplying ISO Guide To Uncertainty of Temperature Measurementmross0355100% (1)
- Physics of Radiology and ImagingDocument426 pagesPhysics of Radiology and ImagingFlorentina Andronescu100% (1)
- Unit 1 - Introduction To ThermodynamicsDocument30 pagesUnit 1 - Introduction To ThermodynamicsAldrin BernardoNo ratings yet
- Warming The Earth and The AtmosphereDocument46 pagesWarming The Earth and The AtmosphereSalih TrexieNo ratings yet
- 04 Heat 1-19Document19 pages04 Heat 1-19Manas AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Chem LabDocument3 pagesChem LabS_Dot587100% (1)
- Nagaland- Stalingrad of the East: A Guide to Holiday Homework ProjectsDocument9 pagesNagaland- Stalingrad of the East: A Guide to Holiday Homework Projectsrishika solankiNo ratings yet
- Sample Cutting Machine GuideDocument16 pagesSample Cutting Machine Guidefatih_hideNo ratings yet
- 1-Heat & Temp - Set 1 - SolnDocument6 pages1-Heat & Temp - Set 1 - SolnBibhash SinghNo ratings yet
- Intro and MeasurementDocument97 pagesIntro and MeasurementCheska ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Sample Paper Level 2 NSO Olympiad Class 6Document3 pagesSample Paper Level 2 NSO Olympiad Class 6Divyanshu VatsalNo ratings yet
- Onion Drying Using Catalytic Infrared Dryer PDFDocument45 pagesOnion Drying Using Catalytic Infrared Dryer PDFSteve DennisNo ratings yet
- Beginners Guide To Using Winols PrintversionDocument20 pagesBeginners Guide To Using Winols PrintversionDaniel Santos75% (4)
- Lecture02 - ResistanceDocument17 pagesLecture02 - ResistanceKarl BelasaNo ratings yet
- Healthy Aquatic Ecosystem at Penrith LakesDocument9 pagesHealthy Aquatic Ecosystem at Penrith LakesSarah MNo ratings yet