Professional Documents
Culture Documents
PaThoPhysiology of Eclampsia
Uploaded by
hailleyannOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
PaThoPhysiology of Eclampsia
Uploaded by
hailleyannCopyright:
Available Formats
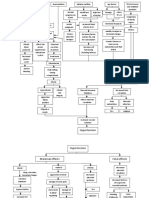
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF ECLAMPSIA
Definition: Eclampsia is the occurrence of generalized convulsion and/ or coma in the setting of pre-eclampsia, with no other
neurological condition.
Predisposing factors Precipitating factors
>Chro nic hypertension >Lifestyle
>Diabetes milletus > Diet
(pregestational)
> Age, Sex
Sensitivity to Angiotensin II
Peripheral and vascular vasospasm caused by increased
cardiac output
Increased blood pressure
rerrepprepressure
Reduced blood supply
Poor placental perfusion Ischemia in liver and
Vasospasm of kidney Eyes
pancreas
Retinal constriction
Reduce fetal nutrient and
Increase Blood flow
oxygen supply s/sx: resistance
>epigastric pain S/sx:
>nausea >Blurred vision
Glomerular degeneration
Fetal death >Vomiting
>Elevated amylase and
creatinine ratio
Reversible blindness
Increase permeability of
glomerular membrane
Serum protein albumin and Decrease glomerular filtration
globulin escape in urine
S/sx: Decrease urine output and
clearance of creatinine
Proteinuria (30ml/hr)
Fluid shift from
Increase Na reabsorption
intracellular to
extracellular
Increase water retention
S/sx: lower extremities
edema
Extreme edema (Generalized body edema)
Lungs Brain Heart
S/Sx;
Pulmonary edema Cerebral edema Cardiac heart failure
Blurred vision
Severe headache
Cerebral congestion S/Sx;
Reflexes
(hyperactive)
Ankle clonus
Increase cerebral irritability
Seizures
If treated: If not treated:
Prevent fetal death FETAL DEATH AND
MATERNAL DEATH
Legend:
Signs and symptom present in patient
Book base signs and symptoms
References:
Adele. Maternal & Child Health Nursing: Care of the Childbearing and Childrearing Family. 5th Edition. Philippines: Lippincott
Williams & Wilkins, 2007.
You might also like
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaYael EzraNo ratings yet
- Pa Tho Physiology of PIHDocument2 pagesPa Tho Physiology of PIHCarren_Louise__8090No ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placenta Pathophysiologyjamie carpioNo ratings yet
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaPearl IbisateNo ratings yet
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 pagesPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramDocument1 pagePathophysiology of Hyperemesis Gravidarum DiagramQuintin MangaoangNo ratings yet
- NCP Case 3Document3 pagesNCP Case 3boomer SeargeNo ratings yet
- Dengue FeverDocument8 pagesDengue Feverramoli1988No ratings yet
- Normal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryDocument35 pagesNormal Spontaneous Vaginal DeliveryJohn Edward EscoteNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument5 pagesPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15No ratings yet
- Anatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDocument4 pagesAnatomy Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaKeith Wesley YbutNo ratings yet
- A Case Analysis OnDocument27 pagesA Case Analysis Onbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Hydrocephalus PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesHydrocephalus PathophysiologyJosephine SNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDareRaymondNo ratings yet
- Discharge Planning FinalDocument5 pagesDischarge Planning FinalRose AnnNo ratings yet
- Midyr Case Study NewDocument18 pagesMidyr Case Study NewAndres Ham Samson BernabeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plans: Ineffective (Uteroplacental) Tissue PerfusionVincent Paul SantosNo ratings yet
- Case Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CDocument4 pagesCase Analaysis On infertility-BALLON-Karlo CMelinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology EclampsiaDocument5 pagesPathophysiology EclampsiaChristine Karen Ang SuarezNo ratings yet
- "Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyDocument3 pages"Acute Coronary Syndrome Non ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction, Hypertensive Cardiovascular Disease, Diabetes Mellitus Type 2, and Community Acquired Pneumonia" Client Centered PathophysiologyCarl Elexer Cuyugan Ano50% (2)
- Case Study AscariasisDocument60 pagesCase Study AscariasisRijane Tabonoc OmlangNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanArvan James Cabugayan TalboNo ratings yet
- Introduction HmoleDocument32 pagesIntroduction HmoleBrian Montales BaggayanNo ratings yet
- NCP: Prenatal InfectionDocument10 pagesNCP: Prenatal InfectionJavieNo ratings yet
- Case Study (Preeclampsia)Document6 pagesCase Study (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaNo ratings yet
- Placent Previa Case Study With Pa Tho PhysiologyDocument6 pagesPlacent Previa Case Study With Pa Tho PhysiologyRey Deemsur Salvilla MolinosNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Output Nursing Care PlanDocument21 pagesCardiac Output Nursing Care Plankoringring100% (1)
- After 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital SignsDocument3 pagesAfter 8 Hours of Nursing Interventions Patient Will Be Able To: Demonstrate Adequate Perfusion. Demonstrate Stable Vital Signsroma_elonaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)Document3 pagesDrug Study - Dexamethasone (Decilone)mikErlhNo ratings yet
- NF - DR - Concept Map - Hyperemesis GravidarumDocument1 pageNF - DR - Concept Map - Hyperemesis GravidarumKyra Bianca R. FamacionNo ratings yet
- Maternal Problems With PowerDocument2 pagesMaternal Problems With PowerAlex CvgNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology PreeclampsiaDocument1 pagePathophysiology PreeclampsiaPATHOSHOPPENo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placenta NCPDocument2 pagesAbruptio Placenta NCPjohncarlo ramos100% (1)
- Eclampsia Pre EclampsiaDocument3 pagesEclampsia Pre EclampsiaOona Nicole Diorico100% (2)
- PROM PathophysiologyDocument1 pagePROM PathophysiologyMichal Irijah ManatlaoNo ratings yet
- Patient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Document5 pagesPatient History-BALLON, KARLO C.Melinda Cariño BallonNo ratings yet
- CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument31 pagesCHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE Secondary To Chronic GlomerulonephritisJerwin Jade Bolor33% (3)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocument1 pagePathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoNo ratings yet
- Patient's Chart - Parenteral SheetDocument3 pagesPatient's Chart - Parenteral SheetRenea Joy ArruejoNo ratings yet
- Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoNo ratings yet
- Patricia Mae T. Miranda: Assessment Family Nursing Care Diagnoses Planning Implementation EvaluationDocument2 pagesPatricia Mae T. Miranda: Assessment Family Nursing Care Diagnoses Planning Implementation EvaluationPatricia Mae MirandaNo ratings yet
- Post Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFDocument2 pagesPost Partum Hemorrhage Nursing Care Plan PDFA sison100% (1)
- Assessing and managing decreased cardiac output due to pregnancy induced hypertensionDocument2 pagesAssessing and managing decreased cardiac output due to pregnancy induced hypertensionThesa FedericoNo ratings yet
- NCP - Gestational HypertensionDocument3 pagesNCP - Gestational HypertensionCameron De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Mrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETDocument5 pagesMrs. Bagent 1-9 BWAKANANG SHETaaron tabernaNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY Acute Pain Related To Laceration 1Document29 pagesCASE STUDY Acute Pain Related To Laceration 1Maria Jessica Dumdum100% (1)
- Hypertonic SolutionsDocument4 pagesHypertonic SolutionsVanessa PaguiriganNo ratings yet
- Hypertensive Disorder I.: DIC/ Disseminated Intravascular CoagulopathyDocument1 pageHypertensive Disorder I.: DIC/ Disseminated Intravascular CoagulopathyKIANA LOUISE ROMANONo ratings yet
- Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument2 pagesPredisposing Factor Precipitating FactorkamotenikimiNo ratings yet
- Pathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDocument3 pagesPathopyshiology-w-Risk-Factors - DTDivynne MadeloNo ratings yet
- All PathoDocument2 pagesAll PathoroseasNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaDocument1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD DM2 CVD Left Basal GangliaJake Caballo100% (1)
- Pathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeDocument2 pagesPathophysiology For HELLP SyndromeRosemarie CarpioNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument3 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureMel Izhra N. MargateNo ratings yet
- Non Modifiable: Modifiable:: (BP 158/87 MMHG)Document1 pageNon Modifiable: Modifiable:: (BP 158/87 MMHG)Quintin MangaoangNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of CVADocument7 pagesPathophysiology of CVAsarzlasco0967% (3)
- Pathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)Document1 pagePathophysiology of HCVD, DM2, CVD (Left Basal Ganglia)rexale ria100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF PREECLAMPSIADocument4 pagesPATHOPHYSIOLOGY SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM OF PREECLAMPSIACarrie A100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailureDocument2 pagesPathophysiology of Congestive Heart FailurePerry Oliver AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument28 pagesRenal Calculihailleyann33% (3)
- NCP CalculiDocument8 pagesNCP CalculihailleyannNo ratings yet
- Placenta PraeviaDocument10 pagesPlacenta PraeviahailleyannNo ratings yet
- Duties or NurseDocument10 pagesDuties or NursehailleyannNo ratings yet
- Eclampsia OutputDocument5 pagesEclampsia OutputhailleyannNo ratings yet
- CP FinalDocument53 pagesCP FinalhailleyannNo ratings yet
- Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument2 pagesAcute Myocardial InfarctionhailleyannNo ratings yet
- MCN Stages of Labor ReviewerDocument2 pagesMCN Stages of Labor ReviewerMira AurumtinNo ratings yet
- OET Writing Criteria 2019 PDFDocument11 pagesOET Writing Criteria 2019 PDFJohn MontyNo ratings yet
- Getting Your Sex Life Off To A Great Start Audiobook PDFDocument20 pagesGetting Your Sex Life Off To A Great Start Audiobook PDFamanNo ratings yet
- FP2020-Vision-in IndiaDocument162 pagesFP2020-Vision-in IndiaNeenu RajputNo ratings yet
- Certeza, Mark Jedrick - Data ReportingDocument5 pagesCerteza, Mark Jedrick - Data ReportingMark Jedrick CertezaNo ratings yet
- The Time of Separation of The Umbilical Cord: PediatricsDocument3 pagesThe Time of Separation of The Umbilical Cord: PediatricsFatma ElzaytNo ratings yet
- Fertility Patients Under COVID-19: Attitudes, Perceptions and Psychological ReactionsDocument10 pagesFertility Patients Under COVID-19: Attitudes, Perceptions and Psychological ReactionsMirjana14No ratings yet
- Prenatal Life - Ii: Environmental Influences On Prenatal DevelopmentDocument12 pagesPrenatal Life - Ii: Environmental Influences On Prenatal DevelopmentJayanth MamundiNo ratings yet
- The Pregnant AdolescentDocument15 pagesThe Pregnant Adolescentnursereview88% (8)
- Fetal Heart Rate Monitoring in Pregnancy and Labour 6.0Document42 pagesFetal Heart Rate Monitoring in Pregnancy and Labour 6.0Wong Lee CheeNo ratings yet
- MOA Lying-In (Template)Document6 pagesMOA Lying-In (Template)Kristin VillasenotNo ratings yet
- Ultrasound of The Pregnant Acute AbdomenDocument16 pagesUltrasound of The Pregnant Acute Abdomenjohn omariaNo ratings yet
- High Risk NewbornDocument10 pagesHigh Risk NewbornEmmy Flor ValmoriaNo ratings yet
- SOGC Guideline No. 292 - AUB in Pre-Menopausal WomenDocument25 pagesSOGC Guideline No. 292 - AUB in Pre-Menopausal WomendubblewalkerNo ratings yet
- Mohammed Gogandy - Obstetric History Sheet & - 40 2007-2008& - 41 PDFDocument2 pagesMohammed Gogandy - Obstetric History Sheet & - 40 2007-2008& - 41 PDFJennifer Ross-ComptisNo ratings yet
- Mousavi 2018Document6 pagesMousavi 2018Alexandra MateiNo ratings yet
- Sagas of The Icelanders Playbooks 3.3Document25 pagesSagas of The Icelanders Playbooks 3.3Angelica PortuguezNo ratings yet
- Normal LaborDocument56 pagesNormal Laborحسام رياض عبد الحسين راضيNo ratings yet
- Stree Roga Vigyan-Mallikarjuna With MCQs PDFDocument20 pagesStree Roga Vigyan-Mallikarjuna With MCQs PDFCHAUKHAMBHA PRAKASHAKNo ratings yet
- Whole Woman's Health v. Jackson Re TX-SB8Document49 pagesWhole Woman's Health v. Jackson Re TX-SB8File 411No ratings yet
- Module 4 NRG 203 Intrapartum - 2023 2024Document20 pagesModule 4 NRG 203 Intrapartum - 2023 2024alliahjaneadlawanNo ratings yet
- MidwifeDocument19 pagesMidwifesung hooNo ratings yet
- Nursing Standards for Labour RoomDocument3 pagesNursing Standards for Labour RoomRenita ChrisNo ratings yet
- Mansfield Et Al-1999-Prenatal DiagnosisDocument6 pagesMansfield Et Al-1999-Prenatal DiagnosisM T Lê VănNo ratings yet
- Mother and Child QuizDocument24 pagesMother and Child QuizRoby Roi De GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Johryl Resaerch ReportDocument14 pagesJohryl Resaerch ReportSANNY OMELANo ratings yet
- 55 Q&A Antepartum NclexDocument8 pages55 Q&A Antepartum NclexKrystelle Jade LabineNo ratings yet
- Applied Therapeutics/Mid Term ExamDocument16 pagesApplied Therapeutics/Mid Term ExamAmina AmiarNo ratings yet
- Vaginal Fluid SimulantDocument5 pagesVaginal Fluid Simulantluck2livNo ratings yet
- POCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3Document62 pagesPOCQI-Slides For Lead Facilitator Ver-3muna WarohNo ratings yet