Professional Documents
Culture Documents
See Chapter 6 in The Textbook.: Integumentary System
Uploaded by
frankynevin10 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesugh
Original Title
2. Slides No Copyrighted Figures - Integumentary System
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentugh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
5 views2 pagesSee Chapter 6 in The Textbook.: Integumentary System
Uploaded by
frankynevin1ugh
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
NOTE:
See chapter 6 in the
To use these slides effectively in your textbook.
studying, you should have your text
open and the course outline available as
you review the slides so that you can
refer to the corresponding figures and
text.
Figure numbers are given on each slide.
Integumentary system
Organ = two or more tissues forming a
larger structure with specialized
function(s)
Integument = covering for protection
Skin and other membranes
Four kinds of membranes
Serous line cavities with no
openings to outside
Example: interior of thoracic
Pleural Lung
cavity membrane
Mucous line cavities with openings
to outside
Example: interior of digestive tract
Synovial joints (details later)
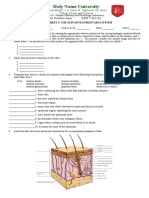
Cutaneous skin Figure 6.1
Functions of skin:
Protection
Keeps pathogens out
Waterproofing
Temperature regulation
Sense of touch
All four major tissue types are present in the skin:
Epithelial in epidermis, blood vessels, sweat
glands, sebaceous glands, hair follicles
Connective in dermis, subcutaneous layer
Muscle arrector pili (smooth muscle)
Nervous nerves, touch and temperature
receptors
Role of the skin in temperature regulation:
Figure 1.7
feedback loop components --
sensors: nerve endings that detect temperature
effectors: blood vessels and sweat glands
You might also like
- WEEK 1 - Skin and Fascia - 2Document42 pagesWEEK 1 - Skin and Fascia - 2otaibynaifNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary SystemDocument4 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of The Integumentary Systemmao4evah0% (1)
- The Integumentary System: Protection, Regulation, and SensationDocument49 pagesThe Integumentary System: Protection, Regulation, and Sensationalmira garciaNo ratings yet
- General Science Unit 4-5 PDFDocument90 pagesGeneral Science Unit 4-5 PDFwildwolfNo ratings yet
- King Hedley II Guided Reading 2Document2 pagesKing Hedley II Guided Reading 2frankynevin1No ratings yet
- Epithelial TissueDocument87 pagesEpithelial Tissueabubeker mohammed100% (1)
- Chapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesDocument49 pagesChapter 4 - Tissues Glands and MembranesNess G. Mamasabulod100% (1)
- Biolab: Animal Tissues Lab Report Name, Date, Course and Section Required For Password: 1409Document5 pagesBiolab: Animal Tissues Lab Report Name, Date, Course and Section Required For Password: 1409RosaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System Lab Report 1Document12 pagesIntegumentary System Lab Report 1api-374265257No ratings yet
- Inisiasi IVDocument39 pagesInisiasi IVjoan wanadriNo ratings yet
- Lab Worksheet No. 5 Integumentary SystemDocument15 pagesLab Worksheet No. 5 Integumentary SystemKarylle Ezra GulifardoNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 IntegumentaryDocument5 pagesActivity 6 Integumentaryhanna castueraNo ratings yet
- Integumentary System: Student Learning ObjectivesDocument3 pagesIntegumentary System: Student Learning ObjectivesYesita AdamyNo ratings yet
- School: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Document3 pagesSchool: San Agustin Elementary School Grade Level: Six Teacher: Jonalvin A. Ke Learning Area: Science Date: SEPTEMBER 5, 2018 (WEDNESDAY)Jonalvin KENo ratings yet
- Chapter+7 +Integumentary+SystemDocument16 pagesChapter+7 +Integumentary+Systemmaryelle conejarNo ratings yet
- Skin Body Tissues and MembraneDocument50 pagesSkin Body Tissues and MembraneNaanmatha PuspanathanNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Angcahan2021 1Document53 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Angcahan2021 1G E MNo ratings yet
- Gallego, Alyzza Faith C. - AP Lab Activity No 2Document4 pagesGallego, Alyzza Faith C. - AP Lab Activity No 2GALLEGO, Alyzza Faith C.No ratings yet
- Organ Systems ModuleDocument6 pagesOrgan Systems ModuleJayNo ratings yet
- Biology Tissue Types GuideDocument11 pagesBiology Tissue Types GuideLindseyNo ratings yet
- Skin and Breast HistologyDocument8 pagesSkin and Breast HistologyPraveena MoganNo ratings yet
- Activity 6 The Integumentary SystemDocument7 pagesActivity 6 The Integumentary SystemEmpleo MaryNo ratings yet
- Review Sheet 3Document3 pagesReview Sheet 3Armileo C AuxteroNo ratings yet
- Lab V Chicken Wing Dissection and Microscopic View of TissuesDocument5 pagesLab V Chicken Wing Dissection and Microscopic View of Tissueswinatategar08No ratings yet
- Types of TissuesDocument7 pagesTypes of TissuesKaren Mae AlcantaraNo ratings yet
- Basic AnatomyDocument2 pagesBasic Anatomyafriesen72No ratings yet
- Basic Histo Plus INTEGUMEN For MidwifeDocument107 pagesBasic Histo Plus INTEGUMEN For MidwifeAuliya ShintaNo ratings yet
- Intergumentary SystemDocument8 pagesIntergumentary SystemJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- MODULe 3 AnaphysioDocument9 pagesMODULe 3 Anaphysiojoshua ordenaNo ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemsDocument17 pagesIntegumentary SystemsXavier BiasonNo ratings yet
- Skin and Fascia Lec 2Document42 pagesSkin and Fascia Lec 2Javaid mukhtarNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYDocument24 pagesANAPHYgrafei pennaNo ratings yet
- Module 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesDocument55 pagesModule 4-Tissues, Glands, and MembranesGlory MuedaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Department: The Integumentary Systemزاهجل اDocument34 pagesNursing Department: The Integumentary Systemزاهجل اوجد عمرNo ratings yet
- Anaphy TissuesDocument4 pagesAnaphy TissuesYo1No ratings yet
- 1a TissuesDocument60 pages1a Tissuesronilynn veranoNo ratings yet
- 3 Week - TissuesDocument55 pages3 Week - TissuesGeevee Naganag Ventula100% (1)
- The Integumentary System Is Made Up of Several Organs and Structures Including The SkinDocument3 pagesThe Integumentary System Is Made Up of Several Organs and Structures Including The SkinAxel NeoNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument16 pagesHistologyHohai ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- I. Integumentary SystemDocument5 pagesI. Integumentary SystemH HNo ratings yet
- The Integumentary System: Structure and Functions of Skin and its AppendagesDocument44 pagesThe Integumentary System: Structure and Functions of Skin and its AppendagesCesar Ivan Ruiz DiazNo ratings yet
- MODUL 2 IMUNOLOGI (English Version)Document13 pagesMODUL 2 IMUNOLOGI (English Version)Dandung Emang KocakxNo ratings yet
- Human Body System and CellsDocument101 pagesHuman Body System and CellsahmedNo ratings yet
- Tissues ReviwDocument56 pagesTissues ReviwGwen YosheenNo ratings yet
- Script VideoDocument4 pagesScript VideoAlicia ValverdeNo ratings yet
- Chapter II IntegumentaryDocument9 pagesChapter II IntegumentaryTitoMacoyTVNo ratings yet
- Types of Tissues #2Document84 pagesTypes of Tissues #2Dana AhmadNo ratings yet
- Genbio ReviewerDocument4 pagesGenbio ReviewerAbayan, Elaine Jewel L.No ratings yet
- 3 Tissue of Human Body NotesDocument11 pages3 Tissue of Human Body Notesghanshyam agnihotryNo ratings yet
- TissuesDocument33 pagesTissuesAnonymous imF0MCd9UNo ratings yet
- Group 6 Defines Key Body MembranesDocument13 pagesGroup 6 Defines Key Body MembranesMarielle RumbaoaNo ratings yet
- Epithelial TissuesDocument31 pagesEpithelial Tissuesmuhammad ijazNo ratings yet
- Tissues and OrgansDocument3 pagesTissues and OrgansAné MurrayNo ratings yet
- Structure of The SkinDocument4 pagesStructure of The Skinmalakdiabmed57No ratings yet
- Integumentary SystemDocument47 pagesIntegumentary SystemMaz AndikaNo ratings yet
- BIOL102SkinAnatomyDocument24 pagesBIOL102SkinAnatomyDonnaliza Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- Body Tissue and IntegumentaryDocument53 pagesBody Tissue and IntegumentarySyikin KadirNo ratings yet
- BBS P03 Four Basic TissuesDocument14 pagesBBS P03 Four Basic TissuesPMIB Matrikulasi FKUI 2018/2019No ratings yet
- Science Unit Most RecentDocument6 pagesScience Unit Most Recentfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Theatre CurriculumDocument4 pagesTheatre Curriculumfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Bob Fosse PaperDocument6 pagesBob Fosse Paperfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Slides No Copyrighted Figures - Skeletal SystemDocument8 pagesSlides No Copyrighted Figures - Skeletal Systemfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Comp 121 Paper 3Document7 pagesComp 121 Paper 3frankynevin1No ratings yet
- Cello Excerpt PDFDocument2 pagesCello Excerpt PDFfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Beauty and The Beast Feb/Mar: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday SaturdayDocument1 pageBeauty and The Beast Feb/Mar: Sunday Monday Tuesday Wednesday Thursday Friday Saturdayfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Cheetah PaperDocument7 pagesCheetah Paperfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Comp 121 Paper 2 3-20Document5 pagesComp 121 Paper 2 3-20frankynevin1No ratings yet
- AWEW Script Final2 Fool ScenesDocument9 pagesAWEW Script Final2 Fool Scenesfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Slides No Copyrighted Figures - MacromoleculesDocument10 pagesSlides No Copyrighted Figures - Macromoleculesfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- KDP Open House Flyer 2017Document1 pageKDP Open House Flyer 2017frankynevin1No ratings yet
- KDP Open House RaffleDocument1 pageKDP Open House Rafflefrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Trump and ClintonDocument6 pagesTrump and Clintonfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Monologue Eval - FrankieDocument2 pagesMonologue Eval - Frankiefrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Monologue Assignment: Due Date: Wednesday, Aug. 31 .: 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Acceptable 1 - Needs ImprovementDocument1 pageMonologue Assignment: Due Date: Wednesday, Aug. 31 .: 4-Excellent 3 - Good 2 - Acceptable 1 - Needs Improvementfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- King Hedley II Guided Reading 3Document2 pagesKing Hedley II Guided Reading 3frankynevin1No ratings yet
- Bruxism MakalahDocument15 pagesBruxism MakalahSuzhanthy ArisonyaNo ratings yet
- Undergraduate Member ApplicationDocument1 pageUndergraduate Member Applicationfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Tectonic Evolution of Manitoba-Saskatchewan Portion of The THO - Ansdell 2005Document20 pagesTectonic Evolution of Manitoba-Saskatchewan Portion of The THO - Ansdell 2005frankynevin1No ratings yet
- Kurts Flin Flon PaperDocument13 pagesKurts Flin Flon Paperfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Syme Eric Charles 1975 SecDocument186 pagesSyme Eric Charles 1975 Secfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Mesothermal Quartz Stuff - Ansdell, KyserDocument29 pagesMesothermal Quartz Stuff - Ansdell, Kyserfrankynevin1100% (1)
- Geology of Flin Flon's Map Area 6Document14 pagesGeology of Flin Flon's Map Area 6frankynevin1No ratings yet
- A Dynamic Epistemic LogicDocument26 pagesA Dynamic Epistemic Logicfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Structural Evolution of Amisk Collage - James RyanDocument23 pagesStructural Evolution of Amisk Collage - James Ryanfrankynevin1No ratings yet
- Tectonic Evolution of Manitoba-Saskatchewan Portion of The THO - Ansdell 2005Document20 pagesTectonic Evolution of Manitoba-Saskatchewan Portion of The THO - Ansdell 2005frankynevin1No ratings yet
- Assignment 1 - Question 3Document3 pagesAssignment 1 - Question 3frankynevin1No ratings yet