Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Osmosis Lab Introduction
Uploaded by
Paperless TwnCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Osmosis Lab Introduction
Uploaded by
Paperless TwnCopyright:
Available Formats
Introduction:
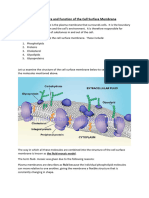
The membrane is one of the organelles located on the surface of the cell, it's act like a
gatekeeper. It made up of the phospholipid bilayer that will determine which materials should
be pass through the membrane. The movement of molecules diffusion between outside and
inside the cell can be determined into two; Passive transport and the active transport. Passive
transport is the movement of the particles moving down the gradients and the active transport
is when the particles move upwards the gradients which provide the ATP or the energy.
Passive transport could lead to two diffusions which are Simple and Facilitated diffusion.
Simple Diffusion occur with the small and non-polar particles; don't have charge, it will flow
through the Gradients. Osmosis occurred at this stage because of the common nonpolar
particles is water which is easily pass through the membranes. The another type is diffusion is
the facilitated diffusion that provides the help of proteins as a channel of transport because
the particles are too large and specific that have to part through the specific type of protein
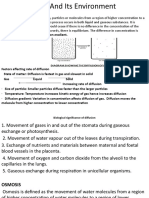
(Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article, 2014).Osmosis is when
solutions are in the same or different concentration between inside and outside the cell which
is separated by the semi-permeable membrane; according to Wood, 2015, p.1 "Membrane that
only allows certain types of particles to move through it under certain conditions" The
permeable membrane will choose the smaller molecules which are solvent; water, to diffuse
through low to high concentration (Nave, n.d.). Osmosis leads to the area of Tonicity.
Tonicity is the enviroments of the concentration which will explain the both side of the cell
membrane ( Port, 2016). Tonicity leads to 3 types of concentration which are the hypertonic
solution, hypotonic solution, and isotonic solution. The Hypertonic solution is a solution
which has more solute compare to another (Hypertonic solution, 2008). The Hypotonic
solution is the solution that has less concentration compare to another (Hypotonic solution,
2008) and the Isotonic solution is when the 2 solution that has the same concentration
opposite the semi-permeable membrane (Brundage, n.d). Cells will act differently toward
different types of Tonicity. If the cell is in the hypotonic solution which means the
concentration outside the cell is lower compared to the cell. In another word, contain more
water. The water will enter the cell until the concentration reaches the equilibrium. Which
may cause the cell to swell or bursts. If the cell is in the hypertonic solution which contains
more concentration. The cell will exceed the water outside to make the concentration
equilibrium which leads to the shrunk of the cell. Lastly, the cell in isotonic solution. The
water that exceeds the cell and enters the cell will be equal and the shape of the cell will
remain as normal (Lui, 2013).
An experiment which will be conducted will lead to the field of the osmosis and tonicity. The
experiment will be using the potato and jelly as the sample to test the reaction of each on the
different types of tonicity solution. First, we used 3 pieces of each sample; 3 pieces potato
chop and 3 pieces of jelly. Weighing of each sample will be done before the experiment.
Samples will be put in each type of tonicity; Hypotonic and hypertonic solution. One piece of
potato and jelly will be put in each type of solution in the separate beaker. Each type of
solution will contain salt water and distilled water. Salt water will represent as the hypertonic
solution and distilled water will be represented as the hypotonic solution. The sample will be
leave in the solution for one hour then there need to be out from the solution to weight. Then
the learner will able compare the pre-experiment weight and post-experiment weight of each
sample. Which will recognize the change of the sample by the reaction of osmosis also
recognize by the appearance because of the cell could be enlarged and smaller. The purpose
Samaphoo Assametankul 5961068
of this experiment is to help the learners understand the reaction of osmosis toward the
different type of concentration. And how the changes of sample relate to the tonicity.
Reference:
Brundage, A. (n.d.). Isotonic Solution: Definition & Example - Video & Lesson Transcript.
Retrieved March 09, 2017, from http://study.com/academy/lesson/isotonic-solution-
definition-example-quiz.html
Hypertonic solution. (2008, August 3). Retrieved March 09, 2017, from http://www.biology-
online.org/dictionary/Hypertonic_solution
Hypotonic solution. (2008, August 3). Retrieved March 09, 2017, from http://www.biology-
online.org/dictionary/Hypertonic_solution
Lui, J. (2013, April 3). Isotonic, Hypotonic, & Hypertonic Solutions. Retrieved March 09,
2017, from https://www.sophia.org/tutorials/isotonic-hypotonic-hypertonic-solutions
Nave, R. (n.d.). Diffusion. Retrieved March 09, 2017, from http://hyperphysics.phy-
astr.gsu.edu/hbase/Kinetic/diffus.html
Passive transport and active transport across a cell membrane article. (2014, October 20).
Retrieved March 09, 2017, from https://www.khanacademy.org/test-prep/mcat/cells/transport-
across-a-cell-membrane/a/passive-transport-and-active-transport-across-a-cell-membrane-
article
Port, T. (2016, March). Diffusion, Osmosis & Tonicity. Retrieved March 09, 2017, from
http://www.scienceprofonline.org/chemistry/diffusion-osmosis-tonicity-effect-osmotic-
pressure-on-cells.html
Wood, D. (2015, February). Semipermeable Membrane: Definition & Overview - Video &
Lesson Transcript. Retrieved March 09, 2017, from
http://study.com/academy/lesson/semipermeable-membrane-definition-lesson-quiz.html
Samaphoo Assametankul 5961068
You might also like
- Fluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceFrom EverandFluids and Electrolytes: An Easy and Intuitive Way to Understand and Memorize Fluids, Electrolytes, and Acidic-Base BalanceRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- Osmosis Lab Report IntroductionDocument2 pagesOsmosis Lab Report Introductionapi-327823961100% (1)
- Jelly IntroDocument1 pageJelly Introapi-341690050No ratings yet
- Cell Membrane Transport ExpDocument4 pagesCell Membrane Transport ExpMary Rose CatalbasNo ratings yet
- Biology Grade 10 Lesson Plan March 6 - March 10Document5 pagesBiology Grade 10 Lesson Plan March 6 - March 10Nicketa AndersonNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER-7Document20 pagesCHAPTER-7criselledalipe12No ratings yet
- Cell Physiology and Cellular MetabolismDocument25 pagesCell Physiology and Cellular MetabolismCla NuvalNo ratings yet
- Bio IntroDocument1 pageBio Introapi-327847414No ratings yet
- Bio Lab IntroDocument2 pagesBio Lab Introapi-327731714No ratings yet
- Lab Intro OsmosisDocument2 pagesLab Intro Osmosisapi-327826901No ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab IntroDocument1 pageOsmosis Lab Introapi-327726527No ratings yet
- Bios - Transport of MaterialDocument46 pagesBios - Transport of MaterialNeseriani AndersonNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport Processes in Plant and Animal CellsDocument8 pagesCell Transport Processes in Plant and Animal CellsJustin Damian Malaki MalubayNo ratings yet
- Sas 7Document5 pagesSas 7Clarrinne Geralence Galo RomoNo ratings yet
- Biochem Laboratory Activity 2Document4 pagesBiochem Laboratory Activity 2Kristine PangahinNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisDocument6 pagesActivity 3 Diffusion and OsmosisThea Calyn WalicanNo ratings yet
- DiffusionDocument32 pagesDiffusionAce Mhac TeñidoNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument25 pagesMovement in and Out of Cellsmajanga johnNo ratings yet
- Las-Q3-Wk6.1 2Document12 pagesLas-Q3-Wk6.1 2Jhude JosephNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Lab ReportDocument3 pagesOsmosis Lab Reportapi-350496922No ratings yet
- Osmosis IntroductionDocument2 pagesOsmosis Introductionapi-335117665No ratings yet
- Membrane Transport Mechanisms and HomeostasisDocument29 pagesMembrane Transport Mechanisms and Homeostasisramadan100% (1)
- Group 6 Written ReportDocument4 pagesGroup 6 Written ReportLuckyGuy25No ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveDocument10 pagesChapter 5: Homeostasis and Transport Lesson 5.2: Cell Transport-Passive and ActiveVanshika VermaNo ratings yet
- CELLSDocument5 pagesCELLSJermaine CorpuzNo ratings yet
- Gene103Lab_DiffusionandOsmosis (2)Document5 pagesGene103Lab_DiffusionandOsmosis (2)bodurr571No ratings yet
- Introduction Lab Report OsmosisDocument1 pageIntroduction Lab Report Osmosisapi-350666771No ratings yet
- Facilitated transport and membrane proteinsDocument3 pagesFacilitated transport and membrane proteinsashNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Membrane Lab ReportDocument7 pagesOsmosis Membrane Lab ReportSandra JabrooNo ratings yet
- Osmosis and Diffusion Lab VocabularyDocument3 pagesOsmosis and Diffusion Lab Vocabularydannyf09No ratings yet
- Transport MechanismsDocument30 pagesTransport MechanismsApril VeraNo ratings yet
- Gr9 - Movement of SubstancesDocument40 pagesGr9 - Movement of SubstancesKara NewmanNo ratings yet
- Cell TransportDocument19 pagesCell TransportOctavio ManciniNo ratings yet
- The Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1Document3 pagesThe Cell and Its Environment: Biology, Ss 1AJAYI PETER100% (1)
- Transport MechanismsDocument6 pagesTransport MechanismsJohn Dave ElloranNo ratings yet
- Investigation 4 Diffusion and Osmosis PDFDocument13 pagesInvestigation 4 Diffusion and Osmosis PDFAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- CELL TRANSPORT Notes SY 2022 2023Document36 pagesCELL TRANSPORT Notes SY 2022 2023Olitres, John Vincent A.No ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of CellsDocument4 pagesMovement in and Out of CellsIndah ParamithaNo ratings yet
- Plant Water Relations Explained in 40 CharactersDocument11 pagesPlant Water Relations Explained in 40 CharactersalekhyaNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument6 pagesOsmosis: From Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopediaallanlopez_2009No ratings yet
- Cell MembranesDocument5 pagesCell MembranesTiaraHadiAshariNo ratings yet
- Movement in and Out of The Cells (Diffusion, Osmosis)Document12 pagesMovement in and Out of The Cells (Diffusion, Osmosis)Mentari Ulfah100% (1)
- Membrane Structure and FunctionDocument11 pagesMembrane Structure and FunctionShiloh FrederickNo ratings yet
- Physiological Practical 1Document4 pagesPhysiological Practical 1Khezia ChalweNo ratings yet
- Diffusion, Osmosis and Surface Area to Volume RatiosDocument11 pagesDiffusion, Osmosis and Surface Area to Volume Ratioskinza yasirNo ratings yet
- Lab Exercise 3: Membrane Transport Mechanisms and Osmosis The Cell CycleDocument13 pagesLab Exercise 3: Membrane Transport Mechanisms and Osmosis The Cell CyclerezamaulanaNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Transport Through Cell MembraneDocument6 pagesModule 3 - Transport Through Cell MembraneGoogle BackupNo ratings yet
- REVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDocument4 pagesREVISION NOTES - B2.2MovementInAndOutOfTheCellDavé TranNo ratings yet
- Osmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCDocument9 pagesOsmosis: XCCC C CC CC CC CC CCCCIwizpv DzimmieNo ratings yet
- Osmosis Active TransportDocument25 pagesOsmosis Active Transportyasser yousriNo ratings yet
- Transport in Plants PDFDocument10 pagesTransport in Plants PDFAlhiza JoaquinNo ratings yet
- Lab Report: Cell TransportDocument4 pagesLab Report: Cell Transportmaieunice75% (4)
- Cellular Function and OsmosisDocument3 pagesCellular Function and OsmosisizzahNo ratings yet
- 4.transport MechanismsDocument94 pages4.transport MechanismsHyacinth RaeNo ratings yet
- Cells And Their EnvironmentDocument14 pagesCells And Their EnvironmentEllaNo ratings yet
- Lab IntroDocument1 pageLab Introapi-328029949No ratings yet
- Role and Significance of Water for PlantsDocument11 pagesRole and Significance of Water for Plantskhmaj9792No ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Mechanisms ExplainedDocument9 pagesCellular Transport Mechanisms Explainedelyza gwenNo ratings yet
- Cell Membrane and Transport ColoringDocument3 pagesCell Membrane and Transport ColoringTeresa GonzNo ratings yet
- Cell Transport LabDocument7 pagesCell Transport Labapi-267594083No ratings yet
- Isaac Newton: Newton's Second LawDocument12 pagesIsaac Newton: Newton's Second LawPaperless TwnNo ratings yet
- Food SciDocument10 pagesFood SciPaperless TwnNo ratings yet
- SugarDocument1 pageSugarPaperless TwnNo ratings yet
- ArchaicDocument25 pagesArchaicPaperless TwnNo ratings yet
- BiologyDocument18 pagesBiologyPaperless TwnNo ratings yet
- InterpolationDocument7 pagesInterpolationElianne GabbayNo ratings yet
- Soundness TestDocument4 pagesSoundness TestC-one Goncalves100% (2)
- Lyft Pec FootprintsDocument1 pageLyft Pec FootprintsZoran TripunovskiNo ratings yet
- 111年下A卷題庫Document10 pages111年下A卷題庫陳奕安No ratings yet
- Masterbatches protect plastics from UV damageDocument1 pageMasterbatches protect plastics from UV damageSidharth JainNo ratings yet
- Kepler's Three Laws of Planetary MotionDocument12 pagesKepler's Three Laws of Planetary MotionAlyssa Rose RamosNo ratings yet
- CE 481 Solid Waste & Environmental PollutionDocument140 pagesCE 481 Solid Waste & Environmental PollutionDamini ThakurNo ratings yet
- Physics Practical Report 5Document8 pagesPhysics Practical Report 5NatashaAnneNo ratings yet
- 4 - 002 Qafco Urea3 Plant High PressureDocument13 pages4 - 002 Qafco Urea3 Plant High PressureJUNAID RAFEYNo ratings yet
- Joint Probability Distributions and Random SamplesDocument22 pagesJoint Probability Distributions and Random SamplesChandrahasa Reddy Thatimakula100% (1)
- Micro Diaphragm Gas Sampling Pumps: Operating and Installation InstructionsDocument12 pagesMicro Diaphragm Gas Sampling Pumps: Operating and Installation Instructionssunilsheelavant100% (1)
- Unit 3 (SAMPLE AND SAMPLE DISTRIBUTIONS)Document32 pagesUnit 3 (SAMPLE AND SAMPLE DISTRIBUTIONS)Zara Nabilah100% (2)
- Lightning Protection System Analysis of High Voltage 70 KV Transmission Line in Area With High Lightning Density, Study Case Sutt 70 KV MalangDocument8 pagesLightning Protection System Analysis of High Voltage 70 KV Transmission Line in Area With High Lightning Density, Study Case Sutt 70 KV MalangGdeKomangFmoNo ratings yet
- Titrimetry (anEm'pnmQwQy)Document102 pagesTitrimetry (anEm'pnmQwQy)AchindA FernandoNo ratings yet
- Role of Energy Loss On Discharge Characteristics of Sluice GatesDocument25 pagesRole of Energy Loss On Discharge Characteristics of Sluice GatesBabak mahmoudiNo ratings yet
- HW1 - Conditions - Olevsky - Mech - Beh - Mater PDFDocument2 pagesHW1 - Conditions - Olevsky - Mech - Beh - Mater PDFwangbutt123No ratings yet
- Performance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161Document25 pagesPerformance of HT & LT Catalyst: Amit Kumar Jha MT (Chemical) # 0247/7161sb1984_hithaldiaNo ratings yet
- Caustic Stress Corrosion Cracking of A Graphite Cast Iron ComponentDocument8 pagesCaustic Stress Corrosion Cracking of A Graphite Cast Iron Componentriza9847No ratings yet
- GE6251 Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Regulation 2013 Lecture NotesDocument112 pagesGE6251 Basic Civil and Mechanical Engineering Regulation 2013 Lecture NotesSasi Dharan100% (1)
- NY Regents Chemistry Exam Scoring KeyDocument12 pagesNY Regents Chemistry Exam Scoring KeyAAVANINo ratings yet
- Design of Rotating Electrical Machines2Document531 pagesDesign of Rotating Electrical Machines2alirozNo ratings yet
- 2nd Mid Assingnment QuestionsDocument3 pages2nd Mid Assingnment QuestionsSatya TejaNo ratings yet
- Electrical Characteristics of CablesDocument32 pagesElectrical Characteristics of CablesSupakint Suteepichatpunt100% (1)
- Prepared By: Ms. Ethel D. Nabor, LPTDocument29 pagesPrepared By: Ms. Ethel D. Nabor, LPTJohn Ralf T. TorrejosNo ratings yet
- Understanding FRP BoomsDocument4 pagesUnderstanding FRP BoomsFernandoNo ratings yet
- Liquid Nitrogen Safety TrainingDocument21 pagesLiquid Nitrogen Safety TrainingSteven James CapuanoNo ratings yet
- Research Paper in MicrowavesDocument10 pagesResearch Paper in MicrowavesManoling PanopioNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Materials An Integrated Learning System 4th Edition Philpot Solutions ManualDocument26 pagesMechanics of Materials An Integrated Learning System 4th Edition Philpot Solutions ManualMarkManntjaid95% (20)
- Why Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsDocument3 pagesWhy Phase Information Is Important For Diagnosing Machinery ProblemsdinhdtNo ratings yet
- CLMD4A Science8Document39 pagesCLMD4A Science8GreyNo ratings yet
- A Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsFrom EverandA Brief History of Intelligence: Evolution, AI, and the Five Breakthroughs That Made Our BrainsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanFrom EverandThe Secret Life of Lobsters: How Fishermen and Scientists Are Unraveling the Mysteries of Our Favorite CrustaceanNo ratings yet
- The Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorFrom EverandThe Revolutionary Genius of Plants: A New Understanding of Plant Intelligence and BehaviorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (137)
- Crypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondFrom EverandCrypt: Life, Death and Disease in the Middle Ages and BeyondRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Wayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldFrom EverandWayfinding: The Science and Mystery of How Humans Navigate the WorldRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (18)
- The Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindFrom EverandThe Consciousness Instinct: Unraveling the Mystery of How the Brain Makes the MindRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (93)
- This Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyFrom EverandThis Is Your Brain On Parasites: How Tiny Creatures Manipulate Our Behavior and Shape SocietyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- 10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessFrom Everand10% Human: How Your Body's Microbes Hold the Key to Health and HappinessRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (33)
- Mother Earth Spirituality: Native American Paths to Healing OurselvesFrom EverandMother Earth Spirituality: Native American Paths to Healing OurselvesRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (11)
- The Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorFrom EverandThe Other Side of Normal: How Biology Is Providing the Clues to Unlock the Secrets of Normal and Abnormal BehaviorNo ratings yet
- All That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesFrom EverandAll That Remains: A Renowned Forensic Scientist on Death, Mortality, and Solving CrimesRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (396)
- Why Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeFrom EverandWhy Fish Don't Exist: A Story of Loss, Love, and the Hidden Order of LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (699)
- The Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildFrom EverandThe Lives of Bees: The Untold Story of the Honey Bee in the WildRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (44)
- The Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceFrom EverandThe Molecule of More: How a Single Chemical in Your Brain Drives Love, Sex, and Creativity--and Will Determine the Fate of the Human RaceRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (515)
- Undeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedFrom EverandUndeniable: How Biology Confirms Our Intuition That Life Is DesignedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- The Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastFrom EverandThe Weather Machine: A Journey Inside the ForecastRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (31)
- The Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceFrom EverandThe Mind & The Brain: Neuroplasticity and the Power of Mental ForceNo ratings yet
- World of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsFrom EverandWorld of Wonders: In Praise of Fireflies, Whale Sharks, and Other AstonishmentsRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (221)
- The Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceFrom EverandThe Dragons of Eden: Speculations on the Evolution of Human IntelligenceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (632)
- The Age of Wood: Our Most Useful Material and the Construction of CivilizationFrom EverandThe Age of Wood: Our Most Useful Material and the Construction of CivilizationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (95)
- The Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsFrom EverandThe Other End of the Leash: Why We Do What We Do Around DogsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (63)