Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 2 Unit Plan
Uploaded by
api-333467509Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chapter 2 Unit Plan
Uploaded by
api-333467509Copyright:
Available Formats
Chapter
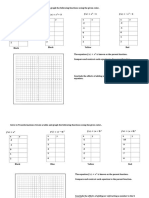
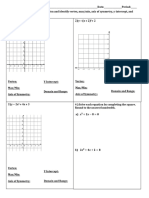
2 Unit Plan: IM2- Graphing Quadratics
1. Start with the end in mind. What does the student need to know and be able to do?
o SWBAT graph Quadratic Equations in Standard Form, Vertex Form and Factored
Form.
o SWBAT convert functions from one form to any other form.
o SWBAT identify critical points on a graph including the vertex, Axis Of
Symmetry, y-intercept, x-intercepts, Domain and Range and 3 other points from
each of the three forms.
o SWBAT to identify and perform transformations on Quadratics including
translations, reflections, and dilations(vertical compression and stretch).
o Standards
A-SSE.3: Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to reveal and
explain properties of the quantity represented by the expression.
(a)Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function it defines.
(b)Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the maximum or
minimum value of the function it defines.
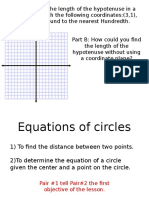
A-REI.4: Solve quadratic equations in one variable.
Use the method of completing the square to transform any
quadratic equation in x into an equation of the form q= (x-p)2-k
that has the same solutions. Derive the quadratic formula from
this form.
Solve quadratic equations by inspection taking square roots
completing the square, The quadratic formula and factoring, as
appropriate to the initial form of the equation. Recognize when the
quadratic formula gets complex solutions and write them as for real
numbers a and b.
F-IF.7: Graph functions expressed symbolically and show key features of the
graph, by hand in simple cases and using technology for more complicated
cases.
Graph linear and quadratic functions and show intercepts, maxima,
and minima.
F-IF.8 :Write a function defined by an expression in different but equivalent
forms to reveal and explain different properties of the function.
Use the process of factoring and completing the square in a quadratic
function to show zeros, extreme values, and symmetry of the graph,
and interpret these in terms of a context.
F-BF.3: Identify the effect on the graph of replacing f(x) by f(x) + k, k f(x), f(kx),
and f(x + k) for special values of k (both positive and negative); and the value of
k given the graphs. Experiment with cases and illustrate an explanation of the
effects on the graph using technology. Include recognizing even and odd
functions from their graphs and algebraic expressions for them.
Choose and produce an equivalent form of an expression to
reveal and explain properties of the quantity represented by the
expression.
Factor a quadratic expression to reveal the zeros of the function
it defines.
Complete the square in a quadratic expression to reveal the
maximum or minimum value of the function it de nes.
Chapter 2 Unit Plan: IM2- Graphing Quadratics
2. Identify curriculum resources.
o Book publisher provides worksheet for each section of the book. The chapters
that apply to the objectives we are chosen are provided below.
o Graphing Standard Form(2-1)
o Transformations (2-3)
o Completing the square (2-4) To graph and Solve for x.
o Factored Form (Use Chapter 1 Trinomials to graph).
3. Identify the declarative knowledge.
o Polynomials
o Factoring
o Terms
o Graphing
o Roots
o x-intercept/Roots/Zeroes
o y-intercept
o vertex
o Axis of Symmetry
o Domain/Range
o Minimum/Maximum
4. Identify the procedural knowledge.
o Operations on Polynomials
o Factoring
o Converting From Standard form to Vertex Form
o Converting From Standard form to Factored Form
o Converting From Vertex form to Standard Form
o Converting From factored form to Standard Form
o Solving for zeros by completing the square
o Solving for Zeros from Factored Form
o Graphing Quadratics
o Perform Transformations on Quadratics
5. Create a learning scale related to the learning goals. Example Below!
NOVICE Students will be able to identify a Quadratic function. Students may be able
to convert from standard form to x-intercept Form.
APPRENTICE Students can graph equations in standard form from plotting points.
Students will be able to approximate the critical value. Students will be able
to convert to some forms of a quadratic.
MASTER Students are able to Graph functions, identify exact critical values and
transformations in any form. Students will be able to convert from one form
to another.
EXPERT Students are able to Graph functions, identify critical values and
transformations from a graph given in any form. Students will be able to
convert from one form to another. Students will be able to create new
functions given x-intercepts and an A-value or given the vertex and an A
value or given the y- intercept, the A value and a point.
6. Create assessment(s).
7. Plan classroom activities and assignments.
You might also like
- Jigsaw Activity Transformations QuadraticsDocument5 pagesJigsaw Activity Transformations Quadraticsapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Backwards Lesson DesignDocument4 pagesBackwards Lesson Designapi-333467509No ratings yet
- 11 5 Day 2Document12 pages11 5 Day 2api-333467509No ratings yet
- Eld Standards Activity 2Document7 pagesEld Standards Activity 2api-333467509No ratings yet
- Converting Between Quadratic FormsDocument1 pageConverting Between Quadratic Formsapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Edmodo Quiz Vertex FormDocument1 pageEdmodo Quiz Vertex Formapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Padlet ActivityDocument1 pagePadlet Activityapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Graphing Quadratics Via TransformationsDocument1 pageGraphing Quadratics Via Transformationsapi-333467509No ratings yet
- El ActivityDocument2 pagesEl Activityapi-333467509No ratings yet
- 11 8 Circles AccomodationsDocument11 pages11 8 Circles Accomodationsapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Chapter 2 Test ADocument2 pagesChapter 2 Test Aapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Eld Goal 14Document10 pagesEld Goal 14api-333467509No ratings yet
- Assessmign ElsDocument8 pagesAssessmign Elsapi-333467509No ratings yet
- 11 8 Circles OriginalDocument8 pages11 8 Circles Originalapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Artifact 1 Goal16Document1 pageArtifact 1 Goal16api-333467509No ratings yet
- At Risk Students Board PolicyDocument4 pagesAt Risk Students Board Policyapi-333467509No ratings yet
- MathketballDocument19 pagesMathketballapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Pyramid ActivityDocument5 pagesPyramid Activityapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Behavior Management PlanDocument1 pageBehavior Management Planapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Quadratic LessonDocument9 pagesQuadratic Lessonapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Seating Chart CompressedDocument3 pagesSeating Chart Compressedapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Conflict ResolutionDocument23 pagesConflict Resolutionapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Integrated Math 2 Syllabus CompressedDocument2 pagesIntegrated Math 2 Syllabus Compressedapi-333467509No ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Teaching Practice Task 2Document2 pagesTeaching Practice Task 2api-456760133No ratings yet
- Saarc Stands For: United Nationsheadquarters, New York City, Official Languages Arabic, ChineseDocument6 pagesSaarc Stands For: United Nationsheadquarters, New York City, Official Languages Arabic, ChineseSamia KhalidNo ratings yet
- A Lesson Plan in Reported SpeechDocument4 pagesA Lesson Plan in Reported SpeechIza Tom100% (3)
- Child Protection Policy LambaDocument13 pagesChild Protection Policy LambaElaine Quinto100% (1)
- Lesson Plan Speaking at ClassDocument1 pageLesson Plan Speaking at ClassAhmad Aiman AzizanNo ratings yet
- Teacher Stress InventoryDocument4 pagesTeacher Stress InventoryLarisa Niculicea100% (8)
- Reference Letter For SarahDocument1 pageReference Letter For Sarahapi-282542897No ratings yet
- Rhyming Words for Pre-K ReadingDocument2 pagesRhyming Words for Pre-K Readingابو مريمNo ratings yet
- Mahouka Koukou No Rettousei - Volume 01 - Enrollment Chapter (I)Document227 pagesMahouka Koukou No Rettousei - Volume 01 - Enrollment Chapter (I)kokutoNo ratings yet
- Nicholas Guerrero ResumeDocument2 pagesNicholas Guerrero ResumeNick GuerreroNo ratings yet
- School Uniforms Should Be AllowedDocument2 pagesSchool Uniforms Should Be AllowedAllon DoradoNo ratings yet
- Effects of Gender On Teachers' Perceptions of School Environment, Teaching Efficacy, Stress and Job SatisfactionDocument11 pagesEffects of Gender On Teachers' Perceptions of School Environment, Teaching Efficacy, Stress and Job Satisfactiondeviraj22No ratings yet
- Classroom Management PlanDocument6 pagesClassroom Management PlanMazerithNo ratings yet
- School WIFA Supplementation FormDocument2 pagesSchool WIFA Supplementation FormSteffi100% (1)
- 2111 HDocument3 pages2111 HWongPangFeiNo ratings yet
- Writing A Literature Review: G.Perkin@lboro - Ac.ukDocument15 pagesWriting A Literature Review: G.Perkin@lboro - Ac.ukG00GLRNo ratings yet
- EXAMEN FINAL Master Cloe, An 2, Sem.2Document6 pagesEXAMEN FINAL Master Cloe, An 2, Sem.2Anina Mariana MihaiNo ratings yet
- Subject Verb AgreementDocument6 pagesSubject Verb AgreementEmelyn HuboNo ratings yet
- Aqa 46552h W Ms Jun15Document11 pagesAqa 46552h W Ms Jun15api-243225219No ratings yet
- The Learning EnvironmentDocument16 pagesThe Learning Environmentaden1122.cbNo ratings yet
- Russian Violin Method Project at Children's Culture CenterDocument35 pagesRussian Violin Method Project at Children's Culture CenterEmmanuel BaylosisNo ratings yet
- Micro TeachingDocument30 pagesMicro TeachingLi ChinNo ratings yet
- Placement and Class GroupingsDocument3 pagesPlacement and Class Groupingsapi-205485325No ratings yet
- Events ProposalDocument8 pagesEvents ProposalAngela Mora AnchetaNo ratings yet
- 20+ Things Your Students Should Know - SAMPLE PAGESDocument11 pages20+ Things Your Students Should Know - SAMPLE PAGESThane1020No ratings yet
- Tools and Techniques for Your Middle School Band ClassroomDocument40 pagesTools and Techniques for Your Middle School Band ClassroomJesús Caro0% (1)
- C Shock Press KitDocument10 pagesC Shock Press KitSusan LiNo ratings yet
- Creative Sparks for Educating the UnderprivilegedDocument95 pagesCreative Sparks for Educating the UnderprivilegedJustin NilanjanNo ratings yet
- Philosophy of EducationDocument2 pagesPhilosophy of EducationMARIA MICHELLE A. HELARNo ratings yet