Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ch8 Review Problems New
Uploaded by
Vic VanceCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch8 Review Problems New
Uploaded by
Vic VanceCopyright:
Available Formats
Ch8.
Conservation of Energy- Review Problems
1. A single conservative force Fx = (6x 12) N (x is in m) acts on a particle
moving along the x axis. The potential energy associated with this force is
assigned a value of + 20 J at x = 0. What is the potential energy at x = 3 m?
Ans. + 29 J
2. A 0.4 kg particle moves under the influence of a single conservative force.
At point A where the particle has a speed of 10 m/s, the potential energy
associated with the conservative force is + 40 J. As the particle moves from
A to B, the force does + 25 J of work on the particle. What is the value of
the potential energy at point B? Ans. + 15 J
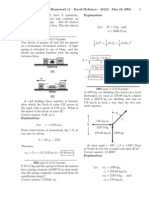
3. A 12 kg block on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to a light
spring (force constant = 0.8 kN/m). The block is initially at rest at its
equilibrium position when a force (magnitude F = 80 N) acting parallel to
the surface is applied to the block, as shown. What is the speed of the block
when it is 13 cm from its equilibrium position? Ans. 0.78 m/s
4.A 0.04 kg ball is thrown from the top of a 30 m tall building (point A) at
an unknown angle above the horizontal. As shown in the figure, the ball
attains a maximum height of 10 m above the top of the building before
striking the ground at point B. If air resistance is negligible, what is the
value of the kinetic energy of the ball at B minus the kinetic energy of the
ball at A? Ans. 12 J
10m
30m
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 1
5. A 2 kg mass is projected from the edge of the top of a 20 m tall building
with a velocity of 24 m/s at some unknown angle above the horizontal.
Disregard air resistance and assume the ground is level. What is the kinetic
energy of the mass just before it strikes the ground? Ans. 970 J
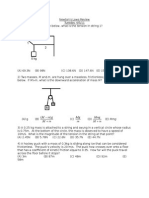
6. A skier weighing 700 N goes over a frictionless circular hill as shown.
If the skier's speed at point A is 9.2 m/s, what is his speed at the top of the
hill (point B).
B
A
10 m
0
50
7. A skier weighing 800 N comes down a frictionless ski run that is circular
(R = 30 m) at the bottom, as shown. If her speed is 12 m/s at point A, what
is her speed at the bottom of the hill (point B)? Ans. 17 m/s
400
30 m
8. A 2 kg block sliding on a horizontal frictionless surface is attached to one
end of a horizontal spring (k = 200 N/m) which has its other end fixed. If
the block has a speed of 4 m/s as it passes through the equilibrium position,
what is its speed when it is 20 cm from the equilibrium position? Ans. 3.5
m/s
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 2
9. A 6 kg block slides along a horizontal surface. If k = 0.2 for the block and
surface, at what rate is the friction force doing work (Power) on the block at
an instant when its speed is 4 m/s? Answer. 47 W
10. The speed of a 4 kg object is given by v = (2t) m/s, where t is in s. At what
rate is the resultant force on this object doing work at t = 1 s? Answer. 16 W
11.A simple pendulum consists of a 2.0 kg mass attached to a 1.0 m long
string. It is released from rest at an angle of 30 (point A) as shown in the
figure. What is Its speed (v) at the lowest point P ? Ans: 1.6 m/s
12. A 2.0-kg block situated on a frictionless incline is connected to a light
spring (k = 100 N/m), as shown. The block is released from rest when the
spring is unstretched. The pulley is frictionless and has negligible mass. What
is the speed of the block when it has moved 0.20 m down the plane? Ans: 60
cm/s
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 3
13. A projectile of mass 0.20 kg is fired with an initial speed of 20 m/s at an
angle of 60o above the horizontal. What is the kinetic energy of the projectile
at its highest point? Ans: 10J
14. A block of mass 2.0 kg is initially moving to the right on a horizontal
frictionless surface at a speed 5.0 m/s. It then compresses a spring of spring
constant 100 N/m. At the instant when the kinetic energy of the block is equal
to the potential energy of the spring, what is compressed distance of the
spring? Ans:0.50 m
15. The figure below, shows an object of mass m = 1.00 kg starting from rest.
It first slides a distance 45.0 cm down a frictionless inclined surface and then
slides across a rough horizontal surface whose coefficient of kinetic friction is
0.150. What is the maximum distance (d) travelled by the object across the
horizontal surface?
16. A block of mass 2.00 kg is released from rest and slides down a rough
track of radius R = 1.00 m as shown in the figure. If the speed of the block at
the bottom of the track is 4.00 m/s, what is the work done by the frictional
force acting on the block?
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 4
17. In the figure, a 2.0 kg object slides on a frictionless horizontal surface
toward a spring. The speed of the object just before it hits the spring is 6.0
m/s and its speed when the spring is compressed 15 cm is 3.7 m/s. Find the
spring constant of the spring.
18. A ball of mass 2.0-kg is kicked with an initial speed of ( = 5.0 +
5.0)/. What is the ratio of the potential energy, Ug (relative to ground
level) to the kinetic energy, KE of the projectile at its highest point ? Ans: 1.0
19. A 0.80-kg object tied to the end of 2.0-m string swings as a pendulum. At
the lowest point of its swing, the object has a kinetic energy of 10J.
Determine the speed of the object at the instant when the string makes an
angle of 50 with the vertical. Ans: 3.3 m/s
20. A single force acts on a 5.0 kg object in such a way that the position of
the object as a function of time is given by x = 10.0 t 5.0 t2, with x is in
meters and t is in seconds. Find the work done on the object from t = 0 to t =
4.0 s.
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 5
21. A 3.0-kg block is on a horizontal surface. The block is at rest when, at t
= 0, a force F = 12 N acting parallel to the surface is applied to the block
causing it to accelerate. The coefficient of kinetic friction between the block
and the surface is 0.20. At what rate is the force F doing work on the block
at t = 2.0 s? 49W
22. If electricity costs 6.00/kWh (kilowatt-hour), how much would it cost
you to run a120 W stereo system 4.0 hours per day for 4.0 weeks? Ans: $
0.81
23. A child pulls on a wagon with a horizontal force of 75 N. If the wagon
moves horizontally a total of 42 m in 3.0 min, what is the average power
generated by the child?
Ans: $ 18 W
24. A car needs to generate 75.0 hp in order to maintain a constant velocity
of 27.3 m/s on a flat road. What is the magnitude of the total resistive force
acting on the car (due tofriction, air resistance, etc.)?
(1 hp = 746 W) Ans: 2.05 103 N
Ch-8 Review Problems Page 6
You might also like
- Physics Practice Problems: Work and EnergyDocument5 pagesPhysics Practice Problems: Work and EnergysaparullahNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument2 pagesWork and EnergyMauricioCuellar100% (1)
- Work - Energy - PowerDocument9 pagesWork - Energy - PowermaryNo ratings yet
- Current Electricity Notes JEE Main and AdvancedDocument49 pagesCurrent Electricity Notes JEE Main and AdvancedHitesh Bhatia0% (1)
- Center of MassDocument5 pagesCenter of MassMahesh VashisthNo ratings yet
- Trigonometry formulae and solving equationsDocument3 pagesTrigonometry formulae and solving equationsSaiful Hasan MasudNo ratings yet
- Work - Power & Energy and Centre of MassDocument20 pagesWork - Power & Energy and Centre of Massaqeeel777No ratings yet
- Physics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument7 pagesPhysics Exam Multiple Choice QuestionsRachel Du PreezNo ratings yet
- Asif Insight Physics OpticsDocument14 pagesAsif Insight Physics OpticsMOHAMMED ASIF67% (3)
- Laws of Motion and FrictionDocument136 pagesLaws of Motion and FrictionPriyankaMishra100% (1)
- Quiz 5Document6 pagesQuiz 5Elizabeth LamasNo ratings yet
- Coordinate GeometryDocument318 pagesCoordinate GeometrySahil Arora100% (1)
- 4 Gravitaional Constant GDocument64 pages4 Gravitaional Constant Ggomathi_nellaiNo ratings yet
- Teaching Notes 1Document61 pagesTeaching Notes 1MOHAMMED ASIF100% (4)
- 287 challengerPhysicsDemoDocument30 pages287 challengerPhysicsDemoAAVANINo ratings yet
- Bronx Science Physics ExamDocument12 pagesBronx Science Physics ExamNobhe MeowNo ratings yet
- Mechanics 2 NotesDocument12 pagesMechanics 2 NotesMaxime Bourgoing100% (1)
- Physics Final Practice Questions SolvedDocument2 pagesPhysics Final Practice Questions SolvedBHAAJI0001100% (1)
- Motion in A Straight Line Test 1Document10 pagesMotion in A Straight Line Test 1meemansa12No ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument10 pagesProjectile MotionwolfretonmathsNo ratings yet
- Rotating PendulumDocument12 pagesRotating Pendulumjerome meccaNo ratings yet
- A Inao 01-06Document53 pagesA Inao 01-06NiZamMAdridistaNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 1 Energy Practice TestDocument7 pagesAP Physics 1 Energy Practice TestNikhita Rajesh100% (1)
- Day 2 Newtons Laws ReviewDocument6 pagesDay 2 Newtons Laws Reviewnoel castilloNo ratings yet
- Electric PotentialDocument10 pagesElectric Potentialzakibrant230% (1)
- Physics Bowl ExamDocument7 pagesPhysics Bowl ExamShilpa GodboleNo ratings yet
- Mechanics Notes 4Document15 pagesMechanics Notes 4niteshNo ratings yet
- Circle Complete Exercise 1676134670830Document86 pagesCircle Complete Exercise 1676134670830Vikrant OjhaNo ratings yet
- InspireDocument19 pagesInspireUWC Australia100% (1)
- World Physics Olympiads Rules and Regulations: Beat The ChampionDocument12 pagesWorld Physics Olympiads Rules and Regulations: Beat The Championjas dwanNo ratings yet
- Displacement and Force in Two Dimensions-1Document2 pagesDisplacement and Force in Two Dimensions-1varaprasadNo ratings yet
- Time: 2hour: Bangladesh Physics Olympiad National Camp-2021Document3 pagesTime: 2hour: Bangladesh Physics Olympiad National Camp-2021Abid KhanNo ratings yet
- AP Physics NotesDocument18 pagesAP Physics Notesfhsphysics100% (1)
- Analytical Geometry Previous YearDocument11 pagesAnalytical Geometry Previous Yearvamsi naniNo ratings yet
- 4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFDocument38 pages4 MotionOneDimensionFull PDFmagiclcjNo ratings yet
- Multiple choice practice questions on circular motion and rotationDocument13 pagesMultiple choice practice questions on circular motion and rotationharshanauocNo ratings yet
- Solutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlDocument45 pagesSolutions of 5 Online Physics BrawlKetul ShahNo ratings yet
- Physics Olympiad QuestionDocument11 pagesPhysics Olympiad QuestionIrtiza HaSanNo ratings yet
- Olympiad Physics INPHO Solved Question Paper 2009Document20 pagesOlympiad Physics INPHO Solved Question Paper 2009RamNo ratings yet
- PhysicsDocument20 pagesPhysicsAnthony HugillNo ratings yet
- ENGINEERING PHYSICS SyllabusDocument2 pagesENGINEERING PHYSICS SyllabusRathinaKumarNo ratings yet
- Where Do Students "Go Wrong" When Solving Newton's Second Law ProblemsDocument19 pagesWhere Do Students "Go Wrong" When Solving Newton's Second Law ProblemsIgnacio RoccoNo ratings yet
- PHM 601 Question Bank-2018Document4 pagesPHM 601 Question Bank-2018Abhishek YadavNo ratings yet
- 84 Vector and Parametric Equations of A PlaneDocument2 pages84 Vector and Parametric Equations of A PlaneRonaldo95163No ratings yet
- FrictionDocument13 pagesFrictionmjchavda8046100% (3)
- IPHO 2011-2015 Problems and SolutionsDocument184 pagesIPHO 2011-2015 Problems and SolutionsCamilo Lim100% (1)
- Part 04 SET (251 - 252)Document3 pagesPart 04 SET (251 - 252)KartikNo ratings yet
- Projectile MotionDocument36 pagesProjectile MotionCharitie Magyan OlaNo ratings yet
- Projectile Motion RangeDocument25 pagesProjectile Motion RangeShirah CoolNo ratings yet
- Chapter 15 ProblemsDocument7 pagesChapter 15 ProblemsekojantiNo ratings yet
- KinematicsDocument33 pagesKinematicstai58No ratings yet
- PSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsDocument10 pagesPSI AP Physics I Dynamics Multiple-Choice QuestionsKarla PereraNo ratings yet
- Class 11 Physics Test Questions on Newton's Laws, Work, Energy and MomentumDocument6 pagesClass 11 Physics Test Questions on Newton's Laws, Work, Energy and MomentumSathya NarayananNo ratings yet
- Rotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentDocument9 pagesRotation Dynamics AssigntyrftyugrroooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooooomentAnju Sahai100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Notes - Student1Document79 pagesChapter 6 Notes - Student1PedroFelipeBravoNo ratings yet
- 8th IPhO Problem and SolutionDocument15 pages8th IPhO Problem and SolutionFarizal HakikiNo ratings yet
- PF Test List - Tribology 2020Document1 pagePF Test List - Tribology 2020Walter Pérez BazánNo ratings yet
- Physics NET/JRF Practice QuestionsDocument44 pagesPhysics NET/JRF Practice QuestionsSibadatta MaharanaNo ratings yet
- Physics of Cavitation: GAS CONTENT and Nuclei: 3.1 Cohesive ForcesDocument20 pagesPhysics of Cavitation: GAS CONTENT and Nuclei: 3.1 Cohesive ForcesAbdelrahman Atef ElbashNo ratings yet
- Atomic Spectroscopy Techniques Sample Introduction SourcesDocument35 pagesAtomic Spectroscopy Techniques Sample Introduction SourcesAndrés PacompíaNo ratings yet
- AB2 - 5 Surfaces and Surface IntegralsDocument17 pagesAB2 - 5 Surfaces and Surface IntegralsnooktabletNo ratings yet
- EECE263 Basic Circuit Analysis Set 7: DiodesDocument30 pagesEECE263 Basic Circuit Analysis Set 7: DiodeswerewaroNo ratings yet
- 1 Ancillary StatisticsDocument5 pages1 Ancillary StatisticsChris VegaNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pump DesignDocument11 pagesCentrifugal Pump DesignPeter PerezNo ratings yet
- Air Permeability: CHE1022: Mechanical Operation Lab Expt No: 9 DateDocument4 pagesAir Permeability: CHE1022: Mechanical Operation Lab Expt No: 9 Date;(No ratings yet
- General Chemistry 1: Topic: The Quantum Mechanical Description of The Atom and It'S Electronic StructureDocument11 pagesGeneral Chemistry 1: Topic: The Quantum Mechanical Description of The Atom and It'S Electronic StructureJennette BelliotNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 Stresses and StrainsDocument25 pagesLecture 1 Stresses and Strainssamurai7_77No ratings yet
- Polymer DegradationDocument12 pagesPolymer DegradationDilaFirizqinaNo ratings yet
- Unit ConversionDocument1 pageUnit ConversionHRK65No ratings yet
- On Solution of Sylvester Equation PDFDocument3 pagesOn Solution of Sylvester Equation PDFAzhar MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Newton Laws of Motion JeopardyDocument19 pagesNewton Laws of Motion JeopardyJessiel GueribaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 20 PDFDocument58 pagesChapter 20 PDFSergio Luis Guerra SánchezNo ratings yet
- Twinning in CrystalsDocument5 pagesTwinning in CrystalsShoaib Imam NaqviNo ratings yet
- Aa - List-Definition-Chemistry-protected PDFDocument10 pagesAa - List-Definition-Chemistry-protected PDFFahad Hameed AhmadNo ratings yet
- Uce Physics QNSDocument21 pagesUce Physics QNSsam lubakeneNo ratings yet
- Elastic Buckling of Plates With HoleDocument16 pagesElastic Buckling of Plates With Hole201087No ratings yet
- Bulk Metallic GlassesDocument43 pagesBulk Metallic GlassesCa NdyNo ratings yet
- (4-2-3) NPTEL - Properties of Cryogenic FluidsDocument45 pages(4-2-3) NPTEL - Properties of Cryogenic FluidsWarren RiveraNo ratings yet
- Autocollimators LED 201209 PDFDocument3 pagesAutocollimators LED 201209 PDFchaitanyavundruNo ratings yet
- 5.0 Microfine Cement Grout Laboratory Testing and ResultsDocument25 pages5.0 Microfine Cement Grout Laboratory Testing and ResultsTATATAHERNo ratings yet
- The Hamiltonian and Lagrangian Approaches To The Dynamics of Nonholonomic SystemsDocument40 pagesThe Hamiltonian and Lagrangian Approaches To The Dynamics of Nonholonomic SystemsDavid BrigidoNo ratings yet
- Thesis SongDocument150 pagesThesis SongPatrickAndradeNo ratings yet
- CBSE 12th Physics Unsolved Overall Important Question Paper - IIDocument8 pagesCBSE 12th Physics Unsolved Overall Important Question Paper - IIShakti Singh ShekhawatNo ratings yet
- Acetone KineticsDocument8 pagesAcetone KineticsEddie ChuiNo ratings yet
- GEN. PHYSICS 1 (Week 8)Document5 pagesGEN. PHYSICS 1 (Week 8)Jeanny Mae PesebreNo ratings yet
- Physics 01-03Document3 pagesPhysics 01-03KevleenNo ratings yet