Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Q2 S
Uploaded by
AbdulHaseebArifOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Q2 S
Uploaded by
AbdulHaseebArifCopyright:
Available Formats
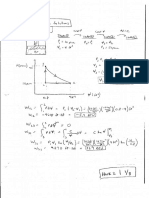
1) For water at 10 bar and 0.0978 m3/kg, find u in kJ/kg.
At 10 bar, the given v is between vf and vg, so the state is mixed. Using the relation for quality:
v v f x (v g v f )
0.0978 .0011273 x(.1944 .001273)
x 0.5
u u f x(u f u g ) 0.5(u f u g ) 1672.6 kJ/ kg
2) For CO2 at 911 psi and 115 F, find v in ft3/lb.
Weve got pressure and temperature, but we don t know if the IGL is valid. Easy enough to check. P = 62 atm, and Pcr =
72.9 atm, so Pr=0.85. T = 575 R and Tcr = 548 R, so Tr = 1.05. From the compressibility chart, z is very close to 0.7, so:
RT 1545 575 ( ft lbf / lbmol R) R ft 3
vz 0.7 0.1077
P 44 911(144) lb / lbmol lbf / ft 3 lb
3) For R134a at 45 psi and 50 F, find h in Btu/lb
From the saturated table, we see that this state is SHV. Were between two pressure and two temperatures, so its a
double interpolation. First, we get the numbers in red, then interpolate between those to get 110.02 Btu/lb.
40 Psi h (Btu/lbm) 60 Psi h (Btu/lbm)
40 F 108.26 40.27 F (Sat) 107.43
45F 110.44 45F 109.61
50F 112.62 50F 111.85
4) For propane at 20 bar and 20 C, find v in ft3/lb
At 20 bar, this is below the saturation temperature, so were CL. Use vg(20 C) = 1.999e-03 m3/kg. Converting to ft3/lb
gives 0.032 ft3/lb.
Extra Credit Bonus (5 points):
For water at 175 ft3/lb and u = 555.8 Btu/lb, find T.
Checking the saturated tables at v = 175 ft3/lb, u is much greater than the value shown, so were probably mixed. Choose
a temperature and calculate x for the v value, then compare to u. Do a second guess, then interpolate to converge to 100
F.
You might also like
- Problems and Solutions for Boiler CalculationsDocument11 pagesProblems and Solutions for Boiler CalculationsJosue Carubio Ricalde Jr.100% (2)
- Sample Problems in ThermodynamicsDocument16 pagesSample Problems in ThermodynamicsVon Eric DamirezNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics - Ideal GasDocument11 pagesThermodynamics - Ideal GasMae Belle AngayNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics 1Document72 pagesThermodynamics 1Victor CapistranoNo ratings yet
- Homework #3 PDFDocument2 pagesHomework #3 PDFAntonio SantoyoNo ratings yet
- 27595149Document5 pages27595149Anshul AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Toaz - Info Chapter 3 Problems 7th Edition PRDocument25 pagesToaz - Info Chapter 3 Problems 7th Edition PRFiras 01No ratings yet
- Thermal Principles ReviewDocument6 pagesThermal Principles ReviewT CNo ratings yet
- Tarea 4 TermodinamicaDocument3 pagesTarea 4 TermodinamicaMario GonzalezNo ratings yet
- ثرموداينمكDocument10 pagesثرموداينمكabdcivilNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamic Units & Properties of WaterDocument7 pagesThermodynamic Units & Properties of WaterRekha ToshniwalNo ratings yet
- Suva 95 (R508B)Document22 pagesSuva 95 (R508B)mdtaheriNo ratings yet
- Thermo 2Document2 pagesThermo 2kj gandaNo ratings yet
- TPSuva 95Document22 pagesTPSuva 95JoelNo ratings yet
- The Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesThe Working Fluid in ThermodynamicsFarouk BassaNo ratings yet
- Set 1Document3 pagesSet 1carlos calibara0% (1)
- Pneumatic PowerDocument28 pagesPneumatic PowerAhmad HamoudaNo ratings yet
- PROPERTY TABLES + EQUATION OF STATE GUIDEDocument66 pagesPROPERTY TABLES + EQUATION OF STATE GUIDEMuhammad Randy AkbarNo ratings yet
- ETD Question Bank 2021-22Document14 pagesETD Question Bank 2021-22Vinay KorekarNo ratings yet
- Chemical Engineering Principles SATsDocument7 pagesChemical Engineering Principles SATsAli Hamza ManzoorNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws ExplainedDocument9 pagesGas Laws ExplainedGineNo ratings yet
- Steam Table and Psychrometric Chart: Mardiana Ahamad ZabidiDocument29 pagesSteam Table and Psychrometric Chart: Mardiana Ahamad ZabidiMuhd SyahmiNo ratings yet
- Presentation ReportDocument8 pagesPresentation ReportJackson ChongNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyDocument38 pagesThermodynamics: Conservation of EnergyAron H OcampoNo ratings yet
- Unit Three Homework Solutions, September 16, 2010: KG M KG M KG M XV V X VDocument6 pagesUnit Three Homework Solutions, September 16, 2010: KG M KG M KG M XV V X VApple StarkNo ratings yet
- Gas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountDocument9 pagesGas Laws: Boyle's Law or The Pressure-Volume Law States That The Volume of A Given AmountArun KarthikeyanNo ratings yet
- T P Const. V Const: F FG F FGDocument4 pagesT P Const. V Const: F FG F FGAiena AzlanNo ratings yet
- Me 211 Examples SolutionsDocument30 pagesMe 211 Examples SolutionsBryan Dominic Gabriel PaduaNo ratings yet
- Flow of FluidsDocument6 pagesFlow of Fluidsapi-3728602No ratings yet
- Thermo 7e SM Chap01-1 ReduddcionDocument33 pagesThermo 7e SM Chap01-1 ReduddcionJonathanNo ratings yet
- Maintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilityDocument7 pagesMaintenance Training: Unit Measurement: Pua Wee Ming Tonnage Operation - ReliabilitypuaweemingNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas Equation and EntropyDocument27 pagesIdeal Gas Equation and EntropyJude Roswel GenerilloNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument3 pagesGas LawsJsn JsnNo ratings yet
- THERMO1 - 3 Evaluating Properties PDFDocument17 pagesTHERMO1 - 3 Evaluating Properties PDFEdmark AldeaNo ratings yet
- Assignment3 SolutionDocument6 pagesAssignment3 SolutionI190845 Samana NayyabNo ratings yet
- LB FT LB Gal LB FT LB: Soal 1Document4 pagesLB FT LB Gal LB FT LB: Soal 1Chan PoleNo ratings yet
- Week 7 Gas LawsDocument53 pagesWeek 7 Gas LawsMica Shane billedo PapaNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument13 pagesGas LawsVenkatNo ratings yet
- Ideal Gas LawDocument21 pagesIdeal Gas Lawjervis GrajoNo ratings yet
- Reviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Document37 pagesReviewlecture-I 20081001 48e3c2399f4d65 74115154Austin BarrilleauxNo ratings yet
- Dryness FractionDocument5 pagesDryness FractionAmy AckerNo ratings yet
- Diesel engine cycle energy transfers per unit massDocument3 pagesDiesel engine cycle energy transfers per unit massGav Pe BenitoNo ratings yet
- Gas LawsDocument41 pagesGas LawsGrey TapesNo ratings yet
- TPSuva 410 ADocument24 pagesTPSuva 410 AJoelNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Bi ND NuDocument6 pagesDifference Between Bi ND NuIzuchucku JohnNo ratings yet
- Entropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDocument26 pagesEntropy Rate Balance For Closed Systems: ExampleDaniel García100% (1)
- Scales of TemperatureDocument31 pagesScales of TemperaturesatejbagalNo ratings yet
- Steam Table: Mollier ChartDocument8 pagesSteam Table: Mollier ChartabdcivilNo ratings yet
- Sec2 2Document34 pagesSec2 2chrisdaman2011No ratings yet
- Latent Heat of VaporizationDocument11 pagesLatent Heat of VaporizationEsther Faith GabrielNo ratings yet
- Aero Review ThermodynamicsDocument122 pagesAero Review ThermodynamicsKen GuanzonNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction PDFDocument3 pagesDryness Fraction PDFPrasant RaoNo ratings yet
- Calculating DrynessDocument3 pagesCalculating DrynessVns VnsNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction PDFDocument3 pagesDryness Fraction PDFPranay NayanNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction PDFDocument3 pagesDryness Fraction PDFVns VnsNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction PDFDocument3 pagesDryness Fraction PDFSreejith SisupalanNo ratings yet
- Dryness Fraction PDFDocument3 pagesDryness Fraction PDFaviralNo ratings yet
- Recommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsFrom EverandRecommended Reference Materials for Realization of Physicochemical Properties: Pressure–Volume–Temperature RelationshipsE. F. G. HeringtonNo ratings yet
- Akhil Jose, Clint Augustine, Shinu Mohanan Malola, Keerthi Chacko. 2015. Scientific Research PublishingDocument1 pageAkhil Jose, Clint Augustine, Shinu Mohanan Malola, Keerthi Chacko. 2015. Scientific Research PublishingAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Serial Number IDM 6.21Document1 pageSerial Number IDM 6.21PapavikaPapavikaNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Wireless Communications: Cellular ConceptDocument52 pagesWireless Communications: Cellular ConceptAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Ad Hoc-Channel PDFDocument9 pagesAd Hoc-Channel PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument5 pagesPDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- 33-005-PCI Datasheet DigitalPendulum MATLAB 10 2013Document2 pages33-005-PCI Datasheet DigitalPendulum MATLAB 10 2013AbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- 1st QuizDocument1 page1st QuizAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- New Text DocumentDocument1 pageNew Text DocumentAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Static Forces and Moments DocumentDocument4 pagesStatic Forces and Moments DocumentAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- FDocument2 pagesFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument6 pagesPDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- sm2 16Document1 pagesm2 16AbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Prob Set 2 SolutionsDocument12 pagesProb Set 2 SolutionsAbdulHaseebArif100% (1)
- 1.engineering Economics Cost Analysis PDFDocument11 pages1.engineering Economics Cost Analysis PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Quizz Week 4 (Number 2)Document1 pageQuizz Week 4 (Number 2)AbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Hwk2Solution PDFDocument13 pagesHwk2Solution PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Q1 SDocument1 pageQ1 SAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- H2 SDocument10 pagesH2 SAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Cammarata L & Yliniemi L (1999) Development of A Self-Tuning Fuzzy Logic Controller (STFLC) For A Rotary Dryer. December 1999 PDFDocument35 pagesCammarata L & Yliniemi L (1999) Development of A Self-Tuning Fuzzy Logic Controller (STFLC) For A Rotary Dryer. December 1999 PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- 8 10 2009 Kou Kong PDFDocument155 pages8 10 2009 Kou Kong PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Ps 1Document2 pagesPs 1AbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- 8esm 02 32 PDFDocument1 page8esm 02 32 PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- Hwk1Solution PDFDocument14 pagesHwk1Solution PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet
- 5Document18 pages5Yahya Ben WalidNo ratings yet
- 8 39 PDFDocument1 page8 39 PDFAbdulHaseebArifNo ratings yet