Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Temp
Uploaded by
Marla MendozaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Temp
Uploaded by
Marla MendozaCopyright:
Available Formats
Temp-It's also a measure of how fast the atoms and molecules of a substance are moving.
Heat-In physics, heat is energy that spontaneously passes between a system and its
surroundings in some way other than through work or the transfer of matter. When a suitable
physical pathway exists, heat flows spontaneously from a hotter to a colder body.
Specific heat-The specific heat is the amount of heat per unit mass required to raise the
temperature by one degree Celsius. The relationship between heat and temperature change is
usually expressed in the form shown below where c is the specific heat.
Modes of heat transfer
Conduction-Conduction is at transfer through solids or stationery fluids. When you touch a
hot object, the heat you feel is transferred through your skin by conduction. Two
mechanisms explain how heat is transferred by conduction: lattice vibration and particle
collision. Conduction through solids occurs by a combination of the two mechanisms; heat is
conducted through stationery fluids primarily by molecular collisions.-
-Conduction is the mode of heat transfer occurs from one part of a substance to another part of
within the substance itself or with another substance which is placed in physical contact. In
conduction, there is no noticeable movement of molecules.
Convection-Convection uses the motion of fluids to transfer heat. In a typical convective
heat transfer, a hot surface heats the surrounding fluid, which is then carried away by fluid
movement such as wind. The warm fluid is replaced by cooler fluid, which can draw more
heat away from the surface. Since the heated fluid is constantly replaced by cooler fluid, the
rate of heat transfer is enhanced.
-In conduction, heat itself is moving; in convection, hot portions of a
fluid move through the body of the fluid. The hot fluid mixes with
the cold fluid, and heat is transferred more quickly than by
conduction.
-CONVECTION:
Conductive heat transfer occurs within a fluid itself and it is carried out by transfer of
one fraction of the fluid to the remaining portion. Hence unlike conduction, transfer of
molecules occurs during convection. Since movement of particles constitutes
convection, it is the macro form of heat transfer. Also convection is only [possible in
fluids where the particles can moved easily and the rate of convective heat transfer
depends on the rate of flow to a great extend. Convection can be of two types:
1. Natural convection: In this type of convection, the movement of
particles which constitutes convection occurs by the variation in densities of
the fluids. As we already know, as temperature increases, the density
decreases and this variation in density will force the fluid to move through
the volume. This cause convection to occur.
2. Forced Convection: The difference between natural convection and
forced convection is that in forced convection, a work is done to make
movement in the fluid. This is done using a pump or blower.
Radiation-Radiative heat transfer does not require a medium to pass through; thus, it is the
only form of heat transfer present in vacuum. It uses electromagnetic radiation (photons),
which travels at the speed of light and is emitted by any matter with temperature above 0
degrees Kelvin (-273 C). Radiative heat transfer occurs when the emitted radiation strikes
another body and is absorbed. We all experience radiative heat transfer everyday; solar
radiation, absorbed by our skin, is why we feel warmer in the sun than in the shade.
-Radiation is the simplest means of heat transfer. Heat radiation is
carried not by moving atoms (as in conduction or convection) but by
electromagnetic waves. Radiation is the only way that heat can
move through a vacuum, and is the reason that even a closed
thermos bottle (which has a vacuum between the inner and outer
parts) will eventually come to the same temperature as its
surroundings.
Effects of heat on matter
Expansion
Coefficient of linear expansion
Coefficient of linear expansion
Coefficient of volume expansion
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- ComputationsDocument10 pagesComputationsFaye Nervanna Alecha AlferezNo ratings yet
- UST Campus Map with Entrance & Exit LocationsDocument1 pageUST Campus Map with Entrance & Exit LocationsRomulo Vincent Perez0% (1)
- Mass SpectrometryDocument15 pagesMass SpectrometryMeghan Norico Cristuta100% (1)
- Chapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia UniversityDocument38 pagesChapter 1 - Chemical Process Diagrams: Department of Chemical Engineering West Virginia Universitybeyond1241No ratings yet
- BP 344 Accessibility Law Quiz: Building Laws for the DisabledDocument7 pagesBP 344 Accessibility Law Quiz: Building Laws for the DisabledMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Answer KeysDocument1 pageAnswer KeysMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Top 1000Document21 pagesTop 1000Pradeep ChandarNo ratings yet
- Quiz For Theory of ArchitectureDocument2 pagesQuiz For Theory of ArchitectureMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Republic Act No. 9266: The Architecture Act of 2004Document7 pagesRepublic Act No. 9266: The Architecture Act of 2004Marla Mendoza100% (1)
- Rule Vii Building/ Occupancy Firewall Provisions Tgfa/ Tla & BHL ATO GuidelinesDocument1 pageRule Vii Building/ Occupancy Firewall Provisions Tgfa/ Tla & BHL ATO GuidelinesMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- January Freebie of The Month CBTLDocument4 pagesJanuary Freebie of The Month CBTLMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 05 General - General RequirementsDocument1 page05 General - General RequirementsMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument2 pagesBuilding UtilitiesMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities AnswersDocument1 pageBuilding Utilities AnswersMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 07 General - Execution & Closeout RequirementsDocument2 pages07 General - Execution & Closeout RequirementsMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 03 Concrete - Concrete FinishingDocument4 pages03 Concrete - Concrete FinishingMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 01 Masonry - Stone MaterialsDocument7 pages01 Masonry - Stone MaterialsMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 05 General - General RequirementsDocument1 page05 General - General RequirementsMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building UtilitiesDocument2 pagesBuilding UtilitiesMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities AnswersDocument1 pageBuilding Utilities AnswersMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key For Monday QuizDocument1 pageAnswer Key For Monday QuizMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Ideapad z500 Datasheet PDFDocument2 pagesIdeapad z500 Datasheet PDFRahul KumarNo ratings yet
- 01 General SummaryDocument2 pages01 General SummaryMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Gonzales Main DoorDocument1 pageGonzales Main DoorMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building TechnologyDocument2 pagesBuilding TechnologyMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Building Utilities QuizDocument3 pagesBuilding Utilities QuizMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
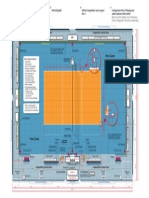
- FIVB VB Official Court Layout 2014Document1 pageFIVB VB Official Court Layout 2014Marla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Working Drawings HandbookDocument143 pagesWorking Drawings HandbookMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Concrete Mixing GuideDocument1 pageConcrete Mixing GuideMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- 8 Sets 600-850 For QuotationDocument1 page8 Sets 600-850 For QuotationMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- College of Architecture: Project LocationDocument6 pagesCollege of Architecture: Project LocationMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Outline: Chapter 1 Problem & Its SettingDocument3 pagesOutline: Chapter 1 Problem & Its SettingMarla MendozaNo ratings yet
- Campus Map For Up DilimanDocument1 pageCampus Map For Up DilimanHanz FerrerNo ratings yet
- CLS 7, Atomic Structure, WSDocument2 pagesCLS 7, Atomic Structure, WSEmerooNo ratings yet
- Autoclaved Aerated Concrete - WikipediaDocument4 pagesAutoclaved Aerated Concrete - WikipediaNagarjun ReddyNo ratings yet
- The Effect of Different Fertilizers On Plant GrowthDocument2 pagesThe Effect of Different Fertilizers On Plant GrowthVeerath தமிழன்0% (2)
- Mixing Eductors Mixing EductorsDocument1 pageMixing Eductors Mixing Eductorsdetreomycyna100% (1)
- 5052 Aluminum Sheet SuppliersDocument13 pages5052 Aluminum Sheet Supplierssanghvi overseas incNo ratings yet
- Practice Redox Reactions QuizDocument2 pagesPractice Redox Reactions Quizrk_gummaluri5334100% (1)
- Global Leader!: L WI REDocument20 pagesGlobal Leader!: L WI REshalometeNo ratings yet
- Fruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible UtilizationDocument20 pagesFruit and Vegetable Waste: Bioactive Compounds, Their Extraction, and Possible UtilizationKrishi AgricultureNo ratings yet
- An800 6Document3 pagesAn800 6jcNo ratings yet
- Abrasion & Impact TestDocument10 pagesAbrasion & Impact TestMuhammad Hafizuddin100% (1)
- Piht0f402 Icmts Icad600tsDocument2 pagesPiht0f402 Icmts Icad600tsamruta21No ratings yet
- Crystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceDocument4 pagesCrystal Appearance/Characteristics Clinical SignificanceAngela LaglivaNo ratings yet
- Philippines Pharmacy Act PenaltiesDocument6 pagesPhilippines Pharmacy Act PenaltiesOdyNo ratings yet
- PMTC Guidance on Cleaning Validation PracticeDocument15 pagesPMTC Guidance on Cleaning Validation PracticehhNo ratings yet
- Establishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFDocument11 pagesEstablishing A Coating Maintenance Plan PDFRicardo MendesNo ratings yet
- Pharmlite Product ListDocument19 pagesPharmlite Product ListbiddumehtaNo ratings yet
- Jak1 Aur El DWG A 0 9035 (D)Document1 pageJak1 Aur El DWG A 0 9035 (D)Budi HahnNo ratings yet
- Dehradun Public School ASSIGNMENT (2019 - 2020) Subject: Science (086) Class - IxDocument4 pagesDehradun Public School ASSIGNMENT (2019 - 2020) Subject: Science (086) Class - Ixbadnight4uNo ratings yet
- Urestone Binder 10-05-11Document17 pagesUrestone Binder 10-05-11Serkan EkingenNo ratings yet
- Total Solutions For Electrocatalysis Research: Discover The ECAT-packagesDocument2 pagesTotal Solutions For Electrocatalysis Research: Discover The ECAT-packagescipta irawanNo ratings yet
- Banana Peels As Paper Final OutputDocument20 pagesBanana Peels As Paper Final OutputA - CAYAGA, Kirby, C 12 - HermonNo ratings yet
- Guidance For Robustness/Ruggedness Tests in Method ValidationDocument48 pagesGuidance For Robustness/Ruggedness Tests in Method ValidationonastasaNo ratings yet
- Determination of Tissue Equivalent Materials of A Physical 8-Year-Old Phantom For Use in Computed TomographyDocument8 pagesDetermination of Tissue Equivalent Materials of A Physical 8-Year-Old Phantom For Use in Computed TomographyInas Fathinah SaepudinNo ratings yet
- Water Flushing Witnessing and TestDocument3 pagesWater Flushing Witnessing and TestNeguib FarahNo ratings yet
- Viruses & Bacteria: Biology 11Document28 pagesViruses & Bacteria: Biology 11Adnan Bhisma RizaldyNo ratings yet
- CHM131 MAC 2019 exam: Density, isotopes, balancing equationsDocument4 pagesCHM131 MAC 2019 exam: Density, isotopes, balancing equationsijah rosmiNo ratings yet