Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Psychiatric Nursing Notes
Uploaded by
Cathy SantosOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Psychiatric Nursing Notes
Uploaded by
Cathy SantosCopyright:
Available Formats
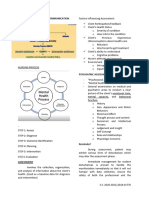
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
PSYCHIATRIC NURSING Counselor
An interpersonal process whereby a professional nurse o Cultivate the art of listening
practitioner assists the individual, the family and the o Verbalize concern
community to promote mental health, prevent mental o We do not give advice, we suggest
illness, cope with the experience of mental illness and
suffering and if necessary, find meaning in the Ward Manager
experience. o Makes sure there are adequate supplies and
that equipment are functioning
K S A o Assign responsibilities and delegate tasks
Knowledge Skills Attitude o Coordination of care
Researcher
Skills in Empathy Creator of a Therapeutic Environment (Milieu)
Nursing (objective, o Structuring the environment
understanding of
the patient) MILIEU THERAPY
Safety
Hopeful for the o Drugs, sharp objects
client o Anything potentially harmful is checked
Norm
ATTITUDES OF A PROFESSIONAL NURSE o Expectations, safety, acceptance, open
Accepting taking client as is, non-judgmental environment, no impositions
Empathy can put shoe in another person, objective Balance
understanding o Consistency vs. flexibility
Consistent set boundaries and structure equal to o Dependence vs. independence
trust Unit Modification
Flexible not too consistent (rigid), able to balance Limit Setting
Hopeful on client o Setting realistic boundaries to clients behavior
Accountable responsible for things we do, to patient, o Implement w/o exemption
superiors, and ourselves o Give what sanctions are expected (not
threatening but informing)
Structure
ROLES OF A NURSE o Physical characteristics of the ward
Teacher o Qualifications of staff
o Relay or convey information to the client
o Must be understood GOALS OF PSYCHIATRIC NURSING
o Consider capabilities of clients to learn Promotive Primary
Preventive Primary
Socializing Agent Curative Secondary
o Initiates conversation, relates to the people in Rehabilitative Tertiary
the community, encourages client to
participate in activities LEVELS OF CARE
o One-on-one then gradually integrate into Primary
society o Promotive healthy with no risk factors to be ill
o Withdrawn active o Preventive healthy but has risk factors to be
Paranoid passive ill
Manipulative matter-of-fact Secondary
Technician o Curative prevent complications
o Doing skills that address the physical and o Early dx through surveillance and case finding
psychological needs of the client o Prompt tx
o Assessment, charting, technical skills o Confinement/ institutional
Parent Surrogate Tertiary
o Doing for the patient what they cannot do for o Rehabilitative prevent relapse and disability
themselves o Optimize function
o Do not encourage dependence o Starts on admission
o Set limits
Patient Advocate THERAPEUTIC RELATIONSHIP
o Knowing their rights and fight for their rights One-on-one relationship
o Rights of Patients: Helping relationship
Right to be free from harm Clinical skills
Right to informed consent A corrective interpersonal experience
o Consent patient
o Details - relative Therapeutic Use of Self
Right to privacy Interpersonal, communication and clinical skills
o Least intrusion Self-awareness is a must!
Right to confidentiality o Done through introspection and listening to
Right to be in a least restrictive what others say
environment o Self-understanding
o Ideal: House/ community
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Joharis Window
Known to you Evaluation of intervention is WORKING PHASE.
Public Self Open window
and others Evaluation of outcome of relationship is TERMINATION
Known to others PHASE.
Semi-public
Closed window but not known to
Self IMPASSE OR BLOCKS IN NURSE-CLIENT RELATIONSHIP
you
You know but
Private Self Hidden window Resistance
others dont know
You and others o Avoidance of instances that are anxiety-
Inner Self Unconscious provoking
do not know
Counter-transference feeling of nurse is transferred to o Client does not want to share, turns his back,
the client does not answer, changes topic purposely
o INTERVENTION: State observation
Transference
Comparison of the Social & Therapeutic Relationship o Shifting of feeling by the patient from
someone significant in the past to the nurse in
Social Therapeutic the present situation
Mutual approval No need for approval o Patient Significant Person (Past) Nurse
Mutual gratification of need Client-centered (present)
o Type of resistance
No structure Structures
o INTERVENTION: State observation
Goal is for pleasure Goal-directed
Counter Transference
o Shifting of feeling from nurse to patient
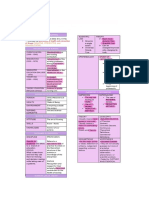
PHASES OF THE NURSE-CLIENT RELATIONSHIP
o Nurse Significant Person (Past) Patient
(present)
1. Pre-orientation
o INTERVENTION: Self-awareness
o Develop self-awareness
Inappropriate Boundaries
o Gather initial information about the patient
o Sharing experiences, meeting the client after
(chart, nurses, relatives)
discharge
Prepare for patient contact
o Beyond limit of boundaries
o Nurse may share as long as it helps
2. Orientation - 1st meeting with patient
Feeling of Sympathy & Encouraging Dependency
o Establish rapport, begin to build trust
o Should be empathy
o Mutually harmonious relationship
o Dependency Mgt:
o Set a contract with the client - expectations,
Assess what patient can do and
parameters, limit setting
take over as needed
o Do the initial assessment of the client
Do task for patient
MSE appearance, behavior,
Let patient do task for himself
thoughts, mood & affect, social,
sensory, memory, judgment, insight)
o Formulate nursing dx and set priorities
COMMUNICATION
Defined as reciprocal exchange of messages
A May be affected by age, sex, educational attainment,
Orientation Phase
D culture and language barrier
P
I Working Phase Context (Setting)
E Dictates role
Setting where communication takes place, determines
3. Working longest phase role and context
o Problem solving occur There must be HARMONY & CONGRUENCE in context, role
o Plan related interventions and outcomes and content.
o Encourage verbalization of feelings
o Assist patient to learn more socially Channel
acceptable behavior Sight, hearing, accessories of communication
o Assist patient to learn more effective coping
patterns
o Assist the client to develop insight MODES OF COMMUNICATION:
o Evaluate problems and goals and modify Verbal oral and written
them as necessary Non-verbal body language
o Alternative problems
Only therapeutic techniques are therapeutic responses.
4. Termination Not all therapeutic techniques are always therapeutic since
o Prepare from orientation phase response must be in context.
o Encourage verbalization of feelings that go
with termination
o May have feelings of sadness or anger
o Must have solidification of parting
o Summarize what he learned in the relationship
and bring it in future relationships
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Non-verbal Aspects of Communication Exploring
Kinesics body movement o Know more about the topic
Proxemics physical spaces between communicators o Tell me more about it.
o Intimate Space (< 1 ft) o Avoid why questions demand explanation
May be threatening o Take note if client still want to explore the
Not done if trust is not established topic
Tell the purpose when entering o Why dont we sit down? declarative
space sentence
Form of intrusion Validating
o Personal Space (1 to 3 ft) o Check for mutual understanding
Comfortable for client o Check if you understand patients message
Should be face to face o . isnt it?
Most acceptable for patient Presenting reality
interaction o Presenting a fact as it is in external reality
o Social Space (3 to 12 ft) Supportive confrontation
Not done during therapeutic o Citing discrepancy in patients behavior
interaction o Alcoholic patients primary defense: denial
Too far Giving feedback/ facilitate self-disclosure
o Public Space (12 ft or more) o Share something to the patient
No eye contact Collaborating
Not suitable for therapeutic o Work with the patient and not for the patient
interaction Focusing
Touch o Directing back to the client
o Suspicious/ paranoid o Flight of ideas
o May convey emotional support shoulder or Reflecting
forearm o Repeat what the patient said
Silence o Direct back to the client what he said
o Give client time to process information and o Patient asks a question, nurse gives back
think about what to say question
o Not all silence are therapeutic o Verbalize feeling implied - Empathy
o If too long, patient may feel uncomfortable o Encourages verbalization of feelings
Paralanguage voice quality or how the language is o You seem angry.
delivered
Restating
COMMUNICATION TECHNIQUES o Repeat what the patient said
o Say it again exactly or paraphrase
Therapeutic Communication Techniques makes patient Summarizing
comfortable to open up o Give a gist of what transpired in the
conversation
Active listening o Give sense of accomplishment to the nurse
o Listening not only w/ ears but the whole body and patient
o Establish eye contact, incline body a little bit Encouraging description of perception
forward, safe distance Encouraging evaluation
Therapeutic silence o Letting the client judge his/her experience
o Allow client to process feeling Placing events in time sequence
Offering self o When did this happen?
Giving recognition
o Call using name Non-therapeutic Communication Techniques
o Acknowledging accomplishment False reassurance
o Enhances clients self-esteem o Falsely reassuring the client not to worry
o Can serve as a reward o Dont worry
Stating observation Belittling feelings
o Noting what you saw, not what you think you o Takes for granted what the patient feels
saw Approval/ Disapproval
o Keeps client aware of what is happening o Extremes are non-therapeutic
Broad opening o Approval giving in
o Good way of starting conversation o Disapproval may exhibit judgment
o What do you want to talk about? Agreeing/ Disagreeing
Accepting o Extremes are non-therapeutic
o Uh huh, yes, I follow o Agreeing giving in
o May be interpreted as an agreement o Disagreeing may exhibit judgment
General leads Giving advice
o More prompting o Telling the client what to do
o Go on, and then o Patient will feel that he does not know what is
Giving information good for him
o Giving a fact that the client needs to know Probing
Clarifying o Exploring beyond clients willingness to explore
o Making clear what is not understood Defending
o What do you mean? o Taking the side of someone
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Behavior is learned, unlearned and modified
Requesting explanation Learned acquisition
o Why? Unlearned extinction of behavior
o Reason o Behavior pleasant repeated learned
Changing the topic behavior
o Patient does not want to talk about a Pleasant reward/ reinforcement
certain topic strengthens behavior
Pleasant behavior learned
Eliminate answer choices like: behavior
1. Authoritarian answers o Behavior + reward (positive reinforcer)=
o I want you to help me ambulate your behavior change
daughter. o Check what behavior is rewardable
2. Close-ended Questions o Learning the behavior is acquiring the
o Do you discuss your problems with behavior
someone? o Aversion therapy behavior is followed by
3. Why questions something unpleasant to decrease behavior
o Why do you feel this way? o Systematic desensitization
4. Dont worry statements o Stress reduction techniques
o Dont worry, the doctor will do everything.
5. Nurse-focused answers V. Psychodynamic/ Developmental/ Psychoanalytic
o I know from experience Model
o Freud/ Erikson
Remember! o How past affects the present
Base your answer on a sound principle not on what o Past affects how a person relates to others
sounds good
Assess what the client knows first o Mental Activity
Focus on the theme of the clients verbalization Conscious - awareness
Choose an answer that demonstrates the nurse Subconscious partly remembered,
empathizing with the patient partly forgotten
Focus on reality; Dont argue, dont disagree Residual painful memories
Choose an answer that allows and encourages
verbalization o 3 Structures of Psyche
Understanding patients condition is the basis of the Id
best therapeutic response o Pleasure principle
Do not pass the buck. Nurse attempts to critically think o Does not tolerate what is
for the answer painful
Look for the answer that personalizes the information o Infant
All components of the answer must be correct o Strong Id Manic
THEORETICAL MODELS OF PATIENT CARE Ego
Explain phenomenon of mental illness o Reality principle
responsible for coping
I. Biologic Model * o Fulcrum/ balance between
Schizophrenia id & superego
o Biological/ medical explanation o Has defensive function
o Genetic predisposition o Coping mechanism to
o Chemical imbalance return to homeostasis
o Structural brain changes - enlargement o May come in the form of
o Biochemical treatment problem solving (most
adaptive coping way)
II. Cognitive Model *
Depression Superego
o Thoughts affect behavior and feelings o Conscience
o Irrational thoughts = irrational behavior o Starts to develop: 1 to 3
o (+) Thoughts (+) Behavior y/o
o (-) Thoughts (-) Behavior o No, limits
o Cognitive therapy/ reconstructing o Weak superego - antisocial
o Challenge (-) thoughts o Very strong superego
III. Social Model depression
o Environment affects behavior
o Milieu Therapy VI. Interpersonal
o Considers totality of environment/ o Sullivan
behavior Significant other plays a big role in
development
IV. Behavioral Model - Freud Anxiety: disapproval of significant
o Learning theories others
o A - Antecedent o Communicable
B - Behavior o People affect people
C - Consequent
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
VII. Existential/ Humanistic o No organic reason
o No regard for the past, only present o Stammering, diarrhea
o Only here and now 15. Symbolization
o Humanistic: Maslows Hierarchy of Needs o Attributing a meaning to an object to
needs NOW represent the unacceptable
o Contradicting with Psychodynamic Model 16. Substitution
o Taking a more attainable goal because the
DEFENSE MECHANISM original goal was unattainable
Relieve tension but does not solve problem 17. Sublimation
Patterns of adaptation o Rechanneling socially unacceptable drives or
Sparing manner impulse into something that is socially
Threat ego will make a way to handle defense acceptable
mechanism (problem solving) 18. Rationalization
Maladaptive or excessive use unhealthy o Using a reason which is not a real reason to
justify
1. Suppression 19. Denial
o Conscious forgetting o Refusal to acknowledge a painful reality as if
2. Repression reality is not there
o Unconscious forgetting
o Common in anxiety disorders CRISIS AND CRISIS INTERVENTION
Crisis
3. Dissociation State of disequilibrium resulting from a stressful event or
o Form of repression a perceived threat where the individuals usual coping
o Forgets concepts about self & identity mechanisms become ineffective in dealing with it
o Forgetting personal details Highly individualized
4. Isolation Immediate problem
o Behavior: does not want to mingle
o Separation of the feeling from the thought of Types:
the event Developmental
5. Regression o Transitions in life/ maturational crisis
o Manifest behavior expected of an earlier o Expected - anticipatory guidance
stage of devt Situational
o Goes back to earlier stage o External events that are threatening w/c a
6. Fixation person finds difficult to handle
o Unable to outgrow behavior expected of an o External stressful events
earlier stage of devt o Events that suddenly happen
o Carries over o Loss of loved one/ separation
7. Identification Adventitious (Situational Crisis)
o Imitates a behavior of a significant person o Traumatic, extraordinary
o Integrates characteristics o Calamities, rape, violence
8. Introjection
o Imitates a behavior of a significant person Balancing Factors determines whether a person will go to crisis
o Incorporates characteristics or not
o Becomes the person the admire Individuals perception of the event
o Used by suicidal people Situational support
Internalized anger Coping mechanisms
9. Displacement
o Transfer of feeling to a less threatening object Event
10. Projection
o Throwing of/or attributing someone ones own Perception of
characteristics what one cannot accept as Event
his
o Blaming
o Used by suspicious people Not a stressor Stressor
Delusion of persecution
11. Undoing
o Repairing or negating something Coping,
o Negating the guilt in compulsion Resources,
o Reverse enactment Support
12. Reaction formation
o Showing the exact opposite of ones wishes or
Effective, Ineffective,
desires Adequate Inadequate
13. Compensation
o Exaggerating a trait to cover for ones
inadequacy
14. Conversion Crisis
o Expressing ones feelings/ conflicts through the
body
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Characteristics of Crisis State o What does the situation mean
Highly individualized 3. Assist the client in managing feelings
Self-limiting 4 to 6 wks o Helpless, powerless
o Short-term management 4. Explore with the client the resources available
o stressor crisis o Assess what coping mechanisms were already
o End varies used
5. Assist the client in action planning
Rarely affects the individual without also affecting the
significant others Techniques of Crisis Intervention
The person is amenable to suggestions problem Abreaction discuss feelings
solving Clarification
Has a growth potential: return to pre-crisis state, to a Suggestion
more distressing situation, or to develop a higher level Manipulation
of functioning Reinforcement of behavior
Support of defenses
Raising self-esteem
Stress
Exploration of solution
RAPE AND SEXUAL ASSAULT
Equilibrium Rape
A sexual act with penile penetration or a penetration
with a blunt object
Ineffective coping W/o consent - 18 y/o, mentally challenged
mechanisms Against the will
Not because of sexual gratification but because of
feeling of inadequacy
Disequilibrium
Sexual Assault
Any other form of forced sexual contact
CRISIS Does not qualify as rape)
If child consents, it is still considered as rape - minor
If with impaired judgment, it is rape
Stressor Crisis
Truths about Rape
It is an act of violence
o Anger rape
Attempt at
reorganization o Destructive way of expressing anger
It is an act of dominance and power
o Power rape/ sadistic rape
Trial & Error There are more females who are raped than males
(Crisis Intervention) There are more acquaintance rape done
o Date rape
o Familiar but not personally connected
o Liquid ecstasy
Effective coping Ineffective coping
Stages of Recovery from Trauma:
Acute Phase (Disorganization)
Resolution Mentally ill o Rape trauma symptoms
o Client may be brought to the hospital
o Injuries/ documentation of rape for legal
charges
Return to state
before crisis Outward Adjustment (Recoil)
o 2 weeks after
NURSE ADOPTS A COUNSELLING ROLE o Composed state, no longer crying, calm on
o Active and directive the outside but in distress inside
o No advice o Should not be interpreted as not needing
Any victim of abuse is on a crisis state emotional support
Patient must have a correct perception of situation o May believe that she does not need support
o Shock, disbelief, denial, silent reaction
Steps in Crisis Intervention: o Trying to be in control
1. Assess the situation ask person to help in identifying o Must undergo debriefing
problem Resolution (Reorganization)
o Physical implication o May sustain reaction or period of growth
o Suicidal tendencies o May cause sexual dysfunctions
o Physical integrity o Successful or unsuccessful
2. Assist the client to develop cognitive awareness of the Rape Trauma Syndrome
event o Sustained maladaptive response to rape
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Referred for proper management Sexual Abuse
o Sexual act w/ child
Rights of a Rape Victim o Playing w/ childs genitalia
Right to gentle treatment o Not in menarche but underwear has blood
Right for informed consent examinations stains, genital pain, dysuria, genital discharge,
Right to refuse a lot of knowledge about sex
Right to confidentiality
Right to privacy Roles of the Nurse
o All legal evidences must be kept intact Primary consideration is the protection of the child.
wash, douche, change clothes, Report any suspected case of child abuse.
bathe
Clothes, underwear 1. The physical needs of the injured/ neglected child must
Proper documentation be met before attempts are made to alter the family
Right to progress according to readiness pattern of functioning
Right for legal assistance 2. Manage the psychological effects of abuse PLAY
THERAPY for children who lack language facility to
Psychotherapeutic Management of Victims of Rape express self
Needs continual empathy, support, and opportunity to o Family dolls, puppets
process the event and intense feelings o Drawing
Keep evidences 3. Manage the abuser/ abusive family
o Avoid cleansing herself o Develop awareness of abusive behavior
Emphasize that it is not her doing o Learn effective way of coping
o Help overcome feeling of guilt
Provide nursing care supportively at the individuals SPOUSE/ PARTNER ABUSE - self-esteem, inadequacy
pace Characteristic Battered Wife Response to Abuse:
Stabilize physical aspect first Believes abuser will reform
Consider the rights of the rape victim Fears leaving due to threat from abuser
Learned helplessness
CHILD ABUSE Isolates self from other relationships
Maltreatment of a child which ranges from violent Feels inadequate, accepts self blame
physical attacks to passive neglect Both are dependent to each other
Maltreatment may be physical or emotional o Husband inadequate
Dynamics underlying child abuse: o Wife believes she deserves it
o Individual factors way of coping
o Societal factors powerless and subordinates, Only way to stop this is to leave the partner; empower the
females woman through crisis intervention, give card of crisis center
o Familial factors multigenerational problem to call for help
(established using genogram) Ensure safe place for victim and children
Abused, abuser and crisis
Cycle of Abuse
Assessment: Tension minor injurious acts, call for help
Physical and Behavioral Indicators Serious battery stage husband relieved
RA 7610 Anti-Child Abuse Law - report suspected Honeymoon stage husband promises not to hurt wife
cases of child abuse anymore
Physical Abuse (Battered Child) - Commission
o Injuries - welts, multicolored bruises (diff stages Serious
Tension
of healing repeated abuse), bald area on build up
battery
head, burns (cigarette burns hidden areas), stage
fractures, dislocations
o Behavior: doesnt want to go home, fear of
abuser
Abuser gives explanations not Honeymoon
consistent w/ childs injuries stage
Aggressive, withdrawn, apathetic,
scared of parent, prefers to overstay The best time to call for help is when it is just starting
in school Must have action plan when abuse starts
Physical Neglect Omission (needs are not provided) o Ask direct question
o Malnourished may engage in child labor Interview done in the comfort room
Begs for food The abuser must also be treated
o No adequate clothing unkempt/ dirty
o No adequate medical attention Nursing Diagnosis Physical first before psychological
o No place to stay - may be street children Impaired tissue integrity
o Assumes adult responsibility Pain
Emotional Abuse Risk for injury
o Berated, humiliated Altered nutrition
o Delays in physical devt, failure to thrive Sleep pattern disturbance
o Anxiety through thumb sucking, nail biting, Fear
enuresis Self-esteem disturbance
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Risk for violence o Heightened sexuality and increases feeling of
Ineffective individual/ family coping closeness and empathy, club drug
Symptomatic management
SUBSTANCE USE DISORDER May be diagnosed w/ urine test w/in 1 to 2 days to trace
Socially maladaptive behavior characterized by abuse substances
of substance or the regular use of such substance Urine should not be diluted
impairs the functioning of individual
CNS Depressants
Substance Abuse vs. Substance dependence Alcohol
Physical dependence vs. Psychological dependence o Most commonly abused substance
Substance intoxication vs. Substance withdrawal o Oldest anti-anxiety
Sedative/ Hypnotics
Definitions: o Valium same effect as alcohol
Substance Abuse o Dangerous to mix alcohol and sedative
o Using a drug in a way that is inconsistent with o If taken therapeutically, no alcohol
medical and social norms and despite
negative consequences Narcotics - Opioids
Substance Dependence more serious problem o Papaver somniferum derivatives of opiates
o Tolerance takes higher dose of substance to o Opium, heroine, codeine (cough syrup),
bring about the same effect morphine (Demerol)
o Withdrawal symptoms substance-specific o Can only bought w/ prescription
manifestations that occur upon reduction/ o Euphoria, sleepy, VS, RR
cessation of substance o Heroin - most common
Intoxication occurs when Tell-tale Sign: Pinpoint pupil non-
substance is within the body - effects reactive to light
on CNS Severe CNS depression Narcan
o Unsuccessful attempts to give up the (Naloxone)
substance Can be passed through the
o More time to get, more time to take the placenta shrill cry of neonates
substance Taken via IV push or main line w/
Physical Dependence with withdrawal symptoms needle marks
Psychological Dependence Risk for blood-borne infections
o Takes the substance to avoid undesirable o Effects of Heroin:
effects of withdrawal Euphoria w/ sleepiness
o Stimulants physical and psychological o Relieve physical and
o Depressants - physical emotional pain
Morphine
CNS Stimulants o Potent respiratory
Amphetamines depressant
o Methamphetamine HCl Shabu o RR < 12 overdose
o Dextrin, Ritalin, Benzedrine o Antidote: Narcan narcotic
Ritalin - ADHD agonist
Pupils constriction
o Brings about euphoria exaggerated form of VS
well-being o Withdrawal from Heroine
o Pupils dilate Early can be likened to beginning
o Cannot sleep, no appetite respiratory infection
o Does not get tired o Runny nose
o Dependent: remain energetic, wants to be o Teary eyes
slim o Sneezing
o Abdominal cramps
Cocaine o Muscle cramps
o Not used for therapeutic use Inhalants
o Almost the same effect as amphetamines o Gasoline, glue, solvents, thinner, nail polish
More potent that amphetamines remover, spray paint, rugby (used by street
o Euphoria, VS, bronchodilation, energetic boys)
o Taken through snorting or sniffing o Headache, LOC, dizziness, lack of
coordination, mirthfulness, mouth ulcers,
Ecstasy slurred speech, unsteady gait, tremors, muscle
o Rush then crash if next dose is not taken weakness, blurred vision, GI upset, nausea
o Takes next dose even if the first one does not and vomiting
lose its effect yet o Rugby - hunger
If they fail, they feel painful o DEATH severe CNS depression
depression - Crash
o Fatigability, painful depression w/c may cause Must only take for 2 weeks to avoid addiction
them to commit suicide
o Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA) Hallucinogens
o Snorting, sniffing red nose w/ lesion Mind altering drugs/ psychomimetics
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Distortion in time and space Breath analyzer level
Colorful surroundings: psychedelic
Synethesia blending of senses, see odor, frightening BAL BEHAVIORS
hallucination (bad trip) 0.05 % Loss of inhibition
Effect of substance can last Up to 0.1 % Anxiety relief, euphoria, loud speech
0.10 to 0.15 Slurred speech, motor incoordination,
Mescaline % moodiness (LEGAL INTOXICATION)
0.2 0.3 % Irritability, black out (memory impairment/
Cannabinols does not remember what happened),
o Least potent tremor, ataxia, stupor
o Marijuana, hemp grass 0.3 % and Unconsciousness
o Dried leaves and dried into rolls tyonke, up
dyutsa euphoria/floating, tachycardia, dry
mouth, increase in appetite, hallucinations, Alcohol Metabolism 10 mL in 90 mins
RED EYES or conjunctival irritation, loss of Complications of Alcohol Use
motivation, change in decision GI stomach absorbs alcohol does not need to
making/judgement, may lead to sterility due reach intestines
to testosterone. o Malnutrition early satiety
o Dagta of cannabis hashish; increase in o Inflammation esophagitis
appetite with preference for sweets hash CNS due to deficiency in Vitamin B
brownies/ space cakes/ space brownies o Neuritis tingling sensation
o Wernickes - Korsakoffs syndrome
PCP Phencyclidine/ Ketamine Reproductive System
o Veterinary anesthesia o Impotence - Testosterone
o Heightened sexuality and closeness CV
o Distortion in memory, dissociation, near death o Cardiomyopathy, CHF
experience Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
o K-hole experience do not remember
anything that happened Nursing Diagnosis r/t Chemical Dependence
Ineffective denial
LSD Ineffective individual coping
o Bloodshot eyes conjunctival irritation Altered family process
o Family can contribute to drinking behaviors
ALCOHOLISM o Enabling behavior kunsintidor
Commonly abused substance o Codependency behaviors of relatives of
Etiology: alcoholics; adjust to the alcoholic
o Biologic genetics Anxiety before and during withdrawal
Altered sensory perception
o Psychodynamic o Hallucination withdrawal
Lack of adaptive coping Altered thought processes
o Denial Impaired verbal communication slurring
o Projection Sleep pattern disturbance
o Rationalization Altered nutrition
Fixated in oral stage o Vitamin B supplement
o Inconsistency, poor role Self-esteem disturbance
modeling, lack of nurturing, Alteration in social interaction
lack of adaptive coping Risk for violence
Id strong
Ego weak (alcohol as coping) PSYCHODYNAMICS OF SUBSTANCE DEPENDENCE
o Personality Profile weak ego, dependent, Unresolved Needs of Early Attachments
manipulative Id Ego
Strong oral Uses denial (should be
o Behavioral
tendencies confronted), rationalization
Learned behavior
Demanding/ (do not allow to explain
manipulative inappropriate behavior) and
o Social - Peer pressure
projection (blaming others
Group therapy mgt is better in
for behavior)
groups
* Learn to delay Accept the person, not the
o Give up a drinking friend
gratification behavior tough love
o Relapse go back to
Uses escape behavior
alcohol-drinking friends
provided by alcohol
Inferior feeling
In psych, do not manage diagnosis, manage behavior
Set limits, no bargaining, maintain consistency
Patient must know that there is a connection between
Blood Alcohol Concentrations/ Levels (BAC/ BAL) to Behavioral
anxiety and maladaptive behavior
Manifestations of Intoxication
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Management of Alcoholism o Antianxiety meds
Short-term Detoxification Seizure
o Process of safely withdrawing from the o Anticonvulsants
substance o Dilantin
o Best done in a controlled environment - o MgSO4 enhance absorption of Vit D
Institution AntiHTN
o Search things and confiscate anything that Bloodshot eyes no management
has alcohol
o Disulfiram Therapy Long term - Rehabilitation foundation is abstinence
Remain sober
Long-term
o Rehabilitation Goals:
o Foundation is abstinence To give up alcohol
o Disulfiram or Antabuse Therapy
Detoxification If drank alcohol Disulfiram
Assessment reaction: HA, n/v, hypoBP, DOB,
Withdrawal Symptoms retching
o Earliest: Tremors o Meds are for safe withdrawal and to prevent
relapse
Stage 1 6 to 8 hours after last drink
o Tremors, headache, n/v, anxiety, sweating Live a positive lifestyle; use other coping strategies
Stage 2 8 to 12 hours o Things you do everyday in life
o Stage 1 + anorexia and insomnia o Group therapy Alcoholics anonymous group
o May start hallucinations o Group - collection of people working together
Intensifying anxiety = perception working towards a common goal
NOT managed with antipsychotics o 8-10 persons
Given anxiolytics o Brings interpersonal learning; more input and
Side effect: seizure threshold feedback
more prone to seizure o Instilling of hope and universality
o Perception: o Altruism feeling of helping others
o Cohesiveness and unity is important; must give
up denial
Metabolism of alcohol lasts for 1.5 hours and gives off
acetaldehyde acetaldehyde dehydrogenase gives off
acetic acid
Therapeutic Goal: Abstinence from the substance
Stage 3 2 to 3 days later Nursing Interventions:
o Stage 2 + seizure Providing for physical and nutritional needs
o Cannot be managed at home Confrontation
o Risk for aspiration Tough love accept person
Group work alcoholics anonymous; leader is a
Stage 4 2 to 5 days after delirium tremens reformed alcoholic
o CNS Depressants Education
Intoxication depressant
Withdrawal stimulant
o CNS Stimulant ANXIETY AND RELATED DISORDERS
Intoxication stimulant Anxiety a subjective feeling of apprehension, dread,
Withdrawal - Depressant or impending doom
o Delirium tremens excitability, agitated, Fear an objective threat
disoriented and confused, VS, seizures, red
eyes Characteristics of Anxiety
Most extreme withdrawal symptom Subjective feeling
Universally seen as unpleasant move people to do
Goal and Priority Management of Withdrawal Patients something
Ensure physiologic integrity and safety of patient Both a stressor and adaptation
o Quiet, non-stimulating environment A form of energy
Cluster care Occurs in degree
o VS q hour or 2 hours o Mild, moderate, severe, panic
o Safety put up side rails Manifestations:
Restraints (last resort) Mild (+1)
o Offer emotional support o No management, helpful anxiety
o Reorient patient Moderate (+2)
o Well-lighted room o Low pitched voice, less confidence, things are
Illusion misinterpretation of external stimuli getting out of control
Hallucination false perception o Selective inattention chooses non-anxiety
o Present reality provoking events
o Offer to stay
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Allow client to pace, encourage verbalization Repression
and identify stressor first, state observation, Isolation
assistance in problem solving Undoing - repetitive doing w/c
o No need for medications negates anxiety
Severe (+3) Reaction formation
o Fight or flight response, continuous and rapid
speech, feeling of dread, ineffective o Intervention:
reasoning and problem solving, disorientation, Allow the client to engage in the
limited perception compulsion but set time limits
o Use concise and brief statements Modification of schedule
o IM medications Instead of compulsion, distract with
repetitive relaxing activities
Panic (+4) o Music therapy
o Disorganized in all areas, harmful, hysterical, Must jive with the interest of
incoherent, suicide attempts, intelligible, personExpress feelings
overwhelmed, hallucinations (ANXIETY), Do not recognized maladaptive
palpitation, profuse sweating behavior since client already is
o Provide controlled environment aware but cannot control it
o Stay in a small room to prevent feeling o Do not say paulit ulit mo
overwhelmed naman ginagawa yan
o Parenteral anti-anxiety meds Thought stopping stop by using a
o Breath into brown bag repetitive activity
o Rubber band
Types of Anxiety-Related Disorders
Anxiety Disorders (Neurosis) 2. Phobic Disorder
GABA inhibitory neurotransmitter o Irrational fear of something outside the body
Etiology: o Defense Mechanisms:
o Interpersonal theory Displacement - transfer conflict to a
o Psychodynamic (Freud) anxiety is caused by situation outside
conflict of id and ego, or sexual/oedipal Repression
conflicts that is repressed Symbolization
o Hyperactivity of autonomic nervous system o Phobia may just be a symbol of conflict
Unacceptable feeling, Agoraphobia fear of open space
desire, or wish Claustrophobia fear of closed
spaces
Social phobia fear of being in a
Repression (unconscious situation where one can be
forgetting) embarrassed or be humiliated
o Avoidance to prevent experiencing distressing
Stimulus related to situation
unacceptable o May have phobia but does not have function
impairment
o Intervention:
Consciousness Safety priority concern
o Example: avoidance may
cause the client to jump off
Anxiety and unpleasant a building to avoid the
feeling phobia
Positive reinforcement (Behaviorist
approach)
Behaviors to negate Systematic desensitization
anxiety
Flooding implosive therapy
bombardment of stimulus
Disorder
3. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
o Continuous anxiety for 6 months
1. Obsessive Compulsive Disorder o Diffuse and free-floating (not attached to a
o Obsessions irrational repetitive thoughts that specific thing)
a person cannot control
o Compulsions irrational repetitive actions that 4. Panic Disorder
a person cannot control o Sudden onset
o Obsessions & compulsions control the person o Short duration (5 mins -1 hour)
o Anxiety causes repetitive thought which o Recurrent
translates into an uncontrollable behavior o High intensity
(compulsion negating anxiety, ineffective
coping) 5. Post-traumatic Stress Disorder
o Obsession is related to compulsion o Stress after a traumatic event
o Defense Mechanisms: o Maintains life of being a victim, controlled by
the event
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Disasters, calamities, violence, war hygiene, sugarless
o Should last 1 month gum/ sour candy
o Manifestations: Constipation -
Flashback (re-experiences the laxative
event) Urinary retention
Emotional numbness (avoidance) palpate bladder,
Cannot sleep or eat stimulate
Muscle tension, cannot concentrate, Blurring of vision
guilt feelings, irritability safety adequate
o Interventions: lighting
Establish trusting relationship Nausea give w/
Talk about the situation vividly until meals
person is able to tell the story without o Orthostatic Hypotension
feeling upset Check BP first
(lying then sitting)
Grounding Decrease of > 20
o Can you feel you hand? mmHg
o Can you feel your feet on Rise slowly from
the ground? bed
Dizziness, pallor,
Nursing Management: nausea, tachyPR
Minimize the clients anxiety and provide for the safety Adverse Effects:
of the client o Dependence
o Assess the level of anxiety Do not take
o Maintain a calm non-threatening environment longer than 2-3
o Reassure the client of his safety conveyed wks
through your physical presence Withdrawal should
o Administer tranquilizers as ordered be done
Initially, allow plenty of time for rituals, then gradually gradually
begin limit setting o Paradoxi
o Set time for compulsions & activity c
o Allow pt to do compulsions if attack occurs excitem
during activities ent
Encourage verbalization o Anti-depressants
Encourage client to talk about traumatic experience Anafranil (Clomipramine HCl)
under non-threatening condition (debriefing) Prozac (Fluoxetine HCl)
o Intense but progressive
Assist in developing more effective coping Psychotherapy
When level of anxiety has been reduced, explore w/ o Dream analysis
the client or teach client signs & symptoms of o Hypnosis
escalating anxiety & ways to interrupt its progression Milieu Therapy
(Stress mgt techniques) o Non-stimulating, calm environment
For the client w/ phobia, desensitize or involve the
client rather than allowing avoidance Behavior Modification
o Gradually expose client to feared object o Recognition of coping
Treatment Modalities Critical incident a situation or event that causes distressing,
Pharmacotherapy dramatic or profound change or disruption in physical or
o Anti-anxiety psychological functioning
Anxiety GABA anxiolytics
GABA Critical Incident Stress Debriefing (CISD) Protocol Key Points
1. Assess the impact of the critical incident on support
personnel and survivors
Examples: 2. Identify immediate issues surrounding problems
o Valium (Diazepam) involving safety & security
o Librium (Chlordiazepoxide) 3. Use defusing for the ventilation of thoughts, emotions,
o Midazolam (Dormicum) and experiences associated w/ the event
o Xanax (Alprazolam) 4. Predicts events and reactions to come in the aftermath
Side Effects: of the event so survivor can prepare and plan
o CNS Depressants 5. Conduct a systematic review of the critical incident.
CNS Look for maladaptive responses to the trauma
depressants & 6. Bring closure to the incident and ground to resources to
stimulants start rebuilding process
Do not allow 7. Re-entry (recovery) into the community/ workplace
activities requiring
alertness
o Cholinergic Effects
Dry mouth - OFI, DYNAMICS OF SOMATOFORM DISORDERS
adequate oral Not medically ill
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Primary gain Somatoform Disorder VS Malingering
o Direct advantage for being sick Malingering
o Decrease anxiety (within) o Planned
Secondary gain o FAKE, deliberate
o Other advantages from the environment o Conscious simulation of illness in order to get a
o Ex: attention from members, benefits deliberate gain
o DO NOT GRATIFY SECONDARY GAIN
Nursing Diagnosis
Assessment Altered role performance
Physical manifestations vary depending upon the type Disturbed body image
of somatoform disorder
Goals on Intervention
Somatization Disorder To make the client as functional as his condition will
Varied physical complaints allow to improve the quality of life
(-) in dx exams o Needs are being attended but do not
encourage dependence
Somatoform Pain Disorder o Do not out rightly do things for the patient
Pain is the only manifestation To relieve the symptoms
Do not push awareness of an insight into conflict/
Hypochondriasis problems
Morbid preoccupation To encourage expression of emotional feeling
Doctor shopping o Not physical complaints
o Neutral topics
Conversion Disorder To assist in learning more effective coping strategies
Alteration/ loss in motor and sensory function w/c Psychotherapy
symbolizes the conflict Anti-anxiety and anti-depressants
o Paralysis after fight with mother (motor) Other tx modalities
o Blindness after witnessing crime (sensory) o Stress management techniques
o Meditation and yoga
La belle indifference
o A beautiful indifference PSYCHOPHYSIOLOGIC DISORDERS
o Not concerned w/ loss of function Psychological Factors Affecting Medical Condition
o Physical manifestations absorbed by the body Given medical treatment but not transferred to a
o Absorb anxiety psychiatric unit
o Ex: witness of crime If underlying cause is not treated, physiologic
manifestations may be present
Body Dysmorphic Disorder
Body part is removed already Dissociative Disorders
Defect in body w/c results in cosmetic surgery Unconscious forgetting
Dissociative Amnesia forgets identity
Dissociative Fugue forgets identity, travels to another
Common Characteristics of the Physical Symptoms place and assumes new identity
Real (not fake) to the patient even if not supported by Dissociative Identity Disorder multiple personality;
diagnostic results shifts from one to another; not aware of the other
o Matter-of-fact attitude personalities; WEAK EGO since person is not unified;
o Do not disagree w/ the presence of high incidence in abused and one of the personalities is
manifestation the abuser
o Accept that manifestations are real even if Depersonalization Disorder dream-like state, trance-
diagnosis tests are (-) so that we do not like state; reintegrate the self; comorbidity in
become the source of anxiety schizophrenia
o Pay attention to the person but not on his o Establish what the client knows
body o Keep the patient safe
o Do not allow person to engage on his body o Psychoanalysis
pain (when in conversation)
Occur unconsciously (not DELIBERATE) PSYCHOTIC DISORDERS
o Blame or scold patient with symptoms Psychosis
No underlying structural or organic basis Inability to distinguish from reality and what exists in the
o Use of anti-anxiety meds only mind
o Analgesics pain; partial relief dependent
Anti-anxiety and antidepressant medications Schizophrenia
Placebo may be dependent Thought disorder
Stress reduction techniques Characterized by an disintegration from what the client
o Guided imagery thinks, feels or does
o Breathing exercises Used to be called split personality
o Progressive muscle spasm relaxation of Social withdrawal
specific group of muscles to help relieve Deterioration in function
tension
With 1 and 2 gain do not gratify Etiology
Biological
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Family history Heightened
o Dopamine disturbed information anxiety
processing ability of thinking violence
Excitatory neurotransmitter o Ensure safety of pt and
Structural other people
Psychodynamic Delusion of Reference
o Dysfunctional family relationships o False beliefs that
o Lack of loving and nurturing family conversations are about
o Inconsistency causes tension him
Mother is overprotective and over o Talk loud enough so that
loving while father is cold patient would hear what
o High expressed emotion type of family, low you are talking about
socioeconomic group Stress Vulnerability Delusion of Control
Theory o External force is controlling
him
Assessment Religious Delusion
Manifestations: Bleulers 4 As Somatic Delusion
o Affect o Body is changing in some
Apathy (flat affect), inappropriate way
External manifestation of an emotion o Decayed or removed
Evaluated in intensity Nihilistic Delusion
Incongruence o False belief that a body or
its part does not exist
o Ambivalence
anymore
o Associative looseness
Inability to connect ones thoughts Hallucinations - Distortion in thought process
Fragmented, illogical, incoherent o Alteration/ distortion in sensory perception
o Autism o Visual, auditory common in schizophrenia
Self-absorption o Gustatory, tactile
Does not pay attention to other
stimulus Disorganized Speech
o * Auditory hallucinations o Neologism coining of new words; meaning is
False sensory perception subjective
Talks by himself o Clang Association rhyming words are put
Dangerous if command together
hallucinations Boom, broom, groom
o Word Salad jumbled words put together
DSM V Diagnostic Criteria o Perseveration persistent use of a single
At least 2 of the following, each present for a significant response to varied stimuli
period of time during a 1-month period o Verbigeration repeating words over and
Continuous signs for at least 6 months over before they hear it
o Echolalia repeating heard words
Positive Symptoms: Grossly Disorganized Behavior
Delusions false fixed belief o Rigid behavior
o Alteration in thought process o Very regressed behavior - unkempt
o Types of Delusions based on Content
Delusion of Grandeur Catatonic Behavior
o False belief that one is o Motor manifestations due to mental illness
exulted o Catatonic negativism
o Has a lot of inadequacies o Bizarre/ rigid posture
o Accept belief but do not o Refuse to talk mutism
reinforce o Immobile
o Present reality
o Enhance sense of Negative Symptoms:
importance Alogia poverty of speech
Delusion of Persecution Anhedonia inability to experience pleasure
o Believes that he will be Avolition no drive/ motivation; regression
killed/ harmed Anergia no energy
o Paranoid Asocial few friends, difficulty establishing relationship
o Insecure/ tensed person Inattention inability to sustain attention
o Encourage client to
verbalize feeling to diffuse Brief Psychotic Disorder 2 of the following but less than 1 month
tension
o Potential problem: Violence Shizophreniform 2 of the following more than 1 month but less
o Observe for clients than 6 months
behavior
Types of Schizophrenia
Paranoid Schizophrenia
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Delusions and hallucination Talk to client in case client will open
o Even without paranoia first
Disorganized Schizophrenia Avoid touching paranoid patients
o Disorganized speech and behavior Gradual integration to a group
o Grossly disorganized or catatonic Show that you are genuinely
o Most regressed concerned
Catatonic Schizophrenia Be honest and consistent
o Only motor manifestations present Use therapeutic communication
o Most acute o For concrete thinking
o Can have: Simple
Hyperactivity (stimulus from inside); Be specific
manic (stimulus outside) o For incoherence
Catatonic posturing Clarify
Waxy Flexibility assumes and I do not follow what you are
maintains a position that is imposed saying
by another person o For mutism
Stupor immobile, does not open Talk to client but do not expect to
mouth and eyes, looks unconscious respond
but is aware of surroundings Give client time to talk
Catatonic Negativism does Neutral topics, open-ended
opposite of what he is supposed to questions
do; do not use reverse psychology Therapeutic silence in between
Catatonic Rigidity assumes a stiff Do not reinforce delusions and hallucinations
posture o Do not argue about delusions
Undifferentiated Schizophrenia combination of o Do not reinforce hallucinations
symptoms, cannot be classified o If a patient is acting odd and the nurse
Residual Schizophrenia only negative symptoms suspects he or she is hallucinating, the patient
should be asked about it then present reality
Common Nursing Diagnosis o Help patients to identify the stressors that
Risk for violence self-directed might precipitate hallucinations or delusion
Potential/ risk for other directed violence o Focus on real people and real events
Altered thought process o If happened earlier, stress the connection
o No abstract thinking literal way of between stressor and anxiety
interpreting o Do not explore the false content, explore the
Altered sensory perception feeling
Personal identity disturbance Physiologic and self-care considerations
o Distinguish self from non-self o Circulation
Impaired verbal communication o Nutrition NO NGT attack
Social isolation o Hygiene
Self-care deficit: nutrition, grooming o Paranoid
Altered nutrition: less than body requirements r/t Sealed food packed containers
suspiciousness Same kind of food to other patients
Ineffective coping Do not taste the food
Let him observe preparation
Nursing Intervention Deal with socially inappropriate behavior
Promote safety of client and others
o Verbalization Pharmacologic Management/ Therapeutic Milieu
o Time-out Antipsychotics/ Neuroleptics/ Major Tranquilizers
NO isolation room Blocks dopamine receptors at the post-synaptic area
Least restrictive environment to decrease availability of dopamine
o Medications Delusions and hallucinations would decrease then
Haldol (Anti-psychotic) + Benadryl disappear
(Sedative) Mouth checking
o Restraints Not meant to cure alleviate symptoms
With doctors order Check for adherence
Last resort Maintenance meds:
Document step by step o Phenothiazines:
Firm but not tight Thorazine (Chlorpromazine)
Check circulation nail beds, PR Compazine (Prochlorperazine)
Check q 15 mins Mellaril (Thioridazine)
Remove restraints one at a time for Prolixin (Fluphenazine)
15 mins q 2 Modecate (Fluphenazine
Establish a therapeutic relationship Decanoate)
o Withdrawn patient o Long acting injection
Active friendliness once q3 wks
o Suspicious patient Nozinan (Levomepromazine)
Gain clients trust Stelazine (Trifluoperazine)
Passive friendliness Trilafon (Perphenazine)
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Butyrophenones Rehabilitation:
Haldol (Haloperidol) Compliance to tx
Serenace (Haloperidol) Independence in activities of daily living
o Atypical Antipsychotics Social skills
Risperdal (Risperidone) o Help client to mingle starting on one-on-one
Clozaril (Clozapine) Dealing with future hallucinations
o Blood dyscrasia - CBC o Keep patient busy
Zeldox (Ziprasidone) o Deep thought will become voice
Seroquel (Quetiapine Fumarate) o Thought stopping
Zyprexa (Olanzapine) o Teach to recognize hallucination
Abilify (Aripiprazole) o Ignore hallucinations
Develop more effective coping patterns
Hallucinations must decrease o Role playing test behavior
Side Effects: GRIEVING PROCESS
CNS depression Normal reaction to real or anticipated loss
Anticholinergic effects
Orthostatic effects Phases of the Grieving Process
GI upset with meals E Kbler-Ross 6 months
Photosensitivity long sleeves, sunblock, umbrella, o Denial
sunglasses, walk on shady parts o Anger
Endo changes gynecomastia, amenorrhea o Bargaining
Weight gain o Depression
Extrapyramidal Symptoms (EPS) o Acceptance
o Akathesia Engel
Fidgety, restlessness Shock and disbelief Awareness of the pain
Allow to pace Acceptance
o Akinesia
Weakness, muscle fatigue Duration: 6 months to 1 year or 2 years for older people
o Dystonia
Eyes roll up with a fixed stare Assessment: 3 Major Areas to Assess
(oculogyric crisis) Adequate perception regarding the loss
Tongue protrusion Adequate support while grieving for the loss
Opisthotonos Adequate coping behavior during the process
Torticollis neck torsion
o Pseudoparkinsonism Interventions:
Pill-rolling tremors Allow adaptive denial
Mask-like facies Explore the clients perception and meaning of the loss
Muscle rigidity Encourage to reach out for and accept support
Shuffling gait Encourage the client to examine coping patterns in the
past and present situation of loss
Anti-EPS Drugs Encourage patient to care for self
Akineton (Biperiden)
Artane (Trihexyphenidyl) MAJOR DEPRESSIVE DISORDER
Symmetrel (Amantadine) Pathologic grieving
Cogentin (Benztropine)
Benadryl (Diphenhydramine) anti-cholinergic effect Etiology:
Cognitive
Adverse Effects: o Pessimistic negative concept
Decrease in seizure threshold o Best managed with cognitive therapy
Tardive Dyskinesia Biologic
o Delayed o Genetic predisposition
o Noted in patients who take the meds for a o Norepinephrine, Serotonin
long time o MAO destroys neurotransmitters
o Vermicular movement of tongue Psychodynamic
Lip smacking o Unresolved conflict
Cheek puffing o Debilitating life experience distant past,
Blood dyscrasia spontaneous gum bleeding early life trauma
o CBC leukopenia, agranulocytosis o Reaction to life events
o Low grade fever
Mouth sores Highest risk for suicide
Sore throat o Low esteem
Neuromalignant syndrome (NMS) o Worthless
o Hyperthermia (39 to 41 C), bleeding, muscle o Problem with expressing sadness
stiffness, profuse sweating
o MOST FATAL - Depleted dopamine Major Depressive Disorder vs. Dysthymia (less intense
o Given dopamine agonist but more chronic 2 years)
o Stupor Coma DEATH
Exogenous vs. Endogenous Factors
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Exogenous - outside factors Provide for the clients safety
Psychotherapeutic approaches o Cues and Clues of Suicide
o Endogenous - inside factors Talks about it directly or indirectly
Biologic amenable to ask directly
antidepressants Gives away his valuables
Change in behavior more willing to
mingle w/ others
Loss Starvation
Possession of things that are
potentially harmful
Helplessness/ abandonment Suicidal note
o Age/ Gender
Adolescents, elderly
Hostility Females attempt
Males successful
o Marital Status
Guilty and worthlessness
Single
(low esteem) - SE
Widow
Widower
Internalized Hostility o Attempt to evade rescue
o Recent loss then another loss
o Previous attempt and plan increases the risk
Depression
o Suicide Lethality Assessment Criteria
Plan
Means
Introjection of hostility
o Lethality wrist, overdose
of pills, starvation
o Lethality jugular vein,
Self-mutilation (Suicide) strangulation, sedative +
alcohol, gun shot, jumping,
drowning, drinking poison,
Assessment: At least 5 of the criteria for a minimum of 2 weeks
MVA
Sadness
Do not make the means available
Loss of interest
Must be confined
Worthlessness/ excessive or inappropriate guilt
No suicide contract
Psychomotor disturbance
Confiscate potentially harmful
Diminished ability to concentrate or indecisiveness
objects
Somatic manifestations
o Close observation
o Appetite disturbance
Low lethality - q 15 mins
o Sleep disturbance does not deserve to sleep
High lethality constant, someone
Initial insomnia unable to sleep
should always be w/ patient
Remedial insomnia easily awakens
Irregular intervals
Terminal insomnia wakes up in wee
Room close to nurses station
hours of morning and unable to
Establish a therapeutic relationship with the client and
sleep
verbalize concerns
o Fatigue or loss of energy
o Accept patient
Recurrent thoughts of death
o Spend time w/ patient
o Respond to anger therapeutically
Atypical depression reverse of somatic manifestations
o Kind firmness
Encourage to perform something
Suicide is highest when depression starts to abate.
Engage in repetitive, monotonous,
non-gratifying activity to stimulate
Nursing Diagnosis Commonly Established for a Depressed Person
expression of anger
Altered nutrition more/ less than body requirements
Sleep pattern disturbance
Focus on the clients strength
Anxiety
o Should not remain alone
Ineffective individual coping
o Walk and pace w/ client
Hopelessness no solution
o Music therapy
Powerlessness no energy
o Gradual introduction to group therapy
Self-care deficit
o Recognize accomplishments
Low esteem
o Avoid embarrassing experiences for client
Social isolation
Altered role performance
Create a scheduled and structured but non-
Constipation
demanding envt
Risk/ potential for violence directed to self suicidal
Promote independence by encouraging pt to perform
ADLs
o Small frequent feeding
Interventions
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Pharmacotherapy - Antidepressants o Examples:
Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) Effexor (Venlafaxine HCl)
o Oldest Remeron (Mirtazapine)
o Blocks reuptake of NE and S Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)
o 2 to 3 wks before effect
ELECTROCONVULSIVE THERAPY
o Examples: Somatic therapy due to neurochemical and
Tofranil (Imipramine) neurophysiologic effects
Elavil (Amitriptyline) 70 to 150 volts
Norpramin (Desipramine HCl) all depressed
Aventyl (Nortriptyline)
Doxepin
Anafranil (Clomipramine HCl) Indications:
Surmontil (Trimipramine) Severely depressed not responding to use of
o Side Effects: antidepressants
Anticholinergic same as Acutely suicidal and cannot wait for 2-4 wks
antipsychotics Mental illness like schizophrenia and mania w/c does
CNS depression not respond to meds
EPS
Reuptake Contraindications:
o Going back of neurotransmitters to With pacemaker
presynaptic cell Organic mental disorder tumor, aneurysm - EEG
o Trapped in the synapse Cardiac conditions HTN - ECG
Active bleeding tendencies CBC blood dyscrasias
Respiratory conditions
Fracture
Pregnancy
Nursing Responsibilities:
Consent responsible family member
NPO: 6 to 8 hrs
Shampoo: okay but should be dried well
NO shaving
Remove dentures
Wear loose clothing hospital gown
Check VS baseline
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) o ECT - BP
o May have food-drug interactions Void before procedure
o Avoid Tyramine-rich foods (vasopressor)
HTN crisis Types:
MAO is needed to metabolize Modified - with pre-meds
tyramine o IV Pentothal (Thiopental Na) short-acting
Fresh low in tyramine except sedative
banana, avocado, chicken, meat o Atropine sulfate dry secretions, prevent
liver, fish bradyPR
Processed, brewed or preserved o Anectine (Succinylcholine) muscle relaxant,
foods become tyramine rich aged can cause respitory arrest
cheese, mozzarella, sardines, dried Unmodified no pre-meds
and smoked fish, bagoong, coffee,
wine, chocolate Doctor: applies electrodes to patient
Raisins (fresh grapes - tyramine
rich) Tonic-Clonic Seizure
Cream cheese - tyramine rich Remove electrodes
Effective: Seizure for 30 to 60 secs
o Examples: After seizure:
Parnate (Tranylcypromine) o Turn to sides
Nardil (Phenelzine) o Suction if needed
Marplan (Isocarboxazid) o Check VS
Respiratory arrest Anectine
Specific Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Deep sleep for a while
o Lesser side effects Wake up: Disoriented reorient client
o Watch out for tachycardia, hypomanic May eat as long as gag reflex has returned
episode
o Examples:
Prozac (Fluoxetine)
Zoloft (Sertraline HCl)
Paxil (Paroxetine HCl)
Luvox (Fluvoxamine)
Atypical Antidepressants BIPOLAR MOOD DISORDER
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Etiology: o Do not stay at elevated space - eye to eye
o Biologic level
Genetic o Eye contact but do not stare
NE, S o Escalating phase set limits
Intracellular Na Restraints are applied firmly but not too tightly
o Psychodynamics o Tied on the side of the bed not on side rails
Mania is a defense against o Change client position accordingly
depression Place client in a room that is away from the nurses
Denies underlying depression station
Formation reaction o Single room
Constant struggle between id and o Simple and pastel in color
superego Ensure that nutritional and fluid balance needs are met
Mania externalized hostility o OFI offer every hour or two
Depression internalized hostility o Calories protein finger foods
Mania Id Use short, simple sentences to communicate
Depression Superego Set limits and be consistent matter-of-fact attitude
Confront the behavior, not the patient
Channel excessive energy into socially acceptable
motor activities
o Clean, sweep the floor, distribute linens
Provide solitary activity but something that would not
require concentration
Pharmacotherapy
Anticonvulsants
o Tegretol (Carbamazepine) blood dyscrasia
Assessment: o Epival (Divalproex Na) Valproic Acid
Elevated, expansive mood of at least 1 week and any 3 o Depakote (Divalproex Na)
of the following:
o Pleasurable activities Antimanic - NE and S
Loud colors, activities o Lithium Carbonate oral only
Heavy make-up Blocks release and fastens reuptake
o Increase in goal-directed activities of NE and S
o Psychomotor disturbance Fastens excretion of Na
o Delusion of grandeur manic = low esteem Transposition of IC Na
o Pressure of speech/ loquacious speech o Where lithium is, Na will go
Pressure of speech o Lithium will find NA and
o Fast, rapid spitfire removes Na intracellularly
o Cannot understand o Na EC/ IT/ IV
Loquacious speech o Secreted in the
o Very productive speech renal tubules
o Distractibility Thin line between therapeutic and
o Flight of ideas/ racing thoughts toxic level
o Somatic manifestations Toxic to renal tubules MD orders
o Sarcastic, manipulative, demanding BUN and Crea before lithium is given
Hides weakness the through Therapeutic Serum Level: 0.6 to 1.2
weakness of others mEq/ L
o Up to 1.5 mEq/ L
Nursing Diagnosis Commonly Identified Safeguard Level
Risk for violence safety first o > 1.5 mEq/L TOXICITY
Risk for injury safety first Serum lithium exam: Blood test
Altered nutrition: less than body requirement Does not cure stabilizes the mood
Ineffective individual coping Continue even if not hyper/ manic
Self-care deficit anymore
Self-esteem disturbance
Impaired social interaction
Ineffective role performance Side Effects of Lithium Adverse Effect of Lithium
Fine tremors Gross tremors
Interventions: Polyuria Oliguria
Provide for clients physical safety and safety of those Polydipsia (3L fluids/ day) Vomiting (earliest
around him/her (PRIORITY than physiologic) Nausea manifestation of toxicity)/
o Environmental stimuli Hyper Metallic taste diarrhea
o Provide quiet, non-stimulating environment Motor incoordination
o Low pitched voice, non-confrontational, arms Confusion
on side, palms out Ataxia
o Do not cross arms
o Do not place hands at the back or inside the
pocket
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o The other 3As apraxia, agnosia, aphasia
NO antidote for lithium - dialysis Expressive aphasia
o Stopped if toxicity occurs Perceptive aphasia
o Diuretic excrete Global aphasia
o Na facilitate excretion o Needs assistance and supervision with ADLs
Diuretics are contraindicated while o Direct the client step-by-step
taking lithium polyuria o Approach in full view
Diet: regular Na diet o Use vivid colors
o Na reabsorption of Na and lithium - o Reorient every interaction you have
toxicity o Environment same, consistent
If lithium reaches 3 mEq/ L HD to remove lithium o Sleep-wake cycle disturbance
Insomnia known cause first
COGNITIVE DISORDERS Environmental modifications
Used to be called Organic Mental Disorders
Disorders that affect consciousness, memory, Severe (5 to 10 years)
orientation, attention, perception and language o Personality with emotional changes
disturbance o Deterioration in all areas of function
o Requires 24 supervision, close supervision or
Delirium: Acute confusional state both
Causes: o Irritable and combative
o Physical illness Give time
CHF, uremia, pneumonia, metabolic Distract when angry
d/os, CVA, DHN, infx, etc
o Prescription Drugs: Nursing Diagnosis
Polypharmacy w/ drugs and Risk for injury
anticholinergic effects Altered thought process (memory, confusion,
Dementia: Progressive cognitive deterioration deterioration)
Causes: Impaired communication
o Reversible conditions like: Impaired socialization
Encephalopathy Altered role performance
Infxs like syphilis Self-care deficit
Toxic conditions due to substances Sleep pattern disturbance
like alcohol, metal Low esteem
Caregiver role strain
Dementia of the Alzheimers Type
Etiology: Unknown but with various theories like Interventions:
o Genetics Goal: Promote optimum function and have patience
o Toxin o Promote clients safety and protection from
o Infection injury
o Cholinergic deficit acetylcholine Non-slippery floor
May use cholinesterase blockers Test temperature
o Structural o Structure environment and routine
Neurofibrillary tangles Rearrange room
Neuritis/ senile block Client does not want change
Acetylcholinesterase Consistent, highly structured
Downhill trend o Promote adequate sleep, proper nutrition,
hygiene and activity
Stages: Time away if insists, leave for a
Mild (2 to 3 yrs) while and return after 15 mins
o Forgetfulness is the hallmark Can do what he can do/ able to do
o 4 As Warm milk, warm bath, quiet
Amnesia short term/ recent first environment
o Promote interaction & involvement
Aphasia loss of expressive ability
Reminiscing activities
Apraxia loss of purposeful bodily o Early stage
movt Gardening
Agnosia loss of ability to recognize Interactive activities
o Word and name-finding difficulties o Provide emotional support, acceptance,
o Problem in decision making, judgment and increase worth by letting them perform what
reasoning they know
o Repetitive questioning Allow verbalization of feelings
o Difficulty performing usual activities o Do not come from the side, approach from
o Not too deteriorated yet the front
o Goal: ensure optimum activities, place wall o Reorient patient
clock and calendar inside room o Family/ caregiver support
Moderate (3 to 4 years)
o Confusion and disorientation
o Wandering and sleep disturbance
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Increase self- esteem
EATING DISORDERS Identify good points
Anorexia Nervosa Give recognition when she gains
Does not eat weight
Self-imposed starvation o Assist in expression of feelings
Journaling
Etiology:
Biologic factors: Other Treatment Modalities
o Genetic predisposition Behavior modification
o Dysfunction of the hypothalamus Pharmacotherapy w/ antidepressant
o Serotonin o Elavil (Amitriptyline), Prozac (Fluoxetine HCl)
Developmental factors: Family therapy
o Overprotective/ domineering enmeshed Psychotherapy should have ff-up
family o Discharge if patient has gained almost 90% of
Control and helplessness IBW
o Disturbed body image
o Conflicts about growing up doesnt like to Bulimia Nervosa
be a grown up Characterized by binge eating
o Sees herself as fat o Taking in a lot of food over a short period of
o Preoccupied with losing weight and is afraid time
of gaining weight
Social factor: Assessment:
o Thin is in Recurrent episodes of binge-eating
A feeling of lack of control over eating behaviors
Assessment: Inappropriate compensatory behavior to lose weight
Refusal to maintain body wt at or above minimum (the use of ipecac syrup to induce vomiting)
normal weight Self-evaluation overly influenced by body shape and
Must lose 15 to 25% below normal weight weight
Intense fear of gaining wt Love-hate relationship
VS Normal/ a little above/ below the normal weight
Absence of at least 3 consecutive menstrual cycles
Lanugo endo changes Focus on feelings not on behaviors
Hypoglycemia, fluid and electrolyte imbalance
Compulsive people, good girl in the family, achievers Nursing Interventions:
Set limit to binge-eaters adhere to meal schedule
Management: Assist in identifying feelings associated with binge/
Goal: Gradual steady weight gain of 1-2 lbs/wk purge and facilitate expression of feelings/ alternative
ways
3 Major Objectives: Improve self-esteem
o To re-establish appropriate eating behavior
Re-feeding Program Other tx modalities:
o Desired weight gain 1 to 2 Use of antidepressants
lbs/ wk Cognitive behavior therapy
o 500 1000 kcal/day in
divided amount PERSONALITY DISORDERS
o Small, frequent feeding Personality - Subtotal of physical and mental
o Monitoring the clients characteristics of a person
weight before breakfast Developmental disorder disorder developed before
after voiding, same clothes 18 y/o
and weighing scale Rigid/ inflexible traits impaired function
Behavior Modifications Contract A lifelong pattern, fixated in a certain stage
o For active participation of They are not aware that something is wrong with them
patient, set limits and poor insight
conditions They get admitted in the ward because of other
o Agree that all food will be conditions
eaten for a specified time
o Include patient in tx Excessive/ Rigid/ Inflexible impairs function/ lifestyle
planning, do not force like
parents Cluster A Odd and Eccentric
o Expected wt gain Paranoid
o Encourage participation o Does not rely on other people
Sit w/ client during meals o Questions loyalty of associates
o Observe how much was o Suspicious
eaten and remind contract Schizoid
o Stay in public place o Very shy, timid
o Stay for at least 1 hour after o Few set of friends
DO NOT GIVE LAXATIVE. May disturb o Prefers to be alone
the already disturbed GI, verify with Schizotypal
doctor, give stool softener o Shy and timid
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
o Wants to be alone o If talks echolalia
o W/ magical thoughts believes in superstition o Does not establish eye contact
Disturbed personal identity
o Uses third person
Cluster B Dramatic/ Emotional/ Erratic Engages in repetitive activities
Weak superego Head banging, sometimes ignores nutrition
Limits o Self-absorbed
Antisocial Characteristics of a Nurse:
o Weak superego (conscience) Accepting
o Violate norms and rights of person Reality-based
o Bad record Safe
o Does not feel guilty Consistent
o Manipulative
o Acts out feelings Interventions:
Borderline Goal: Optimize function
o Females
o Dependent child Good Accepting
Independent adult Bad o Eye contact
o Categorized either good or bad only o Spend time with child
o Splitting defense mechanism Reality-based
o Difficult to establish relationship o Impaired personal identity
o Tendency for self-harm o Reinforcing identity
o Impulsive Safe
o Strong need for dependence o Self-harm
o Fears abandonment gives all o Pad side of bed
o Clings to people o Helmet
Histrionic Consistent
o Hysterical, dramatic, seductive o Same environment
o Describes things in a beautiful way
o Likes to be the center of attention Antipsychotic Drugs - Haldol
o Female
Narcissistic Care of a Child with Attention Deficit (Hyperactivity) Disorder
o Exaggerated sense of self (ADHD)
o Wants to be praised/ admired by people Genetic
Biochemical too much stimulant
Cluster C - Anxious/ Fearful Min brain d/o
Does not want rejection Psychosocial factors
Does not want to be criticized o Stress/ disequilibrium in the family
Avoidant Get attention of child before giving instructions
o Likes to have a relationship but scared of Child knows that the other children does not like him
rejection because of his hyperactivity
Dependent o self-esteem
o Depends on other people for decisions
o Low self-esteem Manifestations:
Obsessive-Compulsive Impulsivity AD
o Rigid personality Inattention/ distractibility AD
o Clean, meticulous, organized, willing to work Hyperactivity ADHD
hard
Management:
No specific drug but symptomatic tx Set Limits
o Does not benefit in a lenient upbringing
SELECTED CHILDHOOD DISORDERS o Should not be scolded and point out what is
Autistic Disorder socially unacceptable
Self-absorbed o Quiet, non-stimulating environment
Does not pay attention to others o Classroom front
Enhance self-worth
Etiology: o Behave award
o Genetic o Give recognition to good points
o Biochemical - PKU Short term activities
Remove the child from the upsetting situation (time out)
Impairments of a Child w/ Autism Set time frame
Impairment in social interaction
o Prefer to be with inanimate objects
o Things that spin Drugs: Stimulants
o Security object Improve attention span
Impairment in verbal communication Enhance concentration
o Does not know how to communicate w/ Ritalin (Methylphenidate HCl) paradoxic effect, help
others client focus
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
Mental and Psychiatric Health Nursing
Side Effects: Interventions:
o Insomnia give at daytime: AM til noon Goal: Optimize function
o Appetite give after meals Planning must not be on chronological age but on
o Tics - report developmental age
Teach from simple to complicated
MENTAL RETARDATION o Use visual aids
Developmental disorder of sub-average intellectual Be patient - repetition
capacity Do not be overprotective
Ave IQ: 90 110 o Protect from possible injury
Difficulty in ADLS Protect from teasing of others/ help them become
Adaptive ability more acceptable to others
o Help them smell good
Etiology: o Teach social phrases
Pre-natal Support parents
o Chromosomal aberration 21 chromosomes Parents must not reject their child
o German measles 1st trimester SEPARATION ANXIETY DISORDER
o Malnourished mother Excessive anxiety when being separated from a parent
o PKU School phobia not because of school, but fear of
o Cardiac condition of mother resulting to separation
oxygenation Teach how to become independent
o FAS
o Maternal malnutrition SEXUAL DISORDERS
Perinatal
o Cerebral anoxia
o Traumatic delivery
Forcep/ vacuum
o Abruptio
o Multiple births
o Placenta previa
Postnatal
o Infection meninges/ brain
o Head injury
o Malnutrition
o Lead intoxication
o Poor parenting
Environmental stimulation
Developmental Age/ Mental Age
Highest capability that a child can reach regardless of
the chronological age
Classification:
Description Mental
Degree Range
Age
Profound < 20 IQ
Abilities of 3 y/o
20 40
Severe Contribute to self- 0-3
IQ
care
Self-care
Until grade 2 only
Trainable:
unskilled and
40 55
Moderate skilled work 3-8
IQ
May need
support even in
just minimal
stressor
Until grade 6
Educable:
Vocational
55 70
Mild
IQ
Professional 8 - 12
Cannot move
around
neighborhood
70 to 85
Borderline Slow learning
IQ
University of Santo Tomas College of Nursing / JSV
You might also like
- Psychiatric NursingDocument32 pagesPsychiatric NursingAJ Dalawampu100% (11)
- Psychiatric Nursing Notes PDFDocument12 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notes PDFClaire Lautner95% (60)
- Psychiatric NursingDocument21 pagesPsychiatric NursingFreeNursingNotes92% (38)
- Psychiatric Nursing Interventions and Client CareDocument20 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Interventions and Client Carechio0809100% (4)
- Psychiatric Nursing LectureDocument35 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Lectureɹǝʍdןnos95% (42)
- Mental health nursing techniques for psychiatric careDocument43 pagesMental health nursing techniques for psychiatric careHaru100% (1)
- Psychiatric Nursing Theories and Treatment ModalitiesDocument27 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Theories and Treatment Modalitiesjong52440% (1)
- Mental Health Nursing HandoutDocument27 pagesMental Health Nursing HandoutKim Ramos100% (26)
- Psychiatric Nursing NotesDocument13 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Notesapi-384275892% (26)
- Psychiatric Nursing ReviewDocument16 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Reviewɹǝʍdןnos97% (63)
- 50 Item Psychiatric Nursing Exam IDocument11 pages50 Item Psychiatric Nursing Exam Iɹǝʍdןnos98% (40)
- Medical Surgical NursingDocument59 pagesMedical Surgical NursingChey Dianne Seriña100% (11)
- Psychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Document21 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Bullets (Nle & Nclex)Richard Ines Valino100% (24)
- Psych Nursing Complete Edited Royal PentagonDocument32 pagesPsych Nursing Complete Edited Royal PentagonRichard Ines Valino100% (68)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Review NotesDocument75 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Review Notesstuffednurse92% (146)
- PSYCHIATRIC AND MENTAL HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideFrom EverandPSYCHIATRIC AND MENTAL HEALTH NURSE: Passbooks Study GuideNo ratings yet
- Psych Nursing KemberluDocument23 pagesPsych Nursing KemberluLanzen DragneelNo ratings yet
- Adpie and Therapeutic CommunicationDocument8 pagesAdpie and Therapeutic CommunicationKhrisha Anne DavilloNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric nursingDocument44 pagesPsychiatric nursingmmmartinez1583No ratings yet
- Psychiatric NursingDocument35 pagesPsychiatric NursingARAGON GEMMA LYNNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationDocument4 pagesNursing Care Plan: Nursing Diagnosis Goal Interventions (3) (Reference) Rationale (Reference) EvaluationJulvica HeuwNo ratings yet
- Standards of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing PracticeDocument4 pagesStandards of Psychiatric-Mental Health Nursing PracticeAnna Sofia ReyesNo ratings yet
- Doctor-Patient RelationshipDocument2 pagesDoctor-Patient RelationshipvictorazucenaNo ratings yet
- Good NotesDocument5 pagesGood NotesMikee BoomNo ratings yet
- Traumainformed Practice Working Complex PTSD HandoutDocument34 pagesTraumainformed Practice Working Complex PTSD Handoutcora4eva5699No ratings yet
- Revised. NCP. Jam 1Document3 pagesRevised. NCP. Jam 1ACOB, Jamil C.No ratings yet
- TFN Theorist Table Martin Andrea Bsn1y110Document12 pagesTFN Theorist Table Martin Andrea Bsn1y110Kyla Mae ZabalaNo ratings yet
- 1.病人安全的新流行語-復原力 (講義) 廖熏香Document42 pages1.病人安全的新流行語-復原力 (講義) 廖熏香Tao Chun LiuNo ratings yet
- Benners TheoryDocument2 pagesBenners TheoryjustkatirinNo ratings yet
- Ethics in Psychology Chap 1 ReviewerDocument2 pagesEthics in Psychology Chap 1 ReviewerJermaine Joie GamilNo ratings yet
- TeoriDocument1 pageTeoriMARLENE PERANGNo ratings yet
- Finals TOPDocument14 pagesFinals TOPMary Nhette AvilesNo ratings yet
- Amper 5th Presenter3of3 With Sir KikoDocument15 pagesAmper 5th Presenter3of3 With Sir KikoFrancisco TranceNo ratings yet
- Psychiatric Nursing Lecture 62 Pages Pg. 681 746Document64 pagesPsychiatric Nursing Lecture 62 Pages Pg. 681 746Kyle Valde100% (2)
- Nancy Falls - Embodied PresenceDocument11 pagesNancy Falls - Embodied Presencejohn_harvey_3No ratings yet
- P117 - Module 3Document8 pagesP117 - Module 3Mariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- P117 - Module 2 THE COUNSELORDocument5 pagesP117 - Module 2 THE COUNSELORMariella MarianoNo ratings yet
- Professional AdjustmentDocument12 pagesProfessional AdjustmentNikkie Salazar100% (1)
- 10 Neurodiversity Affirming Principles For TherapistsDocument1 page10 Neurodiversity Affirming Principles For TherapistsBelegan CrengutaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan Goal & Outcome Criteria Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Modificati On Interventi On RationaleDocument7 pagesNursing Care Plan Goal & Outcome Criteria Nursing Intervention Rationale Evaluation Modificati On Interventi On RationaleJan Dee ApuraNo ratings yet
- Observational Skills in Ot - Assessment CourseDocument12 pagesObservational Skills in Ot - Assessment Courseapi-496718295No ratings yet
- Filipino Nursing TheoristsDocument4 pagesFilipino Nursing TheoristsCristina AdolfoNo ratings yet
- Employee Counselling Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesEmployee Counselling Finals ReviewerDANIELLE ADVINCULANo ratings yet
- Clinical Psych Exam 2: Assessment Interview Reliability & ValidityDocument20 pagesClinical Psych Exam 2: Assessment Interview Reliability & ValiditySteffanyNo ratings yet
- Nursing Analysis of Schizophrenia ClientDocument4 pagesNursing Analysis of Schizophrenia ClientMari Ivy PradoNo ratings yet
- Registered Nurse Role at Madison Day SurgeryDocument4 pagesRegistered Nurse Role at Madison Day SurgeryZyrineNo ratings yet
- Professional Adjustment For NursingDocument13 pagesProfessional Adjustment For Nursingprokuno86% (35)
- Patricia BennerDocument22 pagesPatricia BennerMatt MasilonganNo ratings yet
- NCP Chronic ConfusionDocument4 pagesNCP Chronic ConfusionLyka DianaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Rehab MedDocument4 pagesIntroduction To Rehab MedMary PropertiesNo ratings yet
- NCM117 Theory Midterm Exam Reviewer PDFDocument31 pagesNCM117 Theory Midterm Exam Reviewer PDFJesil MaroliñaNo ratings yet
- Dele Concept Ouestionnalre Objechive ÎndivitualDocument10 pagesDele Concept Ouestionnalre Objechive ÎndivitualPriaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan For StrokeDocument5 pagesNursing Care Plan For Strokerusseldabon24No ratings yet
- FEU Psychiatric History and Mental Status ExaminationDocument12 pagesFEU Psychiatric History and Mental Status ExaminationRyan Loyd MarquezNo ratings yet
- Mental Dental - Patient ManagementDocument12 pagesMental Dental - Patient ManagementCristina CisnerosNo ratings yet
- Behaviour Response Flow Chart 5 Nov 2012Document1 pageBehaviour Response Flow Chart 5 Nov 2012jakilaNo ratings yet
- Unit03 Perception, Learning & Attitude in OrganizationsDocument34 pagesUnit03 Perception, Learning & Attitude in OrganizationsThanh LêNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument5 pagesNursing DiagnosisFionaNo ratings yet
- Personality Difficulties and Primary Care 14.10.20Document16 pagesPersonality Difficulties and Primary Care 14.10.20Owen ForsterNo ratings yet
- Final Ovarian Cancer Meigs Pathophysio PDFDocument3 pagesFinal Ovarian Cancer Meigs Pathophysio PDFCathy Santos100% (1)
- OsteomyelitisDocument4 pagesOsteomyelitisCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Distal Femur FractureDocument9 pagesDistal Femur FractureCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular NotesDocument18 pagesCardiovascular NotesCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Running Shoes: Rick BarrettDocument13 pagesRunning Shoes: Rick BarrettCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- OB PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesOB PathophysiologyCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Document1 pageNursing Care Plan (Ineffective Breathing Pattern)Michael Vincent DuroNo ratings yet
- GDM, ITP, UTI, IUFD PathophysiologyDocument2 pagesGDM, ITP, UTI, IUFD PathophysiologyCathy SantosNo ratings yet
- Ecological PyramidsDocument19 pagesEcological Pyramidsnandhinidish100% (1)
- L-Sit ProgressionsDocument2 pagesL-Sit ProgressionsMattNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Report on Chemist Behavior Towards Generic ProductsDocument30 pagesSummer Internship Report on Chemist Behavior Towards Generic ProductsBiswadeep PurkayasthaNo ratings yet
- Maturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) : Genetic and Clinical CharacteristicsDocument5 pagesMaturity-Onset Diabetes of The Young (MODY) : Genetic and Clinical CharacteristicsSarah AgustinNo ratings yet
- Soft Drinks in India: Euromonitor International February 2022Document27 pagesSoft Drinks in India: Euromonitor International February 2022Gayathri22394No ratings yet
- Diagram Alir Dan Deskripsi Proses: Tugas 4Document11 pagesDiagram Alir Dan Deskripsi Proses: Tugas 4FevitaNo ratings yet
- October 2022 Complete Month CA English - CompressedDocument117 pagesOctober 2022 Complete Month CA English - CompressedKing JNo ratings yet
- Wto Unit-2Document19 pagesWto Unit-2Anwar KhanNo ratings yet
- Radiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseDocument8 pagesRadiographic Cardiopulmonary Changes in Dogs With Heartworm DiseaseputriwilujengNo ratings yet
- MMI4804 Quiz 5Document16 pagesMMI4804 Quiz 5Ham Mad0% (1)
- PEMEDocument1 pagePEMERajesh MohananNo ratings yet
- Sip Annex 2a Child-Friendly School Survey-3Document9 pagesSip Annex 2a Child-Friendly School Survey-3aimee duranoNo ratings yet
- Culture Shock and Adaptation StrategiesDocument12 pagesCulture Shock and Adaptation StrategiesMuhammad UsmanNo ratings yet
- Pencak Silat Talent ScoutDocument9 pagesPencak Silat Talent ScoutWisnu Bayu MurtiNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Calendar For DogsDocument3 pagesPregnancy Calendar For DogsVina Esther FiguraNo ratings yet
- BenzophenoneDocument20 pagesBenzophenoneYuuki93No ratings yet
- Workplace EmergenciesDocument39 pagesWorkplace EmergenciesUpul Nishantha ThalpawilaNo ratings yet
- Dapagliflozin Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, WarningsDocument8 pagesDapagliflozin Uses, Dosage, Side Effects, WarningspatgarettNo ratings yet
- Earth Leakage Testing Report: Panel Name: Testing Device: Rccb (Iδn) : 30 MaDocument1 pageEarth Leakage Testing Report: Panel Name: Testing Device: Rccb (Iδn) : 30 MaAmjad AlbahtiNo ratings yet
- Leaving Disasters Behind: A Guide To Disaster Risk Reduction in EthiopiaDocument12 pagesLeaving Disasters Behind: A Guide To Disaster Risk Reduction in EthiopiaOxfamNo ratings yet
- BSHF-101 E.MDocument8 pagesBSHF-101 E.MRajni KumariNo ratings yet
- NHS Trust PolicyDocument52 pagesNHS Trust Policyver_at_workNo ratings yet
- BG Gluc2Document3 pagesBG Gluc2Nghi NguyenNo ratings yet
- FoundationDocument10 pagesFoundationBardoNo ratings yet
- ......... NCP CaseDocument34 pages......... NCP Casevipnikally80295% (19)
- Roberts Race Gender DystopiaDocument23 pagesRoberts Race Gender DystopiaBlythe TomNo ratings yet
- Syllabus ECDO 4225 - Professional Aspects of Nutrition and DieteticsDocument6 pagesSyllabus ECDO 4225 - Professional Aspects of Nutrition and DieteticsOEAENo ratings yet
- Community and Public Health DefinitionsDocument3 pagesCommunity and Public Health DefinitionsSheralyn PelayoNo ratings yet
- Scoring BPSDDocument4 pagesScoring BPSDayu yuliantiNo ratings yet
- FreezingDocument59 pagesFreezingManoj Rathod100% (1)