Professional Documents
Culture Documents
ABS NDI - Guide Section 8 Acceptance Criteria For Hull Welds 5.
Uploaded by
Dagoberto AguilarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
ABS NDI - Guide Section 8 Acceptance Criteria For Hull Welds 5.
Uploaded by
Dagoberto AguilarCopyright:
Available Formats
Section 8: Acceptance Criteria for Hull Welds
SECTION 8 Acceptance Criteria for Hull Welds
1 General (1 September 2011)
This Section contains the acceptance criteria for use in the visual and NDT inspection of Hull welds.
The system operator is to confirm that the surface condition is acceptable prior to carrying out the inspection.
3 Applicable Criteria (1 September 2011)
3.1 Surface Vessels Class A Criteria
Inspection of full penetration welds for all surface vessels 150 m (500 ft) and over, in the midship 0.6L is
to meet the requirements of Class A. Class A may also be specified and applied to surface vessels less than
150 m (500 ft) when special hull material or hull design justifies this severity level.
Full penetration welds in way of integral or independent tanks, except membrane tanks, of all vessels intended
to carry liquefied natural gas (LNG) or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) cargo are to meet the requirements
of Class A.
3.3 Surface Vessels Class B Criteria
Inspection of full penetration welds for surface vessels under 150 m (500 ft), and for welds located outside
midship 0.6L, regardless of the size of the vessels, is to meet the requirements of Class B, provided that
Class A has not been specified in accordance with the special conditions noted in the Class A Criteria above.
3.5 Other Marine and Offshore Structures
Inspection of full penetration welds is to be in accordance with Class A, unless otherwise specified in the
applicable Rules (e.g., ABS Rules for Building and Classing Mobile Offshore Drilling Units).
5 Evaluation from Visual Inspection (VT), Magnetic Inspection (MT)
and Liquid Penetrant Inspection (PT) (1 September 2011)
5.1 Shape
Flaw indications are to be classified as either linear or rounded.
i) Linear flaw indications are classified as having a length equal to or greater than 3 times (3x) the width.
ii) Rounded flaw indications are classified as having a circular or elliptical shape and the length of
the ellipse is less than 3 times (3x) the width.
5.3 Flaw Indications (MT)
All valid indications formed by magnetic particle examination are the result of magnetic leakage fields.
Flaw indications may be relevant, non-relevant, or false.
5.3.1
Relevant indications are produced by leakage fields which are the result of discontinuities.
Relevant indications require evaluation with regard to the acceptance standards stated below.
ABS GUIDE FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE INSPECTION OF HULL WELDS . 2011 45
Section 8 Acceptance Criteria for Hull Welds
5.3.2
Non-relevant indications can occur singly or in patterns as a result of leakage fields created by
conditions that require no evaluation, such as changes in section (like keyways and drilled holes),
inherent material properties (like the edge of a bimetallic weld), magnetic writing, etc.
5.3.3
False indications are not the result of magnetic forces. Examples are particles held mechanically
or by gravity in shallow depressions, or particles held by rust or scale on the surface.
5.5 Evaluation from Surface Inspection
Evaluation from surface inspection is to be made in accordance with the following acceptance criteria.
5.5.1 Weld Appearance, Size and Shape
Welds are to meet the following requirements:
i) Welds are to be regular and uniform with a minimum amount of reinforcement.
ii) Welds are to be free from excessive overlap, excessive convexity, and undersize weld or
underfill.
iii) Thorough fusion shall exist between adjacent layers of weld metal and between weld metal
and base metal.
iv) All craters shall be filled to their specified weld size.
v) For welds exhibiting undercut, refer to 8/5.5.5 below. At the discretion of the Surveyor,
undercut considered non-conforming is subject to be inspected further by other nondestructive
test methods such as magnetic particle method, liquid penetrant method, radiographic method,
or ultrasonic method.
vi) Arc strikes outside the weld groove are to be dressed and removed.
5.5.2 Cracks
Welds are to be free of any type of crack.
5.5.3 Incomplete Fusion
Welds are to be free of any lack of fusion between weld metal and base metal.
5.5.4 Porosity
i) Complete joint penetration (CJP) groove welds in butt joints transverse to the members
subject to tensile stress are not to have piping porosity. For all other complete joint
penetration (CJP) groove welds and full penetration fillet welds, the frequency of piping
porosity is not to exceed one in each 100 mm (4 in.) of length and the maximum diameter
is not to exceed 2.5 mm (0.1 in.).
ii) For fillet welds connecting stiffeners to web and partial penetration fillet welds, the sum
of the piping porosity 1 mm (1/24 in.) or greater in diameter is not to exceed 10 mm (3/8 in.)
in any linear 25 mm (1 in.) of weld and is not to exceed 19 mm (3/4 in.) in any 300 mm (12 in.)
length of weld. The maximum diameter of the piping porosity is not to exceed 2.5 mm
(3/32 in.).
5.5.5 Undercut
Undercut refers to a groove melted in the base metal adjacent to a weld toe at the face or root of
the weld. In addition to visual inspection requirement on undercut in 8/5.5.1 above, undercut
revealed from VT, MT or PT have the following acceptance criteria for butt welds and fillet welds:
i) In primary members, undercut is to be no more than 0.25 mm (0.01 in.) deep when the
weld is transverse to tensile stress under any design loading condition.
46 ABS GUIDE FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE INSPECTION OF HULL WELDS . 2011
Section 8 Acceptance Criteria for Hull Welds
ii) For all other cases:
x Undercut depth up to 0.5 mm (1/64 in.) is acceptable, whatever the length
x Undercut depth up to 0.8 mm (1/32 in.) with a maximum continuous length of 90 mm
(31/2 in.) is acceptable. Adjacent undercuts separated by a distance shorter than the
shortest undercut should be regarded as a single continuous undercut.
iii) Assessment of depth is to be done by visual and mechanical means, and assessment of
depth using magnetic particle or liquid penetrant method is not acceptable
7 Evaluation from Radiographic Inspection
Evaluation from radiographic inspection is to be made in accordance with the following acceptance criteria.
7.1 Cracks
Welds in which radiographs exhibit any type of crack are to be considered unacceptable.
7.3 Incomplete Fusion or Incomplete Penetration
Lack of fusion in any portion of the weld deposit or between the weld deposit and the adjacent base metal
is to be treated as incomplete fusion or incomplete penetration.
7.3.1 Class A and Class B
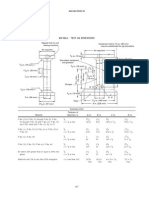
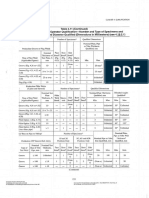
Radiographs of welds exhibiting indications of incomplete fusion or incomplete penetration greater
than those shown in the respective curves of Section 8, Figure 1 for single and total accumulated
length are non-conforming.
7.5 Slag
Non-metallic solid material entrapped in the weld deposit or between the weld deposit and the adjacent
base metal is to be treated as slag.
When determining the total accumulated length of slag for each class, acceptable incomplete fusion or
incomplete penetration indications are to be treated as slag.
7.5.1 Incomplete Fusion
Incomplete penetration and slag indications less than 3 mm (1/8 in.) in length may be evaluated as
slag or porosity, whichever is less restrictive.
7.5.2 Class A
Radiographs of welds exhibiting indications of slag greater than those shown in the respective
curves of Section 8, Figure 2 for single or total accumulated length are non-conforming.
7.5.3 Class B
Radiographs of welds exhibiting indications of slag greater than those shown in the respective
curves of Section 8, Figure 3 for single or total accumulated length are non-conforming.
7.7 Porosity
Gas pockets, circular voids, and well-dispersed tungsten inclusions are to be treated as porosity.
7.7.1 Class A and Class B
Radiographs of welds exhibiting porosity concentrations greater than those shown in the charts of
Section 8, Figures 4 through 10, for any 150 mm (6 in.) weld length, for material ranging from 6.2 mm
(1/4 in.) to 50 mm (2 in.) in thickness, are non-conforming.
ABS GUIDE FOR NONDESTRUCTIVE INSPECTION OF HULL WELDS . 2011 47
You might also like
- Table 6 1 AWS D1 1 D1 1M 2010 PDFDocument1 pageTable 6 1 AWS D1 1 D1 1M 2010 PDFFu AdNo ratings yet
- AA0850126 Rev 02Document10 pagesAA0850126 Rev 02Manish KumarNo ratings yet
- Aws - D1.1M - 2020 - Llo 268Document1 pageAws - D1.1M - 2020 - Llo 268santiago cruzNo ratings yet
- Guided Bend Test Jig Dimension ASME 9Document3 pagesGuided Bend Test Jig Dimension ASME 9esamhamad50% (2)
- Tech Manual MVP Series 2017.1 WIP 3Document73 pagesTech Manual MVP Series 2017.1 WIP 3Chav HoangNo ratings yet
- JIS G3452 PipeDocument0 pagesJIS G3452 PipefaridyeniNo ratings yet
- E390-11 Standard Reference Radiographs For Steel Fusion WeldsDocument4 pagesE390-11 Standard Reference Radiographs For Steel Fusion WeldsAhmed Shaban KotbNo ratings yet
- PMI Testing Ensures Material Specification ComplianceDocument24 pagesPMI Testing Ensures Material Specification ComplianceSANKARAN.KNo ratings yet
- ASME 9 Multi Process Welding Procedures QW200Document2 pagesASME 9 Multi Process Welding Procedures QW200Teodor EzaruNo ratings yet
- Pressure Vessel Inspection ProcedureDocument16 pagesPressure Vessel Inspection Procedurejabir ahmad anarwalaNo ratings yet
- Qw-484A - Suggested Format A For Welder Performance Qualifications (WPQ) )Document2 pagesQw-484A - Suggested Format A For Welder Performance Qualifications (WPQ) )essnelsonNo ratings yet
- BS 2452 (1954)Document30 pagesBS 2452 (1954)siswou100% (1)
- Zzze) I (ZFRP: QW-163 Acceptance Criteria - Bend Tests QW-163 Acceptance Criteria - Bend TestsDocument1 pageZzze) I (ZFRP: QW-163 Acceptance Criteria - Bend Tests QW-163 Acceptance Criteria - Bend TestsSARSAN NDTNo ratings yet
- Catalog Fabricante TechnipDocument9 pagesCatalog Fabricante Technipjimy GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- API 6A RadiographyDocument4 pagesAPI 6A RadiographyminakshissawantNo ratings yet
- Flange Face Surface FinishDocument2 pagesFlange Face Surface FinishJoel Ashley D'SouzaNo ratings yet
- Solderer Performance Qualification (SPQ) - Sample Form: Qualification, AWS B2.3/B2.3MDocument1 pageSolderer Performance Qualification (SPQ) - Sample Form: Qualification, AWS B2.3/B2.3MBernardo LeorNo ratings yet
- Sample PQR Form (GTAW & SMAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Document2 pagesSample PQR Form (GTAW & SMAW - Page 1) Procedure Qualification Record (PQR)Luis Carlos Clericci LimonNo ratings yet
- Brazing BPS 107-1 PDocument5 pagesBrazing BPS 107-1 Pmbe josephNo ratings yet
- AMS 2301 2006 Steel Cleanliness Aircraft QualityDocument15 pagesAMS 2301 2006 Steel Cleanliness Aircraft QualitySinan ChenNo ratings yet
- Method Statement For In-Situ Metallography Test: DCSM Project 2019Document5 pagesMethod Statement For In-Situ Metallography Test: DCSM Project 2019Thinh NguyenNo ratings yet
- JIS Z 2320-1-2007 Non-Destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle Testing - Part 1 General Principles-6 PDFDocument31 pagesJIS Z 2320-1-2007 Non-Destructive Testing - Magnetic Particle Testing - Part 1 General Principles-6 PDFNguyễn Hữu BằngNo ratings yet
- Sa 961 PDFDocument10 pagesSa 961 PDFaruntpeNo ratings yet
- Table 6.7Document2 pagesTable 6.7AngelTinocoNo ratings yet
- NDT-SA-ARAMCO-MCCL-PMI-57 Rev 00 Date 26-June-2023Document16 pagesNDT-SA-ARAMCO-MCCL-PMI-57 Rev 00 Date 26-June-2023SANJEEV YADAVNo ratings yet
- Tigweldarc Alloys: Certification of TestsDocument1 pageTigweldarc Alloys: Certification of TestsArunNo ratings yet
- CSM-QR-02-2, Medical Gas BPS TablesDocument8 pagesCSM-QR-02-2, Medical Gas BPS TablesaadmaadmNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure SpecificationDocument3 pagesWelding Procedure SpecificationMark Jason M. BrualNo ratings yet
- AWS D1.1 vs CSA W47.1 & W59 Standards ReviewDocument25 pagesAWS D1.1 vs CSA W47.1 & W59 Standards Reviewqc_531040655No ratings yet
- Article 4 Metodo UltrasonidoDocument24 pagesArticle 4 Metodo UltrasonidoLessly Lorena Apala RamirezNo ratings yet
- En 13920-2015Document8 pagesEn 13920-2015mihaiNo ratings yet
- ABS Rules & Guides PDFDocument6 pagesABS Rules & Guides PDFJorge Adrian Rojo UbedaNo ratings yet
- Quality Control and Inspection Proposal for 1000-Ton Barge ConstructionDocument9 pagesQuality Control and Inspection Proposal for 1000-Ton Barge ConstructionEbuka NwankwoNo ratings yet
- Sfa-5 31Document10 pagesSfa-5 31Sarvesh MishraNo ratings yet
- WPS Format For Asme Ix - Wps - Gtaw Fcaw GmawDocument1 pageWPS Format For Asme Ix - Wps - Gtaw Fcaw GmawThe Welding Inspections CommunityNo ratings yet
- Wire Rope and Webbing Sling Inspection ReportsDocument2 pagesWire Rope and Webbing Sling Inspection ReportsdharwinNo ratings yet
- PQR 01 PDFDocument2 pagesPQR 01 PDFVijay BhaleraoNo ratings yet
- 625 CRO - SAW Study - Final Report PDFDocument21 pages625 CRO - SAW Study - Final Report PDFAnouar AbdelmoulaNo ratings yet
- Aws D3.5-93PV PDFDocument8 pagesAws D3.5-93PV PDFwalter091011No ratings yet
- 000Document32 pages000TamerGalhoumNo ratings yet
- Norma CWB Cambios en W47.1-2009Document6 pagesNorma CWB Cambios en W47.1-2009Jose ManuelNo ratings yet
- Derrick Sample Report PDFDocument11 pagesDerrick Sample Report PDFRajesh ThorweNo ratings yet
- ISO/AWS/JIS welding material standards updateDocument4 pagesISO/AWS/JIS welding material standards updateHoque AnamulNo ratings yet
- Mobile Offshore Drilling Units 2008: Rules For Building and ClassingDocument14 pagesMobile Offshore Drilling Units 2008: Rules For Building and ClassingmfazioliNo ratings yet
- EGW Welding Wire Guide for 490MPa SteelDocument2 pagesEGW Welding Wire Guide for 490MPa SteelpratishgnairNo ratings yet
- WPS Ernicu 7 R1 3 6 PDFDocument4 pagesWPS Ernicu 7 R1 3 6 PDFandresNo ratings yet
- Kerosene Leak TestDocument3 pagesKerosene Leak TestsapkotamonishNo ratings yet
- AWS D1.1 qualification requirementsDocument2 pagesAWS D1.1 qualification requirementsArul Edwin VijayNo ratings yet
- Dolly TestDocument1 pageDolly TestmaheshNo ratings yet
- Automated UT Inspection of RailsDocument5 pagesAutomated UT Inspection of RailsRamakrishnan AmbiSubbiah0% (1)
- Welding Qualification As Per AWS D1.1Document19 pagesWelding Qualification As Per AWS D1.1Ouni AchrefNo ratings yet
- Manual Et 22 GpsDocument32 pagesManual Et 22 GpsAlex JuarezNo ratings yet
- 171 Gtaw&Smaw Zug Asme (Ade S 5g) WPQDocument4 pages171 Gtaw&Smaw Zug Asme (Ade S 5g) WPQMuhammad Fitransyah Syamsuar PutraNo ratings yet
- RT Acceptance Para. 9.4Document4 pagesRT Acceptance Para. 9.4Yan Ferizal100% (1)
- Aluminum Welding ProceedureDocument14 pagesAluminum Welding ProceedureGregEverett2No ratings yet
- Aws D1.1-Tabla 8.1 - Seccion 8Document1 pageAws D1.1-Tabla 8.1 - Seccion 8cesarNo ratings yet
- Aws Table 8.1 MT PTDocument1 pageAws Table 8.1 MT PTSugianto Tan Lok AnNo ratings yet
- Tabla 8.1 para No Tubulares AWS D1.1 2020 PDFDocument1 pageTabla 8.1 para No Tubulares AWS D1.1 2020 PDFRONALDNo ratings yet
- Acceptable Weld Profiles GuideDocument9 pagesAcceptable Weld Profiles GuideDominic Apollo Robles100% (1)
- IACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel StructuresDocument11 pagesIACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel Structuresalinor_tnNo ratings yet
- IACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel StructuresDocument11 pagesIACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel Structuresalinor_tnNo ratings yet
- Innovation Project Management (2019) PDFDocument566 pagesInnovation Project Management (2019) PDFDagoberto Aguilar100% (3)
- Iso 12944 - Coatings System Guide PDFDocument24 pagesIso 12944 - Coatings System Guide PDFDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Inspecting A Barges Tow Rigging PDFDocument29 pagesInspecting A Barges Tow Rigging PDFDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Astm A435 2012 PDFDocument2 pagesAstm A435 2012 PDFJavier Ricardo Romero Bohorquez33% (3)
- Inspecting A Barges Tow Rigging PDFDocument29 pagesInspecting A Barges Tow Rigging PDFDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- ISO15609-1 Welding Procedure Specification For Metallic MaterialsDocument14 pagesISO15609-1 Welding Procedure Specification For Metallic MaterialsDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Inspection Methods For Wind Turbine BladesDocument25 pagesAdvanced Inspection Methods For Wind Turbine BladesDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Astm17 0303Document5 pagesAstm17 0303Edgardo Emilio CantillanoNo ratings yet
- ASTM E94 2000 Standard Guide For Radiographic Inspection PDFDocument12 pagesASTM E94 2000 Standard Guide For Radiographic Inspection PDFDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Ul 142 PDFDocument92 pagesUl 142 PDFingalejos33% (3)
- Estandar de Referencia Radigráfica para Las Apariencias de Imágenes RadiográficasDocument3 pagesEstandar de Referencia Radigráfica para Las Apariencias de Imágenes RadiográficasDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- ASTM B-209 Especificación para Hojas de AluminioDocument6 pagesASTM B-209 Especificación para Hojas de AluminioDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- DoD PAUT Innovation for Structural Hull Weld InspectionsDocument14 pagesDoD PAUT Innovation for Structural Hull Weld InspectionsHector BeaujonNo ratings yet
- ASNT Level I II III Questions and Answers Book A-Radiographic Testing Method PDFDocument69 pagesASNT Level I II III Questions and Answers Book A-Radiographic Testing Method PDFDagoberto Aguilar100% (7)
- GuideDocument89 pagesGuideAsif HameedNo ratings yet
- A 325M - 03 PDFDocument7 pagesA 325M - 03 PDFsergioNo ratings yet
- ATTAR - ToFD Calculator AntiguoDocument1 pageATTAR - ToFD Calculator AntiguoDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Aws D1.5M-D1.5-2015 RTDocument6 pagesAws D1.5M-D1.5-2015 RTDagoberto Aguilar100% (1)
- Aerospace Casting X-ray GuidelinesDocument32 pagesAerospace Casting X-ray GuidelinesDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- 2012-02-01 FWGIDR 10 Checklist For The Qualification of Digital Detector Array SystemsDocument20 pages2012-02-01 FWGIDR 10 Checklist For The Qualification of Digital Detector Array SystemsDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Welding Procedure PreparationDocument122 pagesWelding Procedure Preparationthe_badass1234100% (21)
- UR - W1 - W31 Requirements Concerning Materials and WeldingDocument267 pagesUR - W1 - W31 Requirements Concerning Materials and WeldingDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- UR - W1 - W31 Requirements Concerning Materials and WeldingDocument267 pagesUR - W1 - W31 Requirements Concerning Materials and WeldingDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- ASTM A563 - 07 Standard Specification For Carbon and Alloy Steel NutsDocument8 pagesASTM A563 - 07 Standard Specification For Carbon and Alloy Steel NutsDagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- UR W28 Welding Procedure Qualification Tests of Steels (Rev.2 Mar 2012)Document25 pagesUR W28 Welding Procedure Qualification Tests of Steels (Rev.2 Mar 2012)Dagoberto AguilarNo ratings yet
- Shipbuilding Quality Standard GuideDocument59 pagesShipbuilding Quality Standard Guidenyaungzin100% (2)
- Offshore Part 1 E-Mar13 PDFDocument49 pagesOffshore Part 1 E-Mar13 PDFJACKNo ratings yet
- IACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel StructuresDocument11 pagesIACS - REC - 20 NDT of Ship Hull Steel Structuresalinor_tnNo ratings yet
- Contractor Job Safety PlanDocument15 pagesContractor Job Safety PlanAnonymous ocCa18RNo ratings yet
- 6 Welding Procedure Qualification & Welder Qualification PDFDocument15 pages6 Welding Procedure Qualification & Welder Qualification PDFParminder Singh100% (2)
- Technician Training Paths OverviewDocument15 pagesTechnician Training Paths OverviewAminovic Mostafa100% (1)
- Dremel CautinDocument28 pagesDremel CautinrcpilotNo ratings yet
- Identify Hazards in the WorkplaceDocument38 pagesIdentify Hazards in the WorkplaceJM Llaban Ramos40% (5)
- MIG Welding and Spot WeldingDocument3 pagesMIG Welding and Spot WeldingHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Jobnumber: 0001 Job Name: Doc - Fullweld01: Parameter Value Parameter ValueDocument9 pagesJobnumber: 0001 Job Name: Doc - Fullweld01: Parameter Value Parameter ValueVengat EshNo ratings yet
- API 653 Calculation TestsDocument20 pagesAPI 653 Calculation TestsAnuradha Sivakumar100% (4)
- Joining Depleted Uranium to Aluminum Using Niobium InterlayerDocument7 pagesJoining Depleted Uranium to Aluminum Using Niobium InterlayertayefehNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1Document6 pagesChapter 1Eugine BalomagaNo ratings yet
- No. Trainer TVI Name: Angela E. CervantesDocument6 pagesNo. Trainer TVI Name: Angela E. CervantesVictor De Jesus Lpt33% (3)
- Ampco Trode 10Document1 pageAmpco Trode 10Hassan Fadel ShehadehNo ratings yet
- Weldability of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel in Centrifugal Compressor Impeller ApplicationsDocument7 pagesWeldability of 17-4 PH Stainless Steel in Centrifugal Compressor Impeller ApplicationsMurad AlamNo ratings yet
- BOC Purging While Welding Brochure351 - 68116 PDFDocument16 pagesBOC Purging While Welding Brochure351 - 68116 PDFAl0611981No ratings yet
- Welding Electrode Manufacturing Plant Production Process MarketDocument71 pagesWelding Electrode Manufacturing Plant Production Process MarketShubham YadavNo ratings yet
- Overview Fusion Welding Standards PDFDocument1 pageOverview Fusion Welding Standards PDFHà Việt ĐứcNo ratings yet
- 000 K-Span-Construction-GuideDocument25 pages000 K-Span-Construction-GuideomermmkaNo ratings yet
- BS MA 41 2 Tonne General Purpose Davits PDFDocument15 pagesBS MA 41 2 Tonne General Purpose Davits PDFMohamed Eid AbassNo ratings yet
- Alberta Welder Apprentice Program OutlineDocument31 pagesAlberta Welder Apprentice Program OutlinedlulsiferNo ratings yet
- Trusco WeldingGaugesDocument2 pagesTrusco WeldingGaugesAnonymous rYZyQQot55No ratings yet
- TG76-15 Felt PDS Sika SarnafilDocument5 pagesTG76-15 Felt PDS Sika SarnafilAndrea Mena GilNo ratings yet
- ASME Code Cases for Nuclear ComponentsN-71-18N-71-18N-122-2N-131-1N-133-3N-154-1N-155-2N-160-1N-192-3N-201-5N-208-1N-213N-243N-249-14N-253-14N-254N-257N-258-2Document14 pagesASME Code Cases for Nuclear ComponentsN-71-18N-71-18N-122-2N-131-1N-133-3N-154-1N-155-2N-160-1N-192-3N-201-5N-208-1N-213N-243N-249-14N-253-14N-254N-257N-258-2Biyong SantocildesNo ratings yet
- Sensores PiezoelétricosDocument15 pagesSensores PiezoelétricosALEX_INSPETORNo ratings yet
- Cold-Formed Member Joint DesignDocument15 pagesCold-Formed Member Joint DesignmabuhamdNo ratings yet
- Bahra Electric - EarthingDocument1 pageBahra Electric - EarthingSalman JoNo ratings yet
- API RP-572 Inspection of Pressure Vessels PresentationDocument26 pagesAPI RP-572 Inspection of Pressure Vessels PresentationIbrahim Eldesoky80% (10)
- Inconel Alloy 740 H PDFDocument24 pagesInconel Alloy 740 H PDFJosé Juan Jiménez AlejandroNo ratings yet
- Internal Floating Roof VesselDocument2 pagesInternal Floating Roof Vesselumair saeed100% (1)
- Ad 036821 001Document1 pageAd 036821 001hai sunNo ratings yet
- Attachment 1 DLT 5017-2007Document67 pagesAttachment 1 DLT 5017-2007Andi Baso Temalala STNo ratings yet