Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Microcontroller and Embedded Systems Course Scheme
Uploaded by
shasky210 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views3 pagesembedded systems
Original Title
Microcontroller & Embedded Systems Schedule
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentembedded systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
119 views3 pagesMicrocontroller and Embedded Systems Course Scheme
Uploaded by
shasky21embedded systems
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
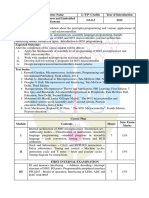
Teaching Scheme Credits
Course Course Name Assigned
Code
Theory Practical Tut. Theory TW/ Tut. Total
Practical
Microcontroller 04 02 --- 04 01 --- 05
and Embedded Hrs./Week Hrs./Week
TEITC503 Systems
Examination Scheme
Course Name Theory Marks TW Pract Oral Total
ical
Course
Internal Assessment End
Code
Semester
Average
Test1 Test2 Exam
Microcontroller and of T1
(T1) (T2)
Embedded Systems & T2
TEITC503 20 20 20 80 25 - 25 150
Pre-requisites: Fundamentals of Computer, Digital Logic Circuits, Computer Organization
and Architecture
Course Objectives:
CEO 1 To conceptualize the basics of embedded systems
CEO 2 To conceptualize the basics of organizational and architectural issues of a
microcontroller.
CEO 3 To learn programming techniques used in microcontroller.
CEO 4 To understand basic concept of ARM processor
CEO 5 To understand fundamentals of real time operating system
Course Outcomes:
A Ability to understand basic structure embedded systems
B Ability to understand basic structure microcontroller.
C Ability to understand basic concepts used in embedded system.
D Ability to program microcontroller.
E Ability to design conceptual embedded system.
University of Mumbai, Information Technology (semester V and VI) (Rev-2012) Page 15
Detailed Syllabus:
Module Detailed Contents Hours
1 Introduction to Embedded Systems: 06
Overview of Embedded System Architecture, Application areas,
Categories of embedded systems, specialties of embedded systems.
Recent trends in embedded systems. Brief introduction to
embedded microcontroller cores CISC, RISC, ARM, DSP and
SoC.
2 The Microcontroller Architecture: 08
Introduction to 8051 Microcontroller, Architecture, Pin
configuration, Memory organization, Input /Output Ports, Counter
and Timers, Serial communication, Interrupts.
3 Assembly Language Programming of 8051: 10
Instruction set, Addressing modes, Development tools, Assembler
Directives, Programming based on Arithmetic & Logical
operations, I/O parallel and serial ports, Timers & Counters, and
ISR.
4 ARM 7 architecture: 10
Architectural inheritance, Detailed study of Programmers model,
ARM Development tools, Instruction set: Data processing, Data
transfer, Control flow. Addressing modes. Writing simple
assembly language programs. Pipelining, Brief introduction to
exceptions and interrupts handling.
5 Embedded / Real Time Operating System: 8
Architecture of kernel, Task and Task scheduler, Interrupt service
routines, Semaphores, Mutex, Mailboxes, Message queues, Event
registers, Pipes, Signals, Timers, Memory management, Priority
inversion problem. Off-the-Shelf Operating Systems, Embedded
Operating Systems, Real Time Operating System (RTOS) and
Handheld Operating Systems.
6 Embedded System - Design case studies: Digital clock, Battery 06
operated smart card reader, Automated meter reading system,
Digital camera.
University of Mumbai, Information Technology (semester V and VI) (Rev-2012) Page 16
Text Books:
1. The 8051 microcontroller & Embedded systems, M. A. Mazidi, J. G. Mazidi, R. D.
McKinlay, Pearson
2. The 8051 microcontroller & Embedded systems, Kenneth J. Ayala, Dhananjay V. Gadre,
Cengage Learning
3. Embedded / real time systems: concepts, design & programming, Black Book, Dr. K.
V. K. K. Prasad, Dreamtech press, Reprint edition 2013
4. Introduction to embedded systems, Shibu K. V., McGraw Hill
5. ARM System on chip Architecture, Steve Furber, Pearson, edition second
Reference Books:
1. Embedded systems an integrated approach, Laya B. Das, Pearson, Third impression,
2013
2. ARM system developers guide, Andrew N. Sloss, Dominic Symes, Chris Wright,
Morgan Kaufmann Publishers
3. Embedded system design A Unified hardware/software Introduction, Frank Vahid, Tony
Givargis, Wiely
4. ARM Technical Reference manual
Term Work: 25 Marks (Total marks) = 15 Marks (Experiment and Case Studies) + 5 Marks
(Assignments) + 5 Marks (Attendance)
The faculty should conduct eight programming practicals/experiments based on the above
syllabus and two case studies based on recent trends in embedded systems.
Oral examination will be based on the above syllabus.
Theory Examination:
Question paper will comprise of 6 questions, each carrying 20 marks.
Total 4 questions need to be solved.
Q.1 will be compulsory, based on entire syllabus.
Remaining question will be randomly selected from all the modules.
Weightage of marks should be proportional to number of hours assigned to each module.
University of Mumbai, Information Technology (semester V and VI) (Rev-2012) Page 17
You might also like
- ASIC Interview Question & Answer - ASIC VerificationDocument3 pagesASIC Interview Question & Answer - ASIC Verificationprodip7No ratings yet
- Software Engineering for Embedded Systems: Methods, Practical Techniques, and ApplicationsFrom EverandSoftware Engineering for Embedded Systems: Methods, Practical Techniques, and ApplicationsRating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (2)
- Transformer Failures, Causes and ImpactDocument4 pagesTransformer Failures, Causes and ImpactveraNo ratings yet
- 15EC62 Arm MC and Es Course File 2018Document10 pages15EC62 Arm MC and Es Course File 2018Nikhil KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitsDocument4 pagesCourse Objectives:: L T P/S SW/F W Total Credit UnitslalaNo ratings yet
- Embedded System (9168)Document5 pagesEmbedded System (9168)Victoria FrancoNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument3 pagesSyllabusDev Shankar PaulNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological UniversityArunmetha SundaramoorthyNo ratings yet
- El402: Embedded System Design CREDITS 5 (L 3, T 0, P 2)Document2 pagesEl402: Embedded System Design CREDITS 5 (L 3, T 0, P 2)निमँलसिंह राउलजीNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Microcontroller FundamentalsDocument6 pagesMicroprocessor and Microcontroller Fundamentalsgoons7777No ratings yet
- Semester 7 dQyISLZoAzDocument10 pagesSemester 7 dQyISLZoAzAadrika GuptaNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor Applications and InterfacingDocument4 pagesMicroprocessor Applications and InterfacingALBERTNo ratings yet
- 17CS005Document2 pages17CS005Koush RastogiNo ratings yet
- Microcontroller Architecture and Organization: Unit IDocument6 pagesMicrocontroller Architecture and Organization: Unit IhemanthdreamzNo ratings yet
- Birla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, KK Birla Goa Campus Instruction Division First Semester 2012-2013 Course HandoutDocument3 pagesBirla Institute of Technology and Science, Pilani, KK Birla Goa Campus Instruction Division First Semester 2012-2013 Course HandoutMeghanand BhamareNo ratings yet
- IA-Course - Syllabus Pages From EL - BE-page 84-IA-2Document3 pagesIA-Course - Syllabus Pages From EL - BE-page 84-IA-2Varuni SawantNo ratings yet
- 5th CE PDFDocument38 pages5th CE PDFDhrumin PatelNo ratings yet
- 21CS43 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsDocument4 pages21CS43 Microcontroller and Embedded SystemsNikhil chandNo ratings yet
- Syllabus MCES-18CS44Document2 pagesSyllabus MCES-18CS44harishNo ratings yet
- Mumbai University (Sem-6 (Rev) ) SyllabusDocument13 pagesMumbai University (Sem-6 (Rev) ) Syllabusamit_sutar14100% (2)
- Microprocessors and MicrocontrollersDocument2 pagesMicroprocessors and MicrocontrollersrahulwasthereNo ratings yet
- Certificate Course in Embedded System Design Using ARM/ Cortex MicrocontrollerDocument4 pagesCertificate Course in Embedded System Design Using ARM/ Cortex MicrocontrollerMadhav KulkarniNo ratings yet
- Syllabus - 5th Semester NEW-1Document12 pagesSyllabus - 5th Semester NEW-1Pritam PaulNo ratings yet
- Ba SyllabusDocument3 pagesBa SyllabusvivekNo ratings yet
- Computer Organization CourseDocument4 pagesComputer Organization CourseShivang AgarwalNo ratings yet
- 6th Sem SyllabusDocument11 pages6th Sem SyllabusRahul SheikhNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: CreditsDocument4 pagesGujarat Technological University: CreditsNiket RathodNo ratings yet
- MICROPROCESSOR THEORY & INTERFACINGDocument6 pagesMICROPROCESSOR THEORY & INTERFACINGusmanzahidNo ratings yet
- Bcse305l Embedded-Systems TH 1.0 70 Bcse305lDocument2 pagesBcse305l Embedded-Systems TH 1.0 70 Bcse305lpsNo ratings yet
- ERTOS Course OutcomesDocument2 pagesERTOS Course OutcomesSyed AshmadNo ratings yet
- Embedded System Design and IC Technology Course DetailsDocument24 pagesEmbedded System Design and IC Technology Course DetailsHannan SatopayNo ratings yet
- Digital Design Using HDL PDFDocument2 pagesDigital Design Using HDL PDFMarvin MayormenteNo ratings yet
- Computer Organizationand Architecture SyllabusDocument3 pagesComputer Organizationand Architecture SyllabuskrupeshNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Design Course OverviewDocument13 pagesEmbedded Systems Design Course OverviewShivaprasad B KNo ratings yet
- UIT's Advanced Digital Electronics CourseDocument3 pagesUIT's Advanced Digital Electronics CourseSoftware EngineerNo ratings yet
- Open Electrive I - 3rd Year VI Semester - AICTE 2020-21 - 9 March 2021Document15 pagesOpen Electrive I - 3rd Year VI Semester - AICTE 2020-21 - 9 March 2021aniruddha sharmaNo ratings yet
- CP MPMC Ay22-23Document12 pagesCP MPMC Ay22-23Vedashree ShetyeNo ratings yet
- Course Specification: Se425 Distributed Control SystemDocument10 pagesCourse Specification: Se425 Distributed Control SystemAmmar AlkindyNo ratings yet
- Microprocessor and Micro - ControllerDocument6 pagesMicroprocessor and Micro - Controllerzahin_13200No ratings yet
- FMTC0302 - Lesson Plan COADocument8 pagesFMTC0302 - Lesson Plan COAdarshankumar999No ratings yet
- Course Plan EsDocument5 pagesCourse Plan EsgyuNo ratings yet
- Bangalore Universty: University Visvesvaraya College of EngineeringDocument8 pagesBangalore Universty: University Visvesvaraya College of Engineeringsaurav bsNo ratings yet
- EE309 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems-ModifiedDocument2 pagesEE309 Microprocessors and Embedded Systems-Modifiedanto5751No ratings yet
- CS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3Document57 pagesCS322 - Computer Architecture (CA) : Spring 2019 Section V3TANZEELA SHAKEELNo ratings yet
- EE445-ABET Form - Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEE445-ABET Form - Course OutlineRaya AwadNo ratings yet
- EE3003 - E S & Ic D: Mbedded Ystems EsignDocument4 pagesEE3003 - E S & Ic D: Mbedded Ystems EsignCharles BradleyNo ratings yet
- Government College of Engineering, Karad Third Year B. Tech. IT505: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument3 pagesGovernment College of Engineering, Karad Third Year B. Tech. IT505: Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerPallavi BhartiNo ratings yet
- Sem 6Document11 pagesSem 6Brahat SinghNo ratings yet
- Course Objectives:: University of Mumbai, Information Technology (Semester V and VI) (Rev-2012)Document4 pagesCourse Objectives:: University of Mumbai, Information Technology (Semester V and VI) (Rev-2012)Falgun PATELNo ratings yet
- CS 4th Semester SyllabusDocument13 pagesCS 4th Semester SyllabusManish KumarNo ratings yet
- 56 SemDocument21 pages56 SemAdithi OG Adithi OGNo ratings yet
- Syllabus EC5001 Embedded SystemsDocument3 pagesSyllabus EC5001 Embedded Systemskavish malakaNo ratings yet
- ES Syllabus (E-Next - In)Document2 pagesES Syllabus (E-Next - In)rahulyadav7405788No ratings yet
- Engineering: Hours ARM ProcessorDocument4 pagesEngineering: Hours ARM ProcessorSuhas PasteNo ratings yet
- CS - ECE - EEE - INSTR F215 Digital Design Handout I Sem 2023-24Document4 pagesCS - ECE - EEE - INSTR F215 Digital Design Handout I Sem 2023-24f20220264No ratings yet
- Mumbai University SyllabusDocument30 pagesMumbai University SyllabusjcijosNo ratings yet
- Subject Code Subject Name Credits: Overview of Computer Architecture & OrganizationDocument4 pagesSubject Code Subject Name Credits: Overview of Computer Architecture & Organizationanon_71491248No ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 5Document5 pagesGujarat Technological University: Page 1 of 5Keval PatelNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: R.V. College of Engineering, BangaloreDocument14 pagesLesson Plan: R.V. College of Engineering, BangaloreVeena Divya KrishnappaNo ratings yet
- Digital Control &mbadded SystemDocument4 pagesDigital Control &mbadded SystemabrahamNo ratings yet
- Verification report for preventative maintenance of medical imaging deviceDocument5 pagesVerification report for preventative maintenance of medical imaging deviceMuhammed RaufNo ratings yet
- Esser Katalog 2013 Voice EvacuationDocument100 pagesEsser Katalog 2013 Voice EvacuationsllazicNo ratings yet
- LG Sound Bar ManualDocument40 pagesLG Sound Bar ManuallonghornsteveNo ratings yet
- A Hybrid Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Technique For Cognitive Radio Networks Using Linear ClassifiersDocument6 pagesA Hybrid Cooperative Spectrum Sensing Technique For Cognitive Radio Networks Using Linear Classifierssuchi87No ratings yet
- SCPT Master ListDocument113 pagesSCPT Master ListPeli JorroNo ratings yet
- TS200 Operation Manual - NewDocument9 pagesTS200 Operation Manual - NewJeffriNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Flow Computers White PaperDocument12 pagesFundamentals of Flow Computers White PaperDave NakpodiaNo ratings yet
- Mcqs cs302Document6 pagesMcqs cs302Abrish AliNo ratings yet
- Digital Communication System Advantages and DisadvantagesDocument7 pagesDigital Communication System Advantages and Disadvantagesbhaskararao vandarapuNo ratings yet
- E LynX Family - BrochureDocument12 pagesE LynX Family - Brochure573563876luNo ratings yet
- MTC 304 Mineral Insulated Thermocouple With Connection HeadDocument1 pageMTC 304 Mineral Insulated Thermocouple With Connection HeadDanut AnghelNo ratings yet
- Von Neumann Machine Architecture (CSO)Document33 pagesVon Neumann Machine Architecture (CSO)TBNo ratings yet
- Series 72 Modutrol IV™ Motors: FeaturesDocument12 pagesSeries 72 Modutrol IV™ Motors: FeaturesEzequias RoquimNo ratings yet
- Week5 Lecture - 3D DesigningDocument14 pagesWeek5 Lecture - 3D DesigningPatrick MoleNo ratings yet
- TPS-Instruction ManualDocument42 pagesTPS-Instruction ManualGheorghe Gabriel CerneanNo ratings yet
- Jeppiaar Engineering College: Question BankDocument15 pagesJeppiaar Engineering College: Question Bankmohanmzcet100% (1)
- RF-Based Multiple Device Control Using MicrocontrollerDocument7 pagesRF-Based Multiple Device Control Using Microcontrollermv mvNo ratings yet
- Beckhoff Main Catalog 2019 Volume2 PDFDocument728 pagesBeckhoff Main Catalog 2019 Volume2 PDFAlexandru DiaconescuNo ratings yet
- Electrical Systems: Scope of WorksDocument4 pagesElectrical Systems: Scope of WorksSaso SaberNo ratings yet
- Flashing Alarm Annunciator Units With Signal Storage FSB 24/16-24 - P USBDocument4 pagesFlashing Alarm Annunciator Units With Signal Storage FSB 24/16-24 - P USBm khNo ratings yet
- Leds DatasheetDocument45 pagesLeds DatasheetThiago CordeiroNo ratings yet
- DOR-230 PCB input signal errorDocument1 pageDOR-230 PCB input signal errorDaniel GatdulaNo ratings yet
- Generator technical guidance on shaft bearing currentsDocument2 pagesGenerator technical guidance on shaft bearing currentsquang_dtd09No ratings yet
- YBS ElevatorCables PDFDocument4 pagesYBS ElevatorCables PDFYBS CablesNo ratings yet
- Fm357 eDocument485 pagesFm357 eRafaelNo ratings yet
- Mobile Robot Chapter 7: The Motors of The Robot (V.4a)Document18 pagesMobile Robot Chapter 7: The Motors of The Robot (V.4a)Carlos RamirezNo ratings yet
- Bef45203 HV Chapter 2 - Breakdown in GassesDocument99 pagesBef45203 HV Chapter 2 - Breakdown in GassesNUR AQILAH MOHD AZMANNo ratings yet
- Isotech Temp CalibratorDocument4 pagesIsotech Temp CalibratorTp PtNo ratings yet