Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Uploaded by
Qais SamadiOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Uploaded by
Qais SamadiCopyright:
Available Formats
GUJARAT TECHNOLOGICAL UNIVERSITY
CIVIL ENGINEERING
SOIL MECHANICS
SUBJECT CODE: 2150609
B.E. 5thSEMESTER
Type of course:Core
Pre-requisites: Geotechniques & Applied Geology (GTAG) and Strength of Materials and Fluid
Mechanics
Rationale: Soil Mechanics is very fundamental subject consisting of determination of various soil
parameters theoretically and experimentally based on laws of mechanics. Any civil engineering structure
needs strong and stable foundation which depends on proper understanding of soil behaviour,
determination and interpretation of soil parameters, determination of stresses in soil. The design of any
foundation system is based on understanding of soil parameters and its implication based on through
interaction with type of structure. The course on Soil Mechanics provides the students basic knowledge on
soil properties, testing procedures, suitability of test and analytical solutions necessary for design and
behaviour of soil.
Content:
Sr. Total Module
Topics
No. hours Weightage
1 Compaction:
Definition, Theory of compaction, Factors affecting compaction,
Laboratory compaction tests, Effect of compaction on soil properties, 06 10
Placement water content, Placement layer thickness, Field control of
compaction, Proctor's needle, Methods of compaction used in field.
2 Shear Strength of Soil :
Mohr's strength theory, Mohr- coulomb's strength theory, Modified
Mohrcoulomb's theory, Shear parameters tests: Direct shear test, 07 20
Unconfined compression test, lab. Vane shear test, Triaxial compression
test, Shear tests based on drainage conditions.
3 Consolidation of Soils :
Compressibility of soils, Definitions and mechanism of consolidation,
Spring analogy, Void ratio and effective stress relation, Related indices,
Assumptions of Terzaghis one dimensional consolidation theory, Time
07 15
factor, One dimensional consolidation tests, Laboratory and theoretical
time curves, Determination of pre-consolidation pressure, Estimation of
consolidation settlement and rate of settlement for uniform pressure
increment in a clay layer.
4 Stability of Slopes: 06 15
Infinite and finite slopes, factor of safety, type of slope failure, stability of
infinite slopes, finite slopes, forms of slip surfaces, limit equilibrium
method and critical stage instability analysis, effects of tension crack and
submergence, C-analysis-method of slices, taylors stability no., Bishops
method.
5 Earth Pressure:
Types of lateral earth pressure, Rankines and Coulombs earth pressure,
Theory and their application for determination of lateral earth pressure 07 20
under different conditions,Rebhanns and Culmanns Graphical methods
of determination of lateral earth pressures.
6 Stress Distribution of Soils: Causes of stress in soil, geostatic
stress,Boussinesques equation, stress distribution diagrams, New-marks
07 15
influence chart Westergards equation, contact pressure, stresses due to
triangular and circular, strip and rectangular loadings.
7 Basics of foundation: Types of foundation, Factors affecting the
02 05
selection of type of foundations, steps in choosing types of foundation.
Suggested Specification table with Marks (Theory):
Distribution of Theory Marks
R Level U Level A Level N Level E Level C Level
20 20 20 25 15 0
Legends: R: Remembrance; U: Understanding; A: Application, N: Analyze and E: Evaluate C: Create and
above Levels (Revised Blooms Taxonomy)
Note: This specification table shall be treated as a general guideline for students and teachers. The actual
distribution of marks in the question paper may vary slightly from above table.
Reference Books:
1) P. Purushothama Raj; Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering; Pearson
2) Education.
3) B.C. Punamia; Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering; Laxmi Pub. Pvt. Ltd.,
4) Delhi.
5) Alamsingh; Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering; CBS Publishers &
6) Distributors, Delhi
7) Taylor D.W.; Fundamentals of Soil Mechanics; Asia Publishing House, Mumbai
8) V. N. S. Murthy; Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering; Sai Kripa Technical
9) Consultants, Banglore
10) Gopal Ranjan, Rao A.S.R.; Basic and applied soil mechanics; New age int. (p) ltd.
11) Arora K.R.; Soil Mechanics & Foundation Engineering; Standard Pub., Delhi
12) Das Braja M; Principles of Geotechnical Engineering; Thomson Asia Pvt. Ltd.
Course Outcome:
After learning the course the students should be able to:
1. This course will provide good understanding of various index (preliminary) and engineering
properties of soil, its determination through various methodology and application for design of
shallow and deep foundation systems for various civil engineering structures.
2. The course covers various topics like compaction, shear strength, consolidation, earth pressure,
stress distribution which gives insight to students to analyise soil parameters based on application
and need of project site.
3. The course will also develop understanding about soil testing procedures, experimentation
techniques and related issues. Simulation of mechanics on soil as a material to understand its
behaviour before failure and estimating its permissible values.
4. The course also discusses details of foundations, its selection procedures as per soil conditions
and various modifications available for various degrees of loads.
List of Experiments/Tutorials:
1. Proctor Compaction Test
2. CBR Test
3. Consolidation /Oedometer test
4. Direct Shear Test
5. Unconfined Compression Test
6. Demonstration of Triaxial test
7. Auger boring/sampling
8. Free swill and swell potential
Open Ended Problems:
Apart from above tutorials/experiments a group of students has to undertake one open ended problem
using sub-soil profile of their local city . Few examples of the same are given below:
1. Development of spread sheets/computer programmes for the determination of shear parameters using
Mohr circle.
2. Power point presentation on any one of the above topic supported with one field application/case study.
List of Open Source Software/learning website:
http://nptel.ac.in/
http://ocw.mit.edu/courses/civil-and-environmental-engineering/
ACTIVE LEARNING ASSIGNMENTS: Preparation of power-point slides, which include videos,
animations, pictures, graphics for better understanding theory and practical work The faculty will
allocate chapters/ parts of chapters to groups of students so that the entire syllabus to be covered. The
power-point slides should be put up on the web-site of the College/ Institute, along with the names of the
students of the group, the name of the faculty, Department and College on the first slide. The best three
works should submit to GTU.
You might also like
- Expert TopicsDocument2 pagesExpert TopicsQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- 100 PointsDocument2 pages100 PointsQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Entrance Letter: To Arghosha Farway SchoolDocument1 pageEntrance Letter: To Arghosha Farway SchoolQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Anchorage LengthDocument23 pagesAnchorage LengthGautam PaulNo ratings yet
- American Code ListDocument1 pageAmerican Code ListQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Internshala Resume GuideDocument8 pagesInternshala Resume Guidenklive11No ratings yet
- How to Write a Cover Letter in 8 Simple StepsDocument23 pagesHow to Write a Cover Letter in 8 Simple StepsQais Samadi100% (1)
- 30day Workout SheetDocument4 pages30day Workout SheetLucian LadicNo ratings yet
- Achievements (1643)Document5 pagesAchievements (1643)Qais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Drought ManagementDocument39 pagesDrought ManagementQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Achievements (1643)Document5 pagesAchievements (1643)Qais SamadiNo ratings yet
- 4000.essential - English.words.4 WWW - Download.irDocument193 pages4000.essential - English.words.4 WWW - Download.irNguyen Hoang Thanh CungNo ratings yet
- 5050 7143 1 PB PDFDocument9 pages5050 7143 1 PB PDFQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument4 pagesPDFQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Design Engineering Report On Glass FiberDocument1 pageDesign Engineering Report On Glass FiberQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Learn Design Thinking Process with ExamplesDocument26 pagesLearn Design Thinking Process with ExamplesPratik NakraniNo ratings yet
- GTU KnowledgeDocument2 pagesGTU KnowledgeQais Samadi0% (3)
- ToDocument6 pagesToQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- Smart CityDocument32 pagesSmart CityQais SamadiNo ratings yet
- 2140603Document3 pages2140603Qais SamadiNo ratings yet
- 2140603Document3 pages2140603Qais SamadiNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Graphical Symbols For General Engineering PDFDocument46 pagesGraphical Symbols For General Engineering PDFJohn Anthoni0% (1)
- IGCC For Power Generation - An Environmentally Benign and Energy Efficient TechnologyDocument22 pagesIGCC For Power Generation - An Environmentally Benign and Energy Efficient TechnologySyed YousufuddinNo ratings yet
- Single stage SAG/AG milling designDocument11 pagesSingle stage SAG/AG milling designrobigedNo ratings yet
- SIKA Catalog 2020 - Infrastructure v20 December 17 PDFDocument60 pagesSIKA Catalog 2020 - Infrastructure v20 December 17 PDFMark anthony GauranoNo ratings yet
- ALRO Profile Extrudate PDFDocument2 pagesALRO Profile Extrudate PDFmindsopenNo ratings yet
- Mixtron Flyer PDFDocument2 pagesMixtron Flyer PDFtribolasNo ratings yet
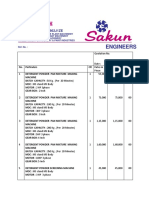
- Common 1 For Detergent Powder and Cake and LiquidDocument6 pagesCommon 1 For Detergent Powder and Cake and LiquidTayyib Khan100% (1)
- Installing DTI - Orig PDFDocument2 pagesInstalling DTI - Orig PDFlenkanfNo ratings yet
- PID a Silvia for precise temperature controlDocument28 pagesPID a Silvia for precise temperature controlErik VikenNo ratings yet
- Gama Bombas de Calor Waterkotte 2012 EDocument8 pagesGama Bombas de Calor Waterkotte 2012 ELuis Campos GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Installation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General Safety InformationDocument12 pagesInstallation, Operation and Maintenance Manual: General Safety InformationAnabel Hernández DíazNo ratings yet
- Investigation of Thermal Performance of Finned, Water-PCM, Double Tube Heat RecoveryDocument21 pagesInvestigation of Thermal Performance of Finned, Water-PCM, Double Tube Heat RecoveryHabib GürbüzNo ratings yet
- Some Guidelines For Choosing A Characterization Method For Petroleum Fractions in Process SimulatorsDocument7 pagesSome Guidelines For Choosing A Characterization Method For Petroleum Fractions in Process SimulatorsBahar MeschiNo ratings yet
- Installation of Lighting System Fans and ReceptaclesDocument6 pagesInstallation of Lighting System Fans and Receptaclesapparao42No ratings yet
- Hand Warmer Project - Stem-ChemDocument13 pagesHand Warmer Project - Stem-Chemapi-306854442No ratings yet
- Limi TTerDocument21 pagesLimi TTerErnestoNo ratings yet
- Latest Trends in MachiningDocument209 pagesLatest Trends in Machiningalexkr16661No ratings yet
- Fixed Belt Conveyor PDFDocument25 pagesFixed Belt Conveyor PDFBunkun15No ratings yet
- Reducing Thermowell Conduction Errors in Gas PipelineDocument4 pagesReducing Thermowell Conduction Errors in Gas PipelineMantiqiNo ratings yet
- Ignition System Components, Operation Checks, and Sensor Inspection GuideDocument19 pagesIgnition System Components, Operation Checks, and Sensor Inspection GuideAman Syah100% (1)
- Robotics: "Gopi, IIIT, RK Valley"Document21 pagesRobotics: "Gopi, IIIT, RK Valley"Hadi HassanNo ratings yet
- Permalite Roofing Manual 3 September 2013Document0 pagesPermalite Roofing Manual 3 September 2013ssss2345No ratings yet
- 9 - Types of Tests On Bricks - Civil LeadDocument14 pages9 - Types of Tests On Bricks - Civil LeadMuhammad HaseebNo ratings yet
- Compuestos TermocromicosDocument2 pagesCompuestos TermocromicosAlfonso RodríguezNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Waste Storage and LabelingDocument7 pagesHazardous Waste Storage and LabelingavieNo ratings yet
- V 01Document4 pagesV 01marco100% (1)
- ENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferDocument36 pagesENGR 340 - Foundations 3 - Ashlock - SchaeferSnaz_nedainNo ratings yet
- Vahterus Plate and Ring Prhe-EnDocument4 pagesVahterus Plate and Ring Prhe-EnMartin CorkeryNo ratings yet
- Possible Questions With AnswersDocument1 pagePossible Questions With AnswersAllaiz g.No ratings yet
- Aixam Lombardini Lgw523-Lgw627 Workshop ManualDocument94 pagesAixam Lombardini Lgw523-Lgw627 Workshop ManualjaumegusNo ratings yet