Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question Bank
Uploaded by
REVANTH KUMAR KCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question Bank
Uploaded by
REVANTH KUMAR KCopyright:
Available Formats
www.alljntuworld.
in JNTU World
QUESTION BANK
UNIT-I
BLOOMS
COURSE
QUESTION TAXONOMY
S. No OUTCOME
LEVEL
a) Define viscosity and derive Newtons law of viscosity.
Knowledge,
b) If the velocity distribution over a plate is given by u= Application
1 2
(2/3)y y , in which u is the velocity in m/s at a distance y meter above 1, 3
the plate, determine the shear stress at y=0 and y=0.15m. Take dynamic
ld
viscosity of fluid as 8.63 poise.
a) Differentiate between U-tube and Inverted U-Tube differential
manometers.
b) As shown in fig, pipe M contains carbon tetrachloride of specific gravity
1.594 under a pressure of 1.05 Kgf/cm2 and pipe N contains oil of specific
2
or
gravity 0.8. If the pressure in the pipe N is 1.75 Kgf/cm and the
manometric fluid is mercury. Determine the difference X between the
levels of mercury. Comprehension,
Application
2 1, 3
W
a) Explain the terms surface tension and vapor pressure.
Comprehension,
b) A 40 mm diameter shaft is rotating at 200 rpm in a bearing of length 120
Application
TU
3 mm. if the thickness of oil film is 1.5mm and dynamic viscosity of oil is 1, 3
0.7Ns/m2. Determine i) torque required to overcome friction in bearing, ii)
power utilized in overcoming viscous resistance.
a) State Newtons law viscosity and explain how viscosity varies with
temperature for liquids and gases.
b) Figure shows a differential manometer connected at two points A & B at
2
A air pressure is 100 KN/m . Determine the absolute pressure at B
JN
Knowledge,
Application
4 1, 3
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
a) An oil film of thickness 1.5mm is used for lubrication between a square
plate of size 0.9m x 0.9m and an inclined plane having an angle of Application,
0
inclination 20 . The weight of the square is 392.4 N and it slides down the
5 plane with a uniform velocity of 0.2 m/s. Determine the dynamic viscosity Knowledge 1, 3
of the oil.
b) Define atmospheric, gauge and vacuum pressures with examples.
a) An inverted u-tube manometer is connected to two horizontal pipes A &
B through which water is flowing. The vertical distance between the axes of
these points is 30 cm. When an oil of sp. gravity 0.8 is used as a gauge fluid,
the vertical heights of water columns in the two limbs of the inverted Application,
6 manometer (when measured from the respective center lines of the pipes) Synthesis 1, 3
ld
are found to be same and equal to 35 cm. Determine the difference of
pressure between the pipes.
b) Derive an expression for surface tension on a liquid droplet.
a) Derive an expression for surface tension on a liquid jet.
0
b) The surface tension of water in contact with air 20 c is given as
or
7 Synthesis, 1, 3
0.0716N/m .The pressure inside the drop let of water is to be 0.0417N/cm 2
Application
greater than the outside pressure. Calculate the diameter of the droplet of
water.
a) The velocity profile of a viscous fluid over a plate is parabolic with vertex
20cm from the plate, where the velocity is 120cm/s. calculate the velocity Application,
gradient and shear stress at distance of 0.5 and 15cm from the plate, given Knowledge
8 1, 3
W
the viscosity of the fluid =6 poise.
b) Define specific gravity, specific volume and weight.
a) An oil film of thickness 1.5mm is used for lubrication between a square
plates is of size 0.9m x 0.9m and an inclined plane having an angle of
inclination 200. The weight of the square is 392.4N and it slides down the
plane with a uniform velocity of 0.2 m/s. Calculate the dynamic viscosity of Application
9 1, 3
the oil.
TU
b) How do you measure the pressure by using manometers and mechanical
gauges?
a) Why does the viscosity of a gas increases with the increases in
temperature while that of a liquid decreases with increase in temperature? Comprehension,
10 Application 1, 3
b) Calculate density, specific weight and weight of 1 litre of petrol of
specific gravity 0.7
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
UNIT-II
BLOOMS
COURSE
QUESTION TAXONOMY
S.No OUTCOME
LEVEL
a) Define path line, stream line steam tube and streak line.
b) Water flows through a pipe AB 1.2 m dia. at 3m/s and then pass through Application,
pipe BC 1.5 m dia. At C the pipe branches, branch CD is 0.8 m dia. And carries Knowledge
1 2
1/3 rd of the flow in AB the flow velocity in branch CE is 2.5 m/s. Calculate the
volume rate of flow in AB, the velocity in BC, the velocity in CD and dia. of CE.
ld
a) Define and state the applications of momentum equation.
Application,
b) A 450 reducing bend is connected in a pipe line, the diameters at the inlet Knowledge
2 and outlet of the bend being 40cm and 20cm respectively. Find the force 2
exerted by water on the bend, if the intensity of the pressure at inlet of bend is
2
21.58N/cm . The rate of flow of water is 500 liters per second.
or
a) State the assumptions and derive Bernoullis equation for flow along a
stream line. Knowledge
3 b) Define and state examples of following flows 2
i) Steady and unsteady ii) Laminar and turbulent
a) Explain body force, surface force and line force with examples
Comprehension,
4 b) How impulse momentum equation can be applied for the force exerted by 2
Application
fluid on the bend pipe.
W
a) The velocity vector in a flow field is given as V = 4x3i - 10 x2yj + 2tk. Application ,
5 Determine the velocity and acceleration of a fluid particle at (2, 1, 3) at time=1. 2
Synthesis
b) Derive continuity equation in one dimensional flow.
a) Derive continuity an expression for continuity equation in three dimensional
flow.
b) The water is flowing through a pipe having diameters 20cm and 15cm at
TU
sections 1 and 2 respectively. The rate of flow through pipe is 40 ltr/s. the Synthesis,
6 2
section 1 is 6 m above datum line and section 2 is 3m above the datum. If the Application
pressure at section 1 is 29.43 N/cm2, Calculate the intensity of pressure at
section 2.
a) 250 lps of water is flowing in a pipe having a diameter of 300 mm. If the pipe
0
is bent by 135 find the magnitude and the direction of the resultant force on Application,
2
7 the bend. The pressure of water flowing is 39.24 N/cm . Knowledge 2
b) Define rotational and irrotational flows with examples.
JN
a) a pipe of diameter 400 mm carries water at a velocity of 25 m/s. the
pressure at the points A & B are given as 29.43 N/cm2 and 22.563 N/cm2 Application,
respectively, while the datum head at A and B are 28 m and 30 m. Calculate the Knowledge
8 loss of head at A and B. 2
b) Define uniform and non-uniform flows with examples.
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
a) The water is flowing through a taper pipe of length 100 m having diameters
600 mm at the upper end and 300 mm at the lower end, at the rate of 50 lps.
The pipe has a slope of 1 in 30; determine the pressure at lower end if pressure Application ,
9 at higher level is 19.62 N/cm2. 2
Synthesis
b) Derive an expression for Eulers equation of a flow along a stream line.
a) A 300 mm diameter pipe carries water under a head of 20 m with a velocity
0
of 3.5 m/s. If the axis of the pipe turns through 45 , calculate the magnitude Application ,
10 and the direction of the resultant force at the bend. Knowledge 2
b) Define compressible and in-compressible flows with examples.
ld
or
W
TU
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
UNIT-III
BLOOMS COURSE
S.No QUESTION TAXONOMY OUTCOME
LEVEL
a) Briefly explain (i)Intake structure (ii)penstock (iii) Anchor Block.
1 Synthesis, 6, 2
b) Draw a neat sketch of a Hydropower plant and show the various elements
Knowledge
and providing it.
a) Explain what is a pumped storage with a neat diagram .what are the
features and uses of it Application ,
ld
2 Knowledge 6, 2
b) Draw a mass curve and explain the use of it in detail
a) Distinguish clearly between the following types of Hydro power plants.
i)Base load and peak Knowledge,
or
3 6, 2
ii)Run of River and pumped storage plants. Application
a) Define energy thickness, momentum thickness and boundary layer
thickness. Synthesis,
4 6, 2
Knowledge
b) Derive an expression for momentum thickness of boundary layer.
W
The annual peak load on a 30 MW power station is 25 MW. The power
station supplies load having maximum demands of 10MW,8.5MW,5.0MW Synthesis,
and 4.5MW.The annual load factor is 45% Application
5 2
Find (i) Average load (ii) Energy supplied per year (iii) Demand factor of the
Power station
TU
power
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
UNIT-IV
BLOOMS COURSE
S.No QUESTION TAXONOMY OUTCOME
ld
LEVEL
a) Differentiate the impulse and reaction turbines.
b) A jet of water 50 mm in diameter issues with a velocity of 10m/sec and Comprehension,
1 impinges normally on a stationary flat plate which moves in forward Application 4
motion. Determine the force exerted by the jet on the plate and the work
done.
or
a) Give the classification of turbines.
b) A jet of water of diameter 60mm moving with a velocity of 40 m/sec, Comprehension,
2 strikes a curved fixed symmetrical plate at the centre. Determine the force Application 4
exerted by the jet of water in the direction of the jet, if the jet is deflected
by an angle of 160 degrees at the outlet of the curved plate.
a) Define the following;
W
i. Unit speed ii. Unit discharge iii. Unit power iv. Degree of
Application ,
reaction
3 Knowledge 4
b) A Pelton wheel having a mean bucket diameter of 1.0 m is running at
1000 r.p.m. the side clearance angle is 150 and discharge through the
nozzle is 0.1 m3/s, determine power available at the nozzle and hydraulic
efficiency of the turbine.
a) Define the following efficiencies;
TU
i. Mechanical ii. Volumetric iii. Overall iv.
Application ,
Hydraulic
4 Knowledge 4
b) A Pelton wheel is having a mean bucket diameter of 1 m and is running
at 1000 rpm. The net head on the Pelton wheel is 700 m. if the side
0 3
clearance angle is 15 and discharge through nozzle is 0.1m /s, calculate: i.
Power available at the nozzle, and ii. Hydraulic efficiency of the turbine.
JN
a) A jet of water 75 mm in diameter having velocity of 20 m/s strikes a
series of the flat plates arranged around the periphery of a wheel such that Synthesis,
each plate appears successively before the jet. If the plates are moving at a Application
5 velocity of 5 m/s, calculate the force exerted by the jet on the plate, the 4
work done per second on the plate and the efficiency of the jet.
b) Derive an expression for force exerted by fluid jet on moving flat plate.
a) A Pelton wheel is to be designed for the following specifications. Shaft
power = 735.75 KW, head = 200 m, speed = 800 rpm, overall efficiency = Application ,
6 th 4
0.86 and jet diameter not to exceed 1/10 of wheel diameter. Determine i.
wheel diameter, ii. No. of jets required and iii. Diameter of jet. Take Cv=0.98 Comprehension
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
and Kv=0.45.
b) Explain the function of draft tube.
a) Draw and explain OC curves of turbines under constant head. Analysis,
b) A turbine is to operate under a head 25 m at 200 rpm. The discharge is 9
7 Application 4
cumec. If the efficiency is 90% , determine the performance of the turbine
under head of 20 m.
a) How to govern the impulse turbines? Explain with a neat sketch.
b) A turbine develops 9000 KW when running at 100 rpm. The head on the Application ,
8 4
ld
turbine is 30 m. if the head on the turbine reduced to 18m, determine the
Comprehension
speed and power developed by the turbine.
a) Explain the terms;
i. Cavitation and ii. Water hammer Application ,
or
9 b) A Kaplan turbine develops 24647.6 KW power at an average head of 39 4
m. assuming speed ratio of 2, flow ratio of 0.6, diameter of the boss = 0.35 x Comprehension
diameter of the runner and an overall efficiency of 90%. Calculate the
diameter, speed and specific speed of the turbine.
a) Derive an expression for specific speed of a turbine.
b) A Francis turbine with an overall efficiency of 75% is required to produce
W
148.25 KW power. It is working under a head of 7.62 m. the peripheral Synthesis,
10 velocity = 0.26 and the radial velocity of flow at inlet is Application 4
0.96 . The wheel runs at 150 rpm and the hydraulic losses in the
turbine are 22% of the available energy. Assuming radial discharge
determine; i. The guide blade angle, ii. The wheel vane angle at inlet and iii.
Diameter of the wheel at inlet.
TU
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
UNIT-V
BLOOMS
COURSE
S.No QUESTION TAXONOMY
OUTCOME
LEVEL
ld
1 a) What is the necessity of priming in centrifugal pumps?
Knowledge,
3
b) A centrifugal pump is to discharge 0.118 m /s at a speed of 1450 rpm against
a head of 25 m. The impeller diameter is 250 mm, its width at outlet is 50 mm Application 5
and manometric efficiency is 75%. Determine the vane angle at the outer
periphery of the impeller.
2 a) Give the classification of centrifugal pumps.
or
b) A centrifugal pump delivers water against a net head of 14.5 m and a design Application ,
speed of 1000 rpm. The vanes are curved back to an angle of 300 with the 5
periphery. The impeller diameter is 300 mm and outlet width 50 mm. Comprehension
determine the discharge of the pump if manometric efficiency 95%.
3 a) Differentiate between centrifugal and reciprocating pumps.
W
b) The diameter of an impeller of a centrifugal pump at inlet and outlet are 30
Application ,
5
cm and 60 cm respectively. Determine the minimum starting speed of the Comprehension
pump, if it works against a head of 30 m.
4 a) Define NPSH in pumps.
Knowledge,
b) The diameters of an impeller of a centrifugal pump at inlet and outlet are 30
cm and 60 cm respectively. The velocity of flow at outlet is 2 m/s and the vanes Application 5
0
are set back at angle of 45 at the outlet. Determine the minimum starting
TU
speed of the pump, if the manometric efficiency is 70%.
5 a) Explain the importance of multistage centrifugal pump.
b) A four stage centrifugal pump has four identical impellers keyed to the same
shaft. The shaft is running at 400 rpm and the total manometric head developed Application ,
by the multistage pump is 40 m. The discharge through the pump is 0.2 m /s.
3 5
0
the vanes of each impeller are having outlet angle as45 . If the width and Comprehension
diameter of each impeller at outlet is 5 cm and 6 cm respectively. Calculate the
manometric efficiency.
JN
6 a) Explain the working of a reciprocating pump with a neat sketch.
b) A double acting reciprocating pump running at 40 rpm is discharging 1 m 3 of Application ,
5
water per minute. The pump has a stroke of 400 mm. the diameter of the piston
is 200 mm. the delivery and suction heads are 20 m and 5 m respectively. Comprehension
Determine the slip of the pump and the power required to drive the pump.
7 a) What is the function of an air vessel in reciprocating pumps?
Knowledge,
b) A single stage centrifugal pump with impeller diameter of 30 cm rotates at
3
2000 rpm and lifts 3 m of water per second to a height of 30 m with an Application 5
efficiency of 75%. Calculate the no. of stages and diameter of each impeller of a
similar multistage pump to lift 5 m3 of water per second to a height of 200 m
when rotating at 1500 rpm.
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
www.alljntuworld.in JNTU World
8 a) Determine the number of pumps required to take water from a deep well
Application,
under a total head of 89 m all the pumps are identical and running at 800 rpm.
The specific speed of each pump is given as 25 while the rated capacity of each
Analysis 5
pump is 0.16 m3/s.
b) Draw and explain characteristic curves of centrifugal pumps.
9 a) Derive an expression for work done by the centrifugal pump.
3
b) A single-acting reciprocating pump running at 30 r.p.m., delivers 0.012 m /s
of water. The diameter of the piston is 25 cm and stroke length 50 cm. Synthesis,
Determine: Application 5
i. The theoretical discharge of the pump
ii. Co-efficient of discharge, and
iii. Slip and percentage slip of the pump.
ld
10 a) Define the following;
i. Manometric efficiency ii. Mechanical efficiency and
iii. Overall efficiency.
Analyze
b) A single-acting reciprocating pump has a plunger of diameter 250 mm and 5
stroke of 350 mm. if the speed of the pump is 60 rpm and it deliver 16.5 lps of
or
water against a suction head of 5 m and a delivery head of 20 m. Determine the
theoretical discharge, coefficient of discharge, the slip, the percentage of slip
and the power required to drive the pump.
W
TU
JN
Downloaded From JNTU World (http://www.alljntuworld.in)
You might also like
- FM &HM Question BankDocument6 pagesFM &HM Question BankChandra SekharNo ratings yet
- KOM Important QuestionsDocument12 pagesKOM Important QuestionsJithin KNo ratings yet
- TRANSMISSION DESIGNDocument18 pagesTRANSMISSION DESIGNMURALI KRISHNAN RNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials Fill in the BlanksDocument3 pagesStrength of Materials Fill in the BlanksAshok Kumar100% (1)
- Fundamentals of Turbomachines: Centrifugal Compressors ExplainedDocument24 pagesFundamentals of Turbomachines: Centrifugal Compressors ExplainedVIRAJ HADKARNo ratings yet
- FMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsDocument5 pagesFMHM - EEE - Final Exam Important QuestionsBhavani Chandra Unique100% (1)
- U2 Working & AuxiliaryDocument48 pagesU2 Working & AuxiliaryNurye Nigus100% (1)
- Hydraulics FinalDocument2 pagesHydraulics FinalAbel Aregay100% (3)
- Machine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsDocument13 pagesMachine Drawing Two Mark QuestionsHimanshuSisodiyaNo ratings yet
- Scheme – E Sample Question Paper for Fluid Mechanics & MachineryDocument4 pagesScheme – E Sample Question Paper for Fluid Mechanics & MachineryaadhanNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureDocument17 pagesUnit 3 CNC Machine Tools: StructureRohit GhulanavarNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Diganta Hatibaruah50% (2)
- CAD CAM Question BankDocument2 pagesCAD CAM Question BankrsdeshmukhNo ratings yet
- ST7203 Steel Structures Question BankDocument12 pagesST7203 Steel Structures Question BankFinney WilsonNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaDocument54 pagesManufacturing Processes (ME361) Lecture 15: Instructor: Shantanu BhattacharyaSahil SundaNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Machinery: UG-CE-Session-2018 Spring-2020Document10 pagesHydraulic Machinery: UG-CE-Session-2018 Spring-2020Salman100% (1)
- Chapter 9 Evaporator ExercisesDocument1 pageChapter 9 Evaporator ExercisesAndrew PantaleonNo ratings yet
- Assignment Cum Tutorial Sheet - 7 (With Solution)Document2 pagesAssignment Cum Tutorial Sheet - 7 (With Solution)HARSHVARDHAN SINGH RATHORENo ratings yet
- Literature SurveyDocument6 pagesLiterature SurveytalhaNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Machinery: Pumps and Their PerformanceDocument52 pagesFluid Mechanics & Machinery: Pumps and Their PerformanceThiruvasagamoorthy KaNo ratings yet
- Design of Transmission System Question BankDocument18 pagesDesign of Transmission System Question BankAravind50% (2)
- Mechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneDocument4 pagesMechanical Advantage of Inclined PlaneShuja MarwatNo ratings yet
- CE2352 DSS 2 Marks With AnswerDocument33 pagesCE2352 DSS 2 Marks With Answerkavithamartin28No ratings yet
- CH 1Document17 pagesCH 1Pawan Bhattarai100% (1)
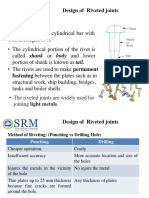
- U-4 - Design of Riveted Joint - SRMDocument87 pagesU-4 - Design of Riveted Joint - SRMsiddharth GautamNo ratings yet
- Manufacturing Technology - I Unit - I: 2 Marks Question & AnswersDocument15 pagesManufacturing Technology - I Unit - I: 2 Marks Question & AnswersSK NAGOOR VALI100% (1)
- KDM 6Document54 pagesKDM 6KarthikeyanRamanujamNo ratings yet
- Question Bank Unit I Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Vibrations: Type ADocument13 pagesQuestion Bank Unit I Chapter 1: Fundamentals of Vibrations: Type AKanhaiyaPrasadNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics Lab ManualDocument43 pagesFluid Mechanics Lab ManualbensonNo ratings yet
- Viva QuestionsDocument3 pagesViva QuestionssanjayshekarncNo ratings yet
- MD ShaftDocument18 pagesMD Shaftiftikhar ahmedNo ratings yet
- Water Resources Engineering AssignmentDocument7 pagesWater Resources Engineering AssignmentAnilkmar P MNo ratings yet
- Tutorial: GEARS II Force AnalysisDocument14 pagesTutorial: GEARS II Force AnalysisNdivhuwo NdivhuwoNo ratings yet
- ME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsDocument16 pagesME6601-Design of Transmission SystemsSecret SecretNo ratings yet
- A7dca BSDZVCFDocument2 pagesA7dca BSDZVCFRAJANo ratings yet
- Machine Design Lab ManualDocument22 pagesMachine Design Lab Manualsarathsaravanan100% (4)
- Notes - Lecture-1-Fluid PropertiesDocument43 pagesNotes - Lecture-1-Fluid PropertiesAbubakar100% (2)
- Moment Diagram PartsDocument10 pagesMoment Diagram Partsنور عليNo ratings yet
- Dimensional Analysis Guide for Fluid MechanicsDocument19 pagesDimensional Analysis Guide for Fluid MechanicsnethmiNo ratings yet
- Types of Cams GuideDocument21 pagesTypes of Cams GuideHarikrishna ShenoyNo ratings yet
- Unit III MCQDocument14 pagesUnit III MCQArun Patil100% (2)
- Nozzle area calculations for steam and gas expansionDocument8 pagesNozzle area calculations for steam and gas expansionAbinCBabuNo ratings yet
- Study Problems PDFDocument33 pagesStudy Problems PDFAbdul Hai MohammedNo ratings yet
- CE8394 Fluid Mechanics and Machinary PDFDocument80 pagesCE8394 Fluid Mechanics and Machinary PDF18M129 Manjeeth SNo ratings yet
- Reaction Turbines ExplainedDocument47 pagesReaction Turbines ExplainedIsmail ibrahim100% (2)
- 28 - 4400 MCQ - IES - GATE - PSUs Mechanical EngineeringDocument21 pages28 - 4400 MCQ - IES - GATE - PSUs Mechanical Engineeringanilm130484meNo ratings yet
- 2 Unit 1 Impact of JetDocument16 pages2 Unit 1 Impact of Jetmohit sonawaneNo ratings yet
- Dynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDocument14 pagesDynamics of Machinery 2 Marks All 5 UnitsDHINAKARANVEEMAN100% (2)
- B. Saint Venant's Theory: (MDSP 1) PageDocument6 pagesB. Saint Venant's Theory: (MDSP 1) PageDhin TolentinoNo ratings yet
- STRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESDocument16 pagesSTRENGTH OF MATERIALS NOTESSrini VasanNo ratings yet
- 04 PPT Mine Fan General PresentationDocument52 pages04 PPT Mine Fan General PresentationHeri WibowoNo ratings yet
- VL2018195002092 Da02Document3 pagesVL2018195002092 Da02ANKUR50% (2)
- Bahir Dar University BiT Engineering ExamDocument17 pagesBahir Dar University BiT Engineering ExamdaveNo ratings yet
- R05220104-Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachineryDocument8 pagesR05220104-Hydraulics and Hydraulic MachinerySRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- Fluid MechanicsDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanicsjayasimha bmNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Fluids and Hydraulic Machines Question BankDocument7 pagesMechanics of Fluids and Hydraulic Machines Question Bankstalinrajesh143No ratings yet
- B.Tech Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines Theory Exam QuestionsDocument2 pagesB.Tech Fluid Mechanics & Fluid Machines Theory Exam QuestionsSparsh PathakNo ratings yet
- Sheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevDocument2 pagesSheet 01 20-21 Properties of Fluid RevBibaswan MukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Code No: 3220304 II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May 2009 (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer Any FIVE Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksDocument7 pagesCode No: 3220304 II B. Tech II Semester Regular Examinations April/May 2009 (Mechanical Engineering) Time: 3 Hours Max. Marks: 80 Answer Any FIVE Questions. All Questions Carry Equal MarksKrishna BhaskarNo ratings yet
- Sorp TivityDocument1 pageSorp TivityREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- RCC Mix Design TemplateDocument9 pagesRCC Mix Design TemplateSatrio UtomoNo ratings yet
- Thixotrpoy ReferenceDocument1 pageThixotrpoy ReferenceREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Aggregate Impact Value Test Procedure and LimitsDocument2 pagesAggregate Impact Value Test Procedure and LimitsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- I-MID Exams Foundation Engineering QuestionsDocument1 pageI-MID Exams Foundation Engineering QuestionsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- AP Model Question Paper For MidDocument2 pagesAP Model Question Paper For MidREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 BitsDocument4 pagesUnit-1 BitsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- RCC Mix Design TemplateDocument9 pagesRCC Mix Design TemplateSatrio UtomoNo ratings yet
- Is 1727 1967Document55 pagesIs 1727 1967VijayKataria0% (1)
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Guidelines ProjectDocument1 pageGuidelines ProjectREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics ObjectiveDocument7 pagesFluid Mechanics ObjectiveREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 BitsDocument4 pagesUnit-1 BitsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- I-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchDocument1 pageI-MID Examinations (Subjective Test) : BranchREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FM .OdtDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FM .OdtREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 BitsDocument4 pagesUnit-1 BitsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 BitsDocument4 pagesUnit-1 BitsREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Assignement 3 FMDocument3 pagesAssignement 3 FMREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TemplateDocument8 pagesLab Report TemplateAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Matrix PDFDocument3 pagesNote Taking Matrix PDFREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Previous Papers 2Document28 pagesPrevious Papers 2REVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Note Taking Matrix PDFDocument3 pagesNote Taking Matrix PDFREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- Lab Report TemplateDocument8 pagesLab Report TemplateAbdul SamadNo ratings yet
- Proven Methods For Design and Operation of Gas Plant Liquid Slug Catching Equipment Gpa 2001 PDFDocument33 pagesProven Methods For Design and Operation of Gas Plant Liquid Slug Catching Equipment Gpa 2001 PDFace4200100% (1)
- Tut 19 DPM ChannelDocument21 pagesTut 19 DPM Channelbecool_bcn75No ratings yet
- Intro To Cloud PhysicsDocument10 pagesIntro To Cloud PhysicsShowna Lee100% (1)
- Venturi Scrubber Theory & ExperimentDocument6 pagesVenturi Scrubber Theory & ExperimentTian Fung Wang100% (1)
- Astm F903Document10 pagesAstm F903MohammedZoheb Hussain100% (2)
- Chapter 2 - Precipitation - EditedDocument26 pagesChapter 2 - Precipitation - EditedAishahShafiqah100% (2)
- Eden, Atlantis and The UFO MythDocument97 pagesEden, Atlantis and The UFO MythLobishome7100% (1)
- A Simple Laboratory Experiment To Measure The Surface Tension of A Liquid in Contact With AirDocument9 pagesA Simple Laboratory Experiment To Measure The Surface Tension of A Liquid in Contact With Airmjs9170No ratings yet
- Grease InterceptorDocument11 pagesGrease Interceptor185412No ratings yet
- United States Patent ToDocument10 pagesUnited States Patent ToDo DornierNo ratings yet
- Upang Cea 4bsce Cie095 P1Document54 pagesUpang Cea 4bsce Cie095 P1Wheng JNo ratings yet
- Electrohydrodynamic Enforcement of Evaporation and Gas FlowDocument7 pagesElectrohydrodynamic Enforcement of Evaporation and Gas FlowMichael ReznikovNo ratings yet
- Separation Equipment Separation Equipment: Section 7 Section 7Document48 pagesSeparation Equipment Separation Equipment: Section 7 Section 7David AL'varado ValenciaNo ratings yet
- R 091825471Document5 pagesR 091825471pgltuNo ratings yet
- TPCurveExplainsOutflowPerformanceDocument2 pagesTPCurveExplainsOutflowPerformanceMuhammad MujahidNo ratings yet
- A Review of Gravity Three - Phase SeparatorsDocument12 pagesA Review of Gravity Three - Phase SeparatorsMelis AllakNo ratings yet
- Tips and Tricks: Voftodpm - 10 Sep 2019: DR Paul Hutcheson Lead Tech Services Engineer, Ansys UkDocument34 pagesTips and Tricks: Voftodpm - 10 Sep 2019: DR Paul Hutcheson Lead Tech Services Engineer, Ansys Ukumair35No ratings yet
- A New Approach For Sizing Finger Slug CatcherDocument15 pagesA New Approach For Sizing Finger Slug CatcherHaryadiNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankDocument9 pagesFluid Mechanics and Hydraulic Machinery Question BankREVANTH KUMAR KNo ratings yet
- IFP Materials PDFDocument52 pagesIFP Materials PDFProcess EngineerNo ratings yet
- Leak Check in GCDocument4 pagesLeak Check in GCfahim2806No ratings yet
- Surface Tension of Molten Aluminum Alloys Measured Under Vacuum and HydrogenDocument6 pagesSurface Tension of Molten Aluminum Alloys Measured Under Vacuum and HydrogenBogdan AndriesNo ratings yet
- 1 Fluid-Properties Tutorial-Solution PDFDocument15 pages1 Fluid-Properties Tutorial-Solution PDFIdate PatrickNo ratings yet
- SurfacetensDocument5 pagesSurfacetensomNo ratings yet
- F25 Mod 3 NotesDocument77 pagesF25 Mod 3 NotesBarrett LongNo ratings yet
- Coalescing Oil Separator DesignDocument22 pagesCoalescing Oil Separator DesignMaxiwendelNo ratings yet
- Quirino State University: Self-Paced Learning ModuleDocument22 pagesQuirino State University: Self-Paced Learning ModuleMaden betoNo ratings yet
- Agglomeration Advisor Oct2010Document5 pagesAgglomeration Advisor Oct2010Hector Andres CabezasNo ratings yet
- Sams DesaltingDocument23 pagesSams DesaltingJose Montenegro100% (4)