Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Mountainview-ITIL V3 Process Poster v3
Uploaded by
Martin LeckCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Mountainview-ITIL V3 Process Poster v3
Uploaded by
Martin LeckCopyright:
Available Formats
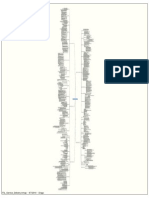
ITIL V3 Processes IT Service Management
Training, Courseware, Consultancy
Goals, Activities, Inputs, Outputs and Roles www.mountainview-itsm.com
Continual Service Improvement
7 Step Improvement Process Service Measurement and Reporting Deming Cycle Plan Do Check Act Continual Service Improvement Model
ITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement
ITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement
ITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement
ITIL V3 Continual Service Improvement
Goal To collect, analyze, process relevant metrics from a process in order to determine its weakness Goal To monitor services and report on improvement opportunities Goal The goal in using the Deming Cycle is steady, ongoing improvement. It is a fundamental tenet Goal To validate monitoring & measuring to validate previous decisions; To direct monitoring &
and establish an action plan to improve the process. of Continual Service Improvement. measuring to set direction for activities to meet set targets. To justify monitoring & measuring
to justify; To intervene to identify a point of intervention including subsequent change
Activities 1 Define what you should measure Activities Service Measurement Activities Plan Establishes goals for improvement including gap analysis, definition of action steps to Activities What is the vision?
2 Define what you can measure Objective (Availability, Reliability, Performance of the Service) close the gap and establishing and implementing measures to assure that the gap has been Where are we now?
3 Gathering the data Developing a Service Measurement Framework closed and benefits achieved. Where do we want to be?
Different levels of measurement and reporting
4 Processing the data Defining what to measure
Do Development and implementation of a project to close the gap. Implementation or How do we get there?
5 Analyzing the data Setting targets improvement of processes and establishing the smooth operation of the process. Did we get there?
6 Presenting and using the information Service management process measurement Check Comparison of the implemented environment to the measures of success established How do we keep the momentum going?
7 Implementing corrective action Creating a measurement framework grid in Plan phase. The comparison determines if a gap still exists between the improvement
Interpreting and using metrics objectives of the process and the operational process state. Repeat the process
Interpreting metrics
Repeat the Process Using measurement and metrics
Act The decision process to determine if further work is required to close remaining gaps,
Creating scorecards and reports allocation of resources necessary to support another round of improvement. Project decisions
CSI policies at this stage are the input for the next round of the lifecycle, closing the loop as input in Plan.
Service Reporting
Reporting policy and rules Repeat the Process
Inputs Each activity has inputs Inputs SLA Targets, SLRs, OLAs, Contracts Inputs Business requirements, External requirements, Security requirements, Request for new service Inputs Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments, Measurable targets,
Service and process measurements Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics
Outputs Each activity has outputs Outputs Service Improvement Program, SLAM Reports Outputs Improved employee morale, New changed services, More effective and efficient processes, Outputs Business vision, mission, goals and objectives, Baseline assessments, Measurable targets
Customer satisfaction, Business results Service & process improvement, Measurements & metrics
Roles Process Owner, Service Manager, CSI Manager, Service Owner Roles Process Owner, Service Manager, CSI Manager, Service Owner Roles Process Owner, Service Manager, CSI Manager, Service Owner Roles Process Owner, Service Manager, CSI Manager, Service Owner
Knowledge Management Process Owner Knowledge Management Process Owner Knowledge Management Process Owner Knowledge Management Process Owner
Reporting Analyst Reporting Analyst Reporting Analyst Reporting Analyst
Service Strategy Service Design Service Operation
Define the Market Develop the Offerings Prepare for Execution Service Level Management Capacity Management Availability Management Event Management Incident Management
Goal To understand the market space and identify opportunities to create value for Customers. Goal To develop outcome-based service that provide the Utility and Warranty to create value to Goal To prepare for and ensure a successful implementation of the Service Strategy by following a Goal To ensure that an agreed level of IT service is provided for all current IT services, and that Goal To ensure that cost-justifiable IT capacity in all areas of IT always exists and is matched to the Goal To ensure that the level of service availability delivered in all services is matched to or exceeds Goal To monitor and control the IT infrastructure to detect, correlate and determine the appropriate Goal To restore normal service operation as quickly as possible and minimize the adverse impact on
customers. rigorous plan. future services are delivered to agreed achievable targets. current and future agreed needs of the business, in a timely manner the current and future agreed needs of the business, in a cost-effective manner. action. To communicate all events that has or can reduce the quality of service to Incident business operations.
Management.
ITIL V3 Service Operation
ITIL V3 Service Operation
Determine, negotiate, document and agree requirements for new or changed services in SLRs Business, Service and Component Capacity Management Instrumentation Identification
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
Activities Define the Strategy and Services Activities Identify the Market Space Activities Strategic assessment Activities Activities Activities Reactive Activities: Activities Activities
ITIL V3 Service Design
ITIL V3 Service Design
ITIL V3 Service Design
Understand the Customers Define Outcome-based Services (value to the customer) Setting objectives Monitor and measure service performance achievements The underpinning activities of Capacity Management: Monitor, measure, analyse and report, service and component availability, Unavailability Event Notification Logging
Understand the Opportunities Develop the Service Portfolio, Pipeline and Catalogue Aligning service assets with customer Outcomes Collate, measure and improve customer satisfaction Utilization monitoring, Response time monitoring, Analysis, Tuning and optimization, analysis, Analyzing the expanded Incident Lifecycle, Service Failure Analysis Event Detection Categorization
Classify and Visualize Services as value-creating patterns Defining critical success factors Produce service reports Implementation, Exploitation of new technology, Designing resilience, Threshold management Proactive Activities: Event Filtering Prioritization
Critical success factors and competitive analysis Conduct service review and instigate improvements and control, Demand Management, Application sizing, Modeling and trending, Baselining, Identifying Vital Business Functions (VBFs), Designing for availability, Base product and Event Significance Determination Initial Diagnosis
Prioritizing investments Review and revise SLAs, service scope OLAs, contracts, UCs Trend analysis, Analytical modeling, Simulation modeling, Producing the Capacity Plan components, Systems management, Service Management processes, High-availability design Event Correlation Escalation
Exploring business potential Develop and document contacts and relationships -Monitoring the capacity Special solutions with full redundancy, Component Failure Impact Analysis, Single Point of Triggering Investigation and Diagnosis
Alignment with customer needs Develop, maintain and operate procedures -Analyzing collected capacity metrics Failure analysis, Fault Tree Analysis, Modelling, Risk Analysis and Management, Availability Response Selection Major Incident Handling
Expansion and growth Log and manage all complaints and compliments -Tuning for optimal capacity testing schedule, Planned and preventative maintenance, Production of the Projected Service Action Review Resolution and Recovery
Differentiation in market spaces Provide the appropriate management information to aid performance management -Implementing capacity improvements through change management Outage (PSO) document, Continual review and improvement Event Closure Closure
Maintain up-to-date SLM document templates and standards -Storage of the monitoring information in the Capacity Database (CDB) Designing for: Redundancy, Reliability, Maintainability, Security, Scalability,
Serviceability
Patterns of Business Activity, Capabilities, Resources, Constraints, Conflicts, Customer assets Value creation, Decision on investments, Asset-based Services, Utility-based Services, Customer constraints, outcomes, tasks Inputs Service Level Requirements, Business information: business strategy, financial plans, Business Impact Inputs Business information: from the organizations business strategy, plans and financial plans, and Business information, Business impact information, Previous Risk Analysis and Assessment Inputs Exceptions to any level of CI performance defined in the design specifications, OLAs or SOPs Inputs Incident record with details sourced from (for example) Service Desk, networks or computer
Inputs Inputs Inputs Inputs
Identification of business outcomes, Understanding of customers, understanding of Analysis: impact, priority, risk and urgency, The Service Portfolio, Pipeline and Service Catalogue, information on their current and future requirements, Service and IT information: from Service reports and a risk register, Service Portfolio and the Service Catalogue, costs, changes, CMS, Exceptions to an automated procedure or process, An exception within a business process that operations, Configuration details from the Configuration Management Database (CMDB),
Change information: forward schedule of changes, CMS, Customer and user feedback and comments Strategy, the IT strategy and plans and current budgets, covering all areas of technology is being monitored by Event Management, The completion of an automated task or job Response from Incident matching against Problems and Known Errors, Resolution details
opportunities SLAs, SLRs, OLA, UCs
Outputs Value creation, Decision on investments, Asset-based Services, Utility-based Services, Outputs Identification of Market space, Outcome-based definition of services, Matching of Service Outputs Strengths, Weaknesses, Distinctive Competencies, Business Strategy, Threat and Outputs Service reports, Service Improvement Plan (SIP), The Service Quality Plan, Service Level Outputs CMIS, Capacity Plan, Service performance information and reports, Workload analysis and Outputs The Availability Management Information System (AMIS), The Availability Plan, Availability and Outputs Incident Management, SNMP messages, which are a standard way of communicating technical Outputs RFC for Incident resolution; Incident record (including resolution and/or Work-arounds),
Identification of business outcomes, Understanding of customers, understanding of portfolio to market space, Service Portfolio (Service Pipeline, Service Catalogue, Retired Opportunities, Prioritization of Investments, Critical Success Factors Agreements (SLAs), Updated Service Level Requirements (SLRs), Operational Level reports, Ad hoc capacity and performance reports, Forecasts and predictive reports, recovery design criteria and proposed, service targets for new or changed services, Service information about the status of components of an IT Infrastructure, Management Information Resolved and closed Incidents, Communication to Customers, Management information
opportunities Services), Business cases, Identification of risks, Pricing, Lines of Service (LOS) Agreements (OLAs), underpinning contracts, Service Review Thresholds, alerts and events availability, reliability and maintainability reports of achievements, Component availability Bases (MIBs) of IT devices, Vendors monitoring tools agent software (reports)
Roles Chief Sourcing Officer; Director of Service Management; Contract Manager; Business Roles Chief Sourcing Officer; Director of Service Management; Contract Manager; Business Roles Chief Sourcing Officer; Director of Service Management; Contract Manager; Business Roles Service Level Manager Roles Capacity Manager Roles Availability Manager Roles Event Manager Roles Incident Manager, Service Desk Manager, Service Desk Agent, Nth-line support
Relationship Manager; Product Manager; Process Owner; Business Representatives Relationship Manager; Product Manager; Process Owner; Business Representatives Relationship Manager; Product Manager; Process Owner; Business Representatives
Develop the Strategic Assets Service Strategy (Creation or Generation) Service Portfolio Management Information Security Management Problem Management
Goal To develop strategic assets in the form of capabilities and resources that provide value to the Goal To define the market space in order to develop service offerings. To understand the resources Goal To proactively manage the investment across the service lifecycle, including those services in Goal To align IT security with business security and ensure that information security is effectively Goal To prevent problems and resulting incidents from happening, to eliminate recurring incidents
customer. and capabilities to establish strategic assets to deliver services that provide value through utility the concept, design and transition pipeline, as well as live services defined in the various managed in all service and Service Management activities and to minimize the impact of incidents that cannot be prevented
and warranty service catalogues and retired services
ITIL V3 Service Operation
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
Activities Develop closed-loop control systems Activities Service Strategy has 4 sub-processes Activities Define: Inventory services, ensure business cases and validate portfolio data Activities Production, review and revision of an overall Information Security Policy and a set of Reactive Problem Management
Activities
ITIL V3 Service Design
Develop strategic assets Define the market Analyze: Maximize portfolio value, align, prioritize & balance supply and demand supporting specific policies Proactive Problem Management
Develop capabilities and resources Develop the offerings Approve: Finalize proposed portfolio, authorize services and resources Communication, implementation and enforcement of the security policies Problem Detection
Develop strategic assets Charter: Communicate decisions, allocate resources and charter services Assessment and classification of all information assets and documentation Problem Logging
Prepare for execution Implementation, review, revision and improvement of a set of security controls and risk Categorization
assessment and responses Prioritization
Monitoring and management of all security breaches and major security incidents Investigation and Diagnosis
Analysis, reporting and reduction of the volumes and impact of security breaches and incidents Workarounds
Schedule and completion of security reviews, audits and penetration tests. Raising a Known Error Record
Problem resolution
Problem Closure
Major Problem Review
Errors detected in the development environment
Inputs Strategic Assessment, Identification of Market space, Outcome-based definition of services, Inputs Business/Customer Requirements; Market Space Analysis; Service Knowledge Management Inputs Service Strategy outputs Inputs Business information. Corporate governance and business security policies and guidelines, Incident Records via recurring incidents, Request Fulfillment feedback and metrics.
Inputs
Matching of Service portfolio to market space, Service Portfolio (Service Pipeline, Service System (SKMS); Service Portfolio; Service Catalogue security plans, Risk Analysis and responses, IT information, Service information, Risk Analysis All proactive Service Lifecycle processes such as Capacity, Availability Management
Catalogue, Retired Services), Business cases, Identification of risks, Pricing, Lines of Service processes and reports, Details of all security events and breaches, Change information, CMS
Outputs Closed-loop system, Service Design Requirements, Service Transition Requirements, Service Outputs Strategies; Policies; Resources and Constraints; Service Level Packages (SLP) - based on Outputs Inventories; Business Case; Service Portfolio; Authorization; Value Proposition; Prioritization; Outputs Security Management Policy, Security Management Information System (SMIS), Revised Management Information, Problem Records , KEDB, Work-arounds , RFCs to Change
Outputs
Operation Requirements, Perspective, Position, Plan and Pattern requirements Communication; Resource allocation security risk assessment reports, Security controls, Audits and audit reports, Security test Management
schedules and plans, Security breaches and major Incidents reports, Supplier security policies
Roles Chief Sourcing Officer; Director of Service Management; Contract Manager; Business Roles Chief Sourcing Officer (CSO); Business Relationship Manager (BRM); Product Manager (PM) Roles Product Manager Roles Security Manager Problem Manager
Roles
Relationship Manager; Product Manager; Process Owner; Business Representatives Director of service management; Contract manager; Business representatives Problem Solving Groups: technical support groups, suppliers support contractors
Process Owner
Financial Management Demand Management Risk Management Service Catalogue Management IT Service Continuity Management Supplier Management Access Management Request Fulfillment
Goal To provides the business and IT with the quantification, in financial terms, of the value of IT Goal To understand and influence Customer demand for Services and the provision of Capacity to Goal To identify and control the exposure to risk, which may have an impact on the delivery of Goal To ensure that a Service Catalogue is produced and maintained, containing accurate Goal To support the overall Business Continuity Management process and ensure that the required
Goal To manage suppliers and the services they supply, to provide seamless quality of IT service to Goal To grant authorized users the right to use a service, while prevent access to non-authorized Goal To provide a channel for users to request and receive standard services for which a pre-defined
services, the value of the assets underlying the provisioning of those services, and the meet these demands services to meet business objectives. To identify the threats and vulnerabilities on service information on all operational services and those being prepared to be run operationally. IT technical and service facilities (including systems, networks, applications, technical support users. To execute the policies and actions defined in Security and Availability Management. approval exists To provide information to users and customers about the availability of services
the business, ensuring value for money is obtained
qualification of operational forecasting. assets and provide measures that mitigate the risk and Service Desk) can be resumed within required, and agreed, business timescales and the procedure for obtaining them. To assist with general information or comments.
ITIL V3 Service Operation
ITIL V3 Service Operation
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
ITIL V3 Service Strategy
Activities Service Valuation Activities Establish Patterns of Business Activity Activities Define a Risk Framework Activities Agreeing and documenting a service definition with all relevant parties Activities Initiation Activities Requesting Access Activities Menu selection
ITIL V3 Service Design
ITIL V3 Service Design
Activities Evaluation of new suppliers and contracts
ITIL V3 Service Design
Service provisioning models and analysis Establish Core Services Packages and Supporting Services Identify the Risks Interfacing with Service Portfolio Management to agree the contents of the Service Portfolio Requirements and Strategy Verification Financial approval
Supplier categorization and maintenance of the Supplier and Contracts Database (SCD)
Funding model alternatives Establish Service Level Packages Identify Risk owners and Service Catalogue Requirements Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Providing Rights Other approval
Establishing new suppliers and contracts
Business Impact Analysis (BIA) Combine SLPs with CSP to build the Service Catalogue with Segmentation Evaluate the Risks Producing and maintaining a Service Catalogue and its contents, in conjunction with the Requirements - Risk Analysis M_o_R Monitoring Identity Status Fulfillment
Supplier and Contract Management and performance
Service Investment Analysis Develop Differentiated Offerings Set Risk Tolerance levels Service Portfolio IT Service Continuity Strategy Logging and Tracking access Closure
Contract renewal and/or termination
Establishing Cost recovery, value centre or accounting centre Identify and select Risk Responses Interfacing with the business and IT Service Continuity Management on the dependencies of Risk Response Measures , Off-site Storage, ITSCM Recovery Options Removing or Restricting Rights
Chargeback Implement Risk Responses business units and their business processes with the supporting IT services, contained within Implementation
Accounting Gain assurances of effectiveness and efficiency the Business Service Catalogue Organizational Planning
Budgeting Embed and Review Interfacing with support teams, suppliers and Configuration Management on interfaces and Testing
Return on Investment Analysis dependencies between IT services and the supporting services, components and CIs Walk-through, Full, Partial, Scenario
Business Case contained within the Technical Service Catalogue On-going Operation
Pre-program ROI Interfacing with Business Relationship Management and Service Level Management to ensure Education, awareness, training, review, testing, Change Management
Post-program ROI that the information is aligned to the business and business process. Invocation
Inputs Demand modeling, Service Portfolio, Service Pipeline, Service Catalogue, retired services Inputs Patterns of Business Activity Inputs Contract Risks, Service Provider Risks, Design Risks, Transition Risks, Operational Risks, Inputs Business information from the organizations business and IT strategy, plans and financial Inputs Business strategy, plans and financial plans, and information on their current and future Inputs An RFC, A Service Request, A request from the appropriate Human Resources Management Inputs Service Desk/Incident Management
Inputs Business information: from the organizations business strategy, plans and financial plans, and
Customer Assets Market Risks, plans, Business Impact Analysis, changes to service requirements, Business requirements, requirements, IT information: from the IT strategy and plans and current budgets, A Business personnel, A request from the manager of a department, who could be performing an HR role,
information on their current and future requirements, Supplier and contracts strategy, Supplier
Customer Outcome Service Portfolio, CMS, Feedback from all other processes Continuity Strategy and a set of Business Continuity Plans: SLAs and SLRs or who could have made a decision to start using a service for the first time.
plans and strategies, Supplier contracts, agreements and targets, budgets
Outputs Service Valuation, service provisioning optimization, planning confidence, service investment Outputs Core Service Packages; Service Level Packages; Lines of Service Outputs Risk responses Outputs The documentation and agreement of a definition of the service, Updates to the Service Outputs Service continuity and recovery plans, ITSCM policy strategies , ITSCM plans , Emergency Outputs Management Information Outputs Self-help systems, Standard Operating Procedures, A strong link is needed between Request
Outputs The Supplier and Contracts Database (SCD), Supplier and contract performance information
analysis, accounting, budgets, charges, fees, compliance, service provisioning models Portfolio: should contain the current status of all services and requirements for services, The Response Plan, Damage Assessment Plan , Salvage Plan , Vital Records Plan, Crisis Identity Fulfillment, Release, Asset and Configuration Management
and reports, Supplier and contract review meeting minutes, Supplier Service Improvement
Service Catalogue Management and Public Relations Plan, Accommodation and Services Plan , Security Plan User information
Plans (SIPs), Supplier survey reports
Roles Financial Manager Roles Business Relationship Manager Roles Risk Manager Roles Service Catalogue Manager Roles IT Service Continuity Manager Roles Access Manager Roles Service Desk
Roles Supplier Manager
Service Desk
Technical and Application Management and Operations Management
Service Transition
Change Management Service Asset & Configuration Mgmt Knowledge Management Service Evaluation Service Validation and Testing Service Transition Planning & Support Release and Deployment Management
Goal To respond to the customers changing business requirements while maximizing value and Goal To define and control the components of services and infrastructure and maintain accurate Goal To enable organizations to improve the quality of management decision making by ensuring Goal To Ensure that the service will be useful to the business is central to successful Service Goal To provide objective evidence that the new/changed service supports the business Goal To plan and coordinate resources to ensure that the requirements of Service Strategy encoded Goal To deploy releases into production and establish effective use of the service in order to deliver
reducing incidents, disruption and re-work. Respond to the business and IT requests for configuration information on the historical, planned and current state of the services and that reliable and secure information and data is available throughout the service lifecycle. Transition and this extends into ensuring that the service will continue to be relevant by requirements, including the agreed SLAs. in Service Design are effectively realized in Service Operations. It is also responsible value to the customer and be able to handover to service operations.
change that will align the services with the business needs. infrastructure. establishing appropriate metrics and measurement techniques. for identifying, managing and controlling the risks of failure and disruption during the transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
ITIL V3 Service Transition
Activities Create and record the RFC Activities Management and Planning Activities Knowledge Management strategy Activities Service evaluation terms Activities Validation and test management Activities Transition strategy Activities Planning
Review RFC and change proposal: Configuration Identification The governance model Evaluation process Plan and design test The Service Transition strategy defines the overall approach to organizing Service Preparation for build, test and Deployment
Filter changes (e.g. incomplete or wrongly routed changes) Configuration Control Organizational changes underway Evaluation plan Verify test plan and test design Transition and allocating resources. Build and Test
Assess and evaluate the change: Status Accounting and Reporting Establishing roles and responsibilities and ongoing funding Understanding the intended effect of a change Prepare test environment Prepare for Service Transition Service testing and pilots
Authorize the change: Verification and Auditing Policies, processes, procedures and methods Understanding the unintended effect of a change Perform tests Review and acceptance of inputs from the other service lifecycle stages Plan and prepare for deployment
Obtain authorization/rejection Technology and other resource requirements Factors for considering the effect of a service change Evaluate exit criteria and report Review and check the input deliverables, e.g. SDP, Service Acceptance Criteria and Perform transfer, deployment and Retirement
Communicate the decision with all stakeholders, in particular the initiator of the Request Performance measures. Evaluation of predicted performance Test clean up and closure evaluation report (see paragraph 4.6.6) Verify deployment
for Change Knowledge transfer Evaluation of actual performance Identifying, raising and scheduling RFCs Early life support
Plan updates Data and information management Risk management Planning and coordinating Service Transition Review and close a deployment
Coordinate change implementation Using the service knowledge management system Planning an individual Service Transition Post implementation review of a deployment through Change Management.
Review and close change Integrated planning Review and close Service Transition
Adopting program and project management best practices
Reviewing the plans
Inputs Policy and strategies for change and release; Request for Change; Change proposal, Plans Inputs Change requests, purchase orders, acquisitions and service requests. Inputs Service Operation Inputs Service package Inputs The Service Package, SLP, Service Provider Interface Definition, Service Design Package, Inputs RFC, CMDB, CMS, SKMS, CAB recommendations, SLAM reports Inputs Authorized RFC, Service package, SLP, SDP, including service model and SAC, IT service
change, transition, release, deployment, test, evaluation and remediation, Current change Operations Staff SDP and SAC Release and Deployment Plans , Acceptance Criteria , RFC continuity plan and related business continuity plan, Service Management and operations plans
schedule and PSO, CMDB, release package, baseline, Test results, test report Problem Management Staff and Transition Staff Test results and report. and standards, Technology and procurement standards and catalogues
Outputs Rejected RFCs, Approved RFCs, Change to the services, service or infrastructure resulting Outputs CMDB, CIs, Attributes, Relationships, SACM provides input to all ITSM processes Outputs Service Knowledge Management Base Outputs Service Portfolio , Service package, SDP, SAC Outputs Configuration baseline of the testing environment, Testing carried out (including options chosen Outputs Policies, processes and practices; service provider interfaces (SPIs), Roles and responsibilities, Outputs Release and deployment plan, Completed RFCs for the release and deployment activities
from approved RFCs, CI, Change schedule, Revised PSO, Authorized change plans, Change Service Operation and Operations Staff Test results and report and constraints encountered), Results from those tests, Analysis of the results, e.g. comparison Transition resource planning and estimation, Transition preparation and training requirements, Service notification, Updated service catalogue with the relevant information about the new or
decisions and actions, Change documents and records, Change Management reports. Problem Management Staff and Transition Staff Evaluation report. of actual results with expected results, risks identified during testing activities. The release and change authorization, Management Information, Transition Plan changed service, New or changed Service Management documentation
Roles Change Manager Roles Service asset manager, Configuration manager, Configuration analyst, Configuration Roles Service Knowledge Management Process Owner Roles Performance and Risk Evaluation Manager Roles Service Test Manager, Build and Test Environment Staff; Test Support: The change manager Roles Service Transition manager Roles Release and Deployment Manager
Change Authority administrator/librarian, CMS/tools administrator, Change manager is responsible for ensuring that tests are developed appropriate to approved changes, Test Early Life Support Deployment Staff
Change Advisory Board (CAB) and Emergency CAB (ECAB) analysts carry out the tests, The developer/supplier is responsible for establishing root cause Release Packaging and Build Manager
Copyright 2010 Mountainview. All rights reserved. Version 3.1 ITIL is a Registered Trademark of the Office of Government Commerce.
You might also like
- Process To PraticesDocument3 pagesProcess To PraticesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideDocument2 pagesITIL 2011 Edition Quick Reference GuideMadhur Sawant100% (2)
- ITIL Process Flows PDFDocument11 pagesITIL Process Flows PDFdanroddNo ratings yet
- Process Vs PraticesDocument1 pageProcess Vs PraticesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Itil and The CMDBDocument5 pagesItil and The CMDBPaul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service DeliveryDocument1 pageITIL Service DeliverygringoricanNo ratings yet
- Itil 2011 Process ModelDocument1 pageItil 2011 Process ModelAlexandru Dan GheorghiuNo ratings yet
- ITIL Handbook WhitepaperDocument42 pagesITIL Handbook WhitepaperRodrigo Silva100% (11)
- Cobit 2019 - IsO20K MappingDocument1 pageCobit 2019 - IsO20K MappingAnish KumarNo ratings yet
- Continual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Definition of CSI InitiativesDocument1 pageContinual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Definition of CSI InitiativesAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Itil Cobit Mapping TemplateDocument6 pagesItil Cobit Mapping Templategobits100% (3)
- Free Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistDocument18 pagesFree Help Desk Evaluation ChecklistNguyen Huu TrungNo ratings yet
- IT4IT Reference Card4Document1 pageIT4IT Reference Card4GuillermoVillalonNo ratings yet
- ITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeaderDocument4 pagesITSM Excellence With Proven Training From The Industry LeadermeetacooldudeNo ratings yet
- CHG Mindmap v4Document1 pageCHG Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enDocument18 pagesChecklist of Recommended ITIL Documents For Processes and Functions enFeleke AfeworkNo ratings yet
- ITIL - Service Validation and TestingDocument17 pagesITIL - Service Validation and TestingFederico MarzulloNo ratings yet
- ITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsDocument5 pagesITIL v.3 Processes & FunctionsAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- CAP Mindmap v4Document1 pageCAP Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2Document43 pagesITIL Service Operation Ver-1.2InvensislearningNo ratings yet
- ITIL - IM KPIs and Reports PDFDocument3 pagesITIL - IM KPIs and Reports PDFkaraspideyNo ratings yet
- ITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapDocument1 pageITIL V3 Service Operation MindmapAllanNo ratings yet
- Checklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018Document18 pagesChecklist of Mandatory Documentation Required by ISO/IEC 20000-1:2018Anas Abu Hijail100% (1)
- ITIL Project Management MethodologyDocument9 pagesITIL Project Management Methodologyapi-3779999No ratings yet
- Interfacing and Adopting ITIL and COBIT PreviewDocument13 pagesInterfacing and Adopting ITIL and COBIT PreviewwilmertorresdNo ratings yet
- ITIL BasicsDocument22 pagesITIL Basicshescribd100% (2)
- Iso 20000 2011.SMDocument36 pagesIso 20000 2011.SMiso20000docsNo ratings yet
- Continual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Process EvaluationDocument1 pageContinual Service Improvement (ITIL CSI) v3 - Process EvaluationAndrea GiulianiNo ratings yet
- Deep Dive: Incident & Problem ManagementDocument6 pagesDeep Dive: Incident & Problem Managementbala2610No ratings yet
- IT Governance - Performance Measures FinalDocument34 pagesIT Governance - Performance Measures FinalYuvi RajhaNo ratings yet
- Pink Elephant SM Implementation RoadmapDocument24 pagesPink Elephant SM Implementation Roadmapkhanhnc2No ratings yet
- CSDM 2.0 White Paper FinalDocument23 pagesCSDM 2.0 White Paper FinalhwyNo ratings yet
- REL Mindmap v4Document1 pageREL Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- BMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperDocument10 pagesBMC - Service Portfolio Management WhitepaperRoss ManningNo ratings yet
- IT Service Management: Using Process To Optimize Technology Resources and Delight CustomersDocument48 pagesIT Service Management: Using Process To Optimize Technology Resources and Delight CustomersJulius Villacruz100% (1)
- ITIL 2011 Foundation Training: ITIL School of ExcellenceDocument97 pagesITIL 2011 Foundation Training: ITIL School of ExcellenceVenki VenkiNo ratings yet
- BMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteDocument4 pagesBMC Remedy IT Service Management SuiteAlexandru SteleaNo ratings yet
- Assessment PDFDocument6 pagesAssessment PDFVamsi aravetiNo ratings yet
- Iso20000 2Document4 pagesIso20000 2Karloz PsyNo ratings yet
- Information Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)Document65 pagesInformation Technology Infrastructure Library (ITIL)Wong Chan WengNo ratings yet
- Exploring ITIL4 Practices Monitor Support FulfilDocument43 pagesExploring ITIL4 Practices Monitor Support FulfilSakuragiNo ratings yet
- ITIL 2011 EbookDocument244 pagesITIL 2011 EbookArin Mukherjee100% (3)
- It Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation ManagerDocument31 pagesIt Service Management: Improvement Plan: BY Uday Mishra, Global It Service Operation Managerrajesh.j162763No ratings yet
- ISO 20k ChecklistDocument7 pagesISO 20k Checklistmaroli_yogeshNo ratings yet
- Example Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateDocument13 pagesExample Copy of ETS Service Catalog TemplateSatish KumarNo ratings yet
- Axios Why ITSM Maturity Should Drive Solution ReplacementDocument57 pagesAxios Why ITSM Maturity Should Drive Solution ReplacementAdnan AbuShahadNo ratings yet
- ITIL-Service StrategyDocument11 pagesITIL-Service StrategyTùng Phạm100% (1)
- ITIL & ServiceDesk PlusDocument40 pagesITIL & ServiceDesk PlusArthur EkowNo ratings yet
- PinkSCAN Change MGMTDocument8 pagesPinkSCAN Change MGMTMartin LeckNo ratings yet
- Itil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeDocument16 pagesItil Capacity Management More Than Charts Over CoffeeAhmed M. EzzatNo ratings yet
- ITSM Process Model v.1.0Document17 pagesITSM Process Model v.1.0DaptarDoangNo ratings yet
- ITIL Service Transition Poster PDFDocument1 pageITIL Service Transition Poster PDFDominic Benedito100% (6)
- FIN Mindmap v4Document1 pageFIN Mindmap v4Paul James BirchallNo ratings yet
- BACE Marketing Presentation FINALDocument14 pagesBACE Marketing Presentation FINALcarlosfelix810% (1)
- KrauseDocument3 pagesKrauseVasile CuprianNo ratings yet
- Minor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsDocument49 pagesMinor Ailments Services: A Starting Point For PharmacistsacvavNo ratings yet
- 88 - 02 Exhaust Manifold Gasket Service BulletinDocument3 pages88 - 02 Exhaust Manifold Gasket Service BulletinGerrit DekkerNo ratings yet
- Ver Notewin 10Document5 pagesVer Notewin 10Aditya SinghNo ratings yet
- ArpitResumeISM PDFDocument1 pageArpitResumeISM PDFchethan rNo ratings yet
- Overcurrent CoordinationDocument93 pagesOvercurrent CoordinationKumar100% (1)
- United States v. Manuel Sosa, 959 F.2d 232, 4th Cir. (1992)Document2 pagesUnited States v. Manuel Sosa, 959 F.2d 232, 4th Cir. (1992)Scribd Government DocsNo ratings yet
- Syed Hamid Kazmi - CVDocument2 pagesSyed Hamid Kazmi - CVHamid KazmiNo ratings yet
- Rehabilitation and Retrofitting of Structurs Question PapersDocument4 pagesRehabilitation and Retrofitting of Structurs Question PapersYaswanthGorantlaNo ratings yet
- Design & Construction of New River Bridge On Mula RiverDocument133 pagesDesign & Construction of New River Bridge On Mula RiverJalal TamboliNo ratings yet
- CBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIDocument72 pagesCBC Building Wiring Installation NC IIFaysbuk KotoNo ratings yet
- Service Manual: Model: R410, RB410, RV410, RD410 SeriesDocument116 pagesService Manual: Model: R410, RB410, RV410, RD410 SeriesJorge Eustaquio da SilvaNo ratings yet
- PovidoneDocument2 pagesPovidoneElizabeth WalshNo ratings yet
- Kompetensi Sumber Daya Manusia SDM Dalam Meningkatkan Kinerja Tenaga Kependidika PDFDocument13 pagesKompetensi Sumber Daya Manusia SDM Dalam Meningkatkan Kinerja Tenaga Kependidika PDFEka IdrisNo ratings yet
- Braga - 2016 - On Standing's A Precariat Charter - Confronting The Precaritisation of Labour in Brazil and PortugalDocument12 pagesBraga - 2016 - On Standing's A Precariat Charter - Confronting The Precaritisation of Labour in Brazil and PortugalLiam MurciaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixDocument53 pagesChapter 2 A Guide To Using UnixAntwon KellyNo ratings yet
- Aluminium Extrusion Industry in IndiaDocument3 pagesAluminium Extrusion Industry in Indiakalan45No ratings yet
- Service Manual Lumenis Pulse 30HDocument99 pagesService Manual Lumenis Pulse 30HNodir AkhundjanovNo ratings yet
- Ficha Tecnica 320D3 GCDocument12 pagesFicha Tecnica 320D3 GCanahdezj88No ratings yet
- Installation and User's Guide For AIX Operating SystemDocument127 pagesInstallation and User's Guide For AIX Operating SystemPeter KidiavaiNo ratings yet
- SC-Rape-Sole Testimony of Prosecutrix If Reliable, Is Sufficient For Conviction. 12.08.2021Document5 pagesSC-Rape-Sole Testimony of Prosecutrix If Reliable, Is Sufficient For Conviction. 12.08.2021Sanjeev kumarNo ratings yet
- Lenskart SheetDocument1 pageLenskart SheetThink School libraryNo ratings yet
- Random Variable N N Mean or Expected Value: Number of Ducks Type of Duck AmountDocument2 pagesRandom Variable N N Mean or Expected Value: Number of Ducks Type of Duck AmountAngie PastorNo ratings yet
- Go Ask Alice EssayDocument6 pagesGo Ask Alice Essayafhbexrci100% (2)
- Te 1569 Web PDFDocument272 pagesTe 1569 Web PDFdavid19890109No ratings yet
- Load Sharing Strategies in Multiple Compressor Refrigeration SystemsDocument8 pagesLoad Sharing Strategies in Multiple Compressor Refrigeration SystemsLiu YangtzeNo ratings yet
- Bill Swad's Wealth Building Strategies - SwadDocument87 pagesBill Swad's Wealth Building Strategies - Swadjovetzky50% (2)
- EE1000 DC Networks Problem SetDocument7 pagesEE1000 DC Networks Problem SetAmit DipankarNo ratings yet
- Nisha Rough DraftDocument50 pagesNisha Rough DraftbharthanNo ratings yet