Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Electical Circuit and Machine - Revised
Uploaded by
Debendra Bahadur RautOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Electical Circuit and Machine - Revised
Uploaded by
Debendra Bahadur RautCopyright:
Available Formats
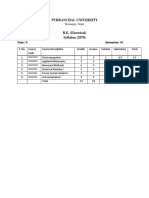
ELECTRIC CIRCUIT AND MACHINES
BEG221EI
Year: 2 Semester: 1
Teaching Examination Scheme Total Marks Remarks
Schedule
Hours/
week
Final Internal
Assessments
Theory Practical Theory Marks Practical
Marks
L P T Duration Marks Duration Marks
Hours
8 2 12
3 2/2 2 3 0 -- -- 20 5 5
Course Content;
1.0 Introduction: (2 hours)
1.1 Energy sources and productions
1.2 Generation, transmission and distribution of electrical power.
2.0 Passive elements and laws in electrical engineering: (7 hours)
2.1 Electric current and emf
2.2 Resistance, resistivity, temperature coefficient of resistance, variation of resistance with
temperature
2.3 Series and parallel combination of resistor.
2.4 Ohms law and its application.
2.5 Inductor, induction, inductance in series and parallel.
2.6 Faradays laws of electromagnetic induction.
2.7 Capacitance, capacitor in series and parallel.
2.8 Kirchoffs Law and their application using mesh analysis and nodal analysis method.
3.0 Network theorems: (7 hours)
3.1 Star-delta transformation and Delta-star transformation
3.2 Thevenins Theorem
3.3 Super position theorem
3.4 Maximum power transmission theorem
4.0 A.C Fundamentals (8hours)
4.1 Generation of AC
4.2 Waveform and terms used in AC
4.3 Average and r.m.s values of current and voltage
4.4 Phasor representation- resistive, inductive, capacitive circuits, voltage and current
waveforms.
4.5 Series RC, Series RL, Series and parallel RLC circuit and their phasor representation.
Proposed for revision on Mangsir 2068
4.6 Resonance in Series and parallel RLC circuit.
4.7 Power factor.
5.0 Lighting devices, wiring system and protective devices (2 hour)
5.1 Different types of lighting system
Incandescent
Tungsten- halogen
Compact florescent lamp
Tubular Florescent
5.2 Types of wiring
Open wiring
Conceal wiring
5.3 Grounding/Earthing
5.4 System grounding, Equipment Grounding
5.5 Types of grounding
5.6 Definitions of protection devices
Fuse
MCB
Lightning arrestor
6.0 Transformer: (5 hours)
6.1 Transformer-Construction, working principle
6.2 Emf equation of transformer
6.3 Voltage and current transformation ratio of transformer
6.4 Losses and efficiency of transformer.
7.0 D.C machines: (7 hours)
7.1 D.C generators: operating principle of dc generator, method of excitation, armature
reaction.
7.2 D.C motor: Operating principle of dc motor, back emf in dc motor, types of d.c motor and
their characteristic.
8.0 A.C machines: (7 hours)
8.1 Induction motor: Introduction and construction of three phase induction motor, operating
principle of three phase induction motor.
8.2 Synchronous Machine:
8.2.1 Synchronous Generator: Construction of synchronous generator, advantages of
rotating magnet system and stationary armature system, parallel operation and
synchronization.
8.2.2 Synchronous Motor: Synchronous speed, Construction and operating principle
of synchronous motor.
Textbooks:
1. Basic Electrical Engineering, A. Kasatkin and M. Perakalin, MIR Publisher,
Moscow, 1970.
Proposed for revision on Mangsir 2068
2. Electrical Engineering- An introductions, Steven E. Schwarz and William G.
Oldhan, Holt, Rinehart and Winston Publishers, New Yourk, 1984.
3. A textbook of Electrical Technology, B.L.Theraja and A.K.Theraja,S.Chand and
company Ltd.
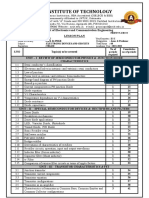
Marks distribution: (Electric Circuit and Machines)
Chapter Hours Mark distribution
1 2 6
2 7 12
3 7 16
4 8 12
5 2 4
6 5 10
7 7 10
8 7 10
2,3,4,5,7,8 4*4=16
Note:
Students have to answer ____ questions out of _____.
The marks distribution may differ slightly.
Proposed for revision on Mangsir 2068
You might also like
- Electric Circuit & MachinesDocument2 pagesElectric Circuit & MachinesAnil MarsaniNo ratings yet
- Be Civil 3rd Semester Syllabus1492571380 PDFDocument17 pagesBe Civil 3rd Semester Syllabus1492571380 PDFMadrid A-ameer TamangNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuits CourseDocument3 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuits Coursesahale sheraNo ratings yet
- BDU Electrical Machines Electronics FundamentalsDocument4 pagesBDU Electrical Machines Electronics FundamentalswondieNo ratings yet
- Sem 4 PDFDocument19 pagesSem 4 PDFmaziyaNo ratings yet
- Sem 6Document29 pagesSem 6Abhishek ShekharNo ratings yet
- EEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Document2 pagesEEE2002 Semiconductor Devices and Circuits - Win - 17 - 18Srirevathi BalapattabiNo ratings yet
- Applied MechatronicsDocument17 pagesApplied MechatronicsWilliam Hamonangan SiahaanNo ratings yet
- Theory: Total 18 - 80 320 - 400Document20 pagesTheory: Total 18 - 80 320 - 400Itz AjiTNo ratings yet
- Electrical EngineeringDocument22 pagesElectrical EngineeringArushi MohapatraNo ratings yet
- Sylllabus of 4th Semester - 25062022Document26 pagesSylllabus of 4th Semester - 25062022Suman GhoshNo ratings yet
- Linear ElectronicsDocument4 pagesLinear ElectronicsGreesh MaheshwariNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument4 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics EngineeringshishirNo ratings yet
- Syllabus in Fund. Elec3cty and Elec2ronicsDocument6 pagesSyllabus in Fund. Elec3cty and Elec2ronicsJohn Raymund MabansayNo ratings yet
- Purbanchal University: Biratangar, NepalDocument15 pagesPurbanchal University: Biratangar, NepalRam Krishna ThapaNo ratings yet
- The Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon NemsadzeDocument231 pagesThe Georgian Technical University The Department of Electrical Engineering and Electronics Simon Nemsadzepeter vanderNo ratings yet
- Electrical Engineering IIDocument2 pagesElectrical Engineering IIAprajita KayasthaNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringDocument20 pages3.1 Fundamentals of Electrical EngineeringmadhurithaNo ratings yet
- Mikael Sahrling - Fast Techniques For Integrated Circuit Design-Cambridge University Press (2019)Document258 pagesMikael Sahrling - Fast Techniques For Integrated Circuit Design-Cambridge University Press (2019)GiridharKumar Gudimetla100% (1)
- Nria20 Edc Lesson PlanDocument2 pagesNria20 Edc Lesson PlanD. Ravi ShankarNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem 4 Electrical EngineeringDocument31 pages4th Sem 4 Electrical EngineeringSajan MahatoNo ratings yet
- Course in Electrical Machines and SystemsDocument85 pagesCourse in Electrical Machines and SystemsvozoscribdNo ratings yet
- Applied MechatronicDocument16 pagesApplied MechatronicDuong Van Tu33% (3)
- 18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFDocument125 pages18eln mergedPDFdocs PDFsuhas kumarNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Simulation of Grid Connected PV SystemDocument86 pagesModeling and Simulation of Grid Connected PV SystemKandarp Mathane100% (2)
- IIT Roorkee Electronics SyllabusDocument3 pagesIIT Roorkee Electronics Syllabusadsfasfd123No ratings yet
- Consolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0Document15 pagesConsolidated 4th Sem Scheme and Syllabus Updated0pranavrajrkmvNo ratings yet
- Analog CircuitsDocument2 pagesAnalog CircuitsSai SharanNo ratings yet
- 3361702Document7 pages3361702josephNo ratings yet
- Gujarat Technological University: Diploma in Electrical EngineeringDocument24 pagesGujarat Technological University: Diploma in Electrical EngineeringSagarNo ratings yet
- Nettur Technical Training Foundation DTCDocument170 pagesNettur Technical Training Foundation DTCRANJANI RAGHUNATHANNo ratings yet
- CemDocument95 pagesCemAnonymous hzXy93FAENo ratings yet
- 3rd SEM SYLLABUS..Document24 pages3rd SEM SYLLABUS..FacebookNo ratings yet
- 4th Sem - 4 - Electrical EngineeringDocument36 pages4th Sem - 4 - Electrical Engineeringdgangopadhyay3064No ratings yet
- CMO 97 S. 2017 BS Mechanical Engineering ProgramDocument94 pagesCMO 97 S. 2017 BS Mechanical Engineering Programryan fernandez100% (1)
- Course Outline EDC Dr. HussainDocument6 pagesCourse Outline EDC Dr. Hussainarkhanjee12No ratings yet
- CMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Document93 pagesCMO No. 97 Series of 2017 Policies Standards and Guidelines For The Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering BSME Program Effective Academic Year 2018 2019Jeremiah PuaNo ratings yet
- Common ETC & AEIDocument22 pagesCommon ETC & AEIChittaranjan PaniNo ratings yet
- Electronics IDocument4 pagesElectronics IMark NealNo ratings yet
- BlackbookDocument42 pagesBlackbookJyotsna AnandNo ratings yet
- Basic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (EEE1001Document2 pagesBasic Electrical and Electronics Engineering (EEE1001bhavay 07100% (1)
- BECE206L_ANALOG-CIRCUITS_TH_1.0_0_BECE206LDocument3 pagesBECE206L_ANALOG-CIRCUITS_TH_1.0_0_BECE206LAman TrivediNo ratings yet
- Model Question Bank - EDCDocument12 pagesModel Question Bank - EDCsangeetadineshNo ratings yet
- II I ES Lab Manual PDFDocument80 pagesII I ES Lab Manual PDFDeepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- Important Edc TasksDocument2 pagesImportant Edc TasksUmer Farooq AzamNo ratings yet
- Electrical Craft Principles Volume 2 5th Edition PDFDocument429 pagesElectrical Craft Principles Volume 2 5th Edition PDFRafael olivaresNo ratings yet
- Institut Teknologi Del: ELS2101 - Rangkaian ElektrikDocument4 pagesInstitut Teknologi Del: ELS2101 - Rangkaian ElektrikGottlieb Fyeter SitohangNo ratings yet
- RP 5Document34 pagesRP 5Masood AlamNo ratings yet
- Solar Photovoltaic System With Pi Controller For Maintaing Constant Cpi VoltagesDocument11 pagesSolar Photovoltaic System With Pi Controller For Maintaing Constant Cpi VoltagesAravind ChunduriNo ratings yet
- Eee 6Document28 pagesEee 6nmcdelhiNo ratings yet
- B.Tech Third Semester SyllabusDocument123 pagesB.Tech Third Semester SyllabuskdsahooNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics and Drives Course OutlineDocument3 pagesPower Electronics and Drives Course OutlineBiselary FinahNo ratings yet
- Tutorial LetterDocument14 pagesTutorial LetterGerryRushNo ratings yet
- Ajith Content ACKNOWLEDGEMENTDocument9 pagesAjith Content ACKNOWLEDGEMENTSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Electronic Devices and Circuits: I.J. NagrathDocument11 pagesElectronic Devices and Circuits: I.J. NagrathshivanshNo ratings yet
- Double Frequency Buck ConverterDocument68 pagesDouble Frequency Buck ConverterSanthosh GuduruNo ratings yet
- C-14-Deee-V&vi SemsDocument87 pagesC-14-Deee-V&vi Semsd ramNo ratings yet
- Electronic Control of Switched Reluctance MachinesFrom EverandElectronic Control of Switched Reluctance MachinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (5)
- Internal Assessment-1Document1 pageInternal Assessment-1Debendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Internal Assessment-1Document1 pageInternal Assessment-1Debendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- 0 - MCC Agreement in English PDFDocument155 pages0 - MCC Agreement in English PDFNarayan pyakurelNo ratings yet
- Tutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDocument3 pagesTutorial-2 EE AC, 1-Phase PartDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Final PDFDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship Final PDFDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- 0 - MCC Agreement in English PDFDocument155 pages0 - MCC Agreement in English PDFNarayan pyakurelNo ratings yet
- Compiled Economic Survey English 2019/20Document256 pagesCompiled Economic Survey English 2019/20Hanu ManNo ratings yet
- RETS Nepal UN Report PDFDocument42 pagesRETS Nepal UN Report PDFDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- के हो MCC ?Document77 pagesके हो MCC ?saroj NepaliNo ratings yet
- CS - Bit 4Document3 pagesCS - Bit 4Debendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- 1.3 Energy Management & AuditDocument25 pages1.3 Energy Management & AuditEdd GithaeNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurship Final PDFDocument3 pagesEntrepreneurship Final PDFDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Biogas PDFDocument17 pagesBiogas PDFDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Journal of Renewable EnergyDocument6 pagesJournal of Renewable EnergyDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Annual Report 2010 (62-67)Document84 pagesAnnual Report 2010 (62-67)Debendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Diesel Consumption Litres 12092009Document1 pageDiesel Consumption Litres 12092009Debendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- MSREE Curriculum 2061 December PDFDocument69 pagesMSREE Curriculum 2061 December PDFRavi DuttaNo ratings yet
- SyllabusDocument2 pagesSyllabusDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- MSc Research Proposal Writing GuidelinesDocument2 pagesMSc Research Proposal Writing GuidelinesDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Implementation of Grid-Connected Solar PV With HarmoDocument73 pagesAnalysis and Implementation of Grid-Connected Solar PV With HarmoDebendra Bahadur RautNo ratings yet
- Letusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 SolutionDocument20 pagesLetusc (By Yashvant Kanetkar) Chapter 1 Solutiontooba mukhtarNo ratings yet
- Section 8.2: Monte Carlo Estimation: Discrete-Event Simulation: A First CourseDocument19 pagesSection 8.2: Monte Carlo Estimation: Discrete-Event Simulation: A First CoursessfofoNo ratings yet
- Cl451midsem14 AnswersDocument5 pagesCl451midsem14 AnswersRahul MalhotraNo ratings yet
- DesmosDocument14 pagesDesmosapi-433553650No ratings yet
- Aerospace Engineering Sample Report PDFDocument4 pagesAerospace Engineering Sample Report PDFDuncan LeeNo ratings yet
- Unidrive M700-M701 and M702 Control UG Issue 2 (0478-0353-02) - ApprovedDocument286 pagesUnidrive M700-M701 and M702 Control UG Issue 2 (0478-0353-02) - Approvednorbert0% (1)
- Functions for Physics ClassDocument294 pagesFunctions for Physics ClassdjinachhgdgyudfgNo ratings yet
- 20 Annual: American Mathematics CompetitionsDocument8 pages20 Annual: American Mathematics CompetitionsLong NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Syl&Scheme 1 Styear 2018Document31 pagesSyl&Scheme 1 Styear 2018Aryan GuptaNo ratings yet
- Priority Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderDocument6 pagesPriority Encoder: 4-To-2 Bit Binary EncoderAditya Prakash100% (1)
- Activity 4.2 Polya's StrategyDocument2 pagesActivity 4.2 Polya's StrategyQueenNo ratings yet
- Illustrator Assignment #1Document2 pagesIllustrator Assignment #1cshaver6637No ratings yet
- CSC 270 - Survey of Programming Languages: C++ Lecture 2 - Strings Credited To Dr. Robert SiegfriedDocument49 pagesCSC 270 - Survey of Programming Languages: C++ Lecture 2 - Strings Credited To Dr. Robert SiegfriedIsabellaPeriginaNo ratings yet
- Wolfe - Cellular ThermodynamicsDocument13 pagesWolfe - Cellular Thermodynamicsandres_old_condeNo ratings yet
- Class 10th Model Question Paper Maths PDFDocument6 pagesClass 10th Model Question Paper Maths PDFXxyyzzNo ratings yet
- Vinod, Hrishikesh D. - Hands-On Matrix Algebra Using R (2011) PDFDocument348 pagesVinod, Hrishikesh D. - Hands-On Matrix Algebra Using R (2011) PDFJeison RomeroNo ratings yet
- Quantum simulation of negative hydrogen ion using VQEDocument16 pagesQuantum simulation of negative hydrogen ion using VQEiviNo ratings yet
- Types in DafnyDocument21 pagesTypes in DafnyFelipe HsuNo ratings yet
- GCSE Mathematics 1F MSDocument13 pagesGCSE Mathematics 1F MSMIhaela CorcheNo ratings yet
- Eric Herrmann ResumeDocument1 pageEric Herrmann Resumeapi-237754499No ratings yet
- Elastic-Plastic Incremental Analysis Using ETABSDocument12 pagesElastic-Plastic Incremental Analysis Using ETABSAwrd A AwrdNo ratings yet
- Librecad Users Extensive Manual: 1.1 Documents Purpose and CreditsDocument77 pagesLibrecad Users Extensive Manual: 1.1 Documents Purpose and CreditsAhmad Arif SaktiNo ratings yet
- Amc 14 QsDocument6 pagesAmc 14 Qsjoebloggs_comNo ratings yet
- P5 Maths 2019 SA2 Raffles Girls' Exam PaperDocument35 pagesP5 Maths 2019 SA2 Raffles Girls' Exam PaperAqil SubendiNo ratings yet
- Development and Validation of An Internationally Reliable Short-Form of The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS)Document16 pagesDevelopment and Validation of An Internationally Reliable Short-Form of The Positive and Negative Affect Schedule (PANAS)aldemar reyes alvisNo ratings yet
- Abdullah Abid - Worksheet - FractionsDocument3 pagesAbdullah Abid - Worksheet - FractionsAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Progressive BaccaratDocument36 pagesProgressive BaccaratCarlos Andres0% (1)
- Nishant Vora's 7+ Years Teaching Experience and AwardsDocument60 pagesNishant Vora's 7+ Years Teaching Experience and AwardsArnav AdarshNo ratings yet
- Newton Raphson Method Example-2 F (X) 2x 3-2x-5Document3 pagesNewton Raphson Method Example-2 F (X) 2x 3-2x-5Rashid Abu abdoonNo ratings yet