Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Midterm 1
Uploaded by
tt_aljobory3911Original Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Midterm 1
Uploaded by
tt_aljobory3911Copyright:
Available Formats
ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Electronic Circuits Fall 2002
Midterm 1 Total: 300 points
Problem MT1.1 (100 pts)
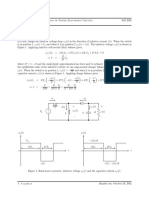
Consider
PSfrag the parallel LC circuit shown below where the current source is a step function given by i s (t) =
replacements
Is u(t). In other words, is (t) = 0 for t < 0 and is (t) = Is for t > 0. Initial conditions on the capacitor before
is (t) switches from 0 to Is are vC (0 ) = 0 and iL (0 ) = 0.
is (t)
iL (t) iC (t)
Is + +
is (t) vL (t) L vC (t) C
t
Figure 1: LC circuit considered in questions 15.
1. (10 pts) Determine vC (0+ ) and iL (0+ ) (i.e., the initial conditions after is (t) switches from 0 to Is ).
2. (10 pts) Write the differential equations for iL (t) and vC (t) for t 0+ .
diL (t) dvC (t)
3. (10 pts) What are the slopes of iL (t) and vC (t) at t = 0+ ? (Evaluate dt and dt at t = 0+ ).
4. (20 pts) Calculate iL (t) and vC (t) for t 0+ . You can use any method you prefer but you must show
all of your work. Make sure that you define any variables you use.
5. (10 pts) Sketch iL (t) and vC (t) for t 0+ . Make sure that you carefully mark all of the important
values on the axes.
6. (20 pts) Suppose that an ideal diode D is added to the original LC circuit as shown below. (a) How
does the presence of the diode change the waveforms for vC (t) and iL (t) that you determined in part
5. Explain in full detail what is happening to the voltages/currents of the capacitor, inductor and the
PSfrag
diode. replacements
(b) Plot vC (t) and iL (t) in the presence of the diode. Make sure that you carefully mark all of
the important valuest on the axes.
7. (10 pts) How much energy (WC ) is stored in the capacitor at t = 0+ and at t = ? How much energy
Is
(WL ) is stored in the inductor at t = 0+ and at t = ?
8. (10 pts) How much energy (Ws ) is delivered by the current source is (t) from t = 0+ to t = ?
iL (t) iC (t)
+ +
is (t) vL (t) L vC (t) C D vD
iD +
Figure 2: LCD circuit considered in questions 6-8.
V. Caliskan 1 October 10, 2002
ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Electronic Circuits Fall 2002
Midterm 1 Total: 300 points
Problem MT1.2 (100 pts)
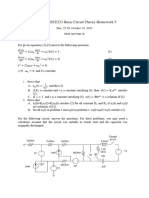
Consider the full-wave rectifier shown in the figure below where vs (t) = Vs sin(t). All four diodes in the
rectifier are ideal.
PSfrag replacements
vD1 D1 D2
is (t) +
+
+
vs (t) vd (t)
Id
D4 D3
iD4
Figure 3: Full-wave rectifier with constant-current load.
1. (10 pts) Calculate and sketch the output voltage vd (t). Clearly indicate which diodes are conducting
during different intervals of operation.
2. (10 pts) What is hvd i, the average value of vd (t)?
3. (10 pts) Calculate and sketch is (t), the source input current.
4. (10 pts) What is his i, the average value of is (t)?
5. (10 pts) What is Is,rms , the rms value of is (t)?
6. (10 pts) Determine and sketch vD1 , the anode to cathode voltage of diode D1 .
7. (10 pts) Determine hvD1 i, the average value of vD1 .
8. (10 pts) Determine and sketch iD4 , the anode to cathode current of diode D4 .
9. (10 pts) Determine hiD4 i, the average value of iD4 .
10. (10 pts) Calculate the power factor kp of the source.
V. Caliskan 2 October 10, 2002
Id
ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Electronic Circuits Fall 2002
Midterm 1 Total: 300 points
Problem MT1.3 (100 pts)
Consider the phase-controlled rectifier shown in the figure below where vs (t) = Vs sin(t). The thyristors
given in the circuit are ideal. Each thyristor is controlled the gate currents given in the figure where the
firing angle is in the range 0 < < .
iG1
is (t) T1
0
+ t
iG1 + 2 2+
2 vs (t) iG2 vd (t) Id
T2
3 iG2
4
/2
3/2
5/2 2 2+
t
7/2 +
Figure 4: Phase-controlled rectifier with constant-current load.
1. (20 pts) Determine and sketch the output voltage vd (t). Clearly indicate which thyristors are con-
ducting during different intervals of operation.
2. (10 pts) Determine and sketch the source current is (t).
3. (10 pts) What is hvd i, the average value of vd (t)?
4. (10 pts) Plot the control characteristics (hvd i vs. ) of this rectifier for 0 < < .
5. (10 pts) Calculate the average power delivered to the load by the voltage source v s (t).
6. (10 pts) Calculate S, the apparent power of voltage source vs (t).
7. (10 pts) Calculate the power factor kp of the source.
8. (10 pts) Is this rectifier capable of inversion? If yes, over what range of is inversion possible.
9. (10 pts) How does the operation of the rectifier change as 0? Comment on what happens to
vd (t), hvd i, is (t) and kp .
V. Caliskan 3 October 10, 2002
You might also like
- State Space Averaging ExplainedDocument50 pagesState Space Averaging ExplainedSomnath MaityNo ratings yet
- R. W. EricksonDocument51 pagesR. W. EricksonVanshika JindalNo ratings yet
- Steady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and EfficiencyDocument128 pagesSteady-State Equivalent Circuit Modeling, Losses, and Efficiencyselaroth168No ratings yet
- Capacitors, Inductors, Sinusoidal Signals and Phasor TransformationDocument38 pagesCapacitors, Inductors, Sinusoidal Signals and Phasor TransformationjunkmailtarsierNo ratings yet
- Ch2 Power Computation 2 in One 2023-09-09Document30 pagesCh2 Power Computation 2 in One 2023-09-09hsiaopeihsuanNo ratings yet
- EE GATE 2017 Forenoon-Sesstion-1Document48 pagesEE GATE 2017 Forenoon-Sesstion-1Hema LathaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 11Document6 pagesAssignment 11Arvind SahuNo ratings yet
- 1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto FDocument5 pages1091 Circuit Theory HW1 Solution: Tera T Giga G (Femto F曾燒餅No ratings yet
- Buck-Boost Converter Analysis and DesignDocument3 pagesBuck-Boost Converter Analysis and DesignNurujjamanKhan0% (1)
- ENAD Problem BookletDocument37 pagesENAD Problem BookletPruthvi NinganurNo ratings yet
- 2021 Eir 211 E01 MemoDocument22 pages2021 Eir 211 E01 MemoVaibhav ParshutamNo ratings yet
- Assignment 4 Alcisto Instrumentation and ControlDocument8 pagesAssignment 4 Alcisto Instrumentation and Controlmatt DonorNo ratings yet
- Calculation of Thermal Equivalent Short-Time CurrentDocument12 pagesCalculation of Thermal Equivalent Short-Time CurrentAnonymous yD6Qpiq3No ratings yet
- Special Topics in Power - 1Document38 pagesSpecial Topics in Power - 1Ravichandran SekarNo ratings yet
- Powersys 3Document39 pagesPowersys 3setsindia3735No ratings yet
- Powersys 4Document39 pagesPowersys 4setsindia3735No ratings yet
- EE2023 Signals & Systems Revision Notes: 1 Circuit Elements and Their ModelsDocument15 pagesEE2023 Signals & Systems Revision Notes: 1 Circuit Elements and Their ModelsFarwaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesDocument25 pagesChapter 1 - Electric Circuit Variables: ExercisesMilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 DC To DC Converters: OutlineDocument25 pagesChapter 5 DC To DC Converters: OutlinemadihaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part IDocument68 pagesChapter 3 Part IDaniel MengeshaNo ratings yet
- Melbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017Document34 pagesMelbourne School of Engineering ELEN30009 Electrical Network Analysis & Design Semester 1, 2017RogerNo ratings yet
- CapacitorDocument2 pagesCapacitorsreekantha reddyNo ratings yet
- R. W. Erickson: Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, BoulderDocument37 pagesR. W. Erickson: Department of Electrical, Computer, and Energy Engineering University of Colorado, BoulderVijay Kumar LoluguNo ratings yet
- Transfer Function and Controller DesignDocument14 pagesTransfer Function and Controller DesignBart llNo ratings yet
- Electrical Transient AnalysisDocument17 pagesElectrical Transient Analysisdeepshikhasharma230191No ratings yet
- ECEN 4797 Homework Assignment #1 AnalysisDocument3 pagesECEN 4797 Homework Assignment #1 Analysisollata kalanoNo ratings yet
- ELEC3400 Signal Processing Course NotesDocument68 pagesELEC3400 Signal Processing Course NotesCallan Fair BearNo ratings yet
- Eel2010 C28Document8 pagesEel2010 C28Dikshant Gupta (B21CI014)No ratings yet
- Week 7Document24 pagesWeek 7Priyank PatelNo ratings yet
- Eca 1 ProblemsDocument15 pagesEca 1 ProblemsAhmed SohailNo ratings yet
- ProblemSet5Solutions PDFDocument4 pagesProblemSet5Solutions PDFIván MartínezNo ratings yet
- Problem Solving of Power ElectronicsDocument4 pagesProblem Solving of Power ElectronicsAlca Li100% (1)
- PE Chap 1.fundamental DefinitionsDocument48 pagesPE Chap 1.fundamental DefinitionsThành Trần BáNo ratings yet
- Esc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsDocument34 pagesEsc201t l10 RC RL CircuitsRachit MahajanNo ratings yet
- EE 4741 Power Electronics: Jungwon Choi, Jwchoi@umn - EduDocument18 pagesEE 4741 Power Electronics: Jungwon Choi, Jwchoi@umn - EduTrung Nam HaNo ratings yet
- Control Schemes For DC-DC Converter Stages For PV/Battery Based Autonomous SystemDocument4 pagesControl Schemes For DC-DC Converter Stages For PV/Battery Based Autonomous SystemBojan BankovicNo ratings yet
- Circuit Theory Lab II Mini Project Sulaiman Rajab ShehuDocument24 pagesCircuit Theory Lab II Mini Project Sulaiman Rajab ShehuSulaiman ShehuNo ratings yet
- Analysis of Common-Collector Colpitts OscillatorDocument8 pagesAnalysis of Common-Collector Colpitts OscillatorFreeFM100% (5)
- CH 2 SlideDocument45 pagesCH 2 Slidemukesh00007No ratings yet
- ESC201T L14 Phasor AnalysisDocument23 pagesESC201T L14 Phasor AnalysisRachit MahajanNo ratings yet
- EE460 Power Electronics Exam SolutionsDocument4 pagesEE460 Power Electronics Exam SolutionsTurki AlsalehNo ratings yet
- EE-211 Linear Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherDocument27 pagesEE-211 Linear Circuit Analysis: Dr. Hadeed Ahmed SherHadeedAhmedSherNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3: Component Models (Contd... ) : Lecturer: Dr. Vinita Vasudevan Scribe: Shashank ShekharDocument5 pagesLecture 3: Component Models (Contd... ) : Lecturer: Dr. Vinita Vasudevan Scribe: Shashank ShekharAniruddha RoyNo ratings yet
- Problem Set 6 SolutionsDocument5 pagesProblem Set 6 SolutionsKrupali ShahNo ratings yet
- C3 1 5 10 Solution PDFDocument5 pagesC3 1 5 10 Solution PDFChanon TonmaiNo ratings yet
- Series - Parallel-RLC CKT EquationDocument13 pagesSeries - Parallel-RLC CKT EquationEjaz MahfuzNo ratings yet
- Network Topology Cutset LoopDocument21 pagesNetwork Topology Cutset Loopkaruneee7003No ratings yet
- Lecture 9-10 Scribed PDFDocument8 pagesLecture 9-10 Scribed PDFAniruddha RoyNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1Jean100% (1)
- TD3 SolutionDocument3 pagesTD3 Solutionboulahdour.ayoub.g55No ratings yet
- DISU231/EECE231 Basic Circuit Theory Homework 5: Fall Semester 2023Document2 pagesDISU231/EECE231 Basic Circuit Theory Homework 5: Fall Semester 2023이주영No ratings yet
- Differential Equation ModelDocument13 pagesDifferential Equation ModelYash BhattNo ratings yet
- Natural and Step Response of Series andDocument71 pagesNatural and Step Response of Series andManar HosnyNo ratings yet
- LAB #7 - Section 02 (15:30-18:30) : File Handling, Numpy and Matplotlib in Python (Due: End of The Lab)Document3 pagesLAB #7 - Section 02 (15:30-18:30) : File Handling, Numpy and Matplotlib in Python (Due: End of The Lab)Gloria HuNo ratings yet
- Variables de EstadoDocument22 pagesVariables de EstadoJaime Alberto Parra PlazasNo ratings yet
- IntroductionDocument11 pagesIntroductionCaio CezarNo ratings yet
- The Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99From EverandThe Spectral Theory of Toeplitz Operators. (AM-99), Volume 99No ratings yet
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsFrom EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsFrom EverandFundamentals of Electronics 1: Electronic Components and Elementary FunctionsNo ratings yet
- CS4230 L3Document27 pagesCS4230 L3tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- CS4230 Parallel Programming Introduction To Parallel AlgorithmsDocument25 pagesCS4230 Parallel Programming Introduction To Parallel Algorithmstt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- EE 5223 Assn: - Date: - : Jyellajo@mtu - EduDocument1 pageEE 5223 Assn: - Date: - : Jyellajo@mtu - Edutt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- EE593Document4 pagesEE593hassanNo ratings yet
- 01 Architecture 1Document45 pages01 Architecture 1tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- San José State University College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering EE239 Smart Grid, Fall 2013Document6 pagesSan José State University College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering EE239 Smart Grid, Fall 2013tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- EE 378: Smart and Renewable Power: Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEE 378: Smart and Renewable Power: Course Outlinett_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- CS4230 Parallel Programming: Mary Hall August 21, 2012Document17 pagesCS4230 Parallel Programming: Mary Hall August 21, 2012tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 5223 SylDocument1 page5223 SylSaadAbdulBasitNo ratings yet
- Syllabus M.tech PSDocument49 pagesSyllabus M.tech PStt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- EE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017Document9 pagesEE379K/EE394V Smart Grids:: Ross Baldick, Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering Spring 2017tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- The z-transform: A guide to its properties and inverseDocument20 pagesThe z-transform: A guide to its properties and inverseMxaz MyzxNo ratings yet
- San José State University College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering EE239 Smart Grid, Fall 2013Document6 pagesSan José State University College of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering EE239 Smart Grid, Fall 2013tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- EE593Document4 pagesEE593hassanNo ratings yet
- EE 378: Smart and Renewable Power: Course OutlineDocument3 pagesEE 378: Smart and Renewable Power: Course Outlinett_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 3 Authors IndexDocument11 pages3 Authors Indextt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB)Document2 pages2017 E-Health and Bioengineering Conference (EHB)tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 4 PublicationDocument6 pages4 Publicationtt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 2-Table of ContentsDocument10 pages2-Table of Contentstt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- CIS197-12b Fall - SyllabusDocument4 pagesCIS197-12b Fall - Syllabustt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Publication 4 18108 6175Document5 pagesPublication 4 18108 6175tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 6 PDFDocument4 pages6 PDFtt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Problem Set 2Document1 pageProblem Set 2tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Case 1:-Fixed Subnet MaskDocument6 pagesCase 1:-Fixed Subnet Masktt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- 11 EE462L H Bridge InverterDocument5 pages11 EE462L H Bridge Invertertt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- IC Design of Power Management Circuits (I)Document40 pagesIC Design of Power Management Circuits (I)tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Due: November 7, 2002 Reading: ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Electronic Circuits Problem Set 7 Fall 2002Document1 pageDue: November 7, 2002 Reading: ECE 445 Analysis and Design of Power Electronic Circuits Problem Set 7 Fall 2002tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Sample Midterm 1Document3 pagesSample Midterm 1tt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- CH 2 SlideDocument45 pagesCH 2 Slidemukesh00007No ratings yet
- Midterm1 PDFDocument3 pagesMidterm1 PDFtt_aljobory3911No ratings yet
- Datos Practicos TIMKENDocument128 pagesDatos Practicos TIMKENneodymioNo ratings yet
- Informatics ProjectDocument9 pagesInformatics Projectapi-480981439No ratings yet
- 10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesDocument9 pages10, Services Marketing: 6, Segmentation and Targeting of ServicesPreeti KachhawaNo ratings yet
- Business Statistics: Methods For Describing Sets of DataDocument103 pagesBusiness Statistics: Methods For Describing Sets of DataDrake AdamNo ratings yet
- John 1.1 (106 Traduções) PDFDocument112 pagesJohn 1.1 (106 Traduções) PDFTayna Vilela100% (1)
- FREE Soroban Abacus Mental Math Learning - BasicDocument74 pagesFREE Soroban Abacus Mental Math Learning - BasicTatyana Sukhomlinova100% (3)
- Bai Tap LonDocument10 pagesBai Tap LonMyNguyenNo ratings yet
- Multiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesDocument5 pagesMultiple Leiomyomas After Laparoscopic Hysterectomy: Report of Two CasesYosef Dwi Cahyadi SalanNo ratings yet
- Drama GuidelinesDocument120 pagesDrama GuidelinesAnonymous SmtsMiad100% (3)
- RBS's Acquisition and Integration of NatWestDocument27 pagesRBS's Acquisition and Integration of NatWestElmira GamaNo ratings yet
- Altered Mental Status: by Diana King, MD, and Jeffrey R. Avner, MDDocument9 pagesAltered Mental Status: by Diana King, MD, and Jeffrey R. Avner, MDchintya claraNo ratings yet
- KnowThem PPT FDocument18 pagesKnowThem PPT FAANANDHINI SNo ratings yet
- Pakistan Resolution Day SpeechDocument1 pagePakistan Resolution Day SpeechTariq Hayat100% (10)
- Analogy and LogicDocument2 pagesAnalogy and LogicCOMELEC CARNo ratings yet
- Pastors Sunday MessageDocument4 pagesPastors Sunday MessageDiana Janica Magalong100% (1)
- Challenges of Quality Worklife and Job Satisfaction for Food Delivery EmployeesDocument15 pagesChallenges of Quality Worklife and Job Satisfaction for Food Delivery EmployeesStephani shethaNo ratings yet
- Soal Uts Clea 2022-2023Document2 pagesSoal Uts Clea 2022-2023estu kaniraNo ratings yet
- Iambic Pentameter in Poetry and Verse ExamplesDocument14 pagesIambic Pentameter in Poetry and Verse ExamplesIan Dante ArcangelesNo ratings yet
- RFQ for cat and dog food from Arbab TradersDocument2 pagesRFQ for cat and dog food from Arbab TradersAnas AltafNo ratings yet
- Psychological ContractDocument14 pagesPsychological ContractvamsibuNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document8 pagesLesson Plan 1api-573197365No ratings yet
- Essay 2Document4 pagesEssay 2api-708904378No ratings yet
- Assignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionDocument6 pagesAssignment Histogram and Frequency DistributionFitria Rakhmawati RakhmawatiNo ratings yet
- KM UAT Plan - SampleDocument10 pagesKM UAT Plan - Samplechristd100% (1)
- Existing culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaDocument9 pagesExisting culture of third-gender students influenced by social mediaGilbert Gabrillo JoyosaNo ratings yet
- CArib LitDocument8 pagesCArib LitNick FullerNo ratings yet
- PV LITERATURE ROUGHDocument11 pagesPV LITERATURE ROUGHraghudeepaNo ratings yet
- BVRT PDFDocument8 pagesBVRT PDFAleena Zaidi100% (1)
- The Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityDocument25 pagesThe Rolle of Surgery in Oncology: Surgery Departement Medical Faculty Ukrida UniversityGian Alodia RisamasuNo ratings yet
- Coefficient of Friction Guide for Caesar II Pipe Stress AnalysisDocument1 pageCoefficient of Friction Guide for Caesar II Pipe Stress AnalysisAlden Cayaga0% (1)