Professional Documents
Culture Documents
World University of Bangladesh: Objective
Uploaded by
shajibOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
World University of Bangladesh: Objective
Uploaded by
shajibCopyright:
Available Formats
WORLD UNIVERSITY OF BANGLADESH
Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering
Course Name: Electronics II Lab
Experiment # 3: STUDY OF LINEAR APPLICATIONS OF OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
AS AN ADDER & SUBTRACTOR
OBJECTIVE:
To investigate the different linear applications of the operational amplifier: inverting summer,
and the difference amplifier.
COMPONENTS:
OPAMP (741) 1 piece
Resistor : 10k 4 pieces
100 k 2 pieces
3.3 k 1 piece
1 M 1 piece
PREVIEW:
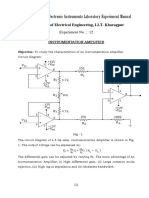
Fig 1. 741 IC (OPAMP) Pin Configuration
Addition: Using the concept of inverting amplifier, the op-amp can be used as an adder
(actually inverting adder) to sum up some input signals. In Figure1 the output of the op-amp is
V0 = - ( E1 + E2 )
It should be noted here that the ratios (Rf /R1 ) and (Rf /R2 ) must be equal to unity.
Fig. 2 Adder circuit
2
The summing amplifier is an application of the inverting op-amp configuration. The summing
amplifier has two or more inputs, and its output age is proportional to the algebraic sum of its
input voltages. Fig. 2-1-4 shows a two-input inverting summing amplifier.
Case-1: If all the three resistors are equal (R1=R2=Rf=R) then
VO = - ( Vinl + Vin2)
The above equation shows that the output voltage has the same magnitude as the sum of two
input voltages but with a ve sign indicating inversion.
EXPERIMENTAL WORK
Notes for the students: Read the theory carefully before starting the experiment. Let your setup
be checked by your lab instructor before connecting to the power supply.
INVERTING ADDER:
3.3k
+2V
DC
+2V
DC
Circuit diagram 1
DIFFERENCE AMPLIFIER:
+2V
DC
+5V
DC
Circuit diagram 2
Procedure:
1. Insert the 741 IC into the breadboard and provide appropriate biasing voltages.
2. Setup the circuits one by one.
3
3. For Summing amplifier
3.1 Assemble an adder circuit with Rf =R1=10k and R2=47k.
3.2 Feed sinusoidal input of amplitude 100mv and frequency 1 KHz to each input.
3.3 Observe the input voltages and output voltage on a CRO
3.4 Find the magnitude of the output voltage and tabulate the reading in Table 2-1-2.
3.5 Compare the experimental results with the theoretical values.
4. For Subtractor / Differential amplifier
4.1 Assemble a differential amplifier circuit with Rf=R1=10k
4.2 Feed V1=100mv and V2=50mv sinusoidal signal of frequency 1 KHz. To get 2
signals from the same source, use a high resistance potentiometer.
4.3 Observe the input and output voltages on a CRO. Find the magnitude of the output
voltage and tabulate the readings in Table 2-1-2.
4.4 Compare the experimental results with the theoretical value.
REPORT:
1. Derive the expressions for the output voltages for the adder and subtractor
circuits.
2. Calculate the output voltage for each of the cases and compare your hand
calculations with the experimental results.
3. Comment on the results.
4. Design a circuit which output is A-B+C.
5. Design a inverting adder circuit which can add three input signals and determine
the output.
You might also like
- Exp7 22FDocument5 pagesExp7 22FAbdullahNo ratings yet
- Operational Amplifiers and Linear Ics: Laboratory ManualDocument114 pagesOperational Amplifiers and Linear Ics: Laboratory ManualDr Jayanthi K BNo ratings yet
- ECE20L - 2 - Expt4Document10 pagesECE20L - 2 - Expt4Niko de LemosNo ratings yet
- Inverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsDocument13 pagesInverting and Non-Inverting Amplifiers: Pre-Lab QuestionsBereket TsegayeNo ratings yet
- Circuits Exp4Document4 pagesCircuits Exp4ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- EE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierDocument6 pagesEE2003-E03 Operational AmplifierntldvlaiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiDocument28 pagesLaboratory Manual: Unified Electronics Laboratory-IiAtul SainiNo ratings yet
- IC and ECAD LabDocument88 pagesIC and ECAD LabVeerayya JavvajiNo ratings yet
- Expt 01Document6 pagesExpt 01shajibNo ratings yet
- Electronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDocument10 pagesElectronics Laboratory DC Power Supply CircuitsDen CelestraNo ratings yet
- Lab.12 Power ElectronicsDocument2 pagesLab.12 Power ElectronicsXHaMzAXNo ratings yet
- Me2143 2Document5 pagesMe2143 2Law Zhan HongNo ratings yet
- Complete LICA Lab ManualDocument54 pagesComplete LICA Lab Manualnuthan9150% (2)
- UEEA1333 Operational Amplifier Lab SimulationDocument4 pagesUEEA1333 Operational Amplifier Lab SimulationKiritoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5-Soliman - ECELABDocument10 pagesExperiment 5-Soliman - ECELABKim SolimanNo ratings yet
- Linear IC Applications Lab Manual (16EC301ADocument53 pagesLinear IC Applications Lab Manual (16EC301Asurendrareddy mandati100% (1)
- Lab 05Document3 pagesLab 05Juan TarquiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitDocument22 pagesLaboratory Report on Integrator and Differentiator CircuitHrivu Dasmunshi (RA1911004010566)No ratings yet
- Course - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersDocument11 pagesCourse - Section: - ECE20L-2 - E06 Group Number: Group MembersLuch ÜNo ratings yet
- Lab 9 Operational AmplifiersDocument6 pagesLab 9 Operational AmplifiersAlisha AasNo ratings yet
- EE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 6: Opamp AmplifiersDocument6 pagesEE 230 - Analog Lab - 2021-22/I (Autumn) Experiment 6: Opamp AmplifiersSruthiNo ratings yet
- Lab 9: Operational Amplifier: Fig (2) - The Equivalent Circuit Op AmpDocument7 pagesLab 9: Operational Amplifier: Fig (2) - The Equivalent Circuit Op AmpGender EstebanNo ratings yet
- Experiment 5Document4 pagesExperiment 5Jay LopezNo ratings yet
- Lab Study of Op-Amp CircuitsDocument8 pagesLab Study of Op-Amp CircuitsDanilo BahorNo ratings yet
- Pre-Lab: Zener Voltage RegulatorDocument4 pagesPre-Lab: Zener Voltage Regulatorمحمد ابو جرادNo ratings yet
- Lica Lab Manual PDFDocument42 pagesLica Lab Manual PDFKashif AliNo ratings yet
- EE2CJ4 Lab3Document4 pagesEE2CJ4 Lab3Eftakher Alam WasiNo ratings yet
- UEEA1333 Practical 1QDocument5 pagesUEEA1333 Practical 1QDorcas cosmasNo ratings yet
- Experiment 1Document2 pagesExperiment 1MeghaNo ratings yet
- EC352 Exp2 B19EC005Document8 pagesEC352 Exp2 B19EC005Atiarsing SurongNo ratings yet
- Measurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment ManualDocument2 pagesMeasurements & Electronic Instruments Laboratory Experiment Manualfirst lastNo ratings yet
- Electronic Unit 1Document35 pagesElectronic Unit 1Sudheer ManepalliNo ratings yet
- Common Emitter Amplifier: EE091 Electronic DevicesDocument8 pagesCommon Emitter Amplifier: EE091 Electronic DevicesVy NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Group 5 - Laboratory No. 5Document14 pagesGroup 5 - Laboratory No. 5Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Experiment No. 2Document16 pagesLaboratory Experiment No. 2johnpaul varonaNo ratings yet
- Circuits Experiment 5Document4 pagesCircuits Experiment 5ilker.ozcelikkanNo ratings yet
- Electric Machines LaboratoryDocument44 pagesElectric Machines Laboratory11mustafa.mNo ratings yet
- EmtDocument115 pagesEmtRaj SharmaNo ratings yet
- Impedance of Series RL Circuits ExplainedDocument10 pagesImpedance of Series RL Circuits ExplainedNicoNo ratings yet
- Differential Amplifier: Out F 1 G G 2 1 2 F 1 1Document5 pagesDifferential Amplifier: Out F 1 G G 2 1 2 F 1 1Shweta DubeyNo ratings yet
- LINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT LAB MANUAL by PRABHU PDFDocument76 pagesLINEAR INTEGRATED CIRCUIT LAB MANUAL by PRABHU PDFprabhu4scribd100% (5)
- EE221 Lab Experiment #4: Inverting Amplifier Investigation: Fall 2014Document5 pagesEE221 Lab Experiment #4: Inverting Amplifier Investigation: Fall 2014MalikAlrahabiNo ratings yet
- Group-5 - Laboratory No. 4Document32 pagesGroup-5 - Laboratory No. 4Angel GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24mahinc021No ratings yet
- Lab 9: Operational Amplifier: Fig (2) - The Equivalent Circuit Op AmpDocument6 pagesLab 9: Operational Amplifier: Fig (2) - The Equivalent Circuit Op AmpGender EstebanNo ratings yet
- Pee Exp-3Document8 pagesPee Exp-3ThunderBird GamerNo ratings yet
- Iec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24Document8 pagesIec Lab - Exp 08 - Fall 23-24rakibulislamakash40No ratings yet
- EEE111 - Lab ManualDocument28 pagesEEE111 - Lab ManualAnindita MishiNo ratings yet
- Laboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiDocument6 pagesLaboratory Manual: EM 222 Circuit Analysis IiHarun KahramanNo ratings yet
- Device Exp 2 Student ManualDocument4 pagesDevice Exp 2 Student Manualgg ezNo ratings yet
- Bee LabDocument23 pagesBee Labdurgesh choudharyNo ratings yet
- Electronics II Lab ManualDocument28 pagesElectronics II Lab ManualArafat HossainNo ratings yet
- Electronics Laboratory Simulation of DC Power Supply CircuitDocument18 pagesElectronics Laboratory Simulation of DC Power Supply CircuitIvan Mark LucasNo ratings yet
- Aec - 2 LabDocument11 pagesAec - 2 LabNarasimha KumarNo ratings yet
- Center For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabDocument9 pagesCenter For Advanced Studies in Engineering, Islamabad Electronics LabHussain HadiNo ratings yet
- AEC Lab ManualDocument70 pagesAEC Lab ManualRohan BoseNo ratings yet
- DEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Document4 pagesDEVICE EXP 2 Student - 2Pablo ChanNo ratings yet
- Op-Amps: Experiment Guide: Part 1: Noninverting Amplifier (A) DC MeasurementsDocument4 pagesOp-Amps: Experiment Guide: Part 1: Noninverting Amplifier (A) DC MeasurementsRohini PalanisamyNo ratings yet
- Expt 01Document6 pagesExpt 01shajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 11Document3 pagesLab 11shajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 12Document2 pagesLab 12shajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 10Document3 pagesLab 10shajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 08Document3 pagesLab 08shajibNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: E #2: S M O U &Document5 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: E #2: S M O U &shajibNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Experiment # 7: To Study The Characteristics of Phase Shift Oscillators ODocument3 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Experiment # 7: To Study The Characteristics of Phase Shift Oscillators OshajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 04Document2 pagesLab 04shajibNo ratings yet
- Class A Power Amp LabDocument3 pagesClass A Power Amp LabshajibNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitDocument2 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitshajibNo ratings yet
- Lab 05Document2 pagesLab 05shajibNo ratings yet
- Index of Electronics II LabDocument2 pagesIndex of Electronics II LabshajibNo ratings yet
- Expt 01Document6 pagesExpt 01shajibNo ratings yet
- World University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitDocument2 pagesWorld University of Bangladesh: Experiment 6: Study of A Wein Bridge Oscillator CircuitshajibNo ratings yet
- JQX 15F (T90)Document1 pageJQX 15F (T90)Amang GayamNo ratings yet
- Cheetah JKM320-340M-60HB-A4-EN-F30Document2 pagesCheetah JKM320-340M-60HB-A4-EN-F30Hüseyin SezenNo ratings yet
- WC-M15i Series SERVICE MANUAL Facsimile ContentsDocument192 pagesWC-M15i Series SERVICE MANUAL Facsimile ContentsArmando MarinNo ratings yet
- GPCB Late Fees CircularDocument2 pagesGPCB Late Fees CircularChirag JainNo ratings yet
- Marantz SR 5004 Service Manual PDFDocument207 pagesMarantz SR 5004 Service Manual PDFRobson LuizNo ratings yet
- Design and Implementation of Variable Power SupplyDocument8 pagesDesign and Implementation of Variable Power SupplySoyebAhmed50% (2)
- FRDocument3 pagesFRThinkplus TradingNo ratings yet
- Emi Stories 476-570 PDFDocument53 pagesEmi Stories 476-570 PDFRishabh BuddhdevNo ratings yet
- User Manual for STI Series Power InvertersDocument24 pagesUser Manual for STI Series Power InvertersGustavo SilvaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - Overview On Digital IC DesignDocument45 pagesChapter 1 - Overview On Digital IC DesignNorjuliana Muhammad TahaNo ratings yet
- Samsung NP-R60+Document54 pagesSamsung NP-R60+marcioNo ratings yet
- Transient Analysis of Synchronous Machines.Document131 pagesTransient Analysis of Synchronous Machines.Gaurav SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Skanmobile User Manual Rev 9Document88 pagesSkanmobile User Manual Rev 9keshav Chauhan100% (1)
- Earthing Design Substation IEEE 80Document2 pagesEarthing Design Substation IEEE 80MELVIN0% (1)
- Transition From MELSEC-A&QnA (Large Type) Series To Q Series Handbook (Fundamentals) L08043enggDocument298 pagesTransition From MELSEC-A&QnA (Large Type) Series To Q Series Handbook (Fundamentals) L08043enggAym BrNo ratings yet
- LM2594 0.5 A, Step-Down Switching Regulator: Marking DiagramsDocument27 pagesLM2594 0.5 A, Step-Down Switching Regulator: Marking DiagramsDandy PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- New Features Guide: ETAP 12.5 - Our Most Powerful Version YetDocument12 pagesNew Features Guide: ETAP 12.5 - Our Most Powerful Version YetAwanRizky1No ratings yet
- Huawei Uae Interview QuestionDocument6 pagesHuawei Uae Interview Questioninfo vistaNo ratings yet
- SRT6KXLI Product Data SheetDocument4 pagesSRT6KXLI Product Data Sheet3maligeNo ratings yet
- Gensys Marine Technical Documentation PDFDocument128 pagesGensys Marine Technical Documentation PDFRic RioNo ratings yet
- Interface Descriptioin JUMO DigiLineDocument52 pagesInterface Descriptioin JUMO DigiLineNatiqNo ratings yet
- Power System Protection Lab 1Document12 pagesPower System Protection Lab 1Ronny VelásquezNo ratings yet
- EST 07 - Fiber Optics QuestionDocument2 pagesEST 07 - Fiber Optics Questionmayandichoso24No ratings yet
- 1734 Um018 - en e PDFDocument130 pages1734 Um018 - en e PDFFERNANDONo ratings yet
- At-8000 EFREM Data SheetDocument2 pagesAt-8000 EFREM Data SheetanilscoobNo ratings yet
- Ds d5b75rb DDocument10 pagesDs d5b75rb DworldwidevisionpvtltdNo ratings yet
- 8.6 MV Feeder Earth-Fault ProtectionDocument20 pages8.6 MV Feeder Earth-Fault Protectionbiviana81No ratings yet
- Magneto Ignition SystemDocument3 pagesMagneto Ignition SystemsameerNo ratings yet
- Cable CapacitanceDocument6 pagesCable Capacitanceadityahivalkar4141No ratings yet
- CASSETTE Inverter YKKJE12 55BZTVMCMORXDocument6 pagesCASSETTE Inverter YKKJE12 55BZTVMCMORXJuanNo ratings yet