Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Exp - 18 Zener Diode PDF
Uploaded by
Venkatalakshmi BandaruOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Exp - 18 Zener Diode PDF
Uploaded by
Venkatalakshmi BandaruCopyright:
Available Formats
ZENER DIODE
Aim:
To study the characteristics of zener diode.
Apparatus:
Zener diode, Variable power supply (0-15V), Resistances, Voltmeter, milliammeter.
Theory:
Zener diode is reverse biased, heavily doped silicon ( or germanium) P-N junction
diode which is operated in the break down region. A P-N junction diode is one-way device
offering low resistance when forward biased and behaving almost as an insulator when
reverse biased. Hence such diodes are mostly used as rectifiers. Normal diodes damages at
the break down voltage. But zener diode is speciall designed to operate in the reverse
breakdown region.
The basic principle of zener diode is the zener breakdown. When the diode is
forward biased and the applied voltage is increaded from zero, in the beginning no current
flows but, current increases rapidly even with a little increasing voltage when internal
barrier voltage is neutralised. It is almost acting as normal diode while forward biasing.
When the diode in reverse biased only small current flows through the diode. As the reverse
voltage is increased from zero, the reverse current increased rapidly. If the reverse bias is
still further increased beyond a certain limit, the function breaks down and reverse current
rises very sharply to a very light value. This critical value of voltage remains constant and is
called break down voltage. The junction offeres zero resistance at this point. This effect is
called zener effect and the diode is called zener diode.
Procedure:
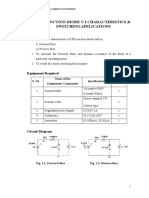
Forward Bias characterstics:
A zener diode is connected in series with a variable
power supply (0-13V), a milliammeter and a resistance R
(1K) as shows figure.The diode is in forward bias.A
voltmeter V2 is connected across the diode to measure P.D
across the diode. The voltage across the diode(V) is kept
0.1 volt and reading in the milliammeter (I) is noted. By
using the power supply the voltage across the diode is increased in steps of 0.1 volt ( or
0.05 volt) and corresponding values of current are measured using milliammeter. The values
are tabulated using milliammeter. The values are tabulated in table.
Reverse Bias Characterstics :
The zener diode, milliammeter ( mA) and resistor
1kohm are connected in series to the regulated power supply
as shown in fig. The diode is now in reverse bias.A voltmeter
'V' is connected across the diode to measure P.D. across it. By
using the power supply the voltage across the diode (Vz) is
kept 5 volts and the reading in the milliammeter (Iz) is noted.
By using the the power supply the volage across the diode is
incresed in steps of 5 volts and the correspinding value of
current are measured using milliammeter. The values are
tabulated in table.
Graphs:
A graph is plotted by
taking voltage along X- axis and
current along Y- axis. The
variation of V and I in the
forward in the variation of Iz and
Vz in the reverse bias are
represented on the same graphs
with different scales for I and Iz .
The forward bias characterstics
are drawn in the first quardrant
and the reverse bias chatacterstics
are drawn in the 3rd quardrant
Observations:
i) Forward Bias
S.NO. V(volt) I (mA)
ii)Reverse bias:
S.NO. Vz(volt) Iz (mA)
Precautions:
1. In measuring V in forward bias and VZ in reverse bias a sensitive
voltmeter must be used.
2. Zener diode should not be connected to the supply unit directly without
the load resistance R.
3. Loose connections are avoided.
Result:
V - I characterstics of a Zener diode are drawn
You might also like
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Full Book Electronics PDFDocument329 pagesFull Book Electronics PDFVasanth Raghavan0% (1)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- UntitledDocument1,098 pagesUntitledjoergenNo ratings yet
- EASA Exam - Module 04 ElectronicsDocument115 pagesEASA Exam - Module 04 Electronicsbika100% (1)
- Objective Que - of EeeDocument149 pagesObjective Que - of EeeNikhil Pareek100% (2)
- Chapter 2 Basic Physics of SemiconductorsDocument42 pagesChapter 2 Basic Physics of SemiconductorsKyusang ParkNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Special Purpose DiodeDocument39 pagesChapter 3 Special Purpose DiodeSyed MuneebNo ratings yet
- Edc MCQ Zener DiodeDocument4 pagesEdc MCQ Zener DiodeUmaNo ratings yet
- Dgca M-4 Mcqs Part-1Document20 pagesDgca M-4 Mcqs Part-1Abhishek SoniNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryDocument53 pagesSemiconductor Devices and Circuits LaboratoryKaryampudi RushendrababuNo ratings yet
- Delhi Public School B.S.City (Physics Practical Class XII)Document4 pagesDelhi Public School B.S.City (Physics Practical Class XII)Pulkit BansalNo ratings yet
- EDC Questions With AnswersDocument80 pagesEDC Questions With AnswersNalini RadhakrishnanNo ratings yet
- Antibag Snatch Alarm System PROJECT. - UnlockedDocument23 pagesAntibag Snatch Alarm System PROJECT. - Unlockedchuck254No ratings yet
- TheoryDocument11 pagesTheoryJatin hemwaniNo ratings yet
- Clipper Circuits - Clipping Circuits, Series, Positive, Negative, Parallel, Biased - D&E NotesDocument6 pagesClipper Circuits - Clipping Circuits, Series, Positive, Negative, Parallel, Biased - D&E NotesManjunath BadigerNo ratings yet
- D IODESDocument62 pagesD IODESCllyan Reyes0% (1)
- Accelerated Life Test of High BrightnessDocument9 pagesAccelerated Life Test of High BrightnessDiepMiuDiepMiuNo ratings yet
- L22 - PN Homojunction - 5 PDFDocument16 pagesL22 - PN Homojunction - 5 PDFPoddutoori Sankeerth ReddyNo ratings yet
- Lecture 19 - Metal-Semiconductor Junction (Cont.) March 19, 2007Document22 pagesLecture 19 - Metal-Semiconductor Junction (Cont.) March 19, 2007mukesh.33No ratings yet
- Bec MCQDocument16 pagesBec MCQJagadish Koundinye100% (1)
- EXPERIMENT 6:observation of The V-I Characteristic of A DiodeDocument5 pagesEXPERIMENT 6:observation of The V-I Characteristic of A DiodeAasifNo ratings yet
- BBEE203 (Module 1)Document47 pagesBBEE203 (Module 1)shilpaNo ratings yet
- Shockley & Pin DiodeDocument27 pagesShockley & Pin Diodekaneesha0% (1)
- DAE Electronics TestDocument15 pagesDAE Electronics TestRehanNo ratings yet
- CRG15T60A83LDocument10 pagesCRG15T60A83LVadim PopovichNo ratings yet
- Semiconductor ElectronicsDocument46 pagesSemiconductor Electronicspraveen2910No ratings yet
- PT4205 PowTechDocument18 pagesPT4205 PowTechJose ReyesNo ratings yet
- Experimental Method 3 PDFDocument14 pagesExperimental Method 3 PDFtungpham2014No ratings yet
- Current Transport Studies of N-Zno/P-Si Hetero-Nanostructures Grown by Pulsed Laser DepositionDocument9 pagesCurrent Transport Studies of N-Zno/P-Si Hetero-Nanostructures Grown by Pulsed Laser DepositionInternational Journal of Application or Innovation in Engineering & ManagementNo ratings yet
- Data SheetDocument5 pagesData SheetMindSet MarcosNo ratings yet
- HW 6 Diodes (2) With SolutionsDocument11 pagesHW 6 Diodes (2) With SolutionsStephen Hou100% (1)