Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Scania Chassis Frames
Uploaded by
aamirmubCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Scania Chassis Frames
Uploaded by
aamirmubCopyright:
Available Formats
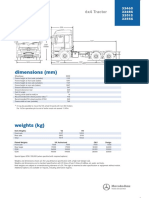
Chassis frames
The Scania chassis frame range
The Scania chassis frame range
The chassis frame range comprises the following frame types:
Frame type F700 F800 F950 F957 F958
Frame width and tolerance -3 -1 +2 -1 +1
770 770 770 770 770
-5 -3 0 -3 -1
Frame profile, U 75 90 90 90 90
9,5
9,5
9,5
Tolerances: height +/-1
8
width +/-3
thickness +/-0.15
270
270
270
270
270
R11 R11
R11 R11 R11
305 340
305 341
305 342
305 343
305 344
Area (cm2) 27,5 33,6 39,4 64,9 69,2
Moment of resistance Wx (cm3) in 194 249 287 438 464
the vertical axis, per beam
Moment of inertia Ix (cm4) in the 2 628 3 364 3 877 5 953 6 315
vertical axis, per beam
Weight (kg) per beam and per metre 21,4 26,2 30,7 50,7 54,0
Issue 1 en-GB 1 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
Chassis frames
The Scania chassis frame range
Frame materials
Mechanical properties
All frame types are made of the same type of steel, with some exceptions for partic- Further information on a specific chassis can be found in the individual chassis spec-
ular markets. ification (ICS).
Yield limit 500-600 N/mm2
Tensile strength Max. 730 N/mm2
Extension Min 21%
Hardness 200 Hv
Impact strength Min 18 J
Wall thickness 3-10 mm
Chemical composition
%C % Si % Mn %P %S % Ec
Max. 0,2 0,5 2,0 0,035 0,015 0,41
Issue 1 en-GB 2 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
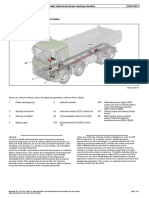
Chassis frames
Structure of chassis frame
Structure of chassis frame
Design of frame side members
The front end of the chassis frame is wider than the rear part. The front part of the
side members is angled outwards 2.7º starting 2,055 mm behind the first front axle.
The external width and angle of the chassis frame are the same for all frame types.
The advantage of this is that components that are fixed to the outside of both frame
side members can be the same size whatever chassis frame they are to be attached to.
Examples are tail lifts and subframes.
2,7° 2 055
Chasis frames may have two different external widths, depending on whether they
are single or double frames:
• 752 mm for F700, F800 and F950
735
• 735 mm for F957 and F958
752
The side members are equally high throughout their length with the exception of low
tractor units with configuration LA4x2MEB or LA6x2/4MLB, which have rear sus-
pension of a different height.
305 345
770
Example chassis frame dimensions
Issue 1 en-GB 3 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
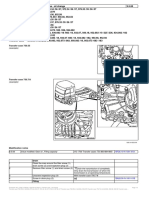
Chassis frames
Structure of chassis frame
Design of the inner frame 326 JR
Frame types F957 and F958 are reinforced with an inner frame.
The inner frame starts 326 mm behind the first front axle and ends the following dis-
tance behind the first driving axle (JR):
• Vehicles with modular holes1 On the chassis frame:
– 1,625 mm on tractor units
305 346
– 1,925 mm on rigid trucks
• Vehicles without modular holes in the chassis frame: JR is measured from the first driving rear axle to the end of the inner frame
– 1,762-1,962 mm depending on the wheel configuration and axle distance
– 3,267 mm on rigid trucks with 8x4*4 wheel configuration
The table on the next page shows the JR measurement for all double frames.
Further information on a specific chassis can be found in the individual chassis spec-
ification (ICS).
1. Modular holes are standardised holes for components or bodywork equipment.
Issue 1 en-GB 4 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
Chassis frames
Structure of chassis frame
Ad is the axle distance, i.e. the distance from the centre of the first front axle to the
centre of the first driving rear axle.
Wheel configuration JR 1,625 mm JR 1,762 mm JR 1,925 mm JR 1,962 mm JR 3,267 mm Notes
6x2A/B with F958 x
6x2A/B with F957 x Tractor
6x2A/B with F957 x Truck
6x2Z with F958 x Tractor
6x2Z with F958 Ad < 4,700 mm Ad >= 4,700 mm Truck
6x2*4 x
6x4A/B x
6x4Z Ad < 4,700 mm Ad >= 4,700 mm
8x2A/B x
8x2Z Ad < 4,700 mm Ad >= 4,700 mm
8x2/4A/B x
8x2*6 x
8x4A/B x
8x4Z Ad < 4,700 mm Ad >= 4,700 mm
8x4*4A/B x
6x6Z Ad < 4,600 mm Ad >= 4,600 mm
Note: A chassis can be specially ordered with an inner frame extending to the end
of the chassis frame. Please contact your Scanias dealer.
Issue 1 en-GB 5 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
Chassis frames
Structure of chassis frame
Design of crossmembers
Crossmembers may be designed in many different ways depending on which chassis
frame they are fitted to and where they are located. Examples:
• Crossmembers may be all in one piece (1). 1
• Some crossmembers are only complete when they are welded together with end
pieces (2 and 3). These crossmembers only exist by themselves in one length. The
length of the finished crossmember varies as the crossmember and the end pieces
are welded together in different ways. 2
• Crossmembers may be single (2) or double (3).
• Crossmembers come in various plate thicknesses depending on the type of chassis
frame.
3
305 347
Example of crossmember design and location on the chassis frame
Issue 1 en-GB 6 (6)
©
Scania CV AB 2009, Sweden
You might also like
- Products Truck VT Hd65 Cargo SpecDocument10 pagesProducts Truck VT Hd65 Cargo SpecAlexey KolmakovNo ratings yet
- Principles of Operation RetarderDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Operation Retardervitor santosNo ratings yet
- Volvo FMX Product Guide Update Euro 6Document30 pagesVolvo FMX Product Guide Update Euro 6wahyu santosoNo ratings yet
- MBSA Actros Specification FADocument4 pagesMBSA Actros Specification FAanon_509618907100% (1)
- Gearbox, Mechanical - I Shift Generation DDocument55 pagesGearbox, Mechanical - I Shift Generation DMurniansyah AnsyahNo ratings yet
- P410CB 8x4 PDFDocument2 pagesP410CB 8x4 PDFAgustinus Yosef100% (1)
- SCN0046 P410 MSZDocument2 pagesSCN0046 P410 MSZCristian ChiruNo ratings yet
- Spec Sheet Scania R520la6x4esz PDFDocument4 pagesSpec Sheet Scania R520la6x4esz PDFMohamadr KmlNo ratings yet
- GR 500EXL 3 - OM2 14E - Cover PDFDocument1 pageGR 500EXL 3 - OM2 14E - Cover PDFvan long BuiNo ratings yet
- Fifth wheel couplings mounting platesDocument2 pagesFifth wheel couplings mounting platesAtmaYudhaNo ratings yet
- ZF-AV110 Presentation EN PDFDocument6 pagesZF-AV110 Presentation EN PDFjasogtiNo ratings yet
- Kenworth Trucks Body & Equipment Mounting GuideDocument106 pagesKenworth Trucks Body & Equipment Mounting GuidesayedNo ratings yet
- Trucks - Diagnostic Technician Drive Train Specialist Training ChecklistDocument30 pagesTrucks - Diagnostic Technician Drive Train Specialist Training ChecklistSameh MohamedNo ratings yet
- Twistlock Inspection & Replacement SOPDocument9 pagesTwistlock Inspection & Replacement SOPncthanhck0% (1)
- Tailor your Volvo FM with endless optionsDocument18 pagesTailor your Volvo FM with endless optionsLuqman Cuopreakt'zNo ratings yet
- Ayoub VolvoDocument1 pageAyoub VolvoAyoub AyoubNo ratings yet
- Miawwhaxor Library Engine Mercy 906Document78 pagesMiawwhaxor Library Engine Mercy 906DwiNo ratings yet
- Technical Data-OM 926 LA-240kW-1300Nm-D926.929-Off Highway US Tier 3Document4 pagesTechnical Data-OM 926 LA-240kW-1300Nm-D926.929-Off Highway US Tier 3SYR SERVICIOS GENERALESNo ratings yet
- Electrohydraulic Dual-Circuit Power Steering, FunctionDocument3 pagesElectrohydraulic Dual-Circuit Power Steering, FunctionAbi Jith100% (1)
- Mid-Range Truck Synchromesh TransmissionDocument2 pagesMid-Range Truck Synchromesh TransmissionPeto AlamNo ratings yet
- C1378Document5 pagesC1378Harry Wart WartNo ratings yet
- Trident AbDocument8 pagesTrident AbSimon Val NitkiewiczNo ratings yet
- Cummins QSX15 Spec & PartsDocument12 pagesCummins QSX15 Spec & Partskevinsims11100% (1)
- Axor WebDocument14 pagesAxor Webkremoso100% (1)
- DC 600 10588 To 11568Document28 pagesDC 600 10588 To 11568Jaime Arreola100% (1)
- DAF MX Engines Infosheet enDocument4 pagesDAF MX Engines Infosheet enRicardo Urio100% (3)
- Maxus Axle Assembly GuideDocument19 pagesMaxus Axle Assembly GuidepeckerrNo ratings yet
- Superstructure Instructions Installation RigidDocument128 pagesSuperstructure Instructions Installation RigidЕвгений АксёновNo ratings yet
- 27volvod13engine 1 en PDFDocument12 pages27volvod13engine 1 en PDFSudipta DubeyNo ratings yet
- S - K 380 p6x4 Heavy .35 E3 N&DDocument5 pagesS - K 380 p6x4 Heavy .35 E3 N&DDanilo Jacobs100% (1)
- SAF-HOLLAND Air Suspension Systems and Axles With DruDocument28 pagesSAF-HOLLAND Air Suspension Systems and Axles With Druspitt157No ratings yet
- New Light Vehicle RequirementsDocument29 pagesNew Light Vehicle RequirementshazopmanNo ratings yet
- Volvo FM-Technical SpecificationsDocument10 pagesVolvo FM-Technical SpecificationsManuel La TorreNo ratings yet
- MX Engine BrochureDocument7 pagesMX Engine BrochureGus SalazarNo ratings yet
- Daily Vehicle Inspection FormDocument2 pagesDaily Vehicle Inspection FormAkhtar QuddusNo ratings yet
- Terex Gottwald Model 3 Harbour Crane: The Entry Model For The 100-Tonne SegmentDocument36 pagesTerex Gottwald Model 3 Harbour Crane: The Entry Model For The 100-Tonne SegmentAri Yandoko100% (1)
- Voss 232 38104 - SuspensionPart - Katalog - Gesamt KomprimiertDocument320 pagesVoss 232 38104 - SuspensionPart - Katalog - Gesamt KomprimiertMatt NagyNo ratings yet
- 422FDocument24 pages422FVictor Raul Osnayo Mamani100% (2)
- 2019 Extended Cab Truck Service ManualDocument98 pages2019 Extended Cab Truck Service ManualJùst ZikoNo ratings yet
- MB TZ3Document60 pagesMB TZ3Anonymous 5XUrk2100% (1)
- MERCEDES-BENZ ACTROS SPECSDocument13 pagesMERCEDES-BENZ ACTROS SPECSRudi Kurniawan100% (1)
- 4054 ACtrossDocument18 pages4054 ACtrossRudi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- JostDocument6 pagesJostAnonymous CJbaFnNo ratings yet
- AtfDocument12 pagesAtffisco4rilNo ratings yet
- CAT Forklift Spec SheetDocument3 pagesCAT Forklift Spec SheetJuan Carlos100% (1)
- Trucks Volvo fh16 Specifications PowertrainDocument4 pagesTrucks Volvo fh16 Specifications PowertrainAmir Bambang YudhoyonoNo ratings yet
- Operation and Maintenace Manual (5-10T)Document102 pagesOperation and Maintenace Manual (5-10T)pablo romeroNo ratings yet
- Text Slide: Truck and Trailer Inspection WorkshopDocument39 pagesText Slide: Truck and Trailer Inspection WorkshopFatih D. PrasetioNo ratings yet
- Transfer Case - Oil ChangeDocument3 pagesTransfer Case - Oil ChangeHariyanto oknesNo ratings yet
- New Actros DashDocument6 pagesNew Actros Dashlesly katherine gutierrez guevara100% (1)
- 01 Intro Fifth Wheel Couplings and Mounting Plates eDocument7 pages01 Intro Fifth Wheel Couplings and Mounting Plates eAbrar HussainNo ratings yet
- The Atego. The Arocs.: Construction Transport. 7.5 To 41 Tonnes GCW. Heavy Haulage. Up To 250 Tonnes GCWDocument84 pagesThe Atego. The Arocs.: Construction Transport. 7.5 To 41 Tonnes GCW. Heavy Haulage. Up To 250 Tonnes GCWpercy f.fNo ratings yet
- Pricelist Acc Actros 2013Document7 pagesPricelist Acc Actros 2013MinaSaeedNo ratings yet
- Aladin Diagnostic For DIWA 5Document4 pagesAladin Diagnostic For DIWA 5nikodjoleNo ratings yet
- Iveco Trakker AD260T38 Tipper SADocument19 pagesIveco Trakker AD260T38 Tipper SACsibiErvinNo ratings yet
- Volvo FHDocument7 pagesVolvo FHCristian ChiruNo ratings yet
- Mercedes-Tech Specs 3341 6x4Document3 pagesMercedes-Tech Specs 3341 6x4NAHASALI11100% (1)
- Slides. Rear Axle RTS2370A. Texto PDFDocument16 pagesSlides. Rear Axle RTS2370A. Texto PDFYery Cruz100% (2)
- Load Chart FT 5 TonDocument1 pageLoad Chart FT 5 TonHerman HutabaratNo ratings yet
- cẩu vr 554Document3 pagescẩu vr 554Phan Ngoc DienNo ratings yet
- Materials 16 02870Document26 pagesMaterials 16 02870aamirmubNo ratings yet
- Öz and Öztürk - 2022 - Effect of Carbon Filler-Modified Epoxy Adhesive OnDocument14 pagesÖz and Öztürk - 2022 - Effect of Carbon Filler-Modified Epoxy Adhesive OnaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Ballistic Resistance of Novel Amorphous-Alloy-Reinforced Perforated ArmorDocument15 pagesBallistic Resistance of Novel Amorphous-Alloy-Reinforced Perforated ArmoraamirmubNo ratings yet
- Progressive Failure Analysis of FRC Containing HoleDocument16 pagesProgressive Failure Analysis of FRC Containing HoleaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Effect of GNP and MWCNT Addition On Lap ShearDocument6 pagesEffect of GNP and MWCNT Addition On Lap ShearaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Medical Adhesives for Skin: Understanding Skin Characteristics and Adhesion PrinciplesDocument12 pagesMedical Adhesives for Skin: Understanding Skin Characteristics and Adhesion PrinciplesaamirmubNo ratings yet
- A Numerical Investigation and Experimental Validation On Chip Morphology of Aluminum Alloy 6061 During Orthogonal MachiningDocument6 pagesA Numerical Investigation and Experimental Validation On Chip Morphology of Aluminum Alloy 6061 During Orthogonal MachiningaamirmubNo ratings yet
- 2014 SCIEI May Sydney Conf Proceedings IACSITDocument5 pages2014 SCIEI May Sydney Conf Proceedings IACSITaamirmubNo ratings yet
- W4B.3.WF2471 4196F1 PDFDocument15 pagesW4B.3.WF2471 4196F1 PDFFernando NCNo ratings yet
- Nematigiv 2018Document41 pagesNematigiv 2018aamirmubNo ratings yet
- Braided Composites ModellingDocument33 pagesBraided Composites ModellingaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Braided Composites ModellingDocument33 pagesBraided Composites ModellingaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Multiscale Modeling of Human Bone: Y. W. Kwon B. R. ClumpnerDocument11 pagesMultiscale Modeling of Human Bone: Y. W. Kwon B. R. ClumpneraamirmubNo ratings yet
- Patient-Specific Bone Multiscale Modelling FracturDocument67 pagesPatient-Specific Bone Multiscale Modelling FracturaamirmubNo ratings yet
- 2116-Article Text (.PDF, Max 100 MB) - 8131-1-10-20180926Document9 pages2116-Article Text (.PDF, Max 100 MB) - 8131-1-10-20180926Marco DeluciaNo ratings yet
- Tese Mestrado Mario Rui Goncalves Da SilvaDocument143 pagesTese Mestrado Mario Rui Goncalves Da SilvaaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Multiobjective optimization of mechanical properties of adhesives based on compositionDocument24 pagesMultiobjective optimization of mechanical properties of adhesives based on compositionaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical EngineeringDocument10 pagesComputer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical EngineeringaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Crossmark: International Journal of Adhesion and AdhesivesDocument7 pagesCrossmark: International Journal of Adhesion and AdhesivesHannan yusuf KhanNo ratings yet
- A Critical Assessment of Block TestDocument11 pagesA Critical Assessment of Block TestaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Lightweight Ceramic Composite Armour SystemDocument5 pagesLightweight Ceramic Composite Armour SystemaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Experimental Investigation On The Ballistic Resistance of Monolithic and Multi-Layred Plates Against Ogival-Nose Rigid Projectiles (2012)Document12 pagesExperimental Investigation On The Ballistic Resistance of Monolithic and Multi-Layred Plates Against Ogival-Nose Rigid Projectiles (2012)aamirmubNo ratings yet
- Symmetric Split Hopkinson CompressionDocument10 pagesSymmetric Split Hopkinson CompressionaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Design and characteristics of hybrid composite armor subjected to projectile impactDocument6 pagesDesign and characteristics of hybrid composite armor subjected to projectile impactaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Impact Pendulum Test Systems PDFDocument8 pagesImpact Pendulum Test Systems PDFHumberto AnguloNo ratings yet
- Paper 77 CEAS2015 v2Document16 pagesPaper 77 CEAS2015 v2aamirmubNo ratings yet
- Medical Adhesives for Skin: Understanding Skin Characteristics and Adhesion PrinciplesDocument12 pagesMedical Adhesives for Skin: Understanding Skin Characteristics and Adhesion PrinciplesaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Computer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical EngineeringDocument10 pagesComputer Methods in Biomechanics and Biomedical EngineeringaamirmubNo ratings yet
- A Novel 3D Evaluation Method For Assessing Bone To Bone Relationships in ClubfootDocument9 pagesA Novel 3D Evaluation Method For Assessing Bone To Bone Relationships in ClubfootaamirmubNo ratings yet
- Modelling and Simulation of Brittle ArmourDocument166 pagesModelling and Simulation of Brittle ArmouraamirmubNo ratings yet
- Peake and Tobak 3D SeparationDocument25 pagesPeake and Tobak 3D SeparationPablitox84No ratings yet
- Best Practice Manual-Fluid PipingDocument43 pagesBest Practice Manual-Fluid Pipingapi-3869476100% (1)
- 2-Theory of SedimentationDocument11 pages2-Theory of SedimentationSheeraz AhmedNo ratings yet
- V2607-DI-T-E3B: Kubota 07 SeriesDocument2 pagesV2607-DI-T-E3B: Kubota 07 SeriesRodrigoThuLokithoPkmz0% (1)
- Tractor Operator AgricultureDocument9 pagesTractor Operator AgricultureConstantin CarpenNo ratings yet
- 32 Landing GearDocument176 pages32 Landing GearMaria Fernanda Nuñez RuizNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet: Ft041En - A - 0313 - 160atjDocument2 pagesTechnical Data Sheet: Ft041En - A - 0313 - 160atjElaine Malazzab PublikoNo ratings yet
- Lee's Disc Apparatus (Theory) Heat & Thermodynamics Virtual LDocument3 pagesLee's Disc Apparatus (Theory) Heat & Thermodynamics Virtual LReddyvari VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Flowfit CPA250: Technical InformationDocument8 pagesFlowfit CPA250: Technical Informationknightfelix12No ratings yet
- Experiment No. 3 Measurement of Specific Weight and Pressure Intensity of LiquidsDocument4 pagesExperiment No. 3 Measurement of Specific Weight and Pressure Intensity of LiquidsChristine KimNo ratings yet
- Circular Motion Week 2Document8 pagesCircular Motion Week 2Solace HusseinNo ratings yet
- Midsized With Big Features.: Horizontal Directional Drilling SystemDocument2 pagesMidsized With Big Features.: Horizontal Directional Drilling SystemJose RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Axial flow fan guideDocument2 pagesAxial flow fan guideThanhNo ratings yet
- Heat Flow Calculations Made Using The V C: Ventilation Test InstrumentsDocument6 pagesHeat Flow Calculations Made Using The V C: Ventilation Test Instrumentsretrospect1000No ratings yet
- Lift Boat Gear Lube: Typical Observations Product DescriptionDocument1 pageLift Boat Gear Lube: Typical Observations Product DescriptionRomankoNo ratings yet
- Product Information: Diesel Extra LD 15W40Document2 pagesProduct Information: Diesel Extra LD 15W40movie hunterNo ratings yet
- 4.DB Flats (1-7) & SMDB TypicalDocument9 pages4.DB Flats (1-7) & SMDB TypicalhpzenNo ratings yet
- Summary On Uniaxial Ratchetting of 6061-T6 Aluminium AlloyDocument18 pagesSummary On Uniaxial Ratchetting of 6061-T6 Aluminium AlloyautalNo ratings yet
- Overallstructure PDFDocument11 pagesOverallstructure PDFChhoan NhunNo ratings yet
- Certificado - Flange Adapter 125MM - XindaDocument3 pagesCertificado - Flange Adapter 125MM - XindaGR CarlosNo ratings yet
- pc200 7 Main Pump Test MethodDocument26 pagespc200 7 Main Pump Test Methodalfred100% (1)
- Check List-For LMI-on Bypassing Protn & Interlocks-OGN/OPS/SYST/005-021Document13 pagesCheck List-For LMI-on Bypassing Protn & Interlocks-OGN/OPS/SYST/005-021rudra singhNo ratings yet
- Tokico P.D. Oil Flowmeter KatalogDocument6 pagesTokico P.D. Oil Flowmeter KatalogPRIMA UTAMA MULYANo ratings yet
- Kia Sportage 2005Document79 pagesKia Sportage 2005hubertocNo ratings yet
- XtraVac Multihead Packaging Lines-LRDocument5 pagesXtraVac Multihead Packaging Lines-LRMohammad SalamaNo ratings yet
- Minicrawler EnglishDocument24 pagesMinicrawler EnglishXUAN LUUNo ratings yet
- Don3.0 Software - Proper Assembly of Flange JointDocument3 pagesDon3.0 Software - Proper Assembly of Flange JointJoshua HobsonNo ratings yet
- A Low-Cost, Open Source Wind TurbineDocument23 pagesA Low-Cost, Open Source Wind TurbineStephen LynchNo ratings yet
- 1009 - Wind Loads On Duopitch Roof Building: DescriptionDocument7 pages1009 - Wind Loads On Duopitch Roof Building: DescriptionKris Lee100% (1)
- Practice Problems - Breath Section PDFDocument68 pagesPractice Problems - Breath Section PDFnickNo ratings yet