Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart
Uploaded by
Jeson Galgo75%(4)75% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views2 pagesuyytfuy uyguyfyytyug uyguyt6ey uyters ytftex uytcytfyu.
Original Title
Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentuyytfuy uyguyfyytyug uyguyt6ey uyters ytftex uytcytfyu.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
75%(4)75% found this document useful (4 votes)
2K views2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart
Uploaded by
Jeson Galgouyytfuy uyguyfyytyug uyguyt6ey uyters ytftex uytcytfyu.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
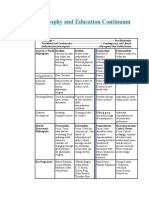
Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart
General or Idealism: Realism: Pragmatism: Existentialism:
World Ideas are the only true Reality exists Universe is dynamic, Reality is subjective,
Philosophies reality, the only thing independent of human evolving. Purpose of within the individual.
worth knowing. mind. World of physical thought is action. Truth is Individual rather than
Focus: Mind objects ultimate reality. relative. external standards.
Focus: Body Focus: Experience Focus: Freedom
Originator(s) Plato, Socrates Aristotle Pierce, Dewey Sartre, Kierkegaard
Curricular Subject matter of mind: Subject matter of Subject matter of social Subject matter of
Emphasis literature, history, physical world: science, experience. Creation of personal choice
philosophy, religion math new social order
Teaching Teach for handling ideas: Teach for mastery of Problem solving: Project Individual as entity within
Method lecture, discussion facts and basic skills: method social context
demonstration, recitation
Character Imitating examples, Training in rules of Making group decisions Individual responsibility
Development heroes conduct in light of consequences for decisions and
preferences
Related Perennialism: Essentialism: Progressivism: Reconstructionism/
Educational Focus: Teach ideas that Focus: Teach the Focus: Ideas should be Critical Theory
Philosophies are everlasting. Seek common core, "the tested by active Focus: Critical
enduring truths which are basics" of information experimentation. pedagogy: Analysis of
constant, not changing, and skills (cultural Learning rooted in world events,
through great literature, heritage) needed for questions of learners in controversial issues and
art, philosophy, religion. citizenship. (Curriculum interaction with others. diversity to provide vision
can change slowly) Experience and student for better world and
centered. social change.
Key Robert Hutchins, William Bagley; John Dewey, George Counts,
Proponents Jacque Maritain, Arthur Bestor, William Kilpatrick J. Habermas,
Mortimer Adler, E. D. Hirsch, Ivan Illich,
Allan Bloom Chester Finn, Henry Giroux,
Diane Ravitch, Paulo Freire
Theodore Sizer
Related Information Processing Behaviorism Cognitivism/ Humanism
Theories of The mind makes Behavior shaped by Constructivism Personal freedom,
Learning meaning through design and determined Learner actively choice,
(Psychological symbol-processing by forces in environment. constructs own responsibility.
Orientations) structures of a fixed body Learning occurs as result understandings of reality Achievement
of knowledge. Describes of reinforcing responses through interaction with motivation
how information is to stimuli. environment and towards highest
received, processed, Social Learning reflection on actions. levels. Control of
stored, and retrieved Learning by observing Student-centered own destiny. Child
from the mind. and imitating others. learning around conflicts centered.
to present knowing Interaction with
structures. others.
Key R. M. Gagne, Ivan Pavlov, Jean Piaget, J.J. Rousseau,
proponents E. Gagne, John Watson, U. Bronfenbrenner, A. Maslow,
Robert Sternberg, B.F. Skinner, Jerome Bruner, C. Rogers,
J.R. Anderson E.L. Thorndike, Lev Vygotsky A. Combs,
Albert Bandura R. May
You might also like
- You, The Teacher, As A Person in SocietyDocument37 pagesYou, The Teacher, As A Person in SocietyShara DuyangNo ratings yet
- General Education FinishedDocument22 pagesGeneral Education FinishedJoshua GarciaNo ratings yet
- Philosopies Contrast Comparison: Prepared By: Arguelles, Bendicio, Pacifico, PaderesDocument3 pagesPhilosopies Contrast Comparison: Prepared By: Arguelles, Bendicio, Pacifico, PaderesKristine Jenyl PacificoNo ratings yet
- EDUC-96-Philosophy-of-Education-Final-Exam (Jeanicar Aninon)Document5 pagesEDUC-96-Philosophy-of-Education-Final-Exam (Jeanicar Aninon)jeanicar artoNo ratings yet
- FAClLITATING: MODULE 4-Lesson 21 MotivationDocument6 pagesFAClLITATING: MODULE 4-Lesson 21 MotivationAr JenotanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - SC Hool As A Social System: Multiple ChoiceDocument9 pagesUnit 2 - SC Hool As A Social System: Multiple Choicerj Turno100% (1)
- Multiple Intelligence Post TestDocument6 pagesMultiple Intelligence Post TestLyn nunezNo ratings yet
- QUESTIONNAIREDocument9 pagesQUESTIONNAIRERishel Mae Besinga PantallanoNo ratings yet
- Components of CurriculumDocument61 pagesComponents of CurriculumResmining Istigfarin100% (1)
- Quiz 1Document22 pagesQuiz 1Belle ManuelNo ratings yet
- Idealism in EducationDocument9 pagesIdealism in EducationAnonymous doCtd0IJDN100% (1)
- North Luzon Philippines State College: Adal A Dekalidad, Dur-As Ti PanagbiagDocument1 pageNorth Luzon Philippines State College: Adal A Dekalidad, Dur-As Ti PanagbiagAdrian DoctoleroNo ratings yet
- Principles of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesDocument2 pagesPrinciples of Teaching Prelim Exam NotesMaybza ArellanoNo ratings yet
- The Philosophical Heritage of EducationDocument20 pagesThe Philosophical Heritage of EducationPatricia Honey CeleroNo ratings yet
- Prelim Facilitating Learner Centered TeachingDocument6 pagesPrelim Facilitating Learner Centered TeachingHarrison Q. PlazaNo ratings yet
- Assignment 5250Document2 pagesAssignment 5250Queenoviah FiercieneNo ratings yet
- The Teacher and The School Curriculum Prelim ExamDocument2 pagesThe Teacher and The School Curriculum Prelim ExamNel BorniaNo ratings yet
- Natural IntegrationDocument5 pagesNatural IntegrationNiña Amato50% (2)
- Activity 18 321-340Document3 pagesActivity 18 321-340FatimaNo ratings yet
- Prof. Ed - Prof. JudyDocument12 pagesProf. Ed - Prof. JudyJunril CabadongaNo ratings yet
- ProfEd 102 Educational Assessment of Students With Additional NeedsDocument4 pagesProfEd 102 Educational Assessment of Students With Additional NeedsRazelle Angiela AvorqueNo ratings yet
- FileDocument95 pagesFileArcie Catli0% (1)
- Educational Aims of PragmatismDocument2 pagesEducational Aims of Pragmatismcarie_erica100% (2)
- Professional Education Exam DrillDocument49 pagesProfessional Education Exam DrillWilson Agustin100% (3)
- Prelim ExamDocument4 pagesPrelim ExamKier VillegasNo ratings yet
- General Education: 2 Semester, Academic Year 2019-2020 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDocument3 pagesGeneral Education: 2 Semester, Academic Year 2019-2020 Building and Enhancing New Literacies Across The CurriculumDaewin SeratoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 QuizDocument3 pagesChapter 4 QuizRioMagadiaOrpiano100% (2)
- Philosophical and Pedagogical Approach of Curriculum and Curriculum DevelopmentexistentialismDocument4 pagesPhilosophical and Pedagogical Approach of Curriculum and Curriculum DevelopmentexistentialismClaire E Joe100% (1)
- Course Title: Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching Course Description: This Course Explores The Fundamental PrinciplesDocument2 pagesCourse Title: Facilitating Learner Centered Teaching Course Description: This Course Explores The Fundamental PrinciplesLaurence Bernard Balbin II100% (3)
- Topic 5 Orchestraring Play (Setting The Stage)Document15 pagesTopic 5 Orchestraring Play (Setting The Stage)FanizahNo ratings yet
- Educ 213 The Teacher and The School Curriculum ReviewerDocument4 pagesEduc 213 The Teacher and The School Curriculum ReviewerMariel DepaudhonNo ratings yet
- UPH RequirementDocument45 pagesUPH RequirementHannah Coleen AndradaNo ratings yet
- EL 105 Learning Guide EspirituDocument18 pagesEL 105 Learning Guide EspirituDebong EspirituNo ratings yet
- LEARNING MODULE in GMRC of Vml. Paged September 16 2020Document102 pagesLEARNING MODULE in GMRC of Vml. Paged September 16 2020Stephane CabrillosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesDocument14 pagesChapter 1 Learner-Centered Psychological PrinciplesJheny Palamara100% (1)
- Principles of Teaching - Answer KeyDocument7 pagesPrinciples of Teaching - Answer KeyIan Andres DulaogonNo ratings yet
- CH5Document2 pagesCH5Joshua Saguil100% (1)
- Cumulative Learning Theory by R GagneDocument1 pageCumulative Learning Theory by R GagneReyna Mae MarangaNo ratings yet
- Foundation of Education Part 2Document4 pagesFoundation of Education Part 2Analyn L. RosalesNo ratings yet
- A Global TeacherDocument18 pagesA Global TeacherElmor YumangNo ratings yet
- Biography Theodore BrameldDocument3 pagesBiography Theodore BrameldMartha RussoNo ratings yet
- PED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2Document4 pagesPED-101-Lesson-2-14-Learner-Centered-Psychological-Principles 2YuriNo ratings yet
- EDUC 13 - Midterm ExaminationDocument6 pagesEDUC 13 - Midterm ExaminationSaxrim TagubaNo ratings yet
- EDUC 5: The Teaching Profession The Teacher As A PersonDocument23 pagesEDUC 5: The Teaching Profession The Teacher As A PersonSHERRYL KIM GALLEGONo ratings yet
- Nature and Scope: PerennialismDocument5 pagesNature and Scope: PerennialismKashmir FajardoNo ratings yet
- Professional Education Part 2 PDFDocument7 pagesProfessional Education Part 2 PDFNelson Tejara50% (2)
- Prof ED 30 Questions With AnswerDocument6 pagesProf ED 30 Questions With AnswerJoyful DaysNo ratings yet
- For Group QuizDocument2 pagesFor Group QuizAnastasia Enriquez100% (1)
- Seven Philosophies of EducationDocument3 pagesSeven Philosophies of EducationNaruffRalliburNo ratings yet
- ENGLIS major-WPS OfficeDocument29 pagesENGLIS major-WPS OfficeZahara Santi100% (1)
- Lesson 1: Take ActionDocument5 pagesLesson 1: Take ActionRosemary TorresNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed N3Document228 pagesProf Ed N3armand rodriguezNo ratings yet
- Historical Foundation of EducationDocument5 pagesHistorical Foundation of EducationCarolyne DaleNo ratings yet
- Pagadian Answer Keys 4Document285 pagesPagadian Answer Keys 4vanessa doteNo ratings yet
- Jovan To Check and Monitor His ProgressDocument2 pagesJovan To Check and Monitor His Progressjade tagabNo ratings yet
- Alvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1Document2 pagesAlvin Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart 1CHERRY LYNN Y. ROLOYANNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCDocument1 pagePhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart F3 6 BCE2 AJ JMCPrakash Chandra PandeyNo ratings yet
- Philosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Document2 pagesPhilosophy and Education Continuum Chart: Originator(s)Umme Ammara100% (1)
- LogoDocument1 pageLogoJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- School Form 1 (SF 1) : School Register For ShsDocument5 pagesSchool Form 1 (SF 1) : School Register For ShsJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- School Forms Checking Report: Report Code: SFCR1 Annex 1aDocument12 pagesSchool Forms Checking Report: Report Code: SFCR1 Annex 1aJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Raw DataDocument5 pagesRaw DataJeson Galgo0% (1)
- Research Format - Action ResearchDocument4 pagesResearch Format - Action ResearchJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Career CertificateDocument26 pagesCareer CertificateJeson Galgo0% (1)
- Resignation LetterDocument1 pageResignation LetterJeson Galgo100% (1)
- SWT Narrative ReportDocument5 pagesSWT Narrative ReportJeson Galgo75% (8)
- Sex Harvesting Equipment Total Manual Mechanical O E X 2 O E X 2 MaleDocument7 pagesSex Harvesting Equipment Total Manual Mechanical O E X 2 O E X 2 MaleJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Task 1: Identify The Figure of Speech Expressed in The Following SentencesDocument1 pageTask 1: Identify The Figure of Speech Expressed in The Following SentencesJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- DO - s2016 - 27 SHS QS Guidelines PDFDocument11 pagesDO - s2016 - 27 SHS QS Guidelines PDFJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Student Practical Research 2Document7 pagesStudent Practical Research 2Jeson Galgo67% (6)
- Teachers PrayerDocument1 pageTeachers PrayerJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Brigada Eskwela Plan of Activities Grade 9-St. Francis: Dagohoy National High School Poblacion, Dagohoy, BoholDocument3 pagesBrigada Eskwela Plan of Activities Grade 9-St. Francis: Dagohoy National High School Poblacion, Dagohoy, BoholJeson GalgoNo ratings yet
- Dagohoy Integrated Senior High School: Second Place WinnerDocument4 pagesDagohoy Integrated Senior High School: Second Place WinnerJeson Galgo100% (1)
- Automated Form 2 (For DepEd Teachers)Document153 pagesAutomated Form 2 (For DepEd Teachers)Jeson Galgo0% (1)
- Handbook of Organizational Performance PDFDocument50 pagesHandbook of Organizational Performance PDFdjquirosNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Communication (Lynn H. Turner Richard West)Document676 pagesAn Introduction To Communication (Lynn H. Turner Richard West)abubakarsuleiman5206100% (1)
- Understanding The Self NotesDocument4 pagesUnderstanding The Self NotesINTALAN, FRITZ L.No ratings yet
- Quality GurusDocument39 pagesQuality GurusShubham TiwariNo ratings yet
- 2014 Cyber Wellness (Secondary) PDFDocument40 pages2014 Cyber Wellness (Secondary) PDFStella KyungNo ratings yet
- G7-G8 Nail Care (Beauty Care) DLLDocument57 pagesG7-G8 Nail Care (Beauty Care) DLLRia ColladoNo ratings yet
- Standard 3Document10 pagesStandard 3api-254201594No ratings yet
- 1402-Article Text-5255-2-10-20180626Document5 pages1402-Article Text-5255-2-10-20180626Rezki HermansyahNo ratings yet
- Entrepreneurial Self TestDocument2 pagesEntrepreneurial Self TestAngge CortesNo ratings yet
- Best Practices in MCQ ConstructionDocument10 pagesBest Practices in MCQ ConstructionRehan AsadNo ratings yet
- Wgu Obc1 Quizzes & Study Questions - Most RecentDocument34 pagesWgu Obc1 Quizzes & Study Questions - Most RecentsdwewNo ratings yet
- A Value Based Approach To Candidate Selection in LinkedInDocument5 pagesA Value Based Approach To Candidate Selection in LinkedInVeronika SinghNo ratings yet
- Functionalist TheoryDocument5 pagesFunctionalist TheoryFern Hofileña100% (1)
- English Notes For Class 8 and 9 CHPTR 1 To 15Document76 pagesEnglish Notes For Class 8 and 9 CHPTR 1 To 15Anonymous QbjqmG8cg80% (87)
- Burns Et Al., 2000Document13 pagesBurns Et Al., 2000Adhie Trey PrassetyoNo ratings yet
- Psychopaths Among Us, by Robert HerczDocument13 pagesPsychopaths Among Us, by Robert HerczZiyishi WangNo ratings yet
- Summative Test in DissDocument3 pagesSummative Test in DissPearl Arianne Moncada MontealegreNo ratings yet
- From Depression Into CelebrationDocument34 pagesFrom Depression Into CelebrationDoname ReyesNo ratings yet
- Assertion Inventory For Use in Assessment and ResearchDocument2 pagesAssertion Inventory For Use in Assessment and ResearchnerissarvnNo ratings yet
- How (Not What) To Prescribe Nonpharmacologic Aspects of Psychopharmacology 2012Document21 pagesHow (Not What) To Prescribe Nonpharmacologic Aspects of Psychopharmacology 2012Wal AlbuquerqueNo ratings yet
- Performance AppraisalDocument49 pagesPerformance AppraisalSai PrintersNo ratings yet
- DLL For COT 2ndDocument3 pagesDLL For COT 2ndAllan Jovi BajadoNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading and ReasoningDocument34 pagesCritical Reading and Reasoningjollibee torresNo ratings yet
- Proficiency Testing RequirementsDocument5 pagesProficiency Testing RequirementssanjaydgNo ratings yet
- Recruitment MetricsDocument11 pagesRecruitment MetricsNikita PatilNo ratings yet
- Dr. Yanga's College's Inc. Wakas, Bocaue, Bulacan: English 4 DR Fe F. FaundoDocument28 pagesDr. Yanga's College's Inc. Wakas, Bocaue, Bulacan: English 4 DR Fe F. FaundoFernando CruzNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1 Insects TaughtDocument11 pagesLesson Plan 1 Insects Taughtapi-270233181No ratings yet
- Tdgs Stex WorkbookDocument31 pagesTdgs Stex WorkbookvagabondstarNo ratings yet
- Vijanabhairava TantraDocument23 pagesVijanabhairava TantraSreeraj Guruvayoor S100% (5)
- Candidate Assessment Activity: Written Responses To QuestionsDocument2 pagesCandidate Assessment Activity: Written Responses To Questionsmbrnadine belgica0% (1)