Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Cold Formed Steel Design Summary (EN1993) (Runet Software)
Uploaded by
enriquegarbayoOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Cold Formed Steel Design Summary (EN1993) (Runet Software)
Uploaded by
enriquegarbayoCopyright:
Available Formats
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Design tables for Structural Steel Sections (Eurocode 3, EN1993-1-1:2005)
Tables with all the international steel sections, with their dimensions, properties,
classification, resistance and buckling resistance values according to Eurocode 3,
EN1993-1-1:2005. The tables are extended to welded section with dimensions given from the
user.
z
z z z z z z z z
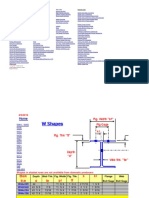
Tables with dimensions and properties of standard steel sections
From the left tree you select the section type e.g.
IPE, HE etc. On the right the table shows all the
standard sections for this group and their
dimensions and properties. Moving up and down
the table on the right the section drawing is shown
in scale (you can grab and move the section
drawing around the window and you can make it
small or bigger with the arrows).
Click or double click on a section
and you obtain analytical report for the
classification, resistance values and buckling
resistance of the selected section.
Symbols
h [mm]: Depth of cross section
b [mm]: Width of cross section
hw [mm]: Web depth
dw [mm ]: Depth of straight portion of web
tw [mm]: Web thickness
tf [mm]: Flange thickness
r [mm]: Radius of root fillet
G [Kg/m]: Mass
A [cm²]: Area
4
Iy [cm ]: Moment of area about axis y-y
Iz [cm4]: Second moment of area about axis z-z
Wy [cm³]: Section modulus about axis y-y
Wz [cm³]: Section modulus about axis z-z
Wpy [cm]: Plastic section modulus about axis y-y
Wpz [cm³]: Plastic section modulus about axis z-z
iy [cm]: Radius of gyration about y-y axis
iz [cm]: Radius of gyration about z-z axis
Avz [cm²]: Shear area parallel to web
Avy [cm²]: Shear area parallel to flanges
4
It [cm ]: Torsional constant
Iw [cm6]: Warping constant
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 1
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Classification and resistance of standard steel sections
Classification of cross section according to EN1993-1-1:2005 §5.5.
Resistance values of cross section according to EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2.
Buckling resistance and lateral buckling resistance according to EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.3
From the tree on the left you select the section with its designation. On the right a drawing of
the section profile is displayed together with the section dimensions and properties.
On the right window are also displayed:
Classification (1,2,3,4) according to EN1993-1-
1:2005 §5.5 for axial loading and loading with
bending moments.
Resistances of the section in compression,
bending in y-y and z-z axis, and shear according
to EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2
Buckling resistance for various buckling
lengths (Lc) according to EN1993-1-1:2005
§6.3.1
Lateral torsional buckling resistance for
various lateral buckling lengths (Llt) according
to EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.3.2
Symbols
NtRd [kN]: Tension resistance EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2.3
NcRd [kN]: Compression resistance EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2.4
Mcrdy [kNm]: Bending resistance about the strong y-y axis EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2.5
Mcrdz [kNm]: Bending resistance about the weak z-z axis EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.2.5
Vcrdz [kN]: Shear resistance in the axis z-z parallel to web EN1993-1-1 §6.2.6
Vcrdy [kN]: Shear resistance in the axis y-y axis parallel to flanges EN1993-1-1:2005
§6.2.6
Nbrdy [kN]: Buckling resistance in compression about the strong y-y or weak z-z axis,
Nbrdz [kN]: for various buckling lengths Lc (1.00,1.50…15 m) EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.3.1
Mbrd1 [kNm]: Lateral torsional buckling resistance for various lengths between constrains
Mbrd2 [kNm]: Llt (1.00,1.50 ….15 m) EN1993-1-1:2005 §6.3.2
Mbrd1: Lateral torsional buckling resistance for constant (uniform) bending moment
diagram along the beam
Mbrd2: Lateral torsional buckling resistance for parabolic bending moment diagram
along the beam
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 2
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Tables with dimensions and properties of user defined welded steel sections
Click and you enter the window
where you can enter the basic dimensions of a
welded steel section. The strength properties of
the section are listed at the same time.
For adding new section or deleting existing
click . Click to stop
editing.
Classification and resistance of user defined welded steel sections
See standard sections.
Parameters
The classification of the sections
the strength and buckling
resistances are produced for four
steel grades, S235, S275, S355
and S450. The names and the
basic values of steel grades can
be changed from
Parameters/Structural steel.
To do changes first click to unlock
The partial factors for materials
0 , 1 , 2 which are use for the
classification and resistance can be changed
from Parameters/ Partial factors for
materials.
To do changes first click to unlock
Coordinate system Sections properties
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 3
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Steel section types included in the program
IPE 80-600
European I-beams IPE A 80-600
IPE O 180-600
IPE V 400-600
IPE 750
HE A 100-1000
European wide flange beams HE AA 100-1000
HE B 100-1000
HEM 100-1000
HE 400-1000
HL 1000/1100
Beams with very wide flanges HD 260x54.1 – 400x1086
Wide flange columns HP 200x57.2 – 400x231
Wide flange bearing piles IPN 80-550
European standard beams W 360x370x134
W 1100x400x499
American wide flange beams UB 178x102x19
UB 914x419x388
British universal beams UC 152x152x23
UC 356x406x634
British universal columns UPN 30-65
UPN 80-400
European standard channels UAP 80-300
UPE 80-400
Channels with parallel flanges L 20x20x3
L 250x250x28
Equal angels L 30x20x3
L 250x90x16
Unequal angels Ø 10.2x1.0
Ø 1016x400
Circular hollow sections 20x20x1.6
400x400x12.5
Square hollow sections cold 40x40x2.6
formed 400x400x20.0
Square hollow sections hot 30x20x1.5
rolled 500x300x12.5
Rectangular hollow sections 50x30x2.6
cold formed 400x260x17.5
Rectangular hollow sections
hot rolled
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 4
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Classification of cross sections ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 5.5
The design of steel elements can be done with elastic or plastic analysis depending on the
class of the cross section.
The design of sections of classes 1 and 2 is based on the plastic resistance, the design of
cross-sections of class 3 is base on elastic resistance and the design of cross-sections of
class 4 is based on elastic resistance and effective cross section properties.
The classification of cross sections in 1, 2, 3 and 4 classes depends on the ratios of thickness
to width of the parts of the cross-section which are in compression according to tables 5.2 of
ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005.
Table 5.2 ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 – Internal compression parts
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 5
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Table 5.2 ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 – Outstanding flanges
Table 5.2 ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 - Angles
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 6
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Ultimate limit states ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2
Tension ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2.3
N Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.5)
N t , Rd
Design plastic resistance of the cross-section.
A fy
N pl , Rd (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.6)
0
Design ultimate resistance of net cross-section at holes for fasteners.
0.9 Anet f u
N u , Rd (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.7)
M2
A area of cross-section
Anet area of net cross-section (minus holes)
f y yield strength of steel
f u ultimate strength of steel
0 , M 2 partial factors for material
Compression ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2.4
N Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.9)
N c , Rd
A fy
N c , Rd for class 1, 2, 3 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.10)
M0
Aeff fy
N c , Rd for class 4 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.11)
M0
A area of cross-section
Aeff effective area of cross-section
fy yield strength of steel
0 partial factors for material
In case the design value of shear is VEd > 0.50 V pl , Rd the reduced yield strength is used.
2
1 fy , where ρ = 2VEd 1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.29)
V pl , Rd
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 7
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Bending moment ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2.5
M Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.12)
M c , Rd
Design resistance of cross section for bending about the principal (y-y) or secondary (z-z)
axis.
W pl , y fy
M y , Rd M pl , y , Rd for class 1, 2 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1,
M0
6.13)
W pl , z fy
M z , Rd M pl , z , Rd for class 1, 2 cross-sections
M0
Wel , y fy
M y , Rd M el , y , Rd for class 3 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.14)
M0
Wel , z fy
M z , Rd M el , z , Rd for class 3 cross-sections
M0
Weff , y fy
M y , Rd M c , y , Rd for class 4 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.15)
M0
Weff , z fy
M z , Rd M c , z , Rd for class 4 cross-sections
M0
W pl , y W pl , z plastic section modulus about principal and secondary axis,
Wel , y Wel , z elastic section modulus about principal and secondary axis,
Weff , y Weff , z effective section modulus about principal and secondary axis,
fy yield strength of steel
0 partial factors for material
When bending moment acts together with axial force design check is performed according to :
M Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.31)
M N , Rd
N
2
M N , Rd M pl , Rd 1 Ed
N pl , Rd
(ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.32)
In case the design value of shear is VEd > 0.50 V pl , Rd the reduced yield strength is used.
2
1 fy , where ρ = 2VEd 1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.29)
V pl , Rd
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 8
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Bi-axial bending ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2.9
M y , Ed M z , Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.41)
M M
y , Rd zRd
For Ι and Η sections: α=2, β=5n, β≥1 (n=NEd/Npl,Rd)
For circular hollow sections: α=2, β=2
For rectangular hollow sections α=β=1.66/(1-1.13 n2)
Shear ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.2.6
VEd
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.17)
Vc , Rd
Plastic shear resistance parallel to the cross-section web.
Avz f y
Vz , Rd V pl , z , Rd (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.18)
3 M 0
Plastic shear resistance parallel to the cross-section flanges.
Avy f y
V y , Rd V pl , y , Rd (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.18)
3 M 0
Avy Avz shear areas parallel to the cross-section web or flanges,
fy yield strength of steel
0 partial factors for material
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 9
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Buckling resistance of uniform members in compression ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.3.1
Buckling resistance due to compression.
N Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.46)
N b , Rd
Af y
N b , Rd for class 1, 2, 3 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.47)
M1
Aeff f y
N b , Rd for class 4 cross-sections (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.48)
M1
The reduction factor is determined from the non-dimensional slenderness
1
2
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.49)
2
0.5 1 0.2 2
Af y 2 l eff I
; N cr ; ;i
N cr 2 i A
non-dimensional slenderness,
N cr elastic critical buckling load,
Lcr equivalent buckling length,
λ slenderness,
i radius of gyration.
The imperfection factor which corresponds to the appropriate buckling curve ao,a,b,c,d
should obtained from Table 6.2 of Eurocode 3, ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005:
Buckling curve ao a b C d
Imperfection factor α 0.13 0.21 0.34 0.49 0.76
Equivalent buckling lengths Lcr/L
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 10
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Table 6.2 ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 Selection of buckling curve of a cross-section
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 11
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Lateral torsional buckling for uniform members ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.3.2
Lateral torsional buckling of uniform members in bending.
M Ed
1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.54)
M b , Rd
LTWy f y
M b, Rd (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.55)
1
Wy = W pl , y for class 1, 2 cross-sections,
Wy = Wel , y for class 3 cross-sections,
Wy = Weff , y for class 4 cross-sections.
The reduction factor LT is determined from the non-dimensional slenderness LT
1
LT 1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.56)
LT 2
LT
2
LT
LT 0.5 1 LT LT 0.2 2LT
Wy f y
LT
M cr
The imperfection factor which corresponds to the appropriate buckling curve a,b,c,d:
Buckling curve a b C d
Imperfection factor αLT 0.21 0.34 0.49 0.76
Recommended values for torsional buckling curves:
Rolled Sections h/b<2 buckling curve a, h/b>2 buckling curve b
Welded sections h/b<2 buckling curve c, h/b>2 buckling curve d
The critical elastic moment for lateral torsional buckling is computed according to Annex F of
Eurocode 3-1-1 (1992).
2 EI z k I w kL GI t
2
C 2 Z g C 3 Z j C 2 Z g C 3 Z j
2
2
M cr C1
kL 2 k w I z 2 EI z
C1, C2, C3, coefficients depending on the loading conditions and support conditions,
for a beam with uniform bending moment diagram C1=1.000, C2=0.000, C3=1.000
for a beam with parabolic bending moment diagram C1=1.132, C2=0.459, C3=0.525
It St. Venant torsional constant,
Iw warping constant,
Iz second moment of inertia about the weak axis,
L beam length between the support points,
k , k w coefficients depending on the support conditions,
Z g distance of shear center from point of load application
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 12
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Uniform members in bending and compression ΕΝ 1993-1-1:2005 § 6.3.4
N Ed M Y , Ed M z , Ed
k yy k yz 1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.61)
x y N Rk / 1 LT M y , Rk / M 1 M z , Rk / M 1
N Ed M Y , Ed M z , Ed
k zy k zz 1 (ΕΝ 1993-1-1, 6.62)
x z N Rk / 1 LT M y , Rk / M 1 M z , Rk / M 1
N Rk Af y
M y , Rk W pl , y f y for class 1, 2 cross-sections
M y , Rk Wel , y f y for class 3 cross-sections,
M y , Rk Weff , y f y for class 4 cross-sections,
M z , Rk W pl , z f y for class 1, 2 cross-sections
M z , Rk Wel , z f y for class 3 cross-sections,
M z , Rk Weff , z f y for class 4 cross-sections.
The interaction coefficients k yy , k yz , k zy , k zz are determined from tables Β.1 and Β.2
Table Β.1 interaction coefficients k yy , k yz , k zy , k zz
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 13
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Table Β.2
Factor Bending axis Points braced in direction
Cmy y-y z-z
Cmz z-z y-y
CmLT y-y y-y
Table Β.3
Bibliography
Eurocode 3, EN1993-1-1:2005
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 14
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Examples
The following examples show how you can choose the right steel sections using the tables in
the program.
Example 1
Steel column 5.20 m.
Axial load G = 80 kN, variable axial load Q = 120 kN.
Steel S 355.
Total axial design load:
Ned =1.35xG+1.50xQ=1.35x80+1.50x120 = 288 kN
Buckling lengths: Liy=5.20 m, Liz=5.20 m
In the main program screen, click .
From the tree control on the left select section type HEA.
Click + and all the sections of type HEA are displayed.
For steel grade S 355 and buckling
length 5.20 m (table values between 5.0
m and 6.0m ), check Nbyrd and Nbzrd
(buckling resistances in compression in
y-y and z-z axis) to be greater than the
design load of the column Ned=288 kN.
Section ΗΕ 180 Α is OK.
For buckling length 6.0m>5.20m, the
section has, buckling resistances in
compression Nbyrd = 900 kN > 288 kN
and Nbzrd = 397 kN >288 kN.
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 15
SteelSectionsEC3 RUNET software
Example 2
Beam 5.80 m with loads.
Permanent load g = 18 kN/m.
Variable load q = 24 kN/m.
Steel S 355.
Design load:
qed = 1.35x18.0+1.50x24.0 = 60.30 kN/m
Maximum design bending moment:
My,ed = 60.30x5.802/8 = 253.6 kNm
Maximum design shearing force:
Vz,ed = 60.30x5.80/2 = 174.9 kN
In the main program screen, click .
From the tree control on the left select section type IPE.
Click + and all the sections of type IPE are displayed.
For steel grade S 355 and lateral buckling length LLt=5.80 m (table 6.0m), check Μbrd2
(parabolic bending moment diagram) to be greater than the maximum bending moment acting
on the beam My,ed = 253.6 kNm.
Section IPE 500 is OK.
For lateral buckling length 6.0m>5.80 m, has resistance in bending moment due to lateral
buckling Μbrd2 = 288 kNm>253.6 kNm
From the table above you can check the resistances in shear and bending.
Shear resistance Vc,rdz = 1227 kN, bending resistance Mc,rdy = 779 kNm.
Copyright RUNET Software www.runet-software.com 16
You might also like
- Design Tables For Structural Steel Sections (Eurocode 3, EN1993-1-1:2005)Document16 pagesDesign Tables For Structural Steel Sections (Eurocode 3, EN1993-1-1:2005)azhar ahmadNo ratings yet
- Aluminum Flat Rolled ProductDocument28 pagesAluminum Flat Rolled ProductVictor camachoNo ratings yet
- Structural Sections - European SpecificationsDocument32 pagesStructural Sections - European Specifications321daiqiNo ratings yet
- LV Motor EQP Global IEC Brochure Rev 190301Document4 pagesLV Motor EQP Global IEC Brochure Rev 190301Victor LinaresNo ratings yet
- Section Wizard TutorialDocument7 pagesSection Wizard TutorialSyed Mohammad Shabber AhmadNo ratings yet
- Cable Support System (Part 3 - Ladder)Document131 pagesCable Support System (Part 3 - Ladder)Dera Nyilong Dera NyilongNo ratings yet
- Third Party Submission Ispat PolskaDocument11 pagesThird Party Submission Ispat Polskaعابد زاهدNo ratings yet
- Sagomario Profili Acciaio ArcelorMittalDocument206 pagesSagomario Profili Acciaio ArcelorMittalvax0100% (1)
- Catalog PDFDocument72 pagesCatalog PDFVIVEK UPADHYAYNo ratings yet
- Part3 Ladder 24-7-19 CompressDocument132 pagesPart3 Ladder 24-7-19 CompressNhut Bang NguyenNo ratings yet
- Ref. No. 432982 - Cat. No. FEN36TD250KF: Representative ImageDocument3 pagesRef. No. 432982 - Cat. No. FEN36TD250KF: Representative ImageFelipe HerosNo ratings yet
- Industrial Dry Coolers for Air Conditioning and Process CoolingDocument2 pagesIndustrial Dry Coolers for Air Conditioning and Process CoolingmoghanmogaNo ratings yet
- Type Sct50 Cable Trunking: Standard Length: 2.4M, Other Lengths Such As 3M Available Upon RequestDocument6 pagesType Sct50 Cable Trunking: Standard Length: 2.4M, Other Lengths Such As 3M Available Upon RequestHAFIZNo ratings yet
- Fv-Kupplung: Couplings General Catalogue - 2015Document28 pagesFv-Kupplung: Couplings General Catalogue - 2015Ivano VerbiNo ratings yet
- Elektrim Full Line Overview 4pgDocument4 pagesElektrim Full Line Overview 4pgSiobhan CogswellNo ratings yet
- 1PTB13 (As Per AC Loadings)Document29 pages1PTB13 (As Per AC Loadings)jasekanNo ratings yet
- Alustar (Perfis & Secções)Document49 pagesAlustar (Perfis & Secções)Jeovani DanielNo ratings yet
- Load Break SwitchDocument4 pagesLoad Break SwitchRifkan MoNo ratings yet
- (Global) StandardIE2IE3Motor AESV AESU 0711Document26 pages(Global) StandardIE2IE3Motor AESV AESU 0711AndriBagusNo ratings yet
- 1PTB13 V3Document29 pages1PTB13 V3jasekanNo ratings yet
- STEEL HANDBOOKDocument261 pagesSTEEL HANDBOOKSAMUEL CRUZALDENo ratings yet
- Strainer Y-Type Production StandardsDocument3 pagesStrainer Y-Type Production StandardsMohamed RaafatNo ratings yet
- OSHA and steel shape worksheet linksDocument472 pagesOSHA and steel shape worksheet linksasdfdf0% (1)
- ArcelorMittal - High-Rise Buildings - WebDocument80 pagesArcelorMittal - High-Rise Buildings - WebAndrei MurariuNo ratings yet
- SteelBook UpdateDocument450 pagesSteelBook UpdateJorge Varela100% (1)
- Channel-Type Instrumentation Tray: Part Numbers - Polyester Resin System, Solid BottomDocument3 pagesChannel-Type Instrumentation Tray: Part Numbers - Polyester Resin System, Solid BottomcesarggssNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Steel StructuresDocument27 pagesAnalysis and Design of Steel Structuresnabinniraula100% (1)
- 3b. Cable Tray-Catalogue (U-Li)Document39 pages3b. Cable Tray-Catalogue (U-Li)arunasuriaNo ratings yet
- Catalog & Cable Ladder System GuideDocument8 pagesCatalog & Cable Ladder System GuidefjbetaNo ratings yet
- Ventilatoare Industriale Axiale PDFDocument27 pagesVentilatoare Industriale Axiale PDFFlorin Alexandru VladNo ratings yet
- Direct drive and belt drive centrifugal fans with VFD controlDocument6 pagesDirect drive and belt drive centrifugal fans with VFD controlTedi A MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Force Ksb-Omega-Pump Sarcina Pe Flanse PDFDocument19 pagesForce Ksb-Omega-Pump Sarcina Pe Flanse PDFRusu DimaNo ratings yet
- Ksb-Omega-Pump Sarcina Pe Flanse PDFDocument56 pagesKsb-Omega-Pump Sarcina Pe Flanse PDFRusu DimaNo ratings yet
- Initial Lumens (LMS) Current (A) Length (MM) : Tubular TypeDocument4 pagesInitial Lumens (LMS) Current (A) Length (MM) : Tubular TypeGautam KumarNo ratings yet
- MB 219-229 PDFDocument11 pagesMB 219-229 PDFAmitava DattaNo ratings yet
- Design of Composite Bridge - WSMDocument26 pagesDesign of Composite Bridge - WSMROHIT SHRESTHANo ratings yet
- Hot Rolled Steel Sections Dimensions StandardDocument4 pagesHot Rolled Steel Sections Dimensions StandardsatyaNo ratings yet
- Seminar nr.1.2 Table of Properties For IPE, HEA, HEB, HEM, UB, UC, UBP Profiles - Eurocode 3Document8 pagesSeminar nr.1.2 Table of Properties For IPE, HEA, HEB, HEM, UB, UC, UBP Profiles - Eurocode 3anisaNo ratings yet
- 08 - Chapter 3 PDFDocument44 pages08 - Chapter 3 PDFMeraj aliNo ratings yet
- RCC43 Wide Beams (A & D)Document30 pagesRCC43 Wide Beams (A & D)ptslabNo ratings yet
- Roof System Trimoterm SNV 16526Document20 pagesRoof System Trimoterm SNV 16526Vojin RodićNo ratings yet
- Design Basis Report ConveyorsDocument7 pagesDesign Basis Report Conveyorsanushree4989No ratings yet
- Ring Beam AT 1, A-IDocument17 pagesRing Beam AT 1, A-IPEng. Tech. Alvince KoreroNo ratings yet
- Addendum For The Rosemount 9901 Safety Instructions Manual 00809-0100-4601Document4 pagesAddendum For The Rosemount 9901 Safety Instructions Manual 00809-0100-4601javier gutierrez pizaNo ratings yet
- Catalog Profile StandardDocument16 pagesCatalog Profile StandardBogdan AndreiNo ratings yet
- Exel International Group IncDocument56 pagesExel International Group InccristopherNo ratings yet
- Pantografo Coelme 1Document2 pagesPantografo Coelme 1Alexander GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Directional Linear Ceiling Diffuser L-5000Document3 pagesDirectional Linear Ceiling Diffuser L-5000Estevan huertasNo ratings yet
- Mr. Somu Benefits of HISTEEL - Somu (TTJ) (23oct18) (Final) PDFDocument30 pagesMr. Somu Benefits of HISTEEL - Somu (TTJ) (23oct18) (Final) PDFSewGuanNo ratings yet
- Structural Steel in Housing - 3rd Edition PDFDocument32 pagesStructural Steel in Housing - 3rd Edition PDFChristopher CarrilloNo ratings yet
- Slab Formwork Technical Instruction Manual: AlufixDocument18 pagesSlab Formwork Technical Instruction Manual: AlufixkrmcharigdcNo ratings yet
- JVC Hr-J4020ua SM PDFDocument53 pagesJVC Hr-J4020ua SM PDFAnthony GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Cylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsFrom EverandCylindrical Compression Helix Springs For Suspension SystemsNo ratings yet
- 110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorFrom Everand110 Integrated Circuit Projects for the Home ConstructorRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- Semiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsFrom EverandSemiconductor Data Book: Characteristics of approx. 10,000 Transistors, FETs, UJTs, Diodes, Rectifiers, Optical Semiconductors, Triacs and SCRsNo ratings yet
- Pipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsFrom EverandPipeline Rules of Thumb Handbook: A Manual of Quick, Accurate Solutions to Everyday Pipeline Engineering ProblemsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (10)
- No Te Vayas de NavarraDocument2 pagesNo Te Vayas de NavarraenriquegarbayoNo ratings yet
- Aveverum Karl Jenkins PDFDocument7 pagesAveverum Karl Jenkins PDFAngelesChambillaMiranda100% (3)
- DG 7 Spanish PDFDocument173 pagesDG 7 Spanish PDFenriquegarbayoNo ratings yet
- Eurocode 3 ActionsDocument158 pagesEurocode 3 ActionsKeeran Montag100% (7)
- SFS - Tornillo Autoroscante TDADocument4 pagesSFS - Tornillo Autoroscante TDAenriquegarbayoNo ratings yet
- Value Chain Engineering Assignemnt IIDocument22 pagesValue Chain Engineering Assignemnt IImaria50% (2)
- ISN SM 50 ManualDocument8 pagesISN SM 50 Manualsinggih bramantyoNo ratings yet
- Badger Range Guard Wet Chemical Cylinder Assemblies: FeaturesDocument4 pagesBadger Range Guard Wet Chemical Cylinder Assemblies: FeaturesLee WenjianNo ratings yet
- cs2071 New Notes 1Document34 pagescs2071 New Notes 1intelinsideocNo ratings yet
- CIRCULAR WATER TANK DESIGN-Layout1 AkhilDocument1 pageCIRCULAR WATER TANK DESIGN-Layout1 AkhilVENKAT KALYANNo ratings yet
- 1st Term Exam Part 2 - QSDocument10 pages1st Term Exam Part 2 - QSMark Anthony TajonNo ratings yet
- Tutorial DataGeosis Office EspañolmtdDocument205 pagesTutorial DataGeosis Office Españolmtdramm70No ratings yet
- AeDocument12 pagesAeRoberto SanchezNo ratings yet
- Trajectory ClusteringDocument58 pagesTrajectory ClusteringPetrick Gonzalez PerezNo ratings yet
- Ladybug5 DatasheetDocument2 pagesLadybug5 DatasheetEloy Ricardo Franco FigueiraNo ratings yet
- 1 Hyperion Essbase Interview QuestionsDocument2 pages1 Hyperion Essbase Interview Questionssen2natNo ratings yet
- MTA Reorganization Letter and BriefDocument9 pagesMTA Reorganization Letter and BriefGersh KuntzmanNo ratings yet
- The Future of HovercraftDocument3 pagesThe Future of Hovercrafthovpod6214100% (4)
- TablesDocument10 pagesTablesScott SiedschlagNo ratings yet
- Terminals of Ecm: For M/TDocument4 pagesTerminals of Ecm: For M/TTdco SonicoNo ratings yet
- AST Waveguide Switch 1 1 PDFDocument5 pagesAST Waveguide Switch 1 1 PDFANTONIO MARMOLNo ratings yet
- Online Ticket Reservation SystemDocument100 pagesOnline Ticket Reservation SystemPiya SharmaNo ratings yet
- The 717Document2 pagesThe 717An LeNo ratings yet
- NT Photocurre Ed Unmultipli Primary NT Photocurre MultipliedDocument50 pagesNT Photocurre Ed Unmultipli Primary NT Photocurre Multipliedmayuri sritharanNo ratings yet
- Rajib Mall Lecture NotesDocument97 pagesRajib Mall Lecture NotesAnuj Nagpal100% (1)
- Validity Checks: Processing ControlsDocument3 pagesValidity Checks: Processing Controlsjhela18No ratings yet
- Serrano y Olalla - Linearization of The Hoek y BrownDocument11 pagesSerrano y Olalla - Linearization of The Hoek y BrownEsteban JamettNo ratings yet
- 0751 VICTAULIC in Mechanical PipingDocument17 pages0751 VICTAULIC in Mechanical PipingsyafiqNo ratings yet
- Atmos GIGA N 32-160Document1 pageAtmos GIGA N 32-160Efril dilen franciscoNo ratings yet
- Icest 2013 02 PDFDocument424 pagesIcest 2013 02 PDFphanduy1310No ratings yet
- Hioki 3554 Battery Tester ManualDocument89 pagesHioki 3554 Battery Tester ManualAndriGunawanNo ratings yet
- An Introduction To Marketing Research by SmithDocument448 pagesAn Introduction To Marketing Research by SmithKali Das100% (1)
- Manajemen Berbasis Nilai, Studi Atas Penerapan Manajemen Berbasis NilaiDocument20 pagesManajemen Berbasis Nilai, Studi Atas Penerapan Manajemen Berbasis NilaitsfNo ratings yet
- 66 67wvh8m8dall BLL-2936104Document50 pages66 67wvh8m8dall BLL-2936104ManunoghiNo ratings yet
- MVC & Web Api - MCQ: Duration: 30mins Marks: 20Document3 pagesMVC & Web Api - MCQ: Duration: 30mins Marks: 20ManuPcNo ratings yet