Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks Explained
Uploaded by
poitfvhjnjnjnjj j0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pageIntrusive igneous rocks form deep underground where magma cools slowly, allowing large mineral grains to form. Extrusive igneous rocks erupt at the surface and cool rapidly, resulting in fine-grained rocks. Clastic sedimentary rocks form from the compaction and cementation of fragments of pre-existing rocks. Chemical sedimentary rocks precipitate out of solution, and biologic sedimentary rocks form from accumulated organic material. Metamorphic rocks undergo changes to their mineral composition and structure from heat, pressure, and fluids, resulting in foliated rocks that show alignment of flat minerals or non-foliated rocks without alignment.
Original Description:
Original Title
rockchart.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentIntrusive igneous rocks form deep underground where magma cools slowly, allowing large mineral grains to form. Extrusive igneous rocks erupt at the surface and cool rapidly, resulting in fine-grained rocks. Clastic sedimentary rocks form from the compaction and cementation of fragments of pre-existing rocks. Chemical sedimentary rocks precipitate out of solution, and biologic sedimentary rocks form from accumulated organic material. Metamorphic rocks undergo changes to their mineral composition and structure from heat, pressure, and fluids, resulting in foliated rocks that show alignment of flat minerals or non-foliated rocks without alignment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
27 views1 pageIgneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks Explained
Uploaded by
poitfvhjnjnjnjj jIntrusive igneous rocks form deep underground where magma cools slowly, allowing large mineral grains to form. Extrusive igneous rocks erupt at the surface and cool rapidly, resulting in fine-grained rocks. Clastic sedimentary rocks form from the compaction and cementation of fragments of pre-existing rocks. Chemical sedimentary rocks precipitate out of solution, and biologic sedimentary rocks form from accumulated organic material. Metamorphic rocks undergo changes to their mineral composition and structure from heat, pressure, and fluids, resulting in foliated rocks that show alignment of flat minerals or non-foliated rocks without alignment.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
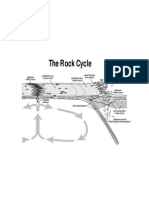
Intrusive igneous rocks are formed from magma that
cools and solidifies deep beneath the Earth's surface.
The insulating effect of the surrounding rock allows the
magma to solidify very slowly. Slow cooling means the
individual mineral grains have a long time to grow, so
they grow to a relatively large size. Intrusive rocks have
a characteristically coarse grain size.
Igneous rocks form when molten
rock (magma) originating from
deep within the Earth solidifies. Extrusive igneous rocks are formed from magma that
The chemical composition of the cools and solidifies at or near the Earth's surface.
magma and its cooling rate Exposure to the relatively cool temperature of the
determine the final rock type. atmosphere or water makes the erupted magma solidify
very quickly. Rapid cooling means the individual mineral
grains have only a short time to grow, so their final size is
very tiny, or fine-grained Sometimes the magma is
quenched so rapidly that individual minerals have no
time to grow. This is how volcanic glass forms.
Clastic sedimentary rocks are made up of pieces
(clasts) of pre-existing rocks. Pieces of rock are
loosened by weathering, then transported to some basin
or depression where sediment is trapped. If the
sediment is buried deeply, it becomes compacted and
cemented, forming sedimentary rock.
Clastic sedimentary rocks may have particles ranging
in size from microscopic clay to huge boulders. Their
names are based on their grain size.
Sedimentary rocks are formed
from pre-existing rocks or pieces Chemical sedimentary rocks are formed by chemical
of once-living organisms. They precipitation. This process begins when water traveling
form from deposits that through rock dissolves some of the minerals, carrying
accumulate on the Earth's them away from their source. Eventually these minerals
surface. are redeposited when the water evaporates away or
when the water becomes over- saturated.
Biologic sedimentary rocks form from once-living
organisms. They may form from accumulated carbon-
rich plant material or from deposits of animal shells.
Foliation forms when pressure squeezes the flat or
elongate minerals within a rock so they become aligned.
These rocks develop a platy or sheet-like structure that
Metamorphic rocks are rocks that reflects the direction that pressure was applied.
have been substantially changed from
their original igneous, sedimentary, or
Non-foliated metamorphic rocks do not have a platy or
earlier metamorphic form.
sheet-like structure. There are several ways that non-
Metamorphic rocks form when rocks
foliated rocks can be produced. Some rocks, such as
are subjected to high heat, high
limestone are made of minerals that are not flat or
pressure, hot, mineral-rich fluids or,
elongate. No matter how much pressure you apply, the
more commonly, some combination of
grains will not align! Another type of metamorphism,
these factors.
contact metamorphism, occurs when hot igneous rock
intrudes into some pre-existing rock. The pre-existing
rock is essentially baked by the heat, changing the
mineral structure of the rock without addition of pressure.
draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft draft
You might also like
- Module 4 (Classification of Rocks)Document2 pagesModule 4 (Classification of Rocks)AkiNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Lesson 4 RocksDocument66 pagesEarth and Life Lesson 4 RocksMagdalena TagubaNo ratings yet
- Earthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Document3 pagesEarthsci Lesson (Rocks&minerals)Ara MaglangitNo ratings yet
- Ns E: Earth Science: There Are Two Types of Igneous RocksDocument4 pagesNs E: Earth Science: There Are Two Types of Igneous RocksMary Joy PalmaNo ratings yet
- Geology For Civil Engineers (Midterm)Document49 pagesGeology For Civil Engineers (Midterm)Jayvee LorenzoNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksDocument7 pagesThe Rock Cycle: Formation of Igneous, Sedimentary and Metamorphic RocksGLENMAR VINEGASNo ratings yet
- Classification of RocksDocument11 pagesClassification of RocksAkshay EverNo ratings yet
- The Classification of RocksDocument21 pagesThe Classification of RocksEric Sylvan D. SalinasNo ratings yet
- Rock cycleDocument2 pagesRock cyclemrinal.lm10No ratings yet
- Rock Cycle Factsheet FINALDocument2 pagesRock Cycle Factsheet FINALMarta CFNo ratings yet
- Metamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandMetamorphic, Igneous and Sedimentary Rocks : Sorting Them Out - Geology for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Types of Rocks Geography Notes For UPSCDocument2 pagesTypes of Rocks Geography Notes For UPSCNEXT LEVEL BASSNo ratings yet
- 4-Types of RocksDocument26 pages4-Types of RocksJessa Mae GastarNo ratings yet
- SSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksDocument11 pagesSSC Petrology: Classification of Igneous, Sedimentary & Metamorphic RocksArianne Mae De Vera GallonNo ratings yet
- ROCKSDocument40 pagesROCKSAngelica Mae PartosaNo ratings yet
- You Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Document12 pagesYou Rock! Well at Least The Earth Rocks!Lance AmoresNo ratings yet
- The Rock Cycle: How Rocks Form and Change Over TimeDocument26 pagesThe Rock Cycle: How Rocks Form and Change Over TimeEsfher Andal EscarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document6 pagesChapter 6api-3749116No ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument4 pagesPETROLOGYJeffer BontesNo ratings yet
- Rocks and Rock FormsDocument14 pagesRocks and Rock FormsJane Aubrey SaliganNo ratings yet
- EALS Lesson-4Document48 pagesEALS Lesson-4kenz.espinosa.22No ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument5 pagesRocks and MineralsRachelle Monn OcsioNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument14 pagesEarth ScienceAhron PatauegNo ratings yet
- Rocks Novemeber 6 10Document15 pagesRocks Novemeber 6 10jomar10glovasaNo ratings yet
- Igneous Sedimentary MetamorphicDocument3 pagesIgneous Sedimentary MetamorphicKezel AtangenNo ratings yet
- Petrology y YyyDocument1 pagePetrology y YyyJaymi MananganNo ratings yet
- Classification of Igneous RocksDocument23 pagesClassification of Igneous RocksAdit8450100% (1)
- Rocks and Minerals - NotesDocument3 pagesRocks and Minerals - NotesBuddhini JNo ratings yet
- Igneous RockDocument2 pagesIgneous RockVenice EdañoNo ratings yet
- Act 2Document4 pagesAct 2Mark Anthony FelicianoNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science Lesson 3: Types of RocksDocument27 pagesEarth and Life Science Lesson 3: Types of RocksRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesDocument6 pagesLesson 4: Classification of Rocks: ObjectivesArabella Balasanos MorfeNo ratings yet
- EARTHSCIErev QRTR 1Document8 pagesEARTHSCIErev QRTR 1Nicole Ann PanaliganNo ratings yet
- Classifying ROCKSDocument21 pagesClassifying ROCKSJherolyn Buenavidez50% (2)
- Classifying Rocks Power Point PresentationDocument21 pagesClassifying Rocks Power Point PresentationDanna BarredoNo ratings yet
- Batuan BekuDocument49 pagesBatuan BekuAdistiNo ratings yet
- Rock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDocument6 pagesRock Types: Igneous, Sedimentary, and MetamorphicDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- Minerals and Rock BatoDocument49 pagesMinerals and Rock BatoLeni B. GarciaNo ratings yet
- Rock Types and Formation: Modified From A Powerpoint Presentation Prepared by Oluseyi Abegunde CputDocument79 pagesRock Types and Formation: Modified From A Powerpoint Presentation Prepared by Oluseyi Abegunde CputOluseyi AbegundeNo ratings yet
- GLY-Chapter 4 PDFDocument15 pagesGLY-Chapter 4 PDFBrendon GovaNo ratings yet
- Classifying RocksDocument24 pagesClassifying RocksJohn Benedict AlbayNo ratings yet
- Earthmaterials Rock Cycle StemscopediaDocument6 pagesEarthmaterials Rock Cycle Stemscopediaapi-506851645100% (2)
- 6 RocksDocument52 pages6 RocksmichaellaNo ratings yet
- Module 4 RocksDocument22 pagesModule 4 RocksAQUINO JAYSON KIERNo ratings yet
- RocksDocument29 pagesRocksjerry100% (1)
- Course No 3 The Rock Cycle 1Document21 pagesCourse No 3 The Rock Cycle 1arachidNo ratings yet
- Earth's Building Blocks: The 3 Types of RocksDocument73 pagesEarth's Building Blocks: The 3 Types of RocksMeera Joy Deboma BlancoNo ratings yet
- Rocks and MineralsDocument58 pagesRocks and MineralsAlbert BugasNo ratings yet
- Earth Sci Igneous ProcessesDocument31 pagesEarth Sci Igneous ProcessesJohn Rey DumaguinNo ratings yet
- Lesson 3 Types of RocksDocument27 pagesLesson 3 Types of RocksRoldan Bibat BoresNo ratings yet
- rocksDocument2 pagesrocksJosephine PerezNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life ScienceDocument18 pagesEarth and Life Scienceamaeamee ameaimeNo ratings yet
- Geology M2 ReviewerDocument7 pagesGeology M2 ReviewerDenjay CatalanNo ratings yet
- ELS The Rocks of The EarthDocument37 pagesELS The Rocks of The Earthkristinemaeosila07No ratings yet
- Types of RocksDocument3 pagesTypes of RocksAbdulhamid Jabar MacabagoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 5 Igneous RocksDocument19 pagesLecture 5 Igneous RocksTechnical GuruNo ratings yet
- Rocks & Minerals ExploitationDocument15 pagesRocks & Minerals ExploitationuibikunNo ratings yet
- Classification of Rocks: Quarter 1, Week 2Document18 pagesClassification of Rocks: Quarter 1, Week 2Ronald ArtilleroNo ratings yet
- Rocks Guided Notes With AnswersDocument3 pagesRocks Guided Notes With Answersapi-231853360100% (1)
- A Method To Integrate Geological Knowledge in Vari PDFDocument17 pagesA Method To Integrate Geological Knowledge in Vari PDFpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Calculate uncertainty in variogramsDocument16 pagesCalculate uncertainty in variogramspoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Shale Hydrocarbon PotentialDocument7 pagesShale Hydrocarbon Potentialpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- AssdddwssmasobwDocument1 pageAssdddwssmasobwpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Was Assdddwssmasobwwss MaasadsadamDocument1 pageWas Assdddwssmasobwwss Maasadsadampoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- DDDWSSMDocument1 pageDDDWSSMpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- DddwssmazobDocument1 pageDddwssmazobpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- ZZZZDocument1 pageZZZZpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- CH 15 PDFDocument24 pagesCH 15 PDFAlfian GilangNo ratings yet
- DddwssDocument1 pageDddwsspoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Openhole Log Analysis and Formation EvaluationDocument1 pageOpenhole Log Analysis and Formation Evaluationpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- CH 16Document18 pagesCH 16poitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Igneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks ExplainedDocument1 pageIgneous, Sedimentary, and Metamorphic Rocks Explainedpoitfvhjnjnjnjj jNo ratings yet
- Rock CycleDocument1 pageRock CyclesiosimorangkirNo ratings yet
- M1 Geology of Sandstone in Ecuador 2017Document17 pagesM1 Geology of Sandstone in Ecuador 2017Eduardo BenalcazarNo ratings yet
- Classify Rocks into Igneous, Sedimentary and MetamorphicDocument9 pagesClassify Rocks into Igneous, Sedimentary and MetamorphicbeaNo ratings yet
- SHS ELS Module 4Document25 pagesSHS ELS Module 4apollo100% (5)
- Engineering Geology Lab Manual: St. Martin'S Engineering CollegeDocument82 pagesEngineering Geology Lab Manual: St. Martin'S Engineering CollegeJai JadavNo ratings yet
- Seismofacies Asri BasinDocument14 pagesSeismofacies Asri BasinnewdenjiNo ratings yet
- Cekungan AkimegahDocument5 pagesCekungan AkimegahMuhammad ArifNo ratings yet
- 120 Field ReportDocument16 pages120 Field ReportAlger Danielle BallonNo ratings yet
- Classifying Sediment Particles by SizeDocument17 pagesClassifying Sediment Particles by SizeEsteban GonzalezNo ratings yet
- A Sedimentary Anayisis Using Wireline LogsDocument29 pagesA Sedimentary Anayisis Using Wireline LogsAngel SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Kaladgi and Bhima BasinDocument20 pagesKaladgi and Bhima BasinLolen Nokcha JamirNo ratings yet
- Hunt Frank RETC 2021 Abrasivity and Cutter Life Assessment For TBM Tunneling in Cobbles and Boulders, RFDocument15 pagesHunt Frank RETC 2021 Abrasivity and Cutter Life Assessment For TBM Tunneling in Cobbles and Boulders, RFswhuntNo ratings yet
- AAPG - Seismic Interpretation of Cabonate Depositional EnvironenmentsDocument17 pagesAAPG - Seismic Interpretation of Cabonate Depositional EnvironenmentsNGT56No ratings yet
- 2021 Casas Minerals-11-00746Document27 pages2021 Casas Minerals-11-00746Ignasi QueraltNo ratings yet
- 2020 - Vallejo Etal - Jurassic To Early Paleogene Sedimentation in The Amazon Region of Ecuador Implications For The Paleogeographic Evolution of Northwestern South AmericaDocument31 pages2020 - Vallejo Etal - Jurassic To Early Paleogene Sedimentation in The Amazon Region of Ecuador Implications For The Paleogeographic Evolution of Northwestern South AmericaPatricio RamonNo ratings yet
- Sandstone Matrix Acidizing Knowledge and Future deDocument12 pagesSandstone Matrix Acidizing Knowledge and Future deazareiforoushNo ratings yet
- Project and Rock Mass Specific Investigation For TunnelsDocument9 pagesProject and Rock Mass Specific Investigation For TunnelsNadim527No ratings yet
- Book Geology in Engineering by S Tabon Excerpt 2022 Edited Drafted 3 23 Pointer 1 Q2 Chapter 3 ExcerptDocument19 pagesBook Geology in Engineering by S Tabon Excerpt 2022 Edited Drafted 3 23 Pointer 1 Q2 Chapter 3 ExcerptMoira Elizabeth SyNo ratings yet
- PorosityDocument70 pagesPorosityابوبكر عبد الباقي100% (1)
- MINERALS AND ROCKS. DemoDocument32 pagesMINERALS AND ROCKS. DemoChrisma BehaganNo ratings yet
- THIN SECTION AND PETROGRAPHY ExperimentDocument17 pagesTHIN SECTION AND PETROGRAPHY Experimentfaizuanismail100% (1)
- 0 DSE Essay Banks (2020) PDFDocument3 pages0 DSE Essay Banks (2020) PDFQuan DouglasNo ratings yet
- CLASSIFY AND EVALUATE RESERVOIR ROCK TYPESDocument30 pagesCLASSIFY AND EVALUATE RESERVOIR ROCK TYPESPipinRioSianturi100% (2)
- Em - 1110 2 3506Document159 pagesEm - 1110 2 3506dannychacon27No ratings yet
- Epithermal Au-Ag Low-Sulfidation - PanteleyevDocument4 pagesEpithermal Au-Ag Low-Sulfidation - Panteleyevnomyaz05No ratings yet
- Barriers to Flow in Tidal Sandstone ReservoirsDocument20 pagesBarriers to Flow in Tidal Sandstone ReservoirsMani BansalNo ratings yet
- PETROLOGYDocument8 pagesPETROLOGYJhunnalou BrotarloNo ratings yet
- The University of Chicago PressDocument17 pagesThe University of Chicago PressziqriiqbalNo ratings yet
- Revision NotesDocument11 pagesRevision NotesAbdulRahman Al AdawiNo ratings yet
- Limestone and Dolomites DescriptionDocument16 pagesLimestone and Dolomites DescriptionHarshaNo ratings yet
- 01 IronDocument21 pages01 IronvhinzsanguinaryNo ratings yet