Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Uploaded by
Ronald KahoraOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Uploaded by
Ronald KahoraCopyright:
Available Formats
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Your guide to safer boiler operation
Your guide to safer boiler operation BOILER CHEMICAL INFORMATION
CLICK ANYWHERE to RETURN to
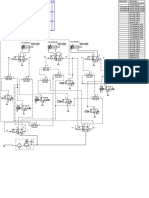
A at InspectApedia.com
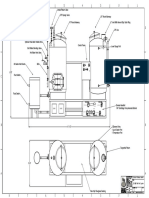
4 1
8 C
5 Supply main D
2 E
ASME
B Relief valve
Check
valve
City water
supply
8
6 Fill valve
normally
used
3 7
Hot water boiler
Pump
Return main
Steam boiler Hot-water boiler
1. Safety valve Steam boiler A. Expansion tank
Hot-water boiler
2. Safety
1. Low-water valvecutoffSteam boiler B.A.Low-water
Expansion cutoff
Hot-water
tank boiler
3.Safety
1.2. Water column
valve
Low-water cutoff blow-down valve C.A.
B. Combination
Expansion
Low-water temperature/pressure
tank
cutoff
4.Low-water
2.3. Pressuretrols
Water column (one
cutoff is high-limit
blow-down valvesafety) gauge
C. or altitude/temperature
B. Combination
Low-water cutoff gauge
temperature/pressure
5. Steam
3.4.Water pressure-gauge
column(one
Pressuretrols blow-down valvesafety)
is high-limit D. Operating
C. Combination
gauge aquastattemperature/pressure
or altitude/temperature gauge
6.Pressuretrols
4.5. Water column
Steam clean-out
pressure-gauge
(one (cross tee)
is high-limit safety) E.D.High-limit
Operating
gauge safety
aquastataquastat
or altitude/temperature gauge
7.
6. Bottom
Water blow-off
column
5. Steam pressure-gauge and
clean-out drain valve
(cross tee) E. High-limit
D. Operating aquastatsafety aquastat
8.Water
6.7. Low-water
Bottom column cutoff/blow-off
blow-off and drain
clean-out valve
(crossvalve
tee) E. High-limit safety aquastat
Note:
7.8. Second
Low-water
Bottom low-water-cutoff
cutoff/blow-off
blow-off and drain valve not shown in diagram
valve
8.Note:
Low-waterSecondcutoff/blow-off
low-water-cutoff not shown in diagram
valve
Boiler water-level – The first duty when taking over a boiler-room shift is to make certain the pipe, fittings and valves
betweenNote: the water Second
glasslow-water-cutoff
and boiler are free notandshownopeninbydiagram
blowing down the water column and water glass and noting the
Boiler water-level – The first duty when taking over a boiler-room shift is to make certain the pipe, fittings and valves
promptness of the return of water to the glass.
betweenwater-level
Boiler the water glass and first
– The boiler are when
duty free and takingopen by ablowing
over downshift
boiler-room the water column
is to make and water
certain glass
the pipe, and noting
fittings the
and valves
promptness
between of the return of water toare
thefreeglass.
The most important rule – The most important rule for the safe operation of boilers is to maintain the proper water- the
the water glass and boiler and open by blowing down the water column and water glass and noting
promptness
level at all of the return
times, and as of water to
constant the glass.
a level as conditions will permit. If water is not visible in the water glass, shut the boiler
The most important rule – The most important rule for the safe operation of boilers is to maintain the proper water-
off immediately until a safe water-level has been determined.
levelmost
The at all times,
important and as constant
rule – The a level
most as important
conditionsrule willforpermit. If water
the safe is notof
operation visible
boilers in is
thetowater glass,the
maintain shut the boiler
proper water-
off
level immediately
at all times, until
and a
as safe water-level
constant a level has
as been determined.
conditions will permit. If water
Low-water and feedwater controls – The low-water cutoff is the most important electrical/mechanical device on is not visible in the water glass, shut the boiler
offyour
immediately until a safeawater-level
boiler for maintaining safe water-level. has been determined.
If a low-water condition develops, it could very well result in an overheating and
Low-water
explosion of your and feedwater
boiler. The low-water controls – The low-water
cutoff should be tested atcutoff is the most important electrical/mechanical device on
least weekly.
your boiler for maintaining a safe water-level.
Low-water and feedwater controls – The low-water cutoff is the most If a low-water condition develops, it could very well
important result in an overheating
electrical/mechanical andon
device
explosion
your of your
boiler for maintaining
Low-water boiler. The low-water
a safe water-level.
cutoff, evaporation cutoff should
test If(steam be
a low-water tested at least
– While
condition
boiler) weekly.
the boiler
develops, is invery
it could operation, shut in
well result offanthe feedwater and
overheating
pump and
explosion ofmonitor
your boiler.the boiler water-level.
The low-water Theshould
cutoff low-water cutoffatshould
be tested shut down the burner before the water level goes
least weekly.
Low-water
out of sight low; cutoff, evaporation
if the burner does not shut testoff,(steam
restart theboiler)
feedwater – While the boiler
pump before is in operation,
the water level goes shut
out ofoffsight
the low
feedwater
and
pump and
immediately monitor the
troubleshoot boiler
the water-level.
low-water The
cutoff to low-water
determine cutoff
the causeshould
of shut
failure.
Low-water cutoff, evaporation test (steam boiler) – While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater
down
The the
boiler burner
must be before
under the water
constant level
attendancegoes
out
by ofproperly
a sight low; if the burner
licensed engineer doesat nottimes
all shutduring
off, restart
this the feedwater pump before the water level goes out of sight low and
test.
pump and monitor the boiler water-level. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner before the water level goes
immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must be under constant attendance
out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level goes out of sight low and
by a properly licensed
Low-water cutoff,engineer
slow drain at alltest
times(steam
during this test. – While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater pump
boiler)
immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must be under constant attendance
byand slowly open the bottom blow valve to drain the water from the boiler. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner
a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Low-water
before the water cutoff,
level goesslow outdrain
of sighttestlow;(steam
if the burner boiler)
does not– While the restart
shut off, boiler the
is infeedwater
operation,pump shut before
off thethefeedwater pump
water level
and
goesslowly
out ofopensightthelowbottom blow valvetroubleshoot
and immediately to drain the water from thecutoff
the low-water boiler.toThe low-water
determine the cutoff
cause should shutThe
of failure. down themust
boiler burner
Low-water cutoff, slow drain test (steam boiler) – While the boiler is in operation, shut off the feedwater pump
before
be under theconstant
water level goes outbyofasight
attendance low;licensed
properly if the burner doesatnot
engineer allshut
timesoff, restart
during thetest.
this feedwater pump before the water level
and slowly open the bottom blow valve to drain the water from the boiler. The low-water cutoff should shut down the burner
goes out of sight low and immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must
before the water level goes out of sight low; if the burner does not shut off, restart the feedwater pump before the water level
be under constant attendance by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
goes out of sight low and immediately troubleshoot the low-water cutoff to determine the cause of failure. The boiler must
be under constant attendance by a properly licensed engineer at all times during this test.
Firing – Aside from the standpoint of economy, maintain the fire as uniformly as possible to avoid an excessive rate of
combustion, undesirable variations in temperature and possible explosions. The destructive force in a boiler explosion is
caused by the instant release of energy stored in the water as heat.
Water gauges – Keep all connections and valves clear. Test by blowing down the water glass and water column regularly.
Gauge cocks or tri-cocks should also be blown regularly.
Safety valves – The safety valve is the most important valve on the boiler. Safety valves prevent dangerous over
pressurization of the boiler. Safety valves are installed in case there is failure of pressure controls or other devices designed
to control the firing rate. All safety valves should be kept free of debris by testing the safety valve regularly. This should be
done when the steam pressure is at approximately 75 percent of the safety-valve set pressure. Safety and safety-relief valves
on low-pressure boilers should be tested at least quarterly, this is in accordance with the National Board Inspection Code.
Blow-down valves – The concentration of solids in the boiler should be measured and the boiler blown-down at such
intervals as necessary to maintain established limits. Blow-down valves are placed at the lowest point of the boiler for the
purpose of blowing sediment or scale from the boiler. They should be maintained in good working order and are to be opened
and closed carefully when used.
Starting fires in a boiler – Before starting fires in a cold boiler or restarting a fire that may have been accidentally
extinguished, the entire fireside of the boiler must be thoroughly ventilated (purged) with the dampers open to remove
unburned gases before attempting to relight the fire. Attempting to start a fire in a boiler with unburned gases is the most
common cause of boiler furnace explosions.
Boiler-room requirement – A current proper engineer’s license and log shall be posted in the boiler room. It is the
responsibility of the owner and the engineer to make sure the boiler is inspected annually.
Hot-water systems – These systems are equipped with expansion tanks for the expansion and contraction of the water
as the temperature varies.
Firing cycle, power burners – The burner will start when the aquastat or pressuretrol calls for heat. The breeching
damper will open and the draft fan will purge the combustion chamber. The main gas or oil valve will be energized when
the pilot or ignition is proved.
Repairs – Any excessive overheating or burning, and any major repairs, must be reported to your boiler inspector.
Classification of boilers – High-pressure boilers are boilers operating at a steam or other vapor pressure in excess of 15
psig, or a water or other liquid boiler in which the pressure exceeds 160 psig, or has a temperature greater than 250 degrees
Fahrenheit. Others are low-pressure boilers.
License requirement – Minnesota Statutes §183.501 states "No person shall be entrusted with the operation of or
operate any boiler, steam engine or turbine who has not received a license of proper grade covering that boiler, steam engine
or turbine.
Study material – The Division of Boiler Inspection has no study material available and suggests you contact your nearest
technical college for classes or resource materials, or contact a library or bookstore for the appropriate book.
The following books may prove useful to boiler operators:
• Special Engineer: Safe Boiler Operation Fundamentals by ATP and Low Pressure Boilers by Frederick
M. Steingress
• Grade "C" licenses: Low Pressure Boilers by Frederick M. Steingress
• Grade "B" licenses: High Pressure Boilers by Frederick M. Steingress and H.J. Frost
• Grade "A" licenses: Steam Plant Operation by Woodruff and Lammers
• Grade "B" and "A" licenses: Stationary Engineering by Steingress, Frost and Walker
This document can be made available in alternative formats, such as large print,
Braille or audio, by calling (651) 284-5031; TTY call 1-800-627-3529.
Revised July 2013
ORIGINAL Source: Minnesota Department of Labor & Industry, https://www.dli.mn.gov/ccld/PDF/guide2saferboiler.pdf
You might also like
- Department of Labor: Guide2saferboilerDocument2 pagesDepartment of Labor: Guide2saferboilerUSA_DepartmentOfLaborNo ratings yet
- Iron Removal Treatment Plant Flow DiagramDocument1 pageIron Removal Treatment Plant Flow DiagramEtcl FactoryNo ratings yet
- KSG 115-119 - PlansDocument4 pagesKSG 115-119 - PlansRashad Biomedical EngineerNo ratings yet
- Roanoke Transformer RecycleDocument1 pageRoanoke Transformer RecycleDavid Adrián EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Dwg. No. 18030007-12.cooling Water SystemDocument1 pageDwg. No. 18030007-12.cooling Water SystemMas Dwi LestariNo ratings yet
- GD-46 Series: YS Housing Equipment Products That Protects "Comfortable" and "Safe" LivingDocument1 pageGD-46 Series: YS Housing Equipment Products That Protects "Comfortable" and "Safe" LivingArstNo ratings yet
- PC210LC-11 Sen06695-01 Troubleshooting For Hydraulic and MechanicalDocument70 pagesPC210LC-11 Sen06695-01 Troubleshooting For Hydraulic and MechanicaldatphuongNo ratings yet
- Masoneilan Power Industry Control SolutionsDocument24 pagesMasoneilan Power Industry Control SolutionsEko PrasetyoNo ratings yet
- Diagrama de Caldera CompletoDocument2 pagesDiagrama de Caldera CompletoedgardoNo ratings yet
- Reliable Solutions For Steam Generation Distribution Applications Brochure en 5180488Document3 pagesReliable Solutions For Steam Generation Distribution Applications Brochure en 5180488AlejandroNo ratings yet
- CAT - Feedwater Protection SystemDocument11 pagesCAT - Feedwater Protection SystemMurli RamchandranNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Diagram D275A-2Document3 pagesHydraulic Diagram D275A-2gire_3pich2005100% (1)
- Utilitas PilotPlantDocument3 pagesUtilitas PilotPlantRaden SukmawatiNo ratings yet
- Roanoke Silo 1 To Silo 2-3Document1 pageRoanoke Silo 1 To Silo 2-3David Adrián EsparzaNo ratings yet
- Catalog - 2016 (Shinwoo Valve) 1.7MDocument20 pagesCatalog - 2016 (Shinwoo Valve) 1.7Mensi116No ratings yet
- WB March 2004Document8 pagesWB March 2004Caterine Jara CeaNo ratings yet
- Boiler Log HourlyDocument2 pagesBoiler Log Hourlymohamed abd el attyNo ratings yet
- 08 Welltest EquipmentDocument4 pages08 Welltest EquipmentdronneNo ratings yet
- TK-508 RH-DemandPump FearureSheetDocument2 pagesTK-508 RH-DemandPump FearureSheetJames LoewenNo ratings yet
- KVS PRESSURE REDUCING VALVEDocument3 pagesKVS PRESSURE REDUCING VALVEThúy VyNo ratings yet
- Boiler Log HourlyDocument2 pagesBoiler Log Hourlyismailenes_66145776No ratings yet
- Skematik Pompa Emerald Tp2-12Document2 pagesSkematik Pompa Emerald Tp2-12Kahfi DinaradjiNo ratings yet
- 9 Plumbing SanitaryDocument1 page9 Plumbing SanitarymdNo ratings yet
- Kinjal AttachedDocument1 pageKinjal AttachedNilay JethavaNo ratings yet
- Principal Drawing Hydraulic Diamec 262Document2 pagesPrincipal Drawing Hydraulic Diamec 262Orlando67% (3)
- Hydraulic Power Pack Minipack HPM TG2 XXX X S N N 05S C18CDDocument1 pageHydraulic Power Pack Minipack HPM TG2 XXX X S N N 05S C18CDjuniorNo ratings yet
- Logo Logo: Kettle Drain Pump Out WhirlpoolDocument1 pageLogo Logo: Kettle Drain Pump Out WhirlpoolchinsiNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Mining Shovels Cat 6060/6060FSDocument9 pagesHydraulic Mining Shovels Cat 6060/6060FSEdison Pfoccori BarrionuevoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulic Mining Shovels Cat 60xx Basic Shovel Hydraulic - System DescriptionDocument24 pagesHydraulic Mining Shovels Cat 60xx Basic Shovel Hydraulic - System DescriptionMiguel Angel RodriguezNo ratings yet
- Automatic Recirculation ValvesDocument6 pagesAutomatic Recirculation ValvesCarlos SolerNo ratings yet
- Pltu Process OverviewDocument1 pagePltu Process OverviewDimasQiNo ratings yet
- Pltu Process Overview PDFDocument1 pagePltu Process Overview PDFTegar Ardian100% (1)
- 3 Week Report: Halini Oil Field - Batch-2Document6 pages3 Week Report: Halini Oil Field - Batch-2Muhammad AwaisNo ratings yet
- Anowara Knit Composite LTD SF-20-ModelDocument1 pageAnowara Knit Composite LTD SF-20-ModelMd SuruzzamanNo ratings yet
- DMF Relief ValveDocument1 pageDMF Relief ValveRealyn BermejoNo ratings yet
- Head TankDocument1 pageHead TankAndrzej KozłowskiNo ratings yet
- MDF - Denah IPALDocument1 pageMDF - Denah IPALIsa Muhammad KhamimNo ratings yet
- SM-Kobelco SK300LC-6E Szervíz (YC07U0623 )Document1,184 pagesSM-Kobelco SK300LC-6E Szervíz (YC07U0623 )Károly Vigh100% (2)
- IFlow Application Diagram 20201015Document10 pagesIFlow Application Diagram 20201015CTHNo ratings yet
- IFlow Application Diagram 20201015Document10 pagesIFlow Application Diagram 20201015CTHNo ratings yet
- Oxy Miser PDFDocument2 pagesOxy Miser PDFRafael CalleNo ratings yet
- The Challenge: Strong Deposit Build-Up The Solution: Selective Cleaning With WaterDocument1 pageThe Challenge: Strong Deposit Build-Up The Solution: Selective Cleaning With WaterErickNo ratings yet
- Schematic Sample HPDocument1 pageSchematic Sample HPMohammad ZeeshanNo ratings yet
- Daikin Refri Cable RXYQ16PTLDocument2 pagesDaikin Refri Cable RXYQ16PTLRicardo Barroso0% (1)
- Boiler Clearances: Peru Sourthern Peru S.ADocument2 pagesBoiler Clearances: Peru Sourthern Peru S.AJohan F. MonroyNo ratings yet
- 3 ProjDocument1 page3 ProjÍtalo Felipe Lira de moraisNo ratings yet
- Drawing Boiler PartsDocument1 pageDrawing Boiler PartsAnonymous FZs3yBHh7No ratings yet
- Western Type WC Indian Type WC: Cold Water Pipe Cold Water PipeDocument1 pageWestern Type WC Indian Type WC: Cold Water Pipe Cold Water PipeNilay JethavaNo ratings yet
- Condensate Feedwater System Part 1Document32 pagesCondensate Feedwater System Part 1Sam RajibNo ratings yet
- Vacuum - Condenser Presentasi 2Document17 pagesVacuum - Condenser Presentasi 2Neon PhoerbaNo ratings yet
- Jpee 2015041311191825Document7 pagesJpee 2015041311191825david limNo ratings yet
- RSW UNIT - Automatic Oil Return SystemDocument1 pageRSW UNIT - Automatic Oil Return SystemMauricioNo ratings yet
- Mer - We - db3120 - Domestic Hot Water Produc DiagramDocument6 pagesMer - We - db3120 - Domestic Hot Water Produc DiagramtienlamNo ratings yet
- Symbols Terms Refrig Air Con - EnglishDocument1 pageSymbols Terms Refrig Air Con - EnglishYang John (Rich-Tech1688)No ratings yet
- Tankless Water Heater DescalingDocument1 pageTankless Water Heater Descalingshunkadu2No ratings yet
- Válvula Control de Bomba - CLAVALDocument4 pagesVálvula Control de Bomba - CLAVALJose CabanaNo ratings yet
- 005 - Cat 6040AC - CAMP SIL BCS4 - Tank Pumps PMSDocument21 pages005 - Cat 6040AC - CAMP SIL BCS4 - Tank Pumps PMSJorby CuadrosNo ratings yet
- FOOD - The Definitive Shoppers Guide PDFDocument27 pagesFOOD - The Definitive Shoppers Guide PDFRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Dry System Manual PDFDocument66 pagesDry System Manual PDFDaneliuc SimionNo ratings yet
- Five CountBaccarat BookDocument138 pagesFive CountBaccarat BookRonald Kahora100% (3)
- 2014 NEC Electrical Instructor Manual and Student Worksheets Level 1 - PDFDocument352 pages2014 NEC Electrical Instructor Manual and Student Worksheets Level 1 - PDFLimuel Espiritu0% (1)
- Franklin Prosperity Report: Low-Cost, Low-Headache Businesses To Start in RetirementDocument17 pagesFranklin Prosperity Report: Low-Cost, Low-Headache Businesses To Start in RetirementRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Baccarat Attack StrategyDocument163 pagesBaccarat Attack StrategyAjay Parihar89% (9)
- Lesson 1Document27 pagesLesson 1Ronald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Loan Payment ScheduleDocument18 pagesLoan Payment ScheduleRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- April 2019 FPRDocument17 pagesApril 2019 FPRRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Input Output: Int. Rate Rate Monthly Int. Rate Years # Pmts Pmts/yr Loan Amt PMT AmtDocument1 pageInput Output: Int. Rate Rate Monthly Int. Rate Years # Pmts Pmts/yr Loan Amt PMT AmtRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Input Output: Int. Rate Rate Years # Pmts Pmts/yr Loan Amt PMT AmtDocument1 pageInput Output: Int. Rate Rate Years # Pmts Pmts/yr Loan Amt PMT AmtRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Accounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerDocument147 pagesAccounting Basics, Part 1: Accrual, Double-Entry Accounting, Debits & Credits, Chart of Accounts Journals And, LedgerThe Three Queens100% (1)
- Radiant Company ManualDocument40 pagesRadiant Company ManualPaunescu BogdanNo ratings yet
- April 2019 FPRDocument17 pagesApril 2019 FPRRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Bookkeeping Forms and Templates Book PDFDocument33 pagesBookkeeping Forms and Templates Book PDFRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Excel 2016 Basic Skills Complete EbookDocument120 pagesExcel 2016 Basic Skills Complete EbookRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- 0818 FranklinDocument17 pages0818 FranklinRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Energysaver - Gov: Tips On Saving Money & Energy at HomeDocument44 pagesEnergysaver - Gov: Tips On Saving Money & Energy at HomeRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- ManualDocument170 pagesManualRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Manual First AidDocument176 pagesManual First AidRonald Kahora100% (2)
- Cost Acco UntingDocument400 pagesCost Acco UntingRuchi Kashyap100% (2)
- Chapter6 MasonryEstimating 0134405501Document8 pagesChapter6 MasonryEstimating 0134405501Ronald KahoraNo ratings yet
- 6th Central Pay Commission Salary CalculatorDocument15 pages6th Central Pay Commission Salary Calculatorrakhonde100% (436)
- Plumbing 101Document234 pagesPlumbing 101Ronald Kahora100% (2)
- ManualDocument170 pagesManualRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- Architectural Standards Graphic Student EditionDocument510 pagesArchitectural Standards Graphic Student EditionRonald Kahora100% (8)
- Trades Math Workbook PDFDocument32 pagesTrades Math Workbook PDFDiyaNegiNo ratings yet
- 2012 NC Building Level 1 Student WorksheetsDocument95 pages2012 NC Building Level 1 Student WorksheetsRonald KahoraNo ratings yet
- April 10, 2015 Strathmore TimesDocument28 pagesApril 10, 2015 Strathmore TimesStrathmore TimesNo ratings yet
- Mining Operational ExcellenceDocument12 pagesMining Operational ExcellencegarozoNo ratings yet
- Pe 1997 01Document108 pagesPe 1997 01franciscocampoverde8224No ratings yet
- Boiler Automation Using PLCDocument91 pagesBoiler Automation Using PLCKishor Mhaske100% (1)
- PM and Presidential Gov'ts Differ Due to Formal Powers and AppointmentDocument3 pagesPM and Presidential Gov'ts Differ Due to Formal Powers and AppointmentNikeyNo ratings yet
- Bamboo in AsiaDocument72 pagesBamboo in Asiafitria lavitaNo ratings yet
- Lala Lajpat Rai College: Public Relations Project Rough Draft Topic: Nike V/S AdidasDocument34 pagesLala Lajpat Rai College: Public Relations Project Rough Draft Topic: Nike V/S AdidasNikitha Dsouza75% (4)
- Computer Programmer or Software Developer or C++ or Visual BasicDocument6 pagesComputer Programmer or Software Developer or C++ or Visual Basicapi-77734404No ratings yet
- Maisie Klompus Resume 02Document1 pageMaisie Klompus Resume 02api-280374991No ratings yet
- DamaDocument21 pagesDamaLive Law67% (3)
- Forty Studies That Changed Psychology 5th Edition PDFDocument2 pagesForty Studies That Changed Psychology 5th Edition PDFsaid hassan0% (1)
- Marie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th GradeDocument50 pagesMarie Bjerede and Tzaddi Bondi 2012 - Learning Is Personal, Stories of Android Tablet Use in The 5th Gradeluiz carvalhoNo ratings yet
- 12V Laptop ChargerDocument12 pages12V Laptop ChargerSharon Babu0% (1)
- Vda. de Villanueva vs. JuicoDocument3 pagesVda. de Villanueva vs. JuicoLucas Gabriel Johnson100% (1)
- PMUY supplementary document titleDocument1 pagePMUY supplementary document titleChandan Kumar Jha69% (67)
- Final ThoughtDocument6 pagesFinal ThoughtHaroon HussainNo ratings yet
- Module 2 - Introduction To A Web-AppDocument17 pagesModule 2 - Introduction To A Web-AppJASPER WESSLYNo ratings yet
- Netflix AccountsDocument2 pagesNetflix AccountsjzefjbjeNo ratings yet
- Time Division Muliple AccessDocument4 pagesTime Division Muliple AccessAbhishek RanaNo ratings yet
- Only PandasDocument8 pagesOnly PandasJyotirmay SahuNo ratings yet
- Understanding ProbabilityDocument14 pagesUnderstanding ProbabilityKajaraiNo ratings yet
- Lecture No 5Document41 pagesLecture No 5sami ul haqNo ratings yet
- Προσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςDocument20 pagesΠροσχέδιο Έκθεσης Γ.Γ. ΟΗΕ για Καλές ΥπηρεσίεςARISTEIDIS VIKETOSNo ratings yet
- Intra Cell HODocument10 pagesIntra Cell HOMostafa Mohammed EladawyNo ratings yet
- Project ProposalDocument6 pagesProject Proposalapi-386094460No ratings yet
- PR-Unit1-ERP EvolutionDocument13 pagesPR-Unit1-ERP EvolutionSiddhant AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Gram-Charlier para Aproximar DensidadesDocument10 pagesGram-Charlier para Aproximar DensidadesAlejandro LopezNo ratings yet
- Probe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideDocument8 pagesProbe Filter 5.1 SNMP Support Reference GuideOrlando MondlaneNo ratings yet
- HHF-1600 Direct-Drive Pump Utilization Parts ListDocument27 pagesHHF-1600 Direct-Drive Pump Utilization Parts ListJohn Simanca100% (1)
- LG Mini Split ManualDocument38 pagesLG Mini Split ManualMark ChaplinNo ratings yet