Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Precorrection
Uploaded by
api-396948926Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Precorrection
Uploaded by
api-396948926Copyright:
Available Formats
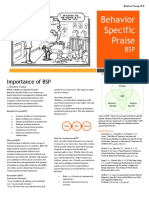
WHAT IS PRE-CORRECTION?
Pre-correction is a PBIS classroom man-
agement technique where teachers re-
mind students of expected behaviors be- PRE-CORRECTION IN DIVERSE
fore an activity rather than punishing for CLASSROOMS:
negative behaviors afterwards.
Pre-correction has been successfully used to
improve behavior and learning for all students,
including students with emotional and learning
IMPLEMENTING PRE-CORRECTION
disabilities and those learning English.
IN YOUR CLASSROOM
Step 1. IDENTIFY THE PROBLEM
BEHAVIORS
Step 2. CHANGE EXPECTATIONS
AND COMMUNICATE NEW ONES
Step 3. PRACTICE NEW ROUTINES
AND PROVIDE REMINDERS
Step 4. POSITIVE REINFORCEMENT
Step 5. MONITOR STUDENT
PROGRESS
Tips to bring pre-correction to your classroom:
Communicate expectations in 4 ways: verbally, in writing, in images and by modeling
Give instructions and expectations in a manner appropriate to your students
Use pre-correction to guide behavior and to remind students of common errors on as-
signments
Be patient. Students need to practice new routines before they become automatic.
Combine pre-correction with plenty of praise when students meet expectations
Success by the numbers:
+ 42.25%- Respectful passing period behavior in middle schools ….
+42% - Reading comprehension in students with learning disabilities ...
+28%- Time on task for students with learning disabilities …
when pre-correction is used.
FURTHER INFORMATION:
University of Louisville : Videos and examples
William and Mary : Dealing with challenging behaviors
Department of Education: Pre-correction intervention guide
References:
Crosby, Crosby, S., Jolivette, K., & Patterson, D. (2006). Using precorrection to manage inappropriate
academic and social behaviors. Beyond Behavior, 16(1), 14-17.
Haydon, T., & Kroeger, S. (2016). Active supervison, precorrection and explicit timing: A high school case
study on classroom behavior. Preventing School Failure, 60(1), 70-78.
Lampi, A., Fenty, N., & Beaunae, C. (2005). Makting the three Ps easier: Praise, proximity and
precorrection. Beyond Behavior, 15(1), 8-12.
Miao, Y., Darch, C., & Rabren, K. (2002). Use of precorrection strategies to enhace reading performance of
studens with learning and behavior problems. Journal of Instructional Psychology, 29(3), 162-
174.
Oswald, K., Safran, S., & Johanson, G. (2005). Preventing trouble: Making schools safer places using
positive behavior upports. Education and Treatment of Children, 28(3), 265-278.
Parks Ennis, R., Schwab, J., & Jolivette, K. (2013). Using precorrectin as a secondary-tier intervention for
reducing problem behaviors in instructional and noninstructional settings. Beyond Behavior, 22
You might also like
- PrecorrectionDocument2 pagesPrecorrectionapi-396767767No ratings yet
- Activity 6-9 JoyDocument18 pagesActivity 6-9 JoyJoy Conejero NemenzoNo ratings yet
- Errorless LeanringDocument18 pagesErrorless Leanringapi-483592133No ratings yet
- Disruptive Behaviour 1Document5 pagesDisruptive Behaviour 1Daniel DubeNo ratings yet
- Classroom Assesment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program: H.Abdulracman, Norjannah D. Beed-General EducationDocument30 pagesClassroom Assesment in The K To 12 Basic Education Program: H.Abdulracman, Norjannah D. Beed-General EducationNor JannahNo ratings yet
- Assessment FinalDocument84 pagesAssessment FinalJan Angiely SollanoNo ratings yet
- Assessment in Support of Learning Chappuis HandoutDocument15 pagesAssessment in Support of Learning Chappuis HandoutRoy VergesNo ratings yet
- (Prelim EDU105 Hazel v. Villanueva BSEScience) .Document4 pages(Prelim EDU105 Hazel v. Villanueva BSEScience) .JoelNo ratings yet
- Roles of Assessment in Instructional DecisionDocument36 pagesRoles of Assessment in Instructional DecisionJason Parel Narte100% (1)
- Principles OF Teaching: Divine Mercy College Foundation Inc. Caloocan City Professional EducationDocument28 pagesPrinciples OF Teaching: Divine Mercy College Foundation Inc. Caloocan City Professional EducationHazrat AliNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Unit Lesson 3Document3 pagesNutrition Unit Lesson 3api-528473581No ratings yet
- Fs5 Fs6 Answer For Every JournalDocument5 pagesFs5 Fs6 Answer For Every JournalRogerNo ratings yet
- ASSESSSMENTDocument15 pagesASSESSSMENTlilianaborNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1 Activity 1Document7 pagesLesson 1 Activity 1Xixo LabNo ratings yet
- Teaching ToolboxDocument24 pagesTeaching Toolboxapi-634989174No ratings yet
- Types of AssessmentsDocument20 pagesTypes of AssessmentsLluvia lluviasNo ratings yet
- New DOCX DocumentDocument17 pagesNew DOCX Documenttulang.mrNo ratings yet
- Evaluations Have A Significant Impact On LearnersDocument2 pagesEvaluations Have A Significant Impact On LearnersAngel EspirituNo ratings yet
- 2 - Theories of Assertive TacticsDocument47 pages2 - Theories of Assertive TacticsyoungpohpingNo ratings yet
- Prof Ed 73Document15 pagesProf Ed 73Rheamar Angel MolinaNo ratings yet
- FS Nov. 19Document6 pagesFS Nov. 19Jepay Villanueva CastroNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Science Test Helps Teachers at Macario B. Asistio Sr. High SchoolDocument3 pagesDiagnostic Science Test Helps Teachers at Macario B. Asistio Sr. High SchoolROWENA NADAONo ratings yet
- Task 5 DiagnostikDocument6 pagesTask 5 DiagnostikEvryan SyahputraNo ratings yet
- 759 Inclusive Education: Bs - Bs - BannerDocument18 pages759 Inclusive Education: Bs - Bs - BannerLizeth JaimesNo ratings yet
- Gapbis Problem Solving Protocol For Dcs Fy14 SampleDocument5 pagesGapbis Problem Solving Protocol For Dcs Fy14 SampleUmbraSeriiNo ratings yet
- Allama Iqbal Open UniversityDocument33 pagesAllama Iqbal Open UniversityZeenat MoambarNo ratings yet
- Behaviour ManagmentDocument4 pagesBehaviour Managmentapi-374602325No ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument8 pagesChapter IRAFFY LAGARTONo ratings yet
- FS 1 Activity 5.1Document6 pagesFS 1 Activity 5.1Aira Gyn PalomariaNo ratings yet
- Oas Community College: DescriptionDocument7 pagesOas Community College: DescriptionTricia Ann A. SodsodNo ratings yet
- Building Basic Assessment CompetenceDocument60 pagesBuilding Basic Assessment CompetenceMary Ann SedanNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1 Episode 10Document3 pagesField Study 1 Episode 10Fredie RamosNo ratings yet
- ED 106 Module (3rd-4th Week)Document6 pagesED 106 Module (3rd-4th Week)Mariza GiraoNo ratings yet
- Field Study 1: The Instructional CycleDocument9 pagesField Study 1: The Instructional CycleMikee GallaNo ratings yet
- Pangasinan State University College of Teacher Education: Written ReportDocument8 pagesPangasinan State University College of Teacher Education: Written ReportMyrna ParasNo ratings yet
- Title ProposalDocument10 pagesTitle ProposalMary Ann TanayNo ratings yet
- FS Episode 10Document11 pagesFS Episode 10Abegail Linaga83% (6)
- PrecorrectionDocument3 pagesPrecorrectionapi-314835832No ratings yet
- Functions and Purposes of Testing in Graphic Organizers and ReflectionsDocument3 pagesFunctions and Purposes of Testing in Graphic Organizers and ReflectionsChery-Ann GorospeNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan: Week 11-1, 11-2 "Quantitative Data Collection 2: Validity and Reliability and Sampling"Document2 pagesLesson Plan: Week 11-1, 11-2 "Quantitative Data Collection 2: Validity and Reliability and Sampling"Sran LouthNo ratings yet
- t1 Teacher Coaching and Development ProcessDocument5 pagest1 Teacher Coaching and Development Processapi-619576791No ratings yet
- Precepting Skills For Precepting ChallengesDocument4 pagesPrecepting Skills For Precepting ChallengesGood MixNo ratings yet
- M4L4Conditions of Validity Reliability and Quality ofDocument7 pagesM4L4Conditions of Validity Reliability and Quality ofElla nicole ArabellaNo ratings yet
- Assessment and Evaluation in Social ScienceDocument37 pagesAssessment and Evaluation in Social SciencealexNo ratings yet
- Reviewer Morata FinalsDocument30 pagesReviewer Morata FinalsTricia NicolasNo ratings yet
- Group 3 Tegr 113Document42 pagesGroup 3 Tegr 113Nicole Kate AsisNo ratings yet
- Written ReportDocument12 pagesWritten ReportAngel JoyNo ratings yet
- Ep 5Document6 pagesEp 5Mari FelizardoNo ratings yet
- Al Lesson 1Document3 pagesAl Lesson 1Jr CastrodesNo ratings yet
- 3rd Activity Sir MarkDocument3 pages3rd Activity Sir MarkMark Nel Venus0% (1)
- Domain 5Document27 pagesDomain 5JANLYN FRANCISCONo ratings yet
- Classroom Management Strategies for TeachersDocument55 pagesClassroom Management Strategies for TeachersJulius Odia OdiaNo ratings yet
- LessonplanDocument6 pagesLessonplangrace.ledresNo ratings yet
- Final Thesis Baby MOTAR Final Na Final Na Talaga For Binding - 1Document84 pagesFinal Thesis Baby MOTAR Final Na Final Na Talaga For Binding - 1Baby Ann MotarNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Champs: Dorie Miller ElementaryDocument55 pagesWelcome To Champs: Dorie Miller Elementarycontrolmachete01No ratings yet
- Lap 19Document5 pagesLap 19Ann KurtNo ratings yet
- Week 8 SeiDocument5 pagesWeek 8 Seiyyyc2w2wwxNo ratings yet
- Leahy ClassroomAssessmentDocument7 pagesLeahy ClassroomAssessmentDebbie SamuelsNo ratings yet
- Millado - Jaymar Jhon - InsightDocument27 pagesMillado - Jaymar Jhon - InsightEdison ThomasNo ratings yet
- Who Packed Your Parachute? Why Multiple Attempts on Assessments Matter: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsFrom EverandWho Packed Your Parachute? Why Multiple Attempts on Assessments Matter: Quick Reads for Busy EducatorsNo ratings yet
- Special Needs AccomidationsDocument4 pagesSpecial Needs Accomidationsapi-383795064No ratings yet
- Positive Self-Talk Part 2Document2 pagesPositive Self-Talk Part 2api-396767767No ratings yet
- Lincs StrategyDocument2 pagesLincs Strategyapi-396767767No ratings yet
- Flyer Praise Notes 2Document2 pagesFlyer Praise Notes 2api-396767767No ratings yet
- Colored OverlaysDocument2 pagesColored Overlaysapi-396767767No ratings yet
- Cooperative Learning HandoutDocument2 pagesCooperative Learning Handoutapi-396767767No ratings yet
- GoodbehaviorgameDocument2 pagesGoodbehaviorgameapi-396767767No ratings yet
- ChoiceboardsDocument2 pagesChoiceboardsapi-396767767No ratings yet
- BSP HandoutDocument8 pagesBSP Handoutapi-396767767No ratings yet
- BehaviorcontractsDocument2 pagesBehaviorcontractsapi-396767767No ratings yet
- 9 MnemonicsDocument2 pages9 Mnemonicsapi-396767767No ratings yet
- Newsletter 20 - January 2008Document12 pagesNewsletter 20 - January 2008Alexander Mendoza100% (1)
- 20dce007 Practical1,2Document63 pages20dce007 Practical1,2Anand BapodaraNo ratings yet
- Graph 1Document11 pagesGraph 1prashanthan balendraNo ratings yet
- Hoyalens SFT Trade BrochureDocument6 pagesHoyalens SFT Trade BrochureevershineopticalNo ratings yet
- David Mind DARK PSYCHOLOGY MASTERY - 3 Books in 1 - Dark Psychology How To Analyze People The Art of MDocument581 pagesDavid Mind DARK PSYCHOLOGY MASTERY - 3 Books in 1 - Dark Psychology How To Analyze People The Art of Mmonikaxd100% (1)
- Veteran Resource Guide For Congressional District 9Document27 pagesVeteran Resource Guide For Congressional District 9RepSinemaNo ratings yet
- Peoria County Jail Booking Sheet For Sept. 22, 2016Document7 pagesPeoria County Jail Booking Sheet For Sept. 22, 2016Journal Star police documentsNo ratings yet
- Fridleifsson BenefitDocument9 pagesFridleifsson BenefitWanambwa SilagiNo ratings yet
- Exchange Online Instruction GuideDocument7 pagesExchange Online Instruction GuideKishor WaghmareNo ratings yet
- 1-1-Over View of PlumbingDocument30 pages1-1-Over View of PlumbingCalvin Paulo MondejarNo ratings yet
- Soal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 7 Chapter 1Document3 pagesSoal Bahasa Inggris Kelas 7 Chapter 1AcizziaChocca57% (7)
- Texas Instruments TI-36x Solar ManualDocument30 pagesTexas Instruments TI-36x Solar Manualsolpo100% (1)
- Plaint Suit For InjunctionDocument7 pagesPlaint Suit For InjunctionfredrickNo ratings yet
- BCG Matrix and Its Significance in Product Mix Analysis - NCK Pharma Solution Private Limited - Powered by Comm100 PDFDocument6 pagesBCG Matrix and Its Significance in Product Mix Analysis - NCK Pharma Solution Private Limited - Powered by Comm100 PDFAkhilesh MenonNo ratings yet
- Inductive Vs Deductive MethodDocument31 pagesInductive Vs Deductive MethodKaren Delfino MosendeNo ratings yet
- Obstacles To God FrienshipDocument6 pagesObstacles To God Frienshipapi-378040460No ratings yet
- From Ramesh - Updated CRO Names 03022021Document90 pagesFrom Ramesh - Updated CRO Names 03022021Vamsi SattiNo ratings yet
- RA 7942 Plus CasesDocument53 pagesRA 7942 Plus CasesJessielleNo ratings yet
- Dos Vs Linux PDFDocument2 pagesDos Vs Linux PDFJawad Sandhu0% (1)
- Senior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsDocument101 pagesSenior Auditor Cost-Accounting-McqsMuhammad HamidNo ratings yet
- GRI 20F-12-B Data SheetDocument3 pagesGRI 20F-12-B Data SheetJMAC SupplyNo ratings yet
- Mid Term Date Sheet - pq0NsApDocument2 pagesMid Term Date Sheet - pq0NsApSahil HansNo ratings yet
- Ceremony - Baby Dedication PDFDocument5 pagesCeremony - Baby Dedication PDFrafaelgsccNo ratings yet
- Buffalo Dairy Farm Project Report 4 Buffaloes, Business Plan, SubsidyDocument6 pagesBuffalo Dairy Farm Project Report 4 Buffaloes, Business Plan, SubsidyManjunadh Padala100% (2)
- How to knit top down sleeves flat (less than 40 charsDocument3 pagesHow to knit top down sleeves flat (less than 40 charsRadu AnghelNo ratings yet
- Fatimah Az-ZahraDocument10 pagesFatimah Az-ZahraYahya AliNo ratings yet
- Central Visayas RDP 2017 2022 Midterm Update 1Document139 pagesCentral Visayas RDP 2017 2022 Midterm Update 1peachai143No ratings yet
- Tooling Guide For High Reliability Electrical Systems Rev. 11 Ver. 1Document202 pagesTooling Guide For High Reliability Electrical Systems Rev. 11 Ver. 1AndersonNo ratings yet
- Forrest GumpDocument4 pagesForrest Gumpcarmenng19900% (1)
- Assignment 3Document9 pagesAssignment 3Hà Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet