Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1990 Camry Wiring Diagram
Uploaded by
Arnold Ayca Mamani0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views7 pagesThis document provides information on the electrical system of the 1990 Toyota Camry, including:
- An introduction that outlines the 12 sections of the manual and how to use it for troubleshooting.
- Section 3 describes how the manual shows each system circuit from the power source to ground points and provides tips on using other sections for troubleshooting.
- Section 4 provides an example of how current flows through the power window system for various operations like manual up, auto down, and locking windows. It also lists voltage measurements for key components.
Original Description:
asdfasdfsdf
Original Title
Foreword
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document provides information on the electrical system of the 1990 Toyota Camry, including:
- An introduction that outlines the 12 sections of the manual and how to use it for troubleshooting.
- Section 3 describes how the manual shows each system circuit from the power source to ground points and provides tips on using other sections for troubleshooting.
- Section 4 provides an example of how current flows through the power window system for various operations like manual up, auto down, and locking windows. It also lists voltage measurements for key components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views7 pages1990 Camry Wiring Diagram
Uploaded by
Arnold Ayca MamaniThis document provides information on the electrical system of the 1990 Toyota Camry, including:
- An introduction that outlines the 12 sections of the manual and how to use it for troubleshooting.
- Section 3 describes how the manual shows each system circuit from the power source to ground points and provides tips on using other sections for troubleshooting.
- Section 4 provides an example of how current flows through the power window system for various operations like manual up, auto down, and locking windows. It also lists voltage measurements for key components.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 7
FOREWORD
This wiring diagram manual has been prepared to provide
information on the electrical system of the 1990 TOYOTA
CAMRY.
Applicable models: SV21, 25 series
VZV21 series
For service specifications and repair procedures of the above
models other than those listed in this manual, refer to the
following manuals;
Manual Name Pub. No.
_ 1990 Camry Repair Manual Volume 1
Volume 2
_ TCCS (3S–FE) Diagnosis Manual
_ ECT (A140E) Diagnosis Manual
_ ECT (A540E) Diagnosis Manual
_ 1990 Model New Car Features
RM151U1
RM151U2
DM011U
DM013U
DM014U
NCF059U
All information in this manual is based on the latest product
information at the time of publication. However, specifications
and procedures are subject to change without notice.
TOYOTA MOTOR CORPORATION
2
INTRODUCTION
This manual consists of the following 12 sections:
No. Section Description
1 INDEX Index of the contents of this manual.
2 INTRODUCTION Brief explanation of each section.
3 HOW TO USE
THIS MANUAL Instructions on how to use this manual.
4 TROUBLE–
SHOOTING Describes the basic inspection procedures for electrical circuits.
5 ABBREVIATIONS Defines the abbreviations used in this manual.
6
GLOSSARY OF
TERMS AND
SYMBOLS
Defines the symbols and functions of major parts.
7 RELAY LOCATIONS Shows position of the Electronic Control Unit, Computer,
Relays, Junction
Block, etc. This section is closely related to the system circuit.
8 ELECTRICAL
WIRE ROUTING
Describes position of the Parts Connectors, Ground points, etc.
This section is closely related to the system circuit.
9
POWER SOURCE
(POWER–LOAD,
Reference)
Describes power distribution from the power supply to various electrical
loads.
10 INDEX Index of the system circuits.
11
SYSTEM CIRCUITS
Electrical circuits of each system are shown from the power supply through
ground points. Wiring connections and their positions are shown and
classified by code according to the connection method. (Refer to the
section, “How to use this manual”).
The “System Outline” and “Service Hints” useful for troubleshooting are
also contained in this section.
GROUND POINTS Shows ground positions of all parts described in this manual.
12 OVERALL
WIRING DIAGRAM Provides circuit diagrams showing the circuit connections.
3
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
This manual provides information on the electrical circuits installed
on vehicles by
dividing them into each system circuit.
The actual wiring of each system circuit is shown from the point
where the power source
is received from the battery as far as each ground point. (All circuit
diagrams are shown
with the switches in the OFF position.)
When troubleshooting any problem, first understand the operation of
the circuit where
the problem was detected (see System Circuit section), the power
source supplying
power to that circuit (see Power Source section), and the ground
points (see Ground
Points section). See the System Outline to understand the circuit
operation.
When the circuit operation is understood, begin troubleshooting of
the problem circuit
to isolate the cause. Use Relay Location and Electrical Wire Routing
sections to find
each part, junction block and wiring harness connectors, wiring
harness and wiring
harness connectors, and ground points of each system circuit.
Internal wiring for each
junction block is also provided for better understanding of
connection within a junction
block.
Wiring related to each system is indicated in each system circuit by
arrows (from
, to ). When overall connections are required, see the Overall Wiring
Diagram
at the end of this manual.
4
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
N
O
5
: System Title
: Indicates a Relay Block. No shading is used and only
the Relay Block No. is shown to distinguish it from the
J/B.
Example: Indicates Relay Block No. 1.
: Indicates the connector to be connected to a part (the
numeral indicates the pin No.)
: Connector Color
Connectors not indicated are milky white in color.
: ( ) is used to indicate different wiring and connector,
etc. when the vehicle model, engine type, or
specification is different.
: Indicates related system.
: Indicates the wiring harness and wiring harness
connector. The wiring harness with male terminal is
shown with arrows ( ).
Outside numerals are pin numbers.
: Represents a part (all parts are shown in sky blue). The
code (e.g. ) is the same as the code used in parts
position.
: Junction Block (The number in the circle is the J/B No.
and the connector code is shown beside it). Junction
Blocks are shaded to clearly separate them from other
parts (different junction blocks are shaded differently for
further clarification).
3B indicates
that it is inside
Junction Block
No. 3.
Example:
: Indicates the wiring color.
Wire colors are indicated by an alphabetical code.
B = Black L = Blue R = Red
BR = Brown LG = Light Green V = Violet
G = Green O = Orange W = White
GR = Gray P = Pink Y = Yellow
The first letter indicates the basic wire color and the
second letter indicates the color of the stripe.
Example: L – Y
(Blue) (Yellow)
: Page No.
: Indicates a sealed wiring harness.
: Indicates a ground point.
: Indicates the pin number of the connector.
The numbering system is different for female and male
connectors.
Example: Numbered in order
from upper left to
lower right
Numbered in order
from upper right to
lower left
The numbering system for the overall wiring diagram is
the same as above.
: When 2 parts both use one connector in common, the
parts connector name used in the wire routing section
is shown in square brackets [ ].
Q
R
S
T
U
V
P
6
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
WITH THE IGNITION SW TURNED ON, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 3 OF THE POWER WINDOW MASTER SW, TERMINAL 2 OF THE POWER
WINDOW CONTROL RELAY
AND TERMINAL 8 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW THROUGH THE DOOR FUSE.
1. DRIVER’S WINDOW “MANUAL UP” OPERATION BY MASTER SW
HOLDING MANUAL SW (DRIVER’S) ON “UP” POSITION LOCATED IN POWER WINDOW MASTER SW, THE CURRENT FLOWS TO TERMINAL 5 OF THE
POWER WINDOW
CONTROL RELAY THROUGH TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER SW _ TERMINAL 2 TO OPERATE A POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY. THUS THE
CURRENT INSIDE THE RELAY
FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 2 OF THE RELAY _ TERMINAL 1 _ TERMINAL 2 OF THE POWER WINDOW MOTOR _ TERMINAL 1 _ TERMINAL 4 OF THE
RELAY _ TERMINAL
3 _ TO GROUND. THE MOTOR TURNS TO RAISE THE WINDOW. RELEASING THIS SW, THE ROTATION OF MOTOR IS STOPPED AND THE WINDOWS
STOP AT DESIRED
POINT.
(FOR THE “MANUAL DOWN” OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE
CHANGED).
2. DRIVER’S WINDOW “AUTO DOWN” OPERATION BY MASTER SW
ONCE THE “AUTO DOWN” BUTTON OF THE MASTER SW IS PUSHED, THE CURRENT FLOWS TERMINAL 9 OF THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL
RELAY THROUGH TERMINAL
3 OF THE MASTER SW _ TERMINALS 8 AND 9 TO OPERATE THE RELAY. THUS THE CURRENT INSIDE THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY
FLOWS FROM TERMINAL
2 OF THE RELAY _ TERMINAL 4 _ TERMINAL 1 OF THE POWER WINDOW MOTOR _ TERMINAL 2 _ TERMINAL 1 OF THE RELAY _ TERMINAL 3 _ TO
GROUND.
THE MOTOR CONTINUES TO ROTATE, ENABLING THEWINDOW TO DESCEND.
WHEN THE WINDOW DESCENDS TO THE END POSITION, THE CURRENT IS CUT OFF TO RELEASE THE AUTO DOWN FUNCTION BASED ON THE
INCREASING CURRENT
BETWEEN TERMINAL 2 OF THE RELAY AND TERMINAL 1 IN RELAY.
3. DRIVER’S WINDOW AUTO DOWN RELEASE OPERATION BY MASTER SW
BY HOLDING THE MANUAL SW (DRIVER’S) IN “UP” POSITION WHILE OPERATING AUTO DOWN. THE CURRENT FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER
SW PASSING THROUGH
TERMINAL 2 FLOWS TO TERMINAL 5 OF THE RELAY AND RELEASES THE AUTO DOWN FUNCTION IN THE POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY.
RELEASING THE HAND FROM
SW, STOPS THE WINDOW AND CONTINUING TO TOUCH THE SW, SWITCHES THE FUNCTION TO MANUAL UP OPERATION.
4. PASSENGER’S WINDOW UP OPERATION (MASTER SW) AND WINDOW LOCK SW OPERATION
HOLDING PASSENGER’S WINDOW SW (MASTER SW) ON “UP”, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 3 OF THE MASTER SW THROUGH
TERMINAL 6 TO TERMINAL 3 OF
THE POWER WINDOW SW (PASSENGER’S) _ TERMINAL 4 _ TERMINAL 2 OF THE MOTOR _ TERMINAL 1 _ TERMINAL 9 OF THE POWER WINDOW
SW _ TERMINAL
7 _ TERMINAL 1 OF THE MASTER SW _ TERMINAL 4 TO GROUND. THE MOTOR RUNS TO RAISE THE WINDOW. RELEASING THIS SW, THE
ROTATION OF MOTOR IS
STOPPED AND WINDOW STOPS AT THE DESIRED POINT.
SWITCHING THE WINDOW LOCK SW IN “LOCK” POSITION, THE CIRCUIT IS OPENED AND STOPS THE MOTOR ROTATION.
(FOR THE DOWN OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE CHANGED).
5. PASSENGER’S WINDOW DOWN OPERATION (POWER WINDOW SW)
HOLDING POWER WINDOW SW ON “DOWN”, THE CURRENT FLOWS FROM TERMINAL 8 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW _ TERMINAL 9 _ TERMINAL 1
OF THE MOTOR _
TERMINAL 2 _ TERMINAL 4 OF THE POWER WINDOW SW _ TERMINAL 3 _ TERMINAL 6 OF THE MASTER SW _ TERMINAL 4 _ TO GROUND. THE
MOTOR RUNS
TO LOWER THE WINDOW.
(FOR THE UP OPERATION, CURRENT FLOWS IN THE REVERSE DIRECTION BECAUSE THE TERMINALS WHERE IT FLOWS ARE CHANGED).
(A) POWER WINDOW MASTER SW
4–GROUND: ALWAYS CONTINUITY
3–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
(B) POWER WINDOW CONTROL RELAY
3–GROUND: ALWAYS CONTINUITY
2–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION
5–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT UP POSITION
8–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT AUTO DOWN POSITION
9–GROUND: APPROX. 12 VOLTS WITH IGNITION SW AT ON POSITION AND MASTER SW AT DOWN OR AUTO DOWN POSITION
WINDOW LOCK SW
OPEN WITH WINDOW LOCK SW AT LOCK POSITION
: PARTS LOCATION
CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE PAGE CODE SEE PAGE
A P4 21 C P5 21 E P6 21
B P2 21 D P3 21
: RELAY BLOCKS
CODE SEE PAGE RELAY BLOCK (RELAY BLOCK LOCATION)
1 16 R/B NO. 1 (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT)
: JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS CONNECTOR
CODE SEE PAGE JUNCTION BLOCK AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
3B 14 J/B NO. 3 AND COWL WIRE (INSTRUMENT PANEL LEFT SIDE)
: CONNECTOR JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS
CODE SEE PAGE JOINING WIRE HARNESS AND WIRE HARNESS (CONNECTOR LOCATION)
D1 26 FRONT DOOR RH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (RIGHT KICK PANEL)
H1 26 FRONT DOOR LH WIRE AND COWL WIRE (LEFT KICK PANEL)
: GROUND POINTS
CODE SEE PAGE GROUND POINT LOCATION
C 24 COWL LEFT
SYSTEM OUTLINE
SERVICE HINTS
Q
R
S
T
U
V
P
7
: Explains the system outline.
: Indicates values or explains the function for reference during troubleshooting.
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of the parts in the
system circuit.
Example: Part A (Power Window Master SW) represents code P4 on page 21 of the
manual.
* The letter in the code is from the first letter of the part, and the number indicates its
order
in parts starting with that letter.
Part is 4th in order
Power Window Master SW
Example: P 4
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of Relay Block
Connectors in the
system circuit.
Example: Connector 1 is described on page 16 of this manual and is installed on the
left side of the
instrument panel.
: Indicates the reference page showing the position on the vehicle of J/B and Wire
Harness in the system
circuit.
Example: Connector 3B connects the Cowl Wire and J/B No. 3. It is described on page
14 of this
manual, and is installed on the instrument panel left side.
: Indicates the reference page describing the wiring harness and wiring harness
connector (the female
wiring harness is shown first, followed by the male wiring harness).
Example: Connector D1 connects the front door RH wire (female) and cowl wire (male).
It is described
on page 26 of this manual, and is installed on the right side kick panel.
: Indicates the reference page showing the position of the ground points on the vehicle.
Example: Ground point C is described on page 24 of this manual and is installed on the
cowl left side.
POWER SOURCE
POWER SOURCE (Power–Load, Reference)
8
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
The Power – Load section, describes which parts each power source (fuses, fusible links, and
circuit breakers) transmits
current to. In the Power Source circuit diagram, the conditions when battery power is supplied to
each system are explained.
Since all System Circuit diagrams start from the power source, the power source system must
be fully understood.
GROUND POINTS
9
The ground points circuit diagram shows the connections from all major parts to the respective
ground points. When
troubleshooting a faulty ground point, checking the system circuits which use a common ground
may help you identify the
problem ground quickly. The relationship between ground points ( , , and shown below) can also
be
checked this way.
10
TROUBLESHOOTING
VOLTAGE CHECK
(a) Establish conditions in which voltage is present at the
check point.
Example:
– Ignition SW on
– Ignition SW and SW 1 on
– Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (SW 2 off)
(b) Using a voltmeter, connect the negative lead to a good
ground point or negative battery terminal, and the
positive lead to the connector or component terminal.
This check can be done with a test light instead of a
voltmeter.
CONTINUITY AND RESISTANCE CHECK
(a) Disconnect the battery terminal or wire so there is no
voltage between the check points.
(b) Contact the two leads of an ohmmeter to each of the
check points.
If the circuit has diodes, reverse the two leads and check
again.
When contacting the negative lead to the diode positive side
and the positive lead to the negative side, there should be
continuity.
When contacting the two leads in reverse, there should be no
continuity.
(c) Use a volt/ohmmeter with high impedance (10 k/V
minimum) for troubleshooting of the electrical circuit.
11
FINDING A SHORT CIRCUIT
(a) Remove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads of the
fuse.
(b) Connect a test light in place of the fuse.
(c) Establish conditions in which the test light comes on.
Example:
– Ignition SW on
– Ignition SW and SW 1 on
– Ignition SW, SW 1 and Relay on (Connect the
Relay) and SW 2 off (or Disconnect SW 2)
(d) Disconnect and reconnect the connectors while
watching the test light.
The short lies between the connector where
You might also like
- Wiring DiagramDocument281 pagesWiring Diagramchinzoo1275% (20)
- Ewd For FJ Cruiser 2007Document339 pagesEwd For FJ Cruiser 2007Mortada AlsonniNo ratings yet
- Wiring Diagrams PDFDocument467 pagesWiring Diagrams PDFAnonymous OMypKzD6MNo ratings yet
- FJ ElectricalDocument339 pagesFJ Electricalbarjani_wNo ratings yet
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Toyota Camry 87-91 Electrical Wiring DiagramDocument185 pagesToyota Camry 87-91 Electrical Wiring DiagramMinh Nhat Phan64% (22)
- Power Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsFrom EverandPower Supply Projects: A Collection of Innovative and Practical Design ProjectsRating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (2)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- J310 KubotaDocument85 pagesJ310 KubotaPOPI1809No ratings yet
- YazakiDocument90 pagesYazakiAisha Marie EsguerraNo ratings yet
- 2005priuswiring ManualDocument390 pages2005priuswiring ManualEnkhbayar Bandi100% (7)
- Diagrama Eelectrico Toyota Prado PDFDocument935 pagesDiagrama Eelectrico Toyota Prado PDFsebastian37688% (8)
- Honda - Prelude - Wiring Diagram - 1992 - 1999Document4,712 pagesHonda - Prelude - Wiring Diagram - 1992 - 1999Kristin OlsonNo ratings yet
- Blocked Rotor TestDocument11 pagesBlocked Rotor TestIjabi100% (1)
- Electrical Troubleshooting ManualDocument12 pagesElectrical Troubleshooting ManualGreg Hanna100% (1)
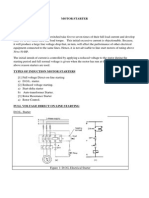
- Motor Starter Ac Motor StartersDocument6 pagesMotor Starter Ac Motor StartersShukor Az100% (1)
- Driller's Console Chapter 4Document26 pagesDriller's Console Chapter 4Nmbvmbjhg Jgjkgj100% (4)
- How Voltage Regulators OperateDocument6 pagesHow Voltage Regulators Operateenriqueuno100% (1)
- Troubleshooting Electrical Noise 3093078-1.0 PDFDocument19 pagesTroubleshooting Electrical Noise 3093078-1.0 PDFAnakin SkywalkerNo ratings yet
- Trane - CentraVac StarterDocument28 pagesTrane - CentraVac StarterSam Wang Chern PengNo ratings yet
- PNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGFrom EverandPNEUMATICS AND AIR CIRCUITS UNDERSTANDING THE CASCADE VALVE AND PLC UNDERSTANDINGNo ratings yet
- AC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCoDocument5 pagesAC Drives and Soft Starter Application Guide - AllenBradleyCojoyama100% (1)
- Avr 100s IngleseDocument65 pagesAvr 100s IngleseVedran GaćeNo ratings yet
- Solar InvereterDocument47 pagesSolar InvereterReshma RaviNo ratings yet
- Section 2 SR Power Conversion System 004 PDFDocument76 pagesSection 2 SR Power Conversion System 004 PDFHarry Wart Wart100% (1)
- IRS S 36-87 - Relay Interlocking SystemDocument34 pagesIRS S 36-87 - Relay Interlocking SystemVikas Srivastav100% (9)
- Project On Ac Voltage Controller Using TriacDocument33 pagesProject On Ac Voltage Controller Using Triackatul830486% (7)
- How To Calculate Locked Rotor Current (IL) From Nameplate DataDocument4 pagesHow To Calculate Locked Rotor Current (IL) From Nameplate DataDeanna Morgan93% (15)
- Handbook On IRS Point Machine With Thick Web SwitchDocument30 pagesHandbook On IRS Point Machine With Thick Web SwitchN.r. Saravanan83% (6)
- ECO-MPU Application GuideDocument23 pagesECO-MPU Application GuideAssir El DjazairiNo ratings yet
- Use of Aux 101 With PCC 2100 - C698auxDocument15 pagesUse of Aux 101 With PCC 2100 - C698auxAndré Alfacinha0% (1)
- E P1 KH2 EJAZai CCVZ G1 KW1600900047Document35 pagesE P1 KH2 EJAZai CCVZ G1 KW1600900047RosNo ratings yet
- Stepping Motor Control CircuitsDocument9 pagesStepping Motor Control CircuitsrfcbaccaratNo ratings yet
- Esquema Chopper 4 QuadrantesDocument20 pagesEsquema Chopper 4 QuadrantesdarkforcesNo ratings yet
- Lab 6 Kawalan MotorDocument20 pagesLab 6 Kawalan MotorMohd FiqrieNo ratings yet
- 6400 ManualDocument44 pages6400 ManualSuresh BabuNo ratings yet
- Chrysler Dakota Part11Document24 pagesChrysler Dakota Part11Sašo Brunšek-BrunoNo ratings yet
- DL 30130 - Extract From The ManualDocument6 pagesDL 30130 - Extract From The ManuallpestanaNo ratings yet
- Ac Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERDocument14 pagesAc Servo Speed Torque Characteristics Measurement Unit - PREMIERAAYUSH KUMARNo ratings yet
- DN 63Document2 pagesDN 63Dimitrios TourassisNo ratings yet
- Stepper Motor Driver Considerations Common ProblemsDocument12 pagesStepper Motor Driver Considerations Common ProblemsErnesto Salomon Jaldín MendezNo ratings yet
- Range Rover - 1997 - 6th EditionDocument579 pagesRange Rover - 1997 - 6th Editionainginer50% (2)
- ECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 16: Control of SPM Synchronous Motor DrivesDocument59 pagesECE 8830 - Electric Drives: Topic 16: Control of SPM Synchronous Motor DrivesHassan SouleymanNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor Drive Using Seven Level Multilevel Inverter For Energy Saving in Variable Torque Load ApplicationDocument8 pagesInduction Motor Drive Using Seven Level Multilevel Inverter For Energy Saving in Variable Torque Load ApplicationAnonymous 22GBLsme1No ratings yet
- 2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710Document5 pages2012 Chevrolet K2500 HD Pickup Silverado: DTC C0710alberto navasNo ratings yet
- Bosch DynastartDocument12 pagesBosch DynastartKkbhuvan KkNo ratings yet
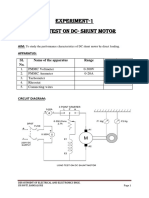
- Exp 7Document11 pagesExp 7John Renzel RiveraNo ratings yet
- Induction Motor ProtectionDocument42 pagesInduction Motor Protectionjayonline_4u91% (11)
- Technical University of Mombasa Controls Power Electronics Lab ReportDocument14 pagesTechnical University of Mombasa Controls Power Electronics Lab ReportFaustin MailuNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiDocument38 pagesLab Manual: Ee 2305 Electrical Machines Lab IiskrtamilNo ratings yet
- Electric Motor 2Document60 pagesElectric Motor 2setsindia3735No ratings yet
- (EM 2) - Lab Manual 4th SemDocument43 pages(EM 2) - Lab Manual 4th SemTime LapserNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 Multi Level Inverters 3.1 InverterDocument8 pagesChapter - 3 Multi Level Inverters 3.1 InverterRama KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Wiper, Washer & Horn: SectionDocument10 pagesWiper, Washer & Horn: Sectionfrank1220uNo ratings yet
- Brake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 PhaseDocument7 pagesBrake Load Test of Squirel Cage Induction Motor 3 Phasejassisc100% (1)
- PS Lab ManualDocument25 pagesPS Lab ManualPhani PhaniNo ratings yet
- 93FWD 8SDocument10 pages93FWD 8SChristian MartinezNo ratings yet
- Application On Three Phase Induction Motor: ObjectivesDocument5 pagesApplication On Three Phase Induction Motor: ObjectivesAdnan AltafNo ratings yet
- Application Guide AC Pilot Wire Relaying System SPD and SPA RelaysDocument24 pagesApplication Guide AC Pilot Wire Relaying System SPD and SPA RelaysSalman SahirNo ratings yet
- 06 EV Manual EnglishDocument96 pages06 EV Manual EnglishMaitry ShahNo ratings yet
- PS Lab ManualDocument25 pagesPS Lab ManualPRAVEEN KUMAR SINGHNo ratings yet
- Induction MatlabDocument12 pagesInduction Matlabgrido002No ratings yet
- Electrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsFrom EverandElectrical Correcting Elements in Automatic Control and Regulation CircuitsNo ratings yet
- Delco Manuals: Radio Model 633, Delcotron Generator Delco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633, Delcotron Generator InstallationFrom EverandDelco Manuals: Radio Model 633, Delcotron Generator Delco Radio Owner's Manual Model 633, Delcotron Generator InstallationNo ratings yet
- Microcor Transmitter 702200MANUALrevCDocument27 pagesMicrocor Transmitter 702200MANUALrevCEdgar I RamirezNo ratings yet
- PP105106 Users ManualDocument52 pagesPP105106 Users ManualdoclozmakNo ratings yet
- Cable List For STG System+ RR Additional Cable - 07.04.2019Document6 pagesCable List For STG System+ RR Additional Cable - 07.04.2019ashish sahaNo ratings yet
- 2VAA001694 - en S Control NTDO02 Digital Output Termination UnitDocument41 pages2VAA001694 - en S Control NTDO02 Digital Output Termination UnitanbarasanNo ratings yet
- User Manual Md69-21: F021008 - Pelorus StandDocument32 pagesUser Manual Md69-21: F021008 - Pelorus StandСКБ ФИОЛЕНТNo ratings yet
- Komatsu Hydraulic Excavator 75r 2 22e5200001 and Up Shop ManualDocument20 pagesKomatsu Hydraulic Excavator 75r 2 22e5200001 and Up Shop Manualkenneth100% (49)
- New Cable Colour Code For Electrical InstallationsDocument5 pagesNew Cable Colour Code For Electrical Installationsavk99No ratings yet
- A5000 Users Manual AsahiDocument72 pagesA5000 Users Manual AsahiBobNo ratings yet
- Sistema Contra IncendiosDocument4 pagesSistema Contra IncendiosMIGUEL ÁNGEL TOMÉNo ratings yet
- Installation and Operating Instructions ForDocument31 pagesInstallation and Operating Instructions ForRachid MoussaouiNo ratings yet
- WEG Ssw04 Soft Starter Manual Br0899.4510 Brochure EnglishDocument101 pagesWEG Ssw04 Soft Starter Manual Br0899.4510 Brochure EnglishSánchez LeticiaNo ratings yet
- Uai B 0214Document4 pagesUai B 0214Jose Puc ManzanillaNo ratings yet
- DTC VCMDocument29 pagesDTC VCMAmor MansouriNo ratings yet
- Fuseology: Amp Rating and Interrupting RatingDocument1 pageFuseology: Amp Rating and Interrupting Ratingbiruk yifruNo ratings yet
- Motor Encoder Feedback (Endat, Hiperface) Interface: Installation ManualDocument58 pagesMotor Encoder Feedback (Endat, Hiperface) Interface: Installation ManualAde Muhamad YunusNo ratings yet
- EFIS-D10A Installation GuideDocument45 pagesEFIS-D10A Installation GuideBruce BNo ratings yet
- Caterpillar 3208 Marine EngineDocument9 pagesCaterpillar 3208 Marine Enginevolkan korkmazNo ratings yet
- GK500 Series Mini AC Motor Drives A01Document83 pagesGK500 Series Mini AC Motor Drives A01FERNANDO DIAZNo ratings yet
- 2840 Series ManualDocument139 pages2840 Series Manual民No ratings yet
- General Lighting Power DbsDocument2 pagesGeneral Lighting Power DbssanaNo ratings yet
- Service Publications: Number SubjectDocument5 pagesService Publications: Number Subjectpiyush agrawalNo ratings yet
- Sitrans Probe Lu Puesta en Marcha Rapida HartDocument162 pagesSitrans Probe Lu Puesta en Marcha Rapida HartJuanFuentesBecerraNo ratings yet
- 2011 National Electrical Code: Communications Cable and Connectivity Association, Inc. (CCCA) Page 1 of 21Document21 pages2011 National Electrical Code: Communications Cable and Connectivity Association, Inc. (CCCA) Page 1 of 21kriangkrai1No ratings yet
- L-Dens 427 Instruction ManualDocument78 pagesL-Dens 427 Instruction ManualPablo SotoNo ratings yet