Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Product Development Organizations - Organizational Structues
Uploaded by
rony16novOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Product Development Organizations - Organizational Structues
Uploaded by
rony16novCopyright:
Available Formats
claims:- make as genereal as possible, avoid absolute definition, create an invention that does not infringe). 6.
Pursue appln: (team may file all
1(INTRO): Product development is the set of activities beginning with the perception of a market opportunity and ending in the production, sale, 9CONCEPT TESTG: 7-step method for testing product concepts: 1. Define the purpose of the concept test 2. Choose a survey population 3. type of ptnt app >defer appln) 7.Reflect on the results of process
and delivery of a product. Characteristics of Successful PD: Product quality, Product cost, Development time, Development cost, Development Choose a survey format. 4. Communicate the concept[Verbal description • Sketch • Photograph or rendering • Storyboard • Video • Simulation •
capability. Challenges of PD: trade-offs, dynamics, details, time pressure, economics, creation, societal and individual needs, team diversity, Interactive multimedia • Physical appearance model • Working prototype] 5. Measure customer response:>Erly in concept 17(Prod Dev Econmcs): Elements of eco analysis:1.Quantitv analysis(Cash inflow &outflow.Bringsmeasur of structure & discipline to
team spirit. Organizational Realities: Lack of empowerment of the team, Functional allegiances transcending project goals, inadequate develpmntphase,custmr is need to pick one of the two concepts.>It ais at the interest of customers at buying the product.>scale(definitely wud assessment of prod dev proj.) 2.Qualitative(captures only those factors that are measurable.captures characteristics of dynamic & competitive
resources, Lack of cross-functional representation on the project team. buy, probably wud buy, might or might nt buy andvice verse) 6. Interpret the results [The model for predicting sales for durables: Q = N x A x environments.interactions between projct& firm/mkt/maccroenvironment).When Should Economic Analysis Be Performed?:Go/no-go
P (Q = sales (annual) • N = number of (annual) purchases • A = awareness x availability (fractions) • P = probability of purchase (surveyed) = Cdef milestones:(should we-launch the prodct/implement selected concpt/develop prodct to address mkt opportunity?.)Operation design&dev
2(DEV. PROCESSES&ORGANIZATN):Sequence of steps/activities that an enterprise employs to conceive ,design & commercialize the product. x Fdef + Cprob x Fprob] Fdef is the fraction of survey respondent that they would definitely purchase • Fprob is the fraction of survey respondent decisn: ( should we- spend money to hirm outside firm to save development tim/launch prodct at 2$ or wait till 6mnths so we can reduce the
Benefits of Prod Devel Process- QA, Cordintn, planning, mngment, improvement. Generic PDP: Planning(phase zero” because it precedes that they would probably purchase • Cdef and Cprob are calibration constant usually established based on company experience with similar cost)1. Build a base-case financial model.(consist of estimtng timing and magnitude of fututr cash flows & then computing NPV of d flow. Timin
the project approval and launch of the actual product development process.This phase begins with opportunity identification guided by corporate products. & mgntude of cash flw estimated by mergingprojct schedule &budgt, sale vol forcast, estmtd prodn cost.>cash flw=devcst,mktg& support ccst,
strategy and includes assessment of technology developments and market objectives.), Concptdevlpmnt(the needs of the target market are 7. Reflect on the results and the process: N- Consider effect of alternative markets. A-Influenced by promotion plans, distribution arrangements P- prodn cst,sales revenu>typicl refinmnts=brkdwn of all cost, inclusion of tax effct,cannibalizatn, ivstmnt tax credits) NPV = cash flow/1.0258 (for 2.5
identified, alternative product concepts are generated and evaluated, and one or more concepts are selected for further development and testing), Design change, make product more appealing, advertising. persent)
systm level design(the definition of the product architecture, decomposition of the product into subsystems and components, and preliminary 2. Perform a sensitivity analysis: (to understand the relationships between financial success and the key assumptions and variables of the
design of key components.), detailed design(complete specification of the geometry, materials, and tolerances of all of the unique parts in the 10(Prodct architectr): in early dev phase. A product can be thought of in both functional and physical terms. Functionalelement = individual model. Vary the values used in the base model using a “what-if” scenarios. Project are influenced by internal and external factors.Internal factors:
product and the identification of all of the standard parts to be purchased from suppliers), testing &refinement(The testing and refinement phase operations that are part of the overall performance of the product. Physicalelements= parts, components, and subassemblies that generate the are factors that the team can influence like, development cost, development time, production cost and product performance.External factors: are
involves the construction and evaluation of multiple preproduction versions of the product), production ramp up(purpose of the ramp-up is to train product’s functions.Thephysical elements are grouped into several major physical building block, which are called chunks.modular factors that the team cannot influence like, competitive environment, product )
the workforce and to work out any remaining problems in the production processes). ConDevPro : Identifying customer needs, Establishing architecture(chunks implement one or few funclelemnts in their entirety.interctn bet betn chunk s well defined and genrllyfundamntl to primy fun of 3. Use the sensitivity analysis to understand project trade-offs.(understand the impact of any chng on the npv&hw to recover if
target specifications, Concept generation, Concept selection, Concept testing, Setting final specifications, Project planning, Economic prod), integral(opp of modular)Types of Modularity: Slot, Bus, Sectional-modular. Implications of architecture: Product change (Upgrade, Add- possibl.sensitivity analysis allows team to compute some trade off rules.limittations of qttv analysis-focus on measurable quantities, it depends on
analysis, . It is aim is to ensure that the product will achieve the profits expected), Benchmarking of competitive products(to position the ons, Adaption, Wear, Consumption, Flexibility in use, Reuse), Product variety, Component standardization, Product performance, validity of assumptions and data, beureaucracy reduces productivity) six intraction b/w: devlop time,product cost, poduct
product in the proper segment and establish the proper price), Modeling and prototyping(Included early proof of concept. Give the ability to Manufacturability and Product DvlpmtMgmt, System Engineering. Establishing the Architecture: 1. Create a schematic of product, 2. Cluster the performance,development cost.
verify assumptions and confirm product performance). Types of processes: Generic(market pull)prodcts(Market opportunity, team finds proper element of schematic (Geometric integration and precision, Function sharing, capabilities of design or prductntechnlgy, Localization of change, 4. Consider the influence of the qualitative factors on project success.(prjct will interct with firm/mkt/mcroenvironment.interaction between
technology), Tchnlgy push(New technology, team finds market), Platform(New product built around an established technological platform), Accommodating variety, Enablngstandardiztn, Probability of interface), 3. Create rough geometric layout, 4. Identify the fundamental and incidental prjt& firm=externatilities, strategic fit,. Between prjct& mkt=competitors, customers,supplier. Between prjct&enivrnmnt=major economic
process intensv(Product characteristic controlled by the process), customized(Product is a variation of existing product), high risk(Technical, or interactions.Delayed Differentiation: 1.The differentiating elements of the product must be concentrated in one or a shifts,govtregultns, social needs)
market uncertainties lead to high risk failure), quick build(Rapid modeling and prototyping enable many design-build test cycles), complex few chunks.2The product and production process must be designed so that the differentiating
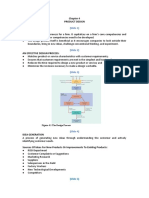
systems(several systems & subsystems). Product Development Organizations• A successful product development depends also on the chunk(s) can be added to the product near the end of the supply chain.Platform planning:Differentiation plan, commonality plan, managing trade 18(Managiing projects):Projectmgnt occurs during project planning & execution. Understanding & representing
structure of the organization that is developing the product.• The organization is formed by establishing links between different functions for off betn DIFF & COM(Platform planning decisions should be informed by quantitative estimates of cost tasks:Sequential,parallel&coupled tasks |DSM|Ganttcharts|PERT|critical path
example:a) Reporting relationships: give rise to the classic notion ofsupervisor and subordinateb) Financial arrangements: Individuals are and revenue implications.Iteration is beneficial. The product architecture dictates the nature of the trade-off between differentiation Base line project planning:[ •Contract book is the Results of the concept development phase plus the project plan • The document is an
linked by being part of the same financial entity (business unit) C) Physical layout: Sharing the same location, office, building,Organizational and commonality).System-level Dsgn Issues: Defining Secondary systems, Estblsngachtctur of chunks, creating detailed interface specs agreement between the development team and the management team. The document contains, the goals, direction and resource requirements.•
structues: functional org, project org, HW proj org, LW proj org. choosing an organizational structure how imp is cross-func integration, how Project task list :A list of tasks to the best knowledge of the team.Small project a task every one to two days. Large project a task every one
critical is cutting-edge functional expertise, can individuals from each function be fully utilized for most duration, project develop 11(ID): 5critical goals ID cnhlpteam:utility appearance, ease of maintenance, low cost, ccommunicatn.ID Process1. Invstgtn of custx needs. month or more. For large projects each task can have it is own plan.After listing the tasks the team assign resources usually in hour-man • Team
speed. 2. Conceptualization.( ID will create visual concepts, while engineers will focus on the technical solution Staffing and organization:Using the data in the plan the team can estimate the number of people required and their skills.Issues often
This is an easy and quick method of creating visual models.thumbnail sketches) 3. Preliminary refinement(Soft models are typically made in full encountered: • Availability of specialized skills • Team members working on multiple projects in parallel • Matching the size of the team with the
scale using foam or foam-core board. They are the second-fastest method—only slightly slower than sketches—used to evaluate concepts.). 4. requirement .38 Elements of the Project Plan • Project Schedule= It shows when the tasks will start and what is the effort needed to sustain the
Further refinement & final concept selctn(switch from soft models and sketches to hard models and information-intensive drawings known as task • Schedule is used to track progress (usually using earned value) • Project milestones are set date that identify events, usually the completion
3(OPPURTUNITY IDENTIFICATION): familiarity with solution likely to be employed, familiarity with need of the soln addressed. Effective renderings. Renderings show the details of the design and often depict the product in use. final refinement step before selecting a concept is to of a task. • Project Budget :Using the plan and the resource identified the budget is calculated • Capital expenditure is estimated also • Cost of
opportunity tournament. Generate large no of oppurtunities, seek high quality opportunity, create high variance in the quality of oppurtunities. create hard models. These testing, materials, prototypes etc. is all included • The largest item is usually the cost of staff • Major companies has a standard format for the
Opportunity identification process. Establish a charter, generate and sense many oppurtunities. Technic for generating oppurtunities-follow models are still technically nonfunctional yet are close replicas of the final design with a very realistic look and feel. They are made from wood, budgeting (why?) 39 Elements of the Project Plan • Project Risk Plan=The team identifies the issues that could go wrong. The team then
personal passion, compile bug list, pull oppurtunities from capabilities(VRIN), study customers, consider implication of trends, imitate but better- dense foam, plastic, or metal; are painted and textured; and have some “working” features). 5. Control drawings or models(Industrial designer identifies the likelihood and consequence of each risk. An action (mitigation) plan is put together to ensure what actions needs to be taken to
(media and marketing activities of other firms, de-commodize a commodity, drive an innovation down market, import geographically isolated issue control drawings or control models at the end of their development work of the final concept. These detail the functionality, features, sizes, reduce the risk. Risk plan is a live document that is regularly visited and updated throughout the whole project.• Modifying the Baseline
innovations), mine your sources – (lead users, representation in social media, universities and government labs, online idea submission). Screen colors, surface finishes and key dimensions. These can be used to make final design models and prototypes). 6. Cordinatn with engg, Plan=The team revisit the baseline plan to ensure that all assumptions are valid. Team can choose to trade off development time, development
oppurtunities.develop promising oppurtunities, select exceptional oppurtunities, reflect on the results and the process. Process: mnfcturng, & external vendors.( ID must continue to work closely with engineering and manufacturing personnel throughout the subsequent cost, product manufacturing cost, product performance and risk. Ex: complete the project more quickly by increasing cost and hiring more people.
Establish a charter(new organizations also have goals like creating a new product related toan area of personal interest. The innovation charter product development process.) Compressing the schedule is the most desired outcome
articulates these goals), Generate and sense many opportunities, Screen opportunities, Develop promising opportunities, Select exceptional mgmt of ID: Tech driven products(concept testng), User driven products(cust need identifctn) Acccelerating projects: Guideline that applies to the project as a whole= • Start project early (Launch can be delayed) • Manage the project
opportunities(RWW), Reflect on the results and the process. Techniques for Generating Opportunities: Follow a Personal Passion, Compile scope • Facilitate the exchange of information, DSM usage can identify the information exchange path between teams • Guidelines that are aimed
Bug Lists, Pull Opportunities from Capabilities(VRIN Valuable, Rare, Inimitable, Non-substitutable.), Study Customers, Consider Implications of 12(DFE): DFE Process: 1. Set DFE agenda:drivers, ,goals, team: Drivers (int-Product quality, Public image, Cost reduction, Innovation, at tasks on the critical path: • Complete individual tasks on the critical path more quickly • Aggregate safety time 41 4 Finish 2 Start 3 3 3 3 5 6 1 3
Trends, Imitate but Better( Drive an innovation “down market, Import geographically isolated innovations), Mine Your Sources (Lead users, Operational safety, Employee motivation, Ethical responsibility, Consumer behavior.ext- Environmental legislation, Market demand, Competition, 9 Project Buffer Feeder Buffer Accelerating Projects • Guidelines that are aimed at tasks on the critical path (cont.): • Eliminate some critical path
Representation in social networks, Universities and government laboratories, Online idea submission). Trade organization, Suppliers, Social pressure), Goals, Team 2. Identify potential envrmntl impacts 3. Selct DFE guidelines 4. Apply DFE tasks entirely • Eliminate waiting delay for critical path resources • Overlap selected critical tasks, see if tasks can be done in parallel • Pipeline
guidelines to initial dsgn. 5. Assess envrmntl impacts 6. Refine Dsgn 7. Reflect on DFE Process and results. Steps in LCA analysis: 1. large tasks, progressive release of information for example • Outsource some tasks 42 Accelerating Projects • Guidelines aimed at couple tasks: •
4(PRODCT PLANNIN): product planning process. 4 Types of PD Projects: New product platforms, Derivatives of existing product platforms, Prepare proposed design options 2. Identify life cycle, including recycling and disposal 3. Identify all materials and energy sources used 4. Identify Perform more iterations quickly, close cooperation between functions to speed the tasks • Decouple tasks to avoid iterations • Consider set of
Incremental improvements to existing products, Fundamentaly new products. Process Develop a product plan and project mission outputs and waste streams 5. Quantify impacts of each material, energy, waste 6. Aggregate impact into categories for comparison. solutions, use set of values instead of points
statements: Identify opportunities, Evaluate and prioritize projects [Competitive Strategy: Technology and cost leadership, Customer focus, Project execution:Coordination Mechanism(Informal communications,Meetings, Schedule display,Weekly Update, Incentives (Project based
Imitative.>>market segmentatn:prod are developed with mkt segmnt mind. >>technlgcl trajctries: evalprogrss of current tech & identify when to 13(DFM):Customer needs and product specifications are useful for guiding the concept phase of product development; however, during the later incentives), Process documents( will assist the team in taking decisions and provide documentations)• Assessing project status • For small
adopt new.>>prod pltfrm:dev new pltfrm or dev dervtv prod.prd pltfrm reltd to techlgy map], Allocate resources and plan timing[Resource development activities teams often have difficulty linking needs and specifications to the specific design issues they face DFM Process(begins projects regular update are easy to obtain from the project lead • For large project, regular project reviews take place • They take place usually on
Allocation: Numerous companies take on many projects, improper planning of resources lead to late delivery of products (late to market), which during concptdevlp ): 1. Estmtemanfctrng cost [Component costs: Standard, custom. Assembly costs: Labor, Equipment & Tooling. a monthly basis • Used to close project phases and actions • Review of cost performance and schedule performance take place during the
negatively affect profitability. Aggregate planning increase the efficiency of resource usage by pursuing only projects that can reasonable be Overheadcosts: Support, Indirect Allocation], Transportation cost, fixed vs variable cost,estcst of stdcompnt(by asking the price from meeting • Corrective actions • Changing the timing and frequency of meetings • Changing (modifying) the project staff • Locating the team
completed with the budgeted resources.Project Timing: takes into account :a) Timing of product intro b) Technology readiness c) Market readiness suppliers or by comparing with similar compont), estcst of custmcompt(Single part = cost of raw material, processing and tooling.Multiple parts together physically • Soliciting more time and effort from the team, beware of burnout • More efforts on critical path • Engaging outside sources •
d) Competition], Complete pre-project planning(Mission Statements: Brief (1sentence) description of the product, Benefit proposition, Key = cost of each subcomponent + cost of assembly + overhead.Raw material cost = (weight of part + scrap allowance) * cost per weight.Processing Changing the project scope or schedule
business goals, Target market(s) for the product, Assumptions and constraints that guide the development effort, Stakeholders.),assumptions costs = costs for the operator(s) of the processing machinery + the cost of using the equipment itself ($/hr).Processing time depend on operation
and constraints. Manufacturing, service, environment. Staffing and other preproject planning activities. Reflect on the results and the and machine used),est assembly cst( (Handling time + Insertion time) * labor rate)
process. 2. Reduce the cost of compnts, (Understand the process constraints and cost drivers, Redesign components to eliminate processing steps,
Choose the appropriate economies of scale for the Part process, Standardize components and processes, Adhere to BLACK BOX component
procurement)
5(IDENTIFY CUST. NEEDS):Gather raw data from customers(interview, focus grp, observe on prod), .choosing customers. The art of elicitin 3. Reduce the cost of assembly (DFA Index= theoretical Min no. of parts * 3 sec/est. total assembly time
customer needs data. During the interview: • Go with the flow • Use visual stimuli and props • Suppress preconceived hypotheses about the Methods to reduce ass. Time- Integrate parts, maximize ease of assembly, cx assembly,
product technology • Have the customer demonstrate the product • Be alert for surprises and the expression of latent needs • Watch for nonverbal 4. Reduce the cost of supporting prodctn- Minimize systematic complexity, Error Proofing.
information.documeting interactions with customers. (audio recording, notes, video recording, still photography). Interpret raw data in terms 5. Consider the impact of DFM decision on other factors. [impact of dfmonDvlpmnt time, dvlpmnt cost, product quality, External
of customer needs 1. What and not how 2. Be specific (the same level of detail as in the raw data) 3. Use positive, not negative phrasing 4. factors(Component reuse: Creating a low cost product for a product could benefit other products (read across), or decide to increase the cost of a
Express the need as an attribute of the product 5. Avoid must and should. Organize the need into a Hierarchy(of primary, secondary, and (if product to benefit another project.Life cycle cost: a product with a toxic material might impact the life cycle cost. Product might incur service cost of
necessary) tertiary Needs) 1. Write each need on separate card or sticky 2. Remove redundant statements 3. Group the cards according to the warranty)].
similarity of the needs they express 4. For each group choose a label 5. Consider creating a supergroup of two to five groups6. Review and edit
organized needs statements.. Establish the relative importance of the needs: It is important to rank the needs identified by user priority. This
can be achieved by:• Relying on the consensus of the team (Quick and inexpensive,less accurate)• Survey customers (Long and costly, but more 14(Prototyping):An approximation of the product along one or more dimension of interest. Types of Prototype: Physical-Analytical,Focused-
accurate), Reflect on the results and the process. Questions asked after completion of the process. Comprehensive. Uses of prototype: Learning(will it wrk), Communication(wit top mgmt, vendors, team membrs, custmr, investr),
Integration(ensure cmpnt and subsystem of prodctwrktoghtr), Milestones(prototypss used to demnstrtetht). Principle of prototyping: analytical
6(PRODT SPECFN): Establishing the target specifications: Start with customer needs, Prepare the list of metrics, Collect competitive prototype are generally more flexible than phy prototype, phy protype are required to detect unanticipated phenomenton, reduce the reisk of costly
benchmarking information(benchmark on i.metrics ii.cust needs), Set ideal and marginally acceptable target values, Reflect on the results and the iteration.Benefits of Prototyping: Reduce the risk of costly Iterations, Expedite other dvlpmnt steps, Restructure Task Dependencies
process. technologies.3D cad model and analysis, free form fabrication..
Setting final specification: Develop technical models of the product, Develop a cost model of the product, Refine the specifications, making Planning of Prototype: 1.Define the purpose of the prototype:Is it for learning, for communication, for integration, for milestones.
trade-offs where necessary, Flow down the specifications as appropriate, Reflect on the results and the process. 2.Establish the level of approximation=It depend on the purpose, if it is to demonstrate a physical functionality like an engine performance you will
need an accurate model.
3.Outline an experimental plan=Define the variables, the test protocol, an indication of what measurement are needed, and a plan analyzing the
7(CONCEPT GEN.): 5 Step method for CG:the activity of concept generation. Structured approaches reduce the likelihood of costly results.
problems. A five step method. 1. Clarify the problem, (Understand the problem, • Decompose a Complex Problem into Simpler Subproblems, 4.Create a schedule for procurement construction and testing=This is a subproject. Ensure that you have a robust schedule for procurement and
Focus Initial Efforts on the Critical Subproblems) 2. Search externally: aim is to find, when possible, an existing solution that can be used, hence testing so that you do not affect the program development.
cutting cost and development time. (Interview lead users • Consult experts • Search patents • Search published literatures • Benchmark related
products), 3. Search Internally (Brainstorming sessions: Suspend Judgment, suggest improvements, or alternative concepts 2. Generate a lot of 15(Robust design): robust setpt id s combinstion of designer parameter values which the product performance is desired under a range of
ideas 3. Welcome ideas that seem infeasible 4. Use graphical and physical media).both individual and group sessions can be useful. Hints operating conditions and manufac variation.Steps of Robust design: 1. Identify control, noise & performance factors 2. Formulate and
for Generating Solution Concepts: Make analogies, wish & wonder, Use related stimuli, Use unrelated stimuli, set quantitative goals, use gallery objective plan (Maximize, Minimize, Target value, Signal to noise ratio) 3. Develop the experimental plan (Full factorial design, Fractional
method) 4. Explore systematically: Concept classification tree provides 4 benefits: 1. Pruning of less promising branches 2. Identification of factorial, Orthogonal array, One factor at a time, Outer & Inner array to test noise factors: additional column for noise array, puter array for noie) 4.
independent approaches to the problem 3. Exposure of inappropriate emphasis on certain branches 4. Refinement of the problem decomposition Run the experiment 5. Conduct the analysis (Computing Objective fn& factor effects by analysis of mean, Mean and Variance to be mentioned
for a particular branch.) concept combination table. Managing the exploration process. 5. Reflect on solution and processes. in answer and signal to noise ratio). 6. Select and confirm factor setpoints 7. Reflect & Repeat
8(CONCPT SELECN): process of selecting best concept.number of ways to select concepts. Structures approach wil lead you best results.CS is
applied throughout the subsequent design and develp process. The ,methodology used toused to selct prod concpt can be use dlater at 16(Patents): IP is an intangible asset created by human intellectual or inspirational activity. Types: patent(utility,design,plant), trademarks,
subsystem level,compnnt or producnprocess.Select Product Concept: • External Decision • Product Champion • Intuition It just seems right • copyright, tradesecret. Ultility patents: relates to new processes, machine , article of manufctr, composition of matter or improvements to this.Law
Multivoting • Web-Based Survey • Pros and Cons • Prototype and test • Decision matrices. Benefits of structured methods: customer focused reuires the patented inventions be Useful, novel, nonobvious. Prepare a disclosure:1.Formulate the strategy &plan(timin of patent appln>type
product, competitive design, Better product-process coordination, Reduced time to product introduction, Effective group decision making, of applcn(regular, provisionl,patentcoopertn treaty)>scope of appln).2.study prior inventions: (team can learn whethr an invention infringe the
Documentation of the decision process] existing unexpired patent>get sense of how similariss their invention to other patents by esearching>develop knowledge enbling membr to craft
2 steps to select a concept: Concept screening and scoring. novel claim )3.Outline claims: (descrbchrctrstc of hteinvention>summry> provide guidance about wht must be described in detail of descriptn)
Steps for concept screening(quickly identify concepts that could be of interest and progress) and scoring(best resoln and is used to 4.Write descrptn of invention; (titles, list of inventors, field of invention, bckgrnd of invent, summary of invn, brief descrpn of drawing, detailed
narrow the idea). 1. Prepare selection Matrix 2. Rate the concepts 3. Rank the concepts 4. Combine and improve the concepts 5. Select one or descripn of invention)5. Refine claims: (claim are set of numrd phrases tht defines sentlelemnt of invent, what exactly is invention. Writing the
more concepts 6. Reflect on the results and the process.
You might also like
- AWS Welding Journal October 2017Document225 pagesAWS Welding Journal October 2017rony16novNo ratings yet
- PDD Presentation Unit IDocument45 pagesPDD Presentation Unit Ikunal shegokarNo ratings yet
- GratingDocument36 pagesGratingRay Gong100% (1)
- New Product Design ProcessDocument4 pagesNew Product Design Processsonam katiyarNo ratings yet
- Oracle Data Integration - An Overview With Emphasis in DW AppDocument34 pagesOracle Data Integration - An Overview With Emphasis in DW Appkinan_kazuki104No ratings yet
- Magoosh IELTS Vocabulary PDFDocument37 pagesMagoosh IELTS Vocabulary PDFOmidNo ratings yet
- Ielts Task 2 How To Write at A 9 LevelDocument37 pagesIelts Task 2 How To Write at A 9 Leveljanit693984% (19)
- A Dimensional Engineering Process For ShipbuildingDocument11 pagesA Dimensional Engineering Process For ShipbuildingWJccnNo ratings yet
- Phases in Product Design and DevelopmentDocument39 pagesPhases in Product Design and DevelopmentJennifer Viola Rebba67% (3)
- Design For Manufacturing Questions and AnswersDocument18 pagesDesign For Manufacturing Questions and Answersyeswanth100% (2)
- Lecture - 5 - Notes 5 - Fracture - Brittle Ductile Transition PDFDocument100 pagesLecture - 5 - Notes 5 - Fracture - Brittle Ductile Transition PDFrony16nov100% (1)
- Wartsila CPP PaperDocument4 pagesWartsila CPP Papergatheringforgardner9550No ratings yet
- Vtol Design PDFDocument25 pagesVtol Design PDFElner CrystianNo ratings yet
- Value AnalysisDocument6 pagesValue AnalysisLln PsgnNo ratings yet
- Product and service design processDocument36 pagesProduct and service design processramjanmsinghNo ratings yet
- ANSYS ACT Developers GuideDocument506 pagesANSYS ACT Developers GuideEDIZONNo ratings yet
- Jarless Con Door DriveDocument16 pagesJarless Con Door DriveRoyal Akash100% (6)
- Product Realization Process:: Documentation, Clear Decisions, Incorporation Of. Collective Experience ProdDocument1 pageProduct Realization Process:: Documentation, Clear Decisions, Incorporation Of. Collective Experience ProdObelay SkinCareNo ratings yet
- Summary Operation ManagementDocument3 pagesSummary Operation ManagementStefanyNo ratings yet
- Product Design - BasicsDocument18 pagesProduct Design - BasicsVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument12 pagesNew Product DevelopmentDiane ChakanzahNo ratings yet
- Operational MnagementDocument4 pagesOperational MnagementjohanaNo ratings yet
- Design Methodology: (Pierre Lambert) : Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument17 pagesDesign Methodology: (Pierre Lambert) : Chapter 1: IntroductionJorge GarrettNo ratings yet
- Product Design Process and TechnologiesDocument18 pagesProduct Design Process and TechnologiesLD GentelisoNo ratings yet
- Design of Goods and ServicesDocument15 pagesDesign of Goods and ServicesZeeshan MajeedNo ratings yet
- Chapter-3 Operation ManagementDocument40 pagesChapter-3 Operation ManagementA Garaad OsmanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 (Entrepreneurship)Document28 pagesChapter 4 (Entrepreneurship)Abdurezak AhmedNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Introduction To Product Design and DevelopmentDocument4 pagesLecture 1 - Introduction To Product Design and DevelopmentKadie EdwardsNo ratings yet
- 0002 - OM SESSION 2 (Chapter 4 - Process Design & Chapter 5 - Innovation & Design in Services & Products)Document49 pages0002 - OM SESSION 2 (Chapter 4 - Process Design & Chapter 5 - Innovation & Design in Services & Products)Tú Anh NguyễnNo ratings yet
- NPD process guideDocument7 pagesNPD process guideRishi GohilNo ratings yet
- AMED 01a PDFDocument30 pagesAMED 01a PDFAbenesh KumaresanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 OM EditedDocument19 pagesChapter 3 OM EditedSeid KassawNo ratings yet
- Why Sustainable Strategy Is CriticalDocument5 pagesWhy Sustainable Strategy Is CriticalAndreas FerryNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument7 pagesNew Product DevelopmentDeepthi VadlaNo ratings yet
- Embedded Systems Assignment: Phases of Embedded Product Development Life Cycle (EDLC)Document14 pagesEmbedded Systems Assignment: Phases of Embedded Product Development Life Cycle (EDLC)Rahul S.KumarNo ratings yet
- Product DevtDocument26 pagesProduct DevtRalph Gene Trabasas FloraNo ratings yet
- Pdve Paper Soultion 2011Document19 pagesPdve Paper Soultion 2011AMIT SOLANKINo ratings yet
- Product Design 1Document14 pagesProduct Design 1Abhishek kumarNo ratings yet
- Value Analysis & Value Engineering: DR - Sanjay RajurkarDocument36 pagesValue Analysis & Value Engineering: DR - Sanjay Rajurkaramy goshNo ratings yet
- Vertical Integration Refers To The Degree A Firm Chooses To: BE BEDocument1 pageVertical Integration Refers To The Degree A Firm Chooses To: BE BETin PortuzuelaNo ratings yet
- 3-Design Planning and Innovation Engg. Presentation1Document13 pages3-Design Planning and Innovation Engg. Presentation1Rohith ReddyNo ratings yet
- Technology Management 3Document6 pagesTechnology Management 3Joju JohnyNo ratings yet
- Differences Between Product Development Past & PresentDocument10 pagesDifferences Between Product Development Past & PresentKunalNo ratings yet
- Product Design & Development: The Generic Process For Developing New ProductsDocument7 pagesProduct Design & Development: The Generic Process For Developing New ProductsRandeep DevNo ratings yet
- CMMI 2.0 GuideDocument12 pagesCMMI 2.0 Guidemcarmendgj74No ratings yet
- Generic Product Development ProcessDocument3 pagesGeneric Product Development Processhannah_clarice0% (1)
- Computation of Demand Income Statement 1Document5 pagesComputation of Demand Income Statement 1Marianne SevillaNo ratings yet
- New Product Development WikipediaDocument9 pagesNew Product Development WikipediaBreylin CastilloNo ratings yet
- Lean Six Sigma ApproachDocument5 pagesLean Six Sigma ApproachAnand BabuNo ratings yet
- Design & Innovation Study Notes (48240)Document33 pagesDesign & Innovation Study Notes (48240)JamesNo ratings yet
- PLCM, Module-3 PPT As Per VTU SyllabusDocument39 pagesPLCM, Module-3 PPT As Per VTU SyllabusSunil Kumar M0% (1)
- 15me835 PLCM Module 3Document24 pages15me835 PLCM Module 3prashanth prabhuNo ratings yet
- Strategic Management of Resources (SMR) Definitions ADocument5 pagesStrategic Management of Resources (SMR) Definitions ANick AndersonNo ratings yet
- Module 2 (Lessons 1 - 6)Document5 pagesModule 2 (Lessons 1 - 6)Pob ReNo ratings yet
- OM Chapter 3Document10 pagesOM Chapter 3abdulwahab kemalNo ratings yet
- Product Planning and Process PlanningDocument19 pagesProduct Planning and Process PlanningjvanandhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 - IntroductionDocument53 pagesChapter 1 - Introductionjeff leonenNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of CADDocument10 pagesFundamentals of CADBharathi KannaNo ratings yet
- New Product DevelopmentDocument4 pagesNew Product DevelopmentZain Ul Abidin RanaNo ratings yet
- EDP 3 Product DevelopmentDocument15 pagesEDP 3 Product DevelopmentAmrut RajkarneNo ratings yet
- UNIT 1 Lecture 1 CAD AutoDocument21 pagesUNIT 1 Lecture 1 CAD AutoMohd InayathNo ratings yet
- CH.4 MENG420 UpdatedDocument6 pagesCH.4 MENG420 UpdatedSANo ratings yet
- UNIT-1: Importance and Scope of Operations ResearchDocument60 pagesUNIT-1: Importance and Scope of Operations Researchkishu085No ratings yet
- Product Life Cycle Management: Module 2 SummaryDocument9 pagesProduct Life Cycle Management: Module 2 SummaryJoker DanNo ratings yet
- 2 DesignofServices&GoodsDocument32 pages2 DesignofServices&GoodsPrateek HosamaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter One (Introduction)Document25 pagesChapter One (Introduction)AbcdNo ratings yet
- General Legal and Quality Requirements For Pressure Equipment in Machine Units or Package UnitsDocument12 pagesGeneral Legal and Quality Requirements For Pressure Equipment in Machine Units or Package Unitsrony16novNo ratings yet
- Gen Neral Tole Rances: Content TsDocument9 pagesGen Neral Tole Rances: Content Tsrony16novNo ratings yet
- Steels For Pressure Vessels According To ASME VIII/1: RequirementsDocument5 pagesSteels For Pressure Vessels According To ASME VIII/1: Requirementsrony16novNo ratings yet
- LS 048-6XX: Technical Purchase SpecificationsDocument5 pagesLS 048-6XX: Technical Purchase Specificationsrony16novNo ratings yet
- LS 492-07 EN 2.0 0900412a8003df7dDocument2 pagesLS 492-07 EN 2.0 0900412a8003df7drony16novNo ratings yet
- Support Design PDFDocument42 pagesSupport Design PDFbalramkinageNo ratings yet
- GlidelocDocument4 pagesGlidelocJithin FrancizNo ratings yet
- ISO 15156-1-2001 Cor 1-2005 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries - Materials For Use in H2S-Containing EnviroDocument3 pagesISO 15156-1-2001 Cor 1-2005 Petroleum and Natural Gas Industries - Materials For Use in H2S-Containing Envirorony16novNo ratings yet
- General Noise Specification: IssueDocument6 pagesGeneral Noise Specification: Issuerony16novNo ratings yet
- Support Design PDFDocument42 pagesSupport Design PDFbalramkinageNo ratings yet
- Lecture - 4 - Notes 4 Recovery, Recrystallization, Hot WorkingDocument55 pagesLecture - 4 - Notes 4 Recovery, Recrystallization, Hot Workingrony16novNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Notes 6.1 FatigueDocument82 pagesLecture 6 Notes 6.1 Fatiguerony16novNo ratings yet
- Lecture 6 Notes 6.1 FatigueDocument82 pagesLecture 6 Notes 6.1 Fatiguerony16novNo ratings yet
- Major Report Instruction and Projects List 2018Document4 pagesMajor Report Instruction and Projects List 2018rony16novNo ratings yet
- A Primer on Duplex Stainless SteelsDocument51 pagesA Primer on Duplex Stainless SteelsAnonymous GE8mQqxNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3 Notes 3 Strengthening MechanismDocument89 pagesLecture 3 Notes 3 Strengthening Mechanismrony16novNo ratings yet
- Major Report Instruction and Projects List 2018Document4 pagesMajor Report Instruction and Projects List 2018rony16novNo ratings yet
- Dislocation Plasticity PDFDocument36 pagesDislocation Plasticity PDFAkcent AdrianNo ratings yet
- Paper6 PDFDocument10 pagesPaper6 PDFrony16novNo ratings yet
- Chap 1 StrengthDocument50 pagesChap 1 StrengthVi GaneshNo ratings yet
- PDMS-Pipework Design User GuideDocument414 pagesPDMS-Pipework Design User GuideShyam Prasad K S75% (4)
- Smart Office ChairDocument3 pagesSmart Office Chairrony16novNo ratings yet
- Table Perio PDFDocument1 pageTable Perio PDFanoopNo ratings yet
- Paper6 PDFDocument10 pagesPaper6 PDFrony16novNo ratings yet
- Mech 6941 DraftDocument41 pagesMech 6941 Draftrony16novNo ratings yet
- Turbine Buyers Guide - Mick Sagrillo & Ian WoofendenDocument7 pagesTurbine Buyers Guide - Mick Sagrillo & Ian WoofendenAnonymous xYhjeilnZNo ratings yet
- 2N3866 Datasheet Rev BDocument5 pages2N3866 Datasheet Rev Bardier34No ratings yet
- 98 99 Anti Lock BrakesDocument101 pages98 99 Anti Lock BrakestrialnaqueraNo ratings yet
- Physical parameters shaping of Farwa Lagoon - LibyaDocument7 pagesPhysical parameters shaping of Farwa Lagoon - LibyaAsadeg ZaidNo ratings yet
- Massive MIMO For Communications With Drone SwarmsDocument26 pagesMassive MIMO For Communications With Drone SwarmsAsher Suranjith JayakumarNo ratings yet
- Eurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 ManualDocument88 pagesEurotech IoT Gateway Reliagate 10 12 Manualfelix olguinNo ratings yet
- Lab Manual MCSE 101Document35 pagesLab Manual MCSE 101Juan JacksonNo ratings yet
- General 04 Fixed Flow Pump To Three TanksDocument13 pagesGeneral 04 Fixed Flow Pump To Three TanksjpalauguillemNo ratings yet
- HI-8592, HI-8593, HI-8594: Single-Rail ARINC 429 Differential Line DriverDocument14 pagesHI-8592, HI-8593, HI-8594: Single-Rail ARINC 429 Differential Line DriversameeppaiNo ratings yet
- UnderstandingCryptology CoreConcepts 6-2-2013Document128 pagesUnderstandingCryptology CoreConcepts 6-2-2013zenzei_No ratings yet
- DSD - Assignment 1 2018Document3 pagesDSD - Assignment 1 2018Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Data AnalysisDocument7 pagesData AnalysisAndrea MejiaNo ratings yet
- 2.6 Rational Functions Asymptotes TutorialDocument30 pages2.6 Rational Functions Asymptotes TutorialAljun Aldava BadeNo ratings yet
- Ibrahim Zeid: RsrecialDocument96 pagesIbrahim Zeid: RsrecialengrodeNo ratings yet
- Is A Calorie Really A Calorie - Metabolic Advantage of Low-Carbohydrate DietsDocument6 pagesIs A Calorie Really A Calorie - Metabolic Advantage of Low-Carbohydrate DietsGustavo CastroNo ratings yet
- GAS-INSULATED SWITCHGEAR MODELS 72kV ADVANCED ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLYDocument6 pagesGAS-INSULATED SWITCHGEAR MODELS 72kV ADVANCED ENVIRONMENTALLY FRIENDLYBudi SantonyNo ratings yet
- 1.11 CHEM FINAL Chapter 11 Sulfuric AcidDocument21 pages1.11 CHEM FINAL Chapter 11 Sulfuric AcidSudhanshuNo ratings yet
- Smart Dustbin using ArduinoDocument22 pagesSmart Dustbin using ArduinoEr Dinesh TambeNo ratings yet
- QAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023Document1 pageQAF10A200S TheTimkenCompany 2DSalesDrawing 03 06 2023LeroyNo ratings yet
- Solution of Homework 4Document4 pagesSolution of Homework 4Kamalakar Reddy100% (2)
- Indian Standards List As On Jan2009Document216 pagesIndian Standards List As On Jan2009Vasudeva Pavan VemuriNo ratings yet
- Unit 10Document18 pagesUnit 10ChaithraMalluNo ratings yet
- DbintfcDocument80 pagesDbintfchnr.uninstallNo ratings yet
- Sec 2 French ImmersionDocument1 pageSec 2 French Immersionapi-506328259No ratings yet
- Linear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials With A Vitreous Silica DilatometerDocument7 pagesLinear Thermal Expansion of Solid Materials With A Vitreous Silica Dilatometerluis_may22No ratings yet