Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Stability Defn
Uploaded by
Ankit VyasOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Stability Defn
Uploaded by
Ankit VyasCopyright:
Available Formats
Density of a substance is its mass per unit volume
Relative Density of a substance is the ratio of the density of that substance and of fresh water.
Pressure is the load per unit area (tm-2)
Thrust is the pressure exerted on a given surface (t)
Archimedes Principle states that when a body is wholly or partially immersed in a fluid, it suffers an apparent loss of weight,
which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced.
Principle of floatation: When a body is floating in a liquid, the weight of liquid displaced equals the weight of body.
Displacement of the ship is the weight of the ship & its contents or the weight of water displaced by the ship in that
condition.
Light Displacement is the mass of the empty ship i.e. without any cargo, fuel, lubricating oil, ballast water, fresh & feed
water in the tanks, consumable stores & passenger or crew & their effects.
Load Displacement is the total mass of the ship when floating is salt water with her loadline at the surface.
Present Displacement is the mass of the ship at present. It is the sum of the light displacement of the ship & everything on
board at present.
Deadweight (DWT) of a ship is the total mass of cargo, fuel, freshwater etc. that a ship can carry when she is floating in salt
water with her summer loadline at the surface. DWT = load disp – light disp.
Water-plane Coefficient (Cw) or coefficient of fineness of the water-plane is the ratio of the area of the
water-plane to the area of a rectangle having the same length & max breadth.
Block Coefficient (Cb) or coefficient of fineness of displacement, at any draft is the ratio of the U/W volume of the ship at
the draft to the volume of a rectangular box having the same extreme dimensions.
Reserve Buoyancy is the volume of the enclosed spaces above the waterline.
Tones per Centimeter (TPC) at any draft are the no. of tones reqd. to change the V/L’s mean draft by one centimeter.
Hydrostatic Draft is the draft at the center of floatation.
Fresh Water Allowance (FWA) is the increase in draft when the ship goes from SW to FW & vice-versa.
The Center of Gravity of a ship is that point through which the force of gravity maybe considered to act vertically
downwards with a force equal to the weight of the ship.
The Center of Buoyancy of a ship is that point through which the force of buoyancy maybe considered to act vertically
upwards with a force equal to the weight of water displaced by it.
List is the transverse inclination caused by unequal distribution of weights on either side of centerline of the V/L i.e. list is
caused when the COG is not on the centerline. It’s an internal cause.
Heel is the transverse inclination of the V/L caused external forces such as wind, waves, centrifugal forces during course
alterations, over-tight moorings at the port etc. .The position of COG remains unaffected.
Transverse Metacentre (M) is the point of intersection of the vertical line through the center of buoyancy in
the upright condition and the vertical line through the CB in a slightly inclined position.
Metacentric Height is the vertical distance between COG and the Metacentre. (GM)
Righting Lever (GZ) When a vessel is heeled, the force of buoyancy acting vertically upwards through the new position of
COB, becomes separated from the COG by a horizontal distance. This distance is called the righting lever.
Righting Moment: When a vessel is heeled, the forces of gravity & buoyancy, being equal & opposite, become separated by
a distance called the righting lever. This forms a couple, which tends to return the vessel to upright. The moment of this
couple is called the righting moment or the moment of statical stability.
You might also like
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (73)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Corporate Finance MCQDocument11 pagesCorporate Finance MCQsinghsanjNo ratings yet
- INGRAM - Grievance DetailsDocument2 pagesINGRAM - Grievance DetailsAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Gmail - Regarding Poor Treatment After ComplaintDocument2 pagesGmail - Regarding Poor Treatment After ComplaintAnkit Vyas100% (1)
- DG Notice Seafarer E-GovDocument1 pageDG Notice Seafarer E-GovAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- GrainDocument2 pagesGrainAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- # 5 Hamburg RulesDocument2 pages# 5 Hamburg RulesAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- IR Web PortalDocument1 pageIR Web PortalAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- HttpsDocument1 pageHttpsAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Indian Railways Complaints Suggestions: Train Name.: Class: From Station: To Station: No of Passenger: 0Document1 pageIndian Railways Complaints Suggestions: Train Name.: Class: From Station: To Station: No of Passenger: 0Ankit VyasNo ratings yet
- # 4 G Armed Security GuardsDocument14 pages# 4 G Armed Security GuardsAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- ASM - Practice Questions - 1Document2 pagesASM - Practice Questions - 1Ankit VyasNo ratings yet
- InformaDocument8 pagesInformaAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- DeckDocument10 pagesDeckAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- The New Jason ClauseDocument1 pageThe New Jason ClauseAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Name: Ankit Vyas Nationality: Indian CDC No: MUM163920 MUI No: N 039207 Rank: Chief OfficerDocument15 pagesName: Ankit Vyas Nationality: Indian CDC No: MUM163920 MUI No: N 039207 Rank: Chief OfficerAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Customer Loyalty: Dr. Suresh MalodiaDocument8 pagesCustomer Loyalty: Dr. Suresh MalodiaAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Inspections and Compliance Directorate: Propeller Clearing Port HazardDocument1 pageInspections and Compliance Directorate: Propeller Clearing Port HazardAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Scan Doc by CamScannerDocument1 pageScan Doc by CamScannerAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Coc Challan 2Document1 pageCoc Challan 2Ankit VyasNo ratings yet
- 05-10 Paris MOU Port State Control New Inspection RegimeDocument1 page05-10 Paris MOU Port State Control New Inspection RegimeAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Second Mate Xam FormatDocument6 pagesSecond Mate Xam FormatAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- Coc Challan 1Document1 pageCoc Challan 1Ankit VyasNo ratings yet
- Data Linker Business ProfileDocument3 pagesData Linker Business ProfileAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- ROR QUES AND ANSDocument19 pagesROR QUES AND ANSAnkit Vyas100% (1)
- SBI SmarttechDocument2 pagesSBI SmarttechAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- ASUSTeK TECHNICAL SUPPORT REQUEST FORM DATEDocument2 pagesASUSTeK TECHNICAL SUPPORT REQUEST FORM DATEEmJay BalansagNo ratings yet
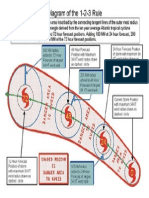
- 123 Rule For TrsDocument1 page123 Rule For Trsanshul_sharma_5No ratings yet
- Specific Items To Be Inspected During An Expanded InspectionDocument4 pagesSpecific Items To Be Inspected During An Expanded InspectionAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- N - 010 Navigating in IceDocument1 pageN - 010 Navigating in IceAnkit VyasNo ratings yet
- 9702p2vectorsallcompleted 150816104932 Lva1 App6891Document17 pages9702p2vectorsallcompleted 150816104932 Lva1 App6891Suman Pant0% (1)
- smts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFDocument497 pagessmts-2 Theory of Structures by B.C. Punmia Text PDFAman Dubey100% (1)
- Wave Forces On Vertical CylinderDocument22 pagesWave Forces On Vertical CylinderInayatul LailiyahNo ratings yet
- Science 8 - Week 3 - Lesson 2 PDFDocument10 pagesScience 8 - Week 3 - Lesson 2 PDFLizaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Document5 pages2019 Summer Question Paper (Msbte Study Resources)Ashish pathareNo ratings yet
- 4th-Qrtr-dll Gr.-9Document29 pages4th-Qrtr-dll Gr.-9harold carbonelNo ratings yet
- Insulation Resistance Testing: Application NoteDocument8 pagesInsulation Resistance Testing: Application Notefernando_aragon2001No ratings yet
- An Improved Quadrilateral Flat Element With Drilling Degrees of Freedom For Shell Structural AnalysisDocument35 pagesAn Improved Quadrilateral Flat Element With Drilling Degrees of Freedom For Shell Structural AnalysisDaniele Di LucaNo ratings yet
- SOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Document43 pagesSOLA2060 Introduction To Electronic Devices Semester 1, 2019Marquee BrandNo ratings yet
- Heating Mechanism Analysis. General OverviewDocument4 pagesHeating Mechanism Analysis. General OverviewVlad TampizaNo ratings yet
- Physics 10 Reviewer Question SheetDocument5 pagesPhysics 10 Reviewer Question SheetAntonette TabilNo ratings yet
- 10 Electric CurrentDocument12 pages10 Electric Currentömer aydınNo ratings yet
- ME 218 - Spring 2018 - Week05 HandoutDocument7 pagesME 218 - Spring 2018 - Week05 HandoutNitin BhatiNo ratings yet
- Chapter Problems - Constant Acceleration FormulasDocument2 pagesChapter Problems - Constant Acceleration FormulasGameMixNo ratings yet
- Etg 1 02Document9 pagesEtg 1 02Tapas RoyNo ratings yet
- United States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 7482,597 B2Document22 pagesUnited States Patent: (10) Patent No.: US 7482,597 B2JustaUser2No ratings yet
- Problem Sheet 3Document2 pagesProblem Sheet 3balochfrahan.2003No ratings yet
- Chemistry 14Document3 pagesChemistry 14BALA GANESHNo ratings yet
- Problem Term oDocument1 pageProblem Term oAnggiariniMutmainahNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics ChapterDocument42 pagesThermodynamics ChapterBuild AteddyNo ratings yet
- Applied Physics Lab Report 3 (Group A4)Document7 pagesApplied Physics Lab Report 3 (Group A4)T RexNo ratings yet
- Swing Angle CalculationDocument4 pagesSwing Angle CalculationRajas Alshi100% (1)
- SEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFDocument4 pagesSEMIKRON DataSheet SKKE 15 07170871 PDFVinicius Veiverberg DillNo ratings yet
- Fluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 104-110Document7 pagesFluid Phase Equilib. 2007, 261, 104-110GióngManAymorickNo ratings yet
- Skema Latihan HabaDocument10 pagesSkema Latihan HabafizikkopuNo ratings yet
- 05 - Beams and FramesDocument10 pages05 - Beams and FramesOn Fan ChowNo ratings yet
- Grade 11 Chemistry - SCH 3U1Document19 pagesGrade 11 Chemistry - SCH 3U1Sasha Kheyson100% (6)
- What Is Tertiary WindingDocument3 pagesWhat Is Tertiary Windingchirag2011No ratings yet
- Fluent ExerciseDocument44 pagesFluent ExerciseDesign guruNo ratings yet
- Self-Powered Psychotronic GeneratorDocument5 pagesSelf-Powered Psychotronic GeneratorevandrojsilvaNo ratings yet