Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Soluition Charpter 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Bryan de Barros0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesOriginal Title
soluition charpter 2.pdf
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
31 views3 pagesSoluition Charpter 2 PDF
Uploaded by
Bryan de BarrosCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
EMA 4324 Problem Set 3a
2.3 Assuming standard states for all reactants and products,
determine the spontaneous direction of the following reactions
by calculating the cell potential (sic):
[a] Cu + 2HCl = CuCl2 + H2 [Cu + 2H+ = Cu+2 + H2]
*****************************************************
Jones is really asking for a calculation of cell voltage!!
[1] Cu+2 + 2e-= Cu, Eo(Cu+2/Cu) = 0.342 v;
[2] 2H+ + 2e-= H2, Eo(H+/H2) = 0.000 v
Reaction [a] proceeds spontaneously in reverse to what is written...
Vcell = 0.342v, reaction [1] proceeds as written [reduction]; reaction
[2] proceeds in reverse [oxidation] the reaction [written as a
reduction reaction] with the more positive potential will proceed as
the reduction reaction in a cell with the less positive [more
negative] reduction reaction proceeding as an oxidation [reduction
in reverse].
[b] Fe + 2HCl = FeCl2 + H2; Fe + 2H+= Fe+2 + H2
Fe+2 + 2e- = Fe, Eo(Fe+2/Fe) = -0.440v [by insp., oxidation]
2H+ + 2e- = H, Eo(H+/H2) = 0.00 [by inspection, reduction]
Vcell = 0.000 - [-0.440] = 0.440 and Fe + 2H + = Fe+2 + H2
[c] 2AgNO3 + Fe = Fe(NO3)2 + 2Ag
Ag+ + 1e- = Ag, Eo(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799v
Fe+2 + 2e- = Fe, Eo(Fe+2/Fe) = -0.440
and Fe + 2Ag+ = Fe+2 + 2Ag, Ecell = 0.799 - (-0.440) = 1.239v
[d] Ag + FeCl3 = FeCl2 + AgCl
Ag+ + 1e- = Ag, Eo(Ag+/Ag) = 0.799v
Fe+3+ 1e- = Fe+2, Eo(Fe+3/Fe+2) = 0.771v
Fe+2 + Ag+ = Fe+3 + Ag, Ecell = 0.799 - 0.771 = 0.028v
[e] 2Al + 3ZnSO4 = Al2(SO4)3 + 3Zn
Zn+2 + 2e- = Zn, Eo(Zn+2/Zn) = -0.763v
Al+3 + 3e- = Al, Eo(Al+3/Al) = -1.662v
2Al + 3Zn+2 = 2Al+3 + 3Zn, Ecell = -0.763 - (-1.662) = 0.899v
2.5 Write the electrochemical half-cell reactions for oxidation and
reduction during uniform corrosion in the following:
[a] aluminum in air-free sulfuric acid
*****************************************************
Al+3 + 3e- = Al [-1.662 v, oxidation];
H+ + 1e- = 1/2H2[0.00 v, reduction]
[b] iron in air-free ferric sulfate solution
*****************************************************
Fe+2 + 2e- = Fe [-0.440, oxidation]
Fe+3 + 1e- = Fe+2 [+0.771, reduction]
SO4-2 + 6e- +8H+ = S + 4H20 [+0.357, depends.....]
[c] carbon steel in aerated seawater [careful here...]
*****************************************************
Fe+2 + 2e- = Fe [-0.440, oxidation]
O2 + 2H2O + 4e- = 4OH- [0.401, reduction]
H+ + 1e- = 1/2H2 [0.00 v, depends....]
Others???
[d] zinc-tin alloy in an oxygen saturated solution of cupric chloride,
stannic chloride and hydrochloric acid
****************************************************
Zn+2 + 2e- = Zn [-0,763, oxidation]
O2 + 2H2O + 4e- = 4OH- [0.401, reduction]
Cu+2 + 2e- = Cu [+0.337, probable reduction]
Cu+2 + 1e- = Cu+1 [+0.153, depends...]
Sn+4 + 2e- = Sn+2 [+0.15, depends]
[e] copper in deaerated seawater [again, be careful...]
*****************************************************
Cu+2 + 2e- = Cu [+0.337, reduction!!!]
H+ + 1e- = 1/2H2 [0.00 v, oxidation!!!]
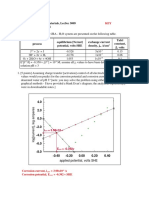
2.6 Copper immersed in concentrated pure hydrochloric acid is observed
to corrode rapidly with the evolution of gas bubbles. Is this contrary
to the results of problem 2.3a? Calculate a cell potential [sic] to
prove your answer, making any necessary assumptions.
******************************************************
According to the chemical [CRC] handbook, the concentration of
“ pure” HCl is 12.0 M. Assuming unit activity coefficients [poor
assumption], pH = -log10[12] = -1.08. Since E(H+/H2) = -0.0592pH,
E(H+/H2) = E(Cu+2/Cu) = 0.064 volts.
E(Cu+2/Cu) = 0.064 = 0.334 - [0.0592/2]log[1/[Cu+2]]
[Cu+2] = 7.56x10-10M!!!!!
You might also like
- Astm - D1475.12152Document4 pagesAstm - D1475.12152Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers - Tension: Standard Test Methods ForDocument14 pagesVulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers - Tension: Standard Test Methods ForPaulo Venicio Alves Vieira100% (1)
- Astm - D573.25993Document6 pagesAstm - D573.25993Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Vulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers - Tension: Standard Test Methods ForDocument14 pagesVulcanized Rubber and Thermoplastic Elastomers - Tension: Standard Test Methods ForPaulo Venicio Alves Vieira100% (1)
- Astm - D2196.12408Document5 pagesAstm - D2196.12408Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - D4400.39339Document4 pagesAstm - D4400.39339Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- G95-87 Standard Test MethodDocument4 pagesG95-87 Standard Test MethodandresjypNo ratings yet
- Astm G58.25944Document8 pagesAstm G58.25944Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - D624.6776Document9 pagesAstm - D624.6776Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - G168.12911Document10 pagesAstm - G168.12911Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - D2805.16103Document6 pagesAstm - D2805.16103Bryan de Barros100% (2)
- Preparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test SpecimensDocument8 pagesPreparing, Cleaning, and Evaluating Corrosion Test SpecimensLê CôngNo ratings yet
- Astm - E2180.29580Document4 pagesAstm - E2180.29580Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - G8.12737Document9 pagesAstm - G8.12737Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm D2196-10Document5 pagesAstm D2196-10Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cathodic Potentials On The Hydrogen Embrittlement Susceptibility of 10Ni5CrMo SteelDocument15 pagesEffect of Cathodic Potentials On The Hydrogen Embrittlement Susceptibility of 10Ni5CrMo SteelBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Hydrogen Permeation Barriers - Basic Requirements, Material Selection, Deposition Methods, and Quality EvaluationDocument7 pagesHydrogen Permeation Barriers - Basic Requirements, Material Selection, Deposition Methods, and Quality EvaluationBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Effect of Cathodic Potentials On The SCC Behavior of E690 Steel in Simulated SeawaterDocument10 pagesEffect of Cathodic Potentials On The SCC Behavior of E690 Steel in Simulated SeawaterBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Techniques To Measure Hydrogen Content in SS 304LDocument30 pagesTechniques To Measure Hydrogen Content in SS 304LBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- StrainGage MeasurementDocument37 pagesStrainGage MeasurementfifafifaNo ratings yet
- Assessing Atmospheric Corrosion with Novel SensorDocument19 pagesAssessing Atmospheric Corrosion with Novel SensorBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- A Study of Strain and Deformation Measurement Using The Arduino Microcontroller and Strain Gauges DevicesDocument7 pagesA Study of Strain and Deformation Measurement Using The Arduino Microcontroller and Strain Gauges DevicesDavid VilcaNo ratings yet
- Atmospheric Corrosion Sensor Based On Strain MeasurementDocument21 pagesAtmospheric Corrosion Sensor Based On Strain MeasurementBryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- NI Strain Gauge TutorialDocument12 pagesNI Strain Gauge TutorialViki Hari Fitrianto100% (3)
- EMA 4324 Problem Set 11 Galvanic Corrosion RatesDocument4 pagesEMA 4324 Problem Set 11 Galvanic Corrosion RatesCANDYNo ratings yet
- Soluition Charpter 5 - 1Document3 pagesSoluition Charpter 5 - 1Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Astm - G33.34087 - 2015Document3 pagesAstm - G33.34087 - 2015Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Solution Charpter 4 - 2Document5 pagesSolution Charpter 4 - 2CANDYNo ratings yet
- Quiz 3 Ema 4324, Stability of Materials, Lecsec 3009 Monday, October 11, 2004Document2 pagesQuiz 3 Ema 4324, Stability of Materials, Lecsec 3009 Monday, October 11, 2004Bryan de BarrosNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5782)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (587)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (890)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (72)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (344)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- Secrets of Leadership, by J. Donald WaltersDocument4 pagesSecrets of Leadership, by J. Donald WaltersMary Kretzmann100% (1)
- The Meaning of The Temple (Leo Schaya) PDFDocument3 pagesThe Meaning of The Temple (Leo Schaya) PDFIsraelNo ratings yet
- Dating - Find Love with the Top Free Dating SiteDocument1 pageDating - Find Love with the Top Free Dating SiteSss NmmNo ratings yet
- Oracle VM Server For Sparc: Key Features and BenefitsDocument4 pagesOracle VM Server For Sparc: Key Features and BenefitsRochdi BouzaienNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Layout Increases ProductivityDocument21 pagesImprovement of Layout Increases ProductivityTesfa TeshomeNo ratings yet
- Upt SMP Negeri 5 Pasarkemis: Dinas PendidikanDocument2 pagesUpt SMP Negeri 5 Pasarkemis: Dinas Pendidikanara ibagaztaNo ratings yet
- Presentation Slides: Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Concepts, Techniques, ApplicationsDocument11 pagesPresentation Slides: Contemporary Strategy Analysis: Concepts, Techniques, ApplicationsMonika SharmaNo ratings yet
- Hockey QuizDocument4 pagesHockey Quizapi-282239158No ratings yet
- Economic Nationalism As A Challenge To Economic LiberalismDocument23 pagesEconomic Nationalism As A Challenge To Economic LiberalismBejmanjinNo ratings yet
- Assignment 3Document9 pagesAssignment 3Hà Minh ĐứcNo ratings yet
- Polysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewDocument9 pagesPolysaccharide, Protein, Lipid-Based Coatings and Their Impact On Fruit Crops: ReviewHimanshu RohillaNo ratings yet
- The Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceDocument4 pagesThe Leaf: Short Notes Class 6 ScienceParimala DhanasekaranNo ratings yet
- What Is Global Strategy? and Why Is It Important?Document12 pagesWhat Is Global Strategy? and Why Is It Important?Mohsin JuttNo ratings yet
- Bayan Ul QuranDocument18 pagesBayan Ul QuransahibafNo ratings yet
- Film Studies Origin and History of Arts and Film's PlaceDocument27 pagesFilm Studies Origin and History of Arts and Film's PlaceNivetha SivasamyNo ratings yet
- Cummingston BoulderingDocument3 pagesCummingston Boulderingg2outdoorNo ratings yet
- Marketing Management 11Document5 pagesMarketing Management 11KNo ratings yet
- School Management Assessment ToolDocument24 pagesSchool Management Assessment ToolMa Abegail Calayag Carangan100% (7)
- Argumentation and DebateDocument6 pagesArgumentation and DebateKristalFaithRamirezPagaduanNo ratings yet
- Latihan Soal Kieso 2Document6 pagesLatihan Soal Kieso 2Dimas Samuel100% (3)
- Exchange Online Instruction GuideDocument7 pagesExchange Online Instruction GuideKishor WaghmareNo ratings yet
- MAT I CES Request Form 137Document1 pageMAT I CES Request Form 137Israel AbarcaNo ratings yet
- Indore - Smart City Proposal - MasterplanDocument92 pagesIndore - Smart City Proposal - MasterplansiddarthsoniNo ratings yet
- R For Data ScienceDocument4 pagesR For Data SciencePrateek SamuelNo ratings yet
- KiG 26 KnjigePrirucnikDocument6 pagesKiG 26 KnjigePrirucnikIvanBagaric0% (1)
- Application Manual - PROFIBUS-DP PDFDocument64 pagesApplication Manual - PROFIBUS-DP PDFcabecavilNo ratings yet
- Adjective Clause: Dependent ClausesDocument8 pagesAdjective Clause: Dependent ClausesRosevelle AyapNo ratings yet
- Summer Internship Project Report ON "Apple V/S Samsung": Sardar Bhagat Singh College of Technology & Management, LucknowDocument4 pagesSummer Internship Project Report ON "Apple V/S Samsung": Sardar Bhagat Singh College of Technology & Management, LucknowMaster PrintersNo ratings yet
- Surgical Emergencies: in Obstetrics & GynecologyDocument20 pagesSurgical Emergencies: in Obstetrics & GynecologyAnonymous hHfqtTNo ratings yet
- Calculation of BoltsDocument22 pagesCalculation of BoltstitieNo ratings yet