Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Earthquakes and Faults
Uploaded by
rhon0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pagehandout
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documenthandout
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
26 views1 pageEarthquakes and Faults
Uploaded by
rhonhandout
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
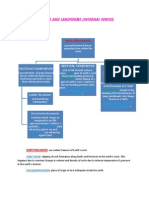
Earthquakes & Faults
Earthquake – a shaking or trembling of the Earth that Fold – a bend produced in rock by forces operative after
is volcanic or tectonic (changes in the structure of the the consolidation of rocks
Earth’s surface) in origin; travels in the form of seismic Anticline – up way fold
waves Syncline – down way fold
Tremor – felt or unfelt movements of Earth’s crust
Geologists – study the Earth’s history & life as recorded
in rocks
Seismologists – experts in the study of earthquakes
PHIVOLCS (Phil. Institute of Volcanology & Seismology)
– LGU that is responsible for giving us information on
what to do before, during & after an earthquake Seismic waves – vibrations caused by an earthquake;
travel in all directions from the focus
Fault – is a break/crack in the Earth’s crust along Seismograph – instrument for detecting & measuring
which significant movement has taken place an earthquake
Types: Seismogram – is the printed record from a
1. Normal (Dip-slip) – caused by tension; block above seismograph
an inclined fault moves down Magnitude – measures the amount & duration
movements of energy released by an earthquake
Intensity – measures the amount of damage caused at
a certain location caused by an earthquake
Forms of Seismic Wave:
A. Body waves – faster waves that travel through
Earth’s interior
Graben – multiple normal faults 1. Primary/P-waves – are the first to arrive at a
seismograph station
2. Secondary/S waves – arrive at recording station
after P waves but before surface waves
B. Surface waves – Slower waves that travel along
Earth’s surface; responsible for much of earthquake
damage
1. Rayleigh waves – result in vertical movement of
2. Reverse/thrust (Dip-slip) – caused by compression; surface
block above an inclined fault moves up 2. Love waves – produce a side-to-side movement
Horst – multiple reverse fault
Focus – the point under the Earth’s surface where the
initial slipping or sliding of rocks takes place
3. Strike-slip – blocks on either side of fault move Epicenter – place on the surface of the Earth just above
horizontally, left or right the focus
Active fault – has generated earthquakes before &
capable of causing more in the future
You might also like
- Shallow Intermediate 70-350 KM Deep: Normal Fault - Dip-Slip Fault in Which TheDocument5 pagesShallow Intermediate 70-350 KM Deep: Normal Fault - Dip-Slip Fault in Which TheLyra Mae BautistaNo ratings yet
- M1 Earthquake HandoutDocument2 pagesM1 Earthquake HandoutWHWHWHWHWWH WWGHWHGWGHWNo ratings yet
- NOTES NO. 1 Earthqukaes and FaultsDocument7 pagesNOTES NO. 1 Earthqukaes and FaultsellaNo ratings yet
- Hand-Out For EarthquakesDocument3 pagesHand-Out For EarthquakesalyssaNo ratings yet
- Faults & Earthqaukes NotesDocument1 pageFaults & Earthqaukes NotesMARISTELA MACARANASNo ratings yet
- Faults & Earthquakes NotesDocument1 pageFaults & Earthquakes NotesMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Gail GeoDocument8 pagesGail GeoEstroga, Lovely MaeNo ratings yet
- Earthquake - Lecture NotesDocument6 pagesEarthquake - Lecture NotesLeandro Remojo JrNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument2 pagesEarthquakecashieentan05No ratings yet
- Sorry Late HeheDocument4 pagesSorry Late Hehechasu nanameNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE 10 Q1W7 Dynamic of the Earth (1)Document25 pagesSCIENCE 10 Q1W7 Dynamic of the Earth (1)toshuaplayzminecraftNo ratings yet
- Earthquake WavesDocument1 pageEarthquake WavesApril Mae BaldozaNo ratings yet
- Overview of The Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesOverview of The Earth ScienceGen StephenNo ratings yet
- Types of Faults and seismic waves explainedDocument30 pagesTypes of Faults and seismic waves explainedYour ArniellaNo ratings yet
- Lecture No. 15 EarthquakesDocument19 pagesLecture No. 15 EarthquakesZuhair TurkmaniNo ratings yet
- Earth ScienceDocument3 pagesEarth SciencejulianaNo ratings yet
- Science 8 Quarter 2Document4 pagesScience 8 Quarter 2Senpi ServerNo ratings yet
- Faults & Earthqaukes NotesDocument1 pageFaults & Earthqaukes NotesMaristela Paraan MacaranasNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Faults PowerpointDocument30 pagesEarthquakes and Faults PowerpointCassiopeia DimatulacNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument30 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsRazel Marie MijaresNo ratings yet
- Science 10-1 Quarter Reviewer: 8 SecondsDocument9 pagesScience 10-1 Quarter Reviewer: 8 SecondsVannie MonderoNo ratings yet
- Earth Science 8 ReviewerDocument11 pagesEarth Science 8 ReviewerBraynell Owen ClaroNo ratings yet
- An Earthquake Is The Vibration of EarthDocument12 pagesAn Earthquake Is The Vibration of EarthJhen BonNo ratings yet
- 2ndQ ReviewerDocument2 pages2ndQ ReviewerAshley Napo pinedaNo ratings yet
- Geog 1 - FinalsDocument5 pagesGeog 1 - FinalsAlexie Anne MariñoNo ratings yet
- Group3 EarthquakeDocument23 pagesGroup3 EarthquakeKiara A.P GajoNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Pieces: Tectonic PlatesDocument17 pagesUnderstanding The Pieces: Tectonic PlatesPrincess Micaela MalolosNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 EARTHQUAKE HAZARDSDocument6 pagesChapter 4 EARTHQUAKE HAZARDSDonna Mae AbonalNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Handout: Causes, Effects and PredictionDocument2 pagesEarthquakes Handout: Causes, Effects and PredictionDione Gale NavalNo ratings yet
- Sci Fil TLE and AP REV 1st QTR-1Document4 pagesSci Fil TLE and AP REV 1st QTR-1Jan Franco FerrerNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument19 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsMasTer CrafT (MasTerCrafT89)No ratings yet
- DisastersDocument8 pagesDisastersjaninepenelope07No ratings yet
- Understanding Seismology and Seismic Wave TypesDocument2 pagesUnderstanding Seismology and Seismic Wave TypesLara GatbontonNo ratings yet
- SeismicWaveBehavior BuildingDocument3 pagesSeismicWaveBehavior BuildingBobby McNattNo ratings yet
- Earthquake Resistant Design FundamentalsDocument15 pagesEarthquake Resistant Design FundamentalsYasserMohsenNo ratings yet
- Case StudyDocument19 pagesCase StudyAnnie EblinNo ratings yet
- SCIENCE ReviewerDocument7 pagesSCIENCE ReviewervincevelasquezNo ratings yet
- EARTHQUAKEDocument61 pagesEARTHQUAKEkenshin copradaNo ratings yet
- Why? and How?: EarthquakesDocument38 pagesWhy? and How?: EarthquakesDiana Rose Gozon100% (1)
- San Francisco EarthquakesDocument24 pagesSan Francisco Earthquakes周牮No ratings yet
- 7.2 EarthquakeDocument21 pages7.2 EarthquakeDarryl Dabu BiscaycaNo ratings yet
- Earthquake ReviewerDocument3 pagesEarthquake ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Earth Movements and Landforms (Internal Forces)Document5 pagesEarth Movements and Landforms (Internal Forces)swapnilamoda100% (1)
- DRRR Earthquake HazardsDocument65 pagesDRRR Earthquake HazardsellekamiyaNo ratings yet
- Geology 05 EarthquakeDocument7 pagesGeology 05 EarthquakeChris RVNo ratings yet
- Seismic WavesDocument23 pagesSeismic WavesAna Cristina Castro-CayabyabNo ratings yet
- Lithosphere and Plate TectonicsDocument4 pagesLithosphere and Plate TectonicsLexaNo ratings yet
- Distaster Risk Reduction ReviewerDocument3 pagesDistaster Risk Reduction ReviewerKimberly LuistroNo ratings yet
- Earth Processes NotesDocument9 pagesEarth Processes NotescalebNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes Volcanoes DiastrophismDocument24 pagesEarthquakes Volcanoes DiastrophismStephanie CañeteNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document5 pagesChapter 4api-3749116No ratings yet
- Earthquake: By: Mrs. M.C. FernandezDocument42 pagesEarthquake: By: Mrs. M.C. Fernandezmarites fernandezNo ratings yet
- Earth Life Science Module 3Document13 pagesEarth Life Science Module 3Rosalyn Pagatpatan BarolaNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes-And-Faults PPT 2014Document33 pagesEarthquakes-And-Faults PPT 2014api-269185515No ratings yet
- Science 2ND Quarter NotesDocument12 pagesScience 2ND Quarter NotesPrecious ShemNo ratings yet
- Earth Science-Finals-ReviewerDocument5 pagesEarth Science-Finals-ReviewerReendelle JamiatreNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument3 pagesScience ReviewerRhyzell Rose CopalNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument4 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsChloe De LeonNo ratings yet
- Unit Iii: Measuring EarthquakeDocument14 pagesUnit Iii: Measuring Earthquakeapi-3859035No ratings yet
- The Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksFrom EverandThe Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksNo ratings yet
- WORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutDocument1 pageWORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutrhonNo ratings yet
- F&MDocument1 pageF&MrhonNo ratings yet
- WORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutDocument1 pageWORK, ENERGY, POWER HandoutrhonNo ratings yet
- Cover PageDocument2 pagesCover Pagerhon100% (1)
- Advanced Earthquake Resistant DesignDocument17 pagesAdvanced Earthquake Resistant Designraju619No ratings yet
- 5 SedimentaryStructures PDFDocument16 pages5 SedimentaryStructures PDFRoberto NepomucenoNo ratings yet
- Kubalikova - Geomorphosite Assessment For GeotourismDocument26 pagesKubalikova - Geomorphosite Assessment For GeotourismRyzal AdnanNo ratings yet
- Reading Test (B) AK Gr4 SECOND TERMDocument6 pagesReading Test (B) AK Gr4 SECOND TERMAsmaa MostafaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology in Tasmania: A Review: Leaman Geophysics, GPO Box 320, Hobart, Tas. 7001Document13 pagesEngineering Geology in Tasmania: A Review: Leaman Geophysics, GPO Box 320, Hobart, Tas. 7001Harf Jucoy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Rocks and The Rock Cycle Notes: Mrs. WeimerDocument43 pagesRocks and The Rock Cycle Notes: Mrs. WeimerFonfo LawrenceNo ratings yet
- Trap and SealDocument39 pagesTrap and SealRezaArtamaviaNo ratings yet
- Karst Without Boundaries.Document376 pagesKarst Without Boundaries.BOUKHELIFANo ratings yet
- (S. K. Haldar (Auth.) ) Introduction To Mineralogy PDFDocument341 pages(S. K. Haldar (Auth.) ) Introduction To Mineralogy PDFAndreé Castro100% (1)
- Reading Comprehension: SubjectsDocument25 pagesReading Comprehension: Subjects078-Muhamad Nickolai Kusuma HNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document15 pagesAssignment 2AmyNo ratings yet
- Stratigraphic Nomenclature of Iranian Oil Consortium Agreement Area PDFDocument64 pagesStratigraphic Nomenclature of Iranian Oil Consortium Agreement Area PDFhesam mosaviNo ratings yet
- Jurnal Sains Informasi Geografi (Jsig)Document8 pagesJurnal Sains Informasi Geografi (Jsig)Harduz PadendenanNo ratings yet
- Earth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Exogenic ProcessesDocument24 pagesEarth and Life Science: Quarter 1 - Module 5: Exogenic Processeshara azurNo ratings yet
- Seismotectonics of The 6 February 2012 MW 6.7 Negros Earthquake, Central PhilippinesDocument17 pagesSeismotectonics of The 6 February 2012 MW 6.7 Negros Earthquake, Central Philippinesjoanna frialesNo ratings yet
- Hydrogeochemistry of Thermal Water From Surface Manifestation at Gunung Ciremai and Its Surrounding, Cirebon, West Java - IndonesiaDocument8 pagesHydrogeochemistry of Thermal Water From Surface Manifestation at Gunung Ciremai and Its Surrounding, Cirebon, West Java - IndonesiaAkbar Nurul FirdausNo ratings yet
- Impacts of Volcanic EruptionDocument24 pagesImpacts of Volcanic EruptionLindsay LooganNo ratings yet
- Sonic LogDocument10 pagesSonic LogSukawan ZakyNo ratings yet
- Geographic l1Document86 pagesGeographic l1Raaja ShekharNo ratings yet
- Glaze Natural Stone ProfileDocument41 pagesGlaze Natural Stone ProfileSanjay RathodNo ratings yet
- Geological Evolution of The Holocene Yarra Delta and Its RelationshipDocument18 pagesGeological Evolution of The Holocene Yarra Delta and Its RelationshipDanny Lam100% (1)
- The Role of Engineering Geology in The Route Selection, Design and Construction of A Road Across The Blue Nile Gorge, EthiopiaDocument29 pagesThe Role of Engineering Geology in The Route Selection, Design and Construction of A Road Across The Blue Nile Gorge, EthiopiaFernando AlegriaNo ratings yet
- Volcano Types ChartDocument2 pagesVolcano Types Chartअरुण कुमार सोनीNo ratings yet
- Vein Type Deposits QuatzDocument9 pagesVein Type Deposits QuatzSenoNo ratings yet
- Bradbury (1971) - Paleolimnology of Texcoco - Evidence From Diatoms PDFDocument22 pagesBradbury (1971) - Paleolimnology of Texcoco - Evidence From Diatoms PDFArturo Palma RamírezNo ratings yet
- Piling in Yuen Long: A Unique ExperienceDocument3 pagesPiling in Yuen Long: A Unique ExperienceSomesh Siddharth100% (1)
- Geologic Time ScaleDocument3 pagesGeologic Time ScaleBogdan Draghici100% (1)
- Volcanism: Mud VolcanoesDocument12 pagesVolcanism: Mud VolcanoesJames Bryan M. PrimaNo ratings yet
- Rock Mass Characterization: EM 1110-1-2908 30 Nov 94Document22 pagesRock Mass Characterization: EM 1110-1-2908 30 Nov 94feiernicoletaNo ratings yet
- ICAO Volcano Watch Operational ProceduresDocument134 pagesICAO Volcano Watch Operational ProceduresCaio Storolli PedronNo ratings yet