Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HDLC Frame Types Explained
Uploaded by
Shahzeb Khan0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesThe first bit is '0' informing the receiver that it is an I-frame. The first 2 bits (11) show that it is a supervisory frame. The last bit is the frame reject information. The information in I-frame is the user information or payload coming from upper layers.
Original Description:
Original Title
HDLC Frame Types
Copyright
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe first bit is '0' informing the receiver that it is an I-frame. The first 2 bits (11) show that it is a supervisory frame. The last bit is the frame reject information. The information in I-frame is the user information or payload coming from upper layers.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
1K views3 pagesHDLC Frame Types Explained
Uploaded by
Shahzeb KhanThe first bit is '0' informing the receiver that it is an I-frame. The first 2 bits (11) show that it is a supervisory frame. The last bit is the frame reject information. The information in I-frame is the user information or payload coming from upper layers.
Copyright:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Available Formats
Download as DOC, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 3
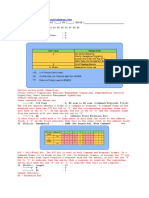
HDLC Frame Types
I-frame S-frame U-frame
I-Frame: Information Frame
Flag Addres Contro Info FCS flag
s l
0 N(S) P/F N(R)
(1- (3-bits) (1- (3-bits)
bit) bit)
Information in I-frame
is the user information or payload coming from upper layers.
Consider the control field of I-frame:
• The first bit is ‘0’ informing the receiver that it is an I-frame
• N(S): Sequence number of frame sent
• P/F bit: Poll/Final bit: P=1 denotes that Primary is active; F=1
denotes that secondary is active. (for details, refer to book)
• N(R): Sequence number of next frame expected
S-Frame: Supervisory Frame
Flag Addres Contro FCS flag
s l
10 Code P/F N(R)
(2-bits) (2-bits) (1-bit) (3-bits)
The first 2 bits (10) show that it is an S-frame.
• Code: Applicable for S and U-frames only. A 2 bit field which
is interpreted as follows:
o 00: RR (Receive Ready)
o 10: RNR (Receive Not Ready)
o 01: REJ (Reject)
o 11 SREJ (Selective Reject)
U-Frame: Unnumbered Frame
Flag Addres Contro Info FCS flag
s l
11 Code P/F Code
(2-bits) (2-bits) (1-bit) (3-bits)
The first 2 bits (11) show that it is a U-frame.
U-frame codes are divided into two sections:
2 bit prefix before P/F bit
3 bit suffix after P/F bit
The important combinations are as shown in the table below:
2 bit 3 bit Functional
Code code Description
00 001 SNRM: Set
Normal Response
Mode
11 000 SARM: Set
Asynchronous
Response Mode
11 100 SABM: Set
Asynchronous
balance Mode
10 001 FRMR: Frame
Reject
Information in U-frame is the Management Information which
is required or managing the network.
You might also like
- PART II: Data Link ControlsDocument38 pagesPART II: Data Link ControlsAkshit NagpalNo ratings yet
- Telecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, NoidaDocument16 pagesTelecommunication Networks 15B11EC611: Dr. Bhagirath Sahu Assistant Professor, JIIT, NoidaRachit GuptaNo ratings yet
- Data Link Protocol: 11.1 Review QuestionsDocument4 pagesData Link Protocol: 11.1 Review QuestionsOso PolNo ratings yet
- Module 2 Part 3Document16 pagesModule 2 Part 3leemong335No ratings yet
- HDLC Protocol ExplainedDocument4 pagesHDLC Protocol ExplainedhardnutNo ratings yet
- Computer Network No9 Cont Mediam Access Control From APCOMSDocument4 pagesComputer Network No9 Cont Mediam Access Control From APCOMSToaster97No ratings yet
- HDLC 1Document4 pagesHDLC 1chakrabortyanjishnu9332No ratings yet
- R2 SignallingDocument55 pagesR2 SignallingSuman GhimireNo ratings yet
- HDLC: High-level Data Link Control ProtocolDocument21 pagesHDLC: High-level Data Link Control ProtocolAkshay GuptaNo ratings yet
- HDLC Data Link Control Protocol: Frame Structure, Transfer Modes and OperationDocument12 pagesHDLC Data Link Control Protocol: Frame Structure, Transfer Modes and OperationadeelNo ratings yet
- Data link 1: MAC addresses, switch tables, and VLAN taggingDocument58 pagesData link 1: MAC addresses, switch tables, and VLAN taggingj7d7ye-709337No ratings yet
- ECE 421 Digital Communication - Flow and Error Control in HDLCDocument29 pagesECE 421 Digital Communication - Flow and Error Control in HDLCHasnaa MahmoudNo ratings yet
- SDH SummaryDocument1 pageSDH SummaryZargham KhanNo ratings yet
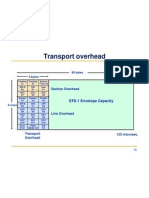
- Transport Overhead: STS-1 Envelope CapacityDocument42 pagesTransport Overhead: STS-1 Envelope CapacityRupali MisriNo ratings yet
- Jdsu Speed Up Your SDH AnalysisDocument1 pageJdsu Speed Up Your SDH AnalysisFelippe CanatoNo ratings yet
- HDLC Frame Format Error DetectionDocument1 pageHDLC Frame Format Error DetectionharshithnittalaNo ratings yet
- HDLC Protocol Explained: Stations, Frames, and Operational ModesDocument14 pagesHDLC Protocol Explained: Stations, Frames, and Operational ModesCosmina RinciogNo ratings yet
- HDLC Media Access Protocol ExplainedDocument6 pagesHDLC Media Access Protocol ExplainedkrgcegNo ratings yet
- HDLCDocument31 pagesHDLCrakeshsingh1No ratings yet
- LAPD (Link Channel Access For D-Channel)Document24 pagesLAPD (Link Channel Access For D-Channel)Shresth BohreNo ratings yet
- High-Level Data Link Control: (HDLC)Document8 pagesHigh-Level Data Link Control: (HDLC)Scaria AlexNo ratings yet
- ISDN PHYSICAL LAYER FUNCTIONSDocument122 pagesISDN PHYSICAL LAYER FUNCTIONSsaraswathi_mitNo ratings yet
- Ring ProtectionDocument20 pagesRing ProtectionionutccieNo ratings yet
- Midterm (2) Exam (4 Pages)Document4 pagesMidterm (2) Exam (4 Pages)Nada FSNo ratings yet
- Midterm Exam 1 (4 Pages, 5 Questions)Document4 pagesMidterm Exam 1 (4 Pages, 5 Questions)Nada FSNo ratings yet
- Technical Reference Options and Adapters Volume 2 3of3Document243 pagesTechnical Reference Options and Adapters Volume 2 3of3kgrhoadsNo ratings yet
- T1/E1/PRI Technology Overview: Connections, Frames & SignalingDocument44 pagesT1/E1/PRI Technology Overview: Connections, Frames & SignalingEl-Hussein HegazyNo ratings yet
- Today S Topic: SS7 - So Simple - If NotDocument90 pagesToday S Topic: SS7 - So Simple - If NotChakravarthi ChittajalluNo ratings yet
- Mod4 Framing HDLC MAC PDFDocument50 pagesMod4 Framing HDLC MAC PDFAyush kumarNo ratings yet
- Layer 2 Framing HDLC (High-Level Data Linl Control) : Giuseppe BianchiDocument13 pagesLayer 2 Framing HDLC (High-Level Data Linl Control) : Giuseppe Bianchihassan_m2222No ratings yet
- SDH Overhead and PointerDocument23 pagesSDH Overhead and PointerMahmoud TahaNo ratings yet
- HDLC Protocol OverviewDocument9 pagesHDLC Protocol OverviewAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- Speed Up Your SDH AnalysisDocument1 pageSpeed Up Your SDH AnalysisgencinozaNo ratings yet
- Token RingDocument45 pagesToken RingKäzi MÖinNo ratings yet
- K1 & K2 Bit DescriptionDocument5 pagesK1 & K2 Bit Descriptionv_mangaloreNo ratings yet
- M-3410a Modbus ProtocolDocument35 pagesM-3410a Modbus ProtocolmaheshNo ratings yet
- OH Section OverheadDocument1 pageOH Section OverheadEusojOremorNo ratings yet
- HDLCDocument25 pagesHDLCGuillermo Del Carpio BaldiviezoNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Notes 09-04-181Document28 pagesComputer Network Notes 09-04-181Learn UpNo ratings yet
- P12Y EN M Gb5 PDFDocument81 pagesP12Y EN M Gb5 PDFHafiz SulafuddinNo ratings yet
- SDH Alarms: Figure 6-9. SDH Maintenance InteractionsDocument4 pagesSDH Alarms: Figure 6-9. SDH Maintenance InteractionsJaideep RajputNo ratings yet
- Omron PLC CPM1A: A Small PLC With Flexible I/ODocument17 pagesOmron PLC CPM1A: A Small PLC With Flexible I/OMuhammad Reihan IskandarNo ratings yet
- Training PPT, SDH Principle, 20040423Document88 pagesTraining PPT, SDH Principle, 20040423Gachanja NjorogeNo ratings yet
- 8 Flow and Error Control TechniquesDocument23 pages8 Flow and Error Control TechniquesRahul AryanNo ratings yet
- How To Get Exact BCCH and BSIC From MRDocument6 pagesHow To Get Exact BCCH and BSIC From MRPaul Kabeya100% (1)
- LIN Protocol SpecificationsDocument17 pagesLIN Protocol Specifications김건정No ratings yet
- Unit Iii I/O Interfacing Reference: Chapter 9 Microcomputer Systems, Cheng Liu, Glenn GibsonDocument337 pagesUnit Iii I/O Interfacing Reference: Chapter 9 Microcomputer Systems, Cheng Liu, Glenn GibsonGomathi PsNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - HDLC: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItDocument15 pagesLecture 12 - HDLC: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItjoelanandrajNo ratings yet
- Lecture 12 - HDLC: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItDocument15 pagesLecture 12 - HDLC: Delivered by Joel Anandraj.E Ap/ItMithun Santhosh YuvarajanNo ratings yet
- Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter: April 2011 Reference Design 1011Document11 pagesUniversal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter: April 2011 Reference Design 1011rishi_lvNo ratings yet
- Data Communication ProtocolsDocument8 pagesData Communication Protocolssubramanyam62No ratings yet
- Select CommandDocument3 pagesSelect CommandhunterrraNo ratings yet
- Telephony Protocol Frame AnalysisDocument14 pagesTelephony Protocol Frame AnalysisRukia WadaatNo ratings yet
- HDLC PROTOCOL DATA LINK LAYERDocument20 pagesHDLC PROTOCOL DATA LINK LAYERLihin HimuraNo ratings yet
- DSM Lookalike Mode for H2NS CPPDocument8 pagesDSM Lookalike Mode for H2NS CPPAlan AhmadNo ratings yet
- The ISDN-Protocol: Chapter 4aDocument26 pagesThe ISDN-Protocol: Chapter 4arncc2011No ratings yet
- Data Link Control Protocols ChapterDocument31 pagesData Link Control Protocols ChapterUmair AslamNo ratings yet
- Oracle Vs Sybase PDFDocument31 pagesOracle Vs Sybase PDFinfombmNo ratings yet
- RotoSim8.5Promo UKDocument2 pagesRotoSim8.5Promo UKPrithviraj DagaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Mano QuestionsDocument7 pagesChapter 3 Mano QuestionsREjosh BonifacioNo ratings yet
- Process Hacker ProcessesDocument4 pagesProcess Hacker ProcessessilcanNo ratings yet
- DP-Hardning: Boot Up DP Failure handling bug searchDocument2 pagesDP-Hardning: Boot Up DP Failure handling bug searchfreddyandresNo ratings yet
- Moving Ocr or Voting Disk From One Diskgroup To AnotherDocument4 pagesMoving Ocr or Voting Disk From One Diskgroup To Anothermartin_seaNo ratings yet
- A Neural Network in 13 Lines of Python (Part 2 - Gradient Descent) - I Am TraskDocument18 pagesA Neural Network in 13 Lines of Python (Part 2 - Gradient Descent) - I Am TraskMuhammad Zaka Ud DinNo ratings yet
- SQL TutorialDocument41 pagesSQL TutorialTsegaye HailuNo ratings yet
- Full Adder Using MultiplexerDocument4 pagesFull Adder Using Multiplexermohiuddin_vu67% (3)
- Difference Between Browsing and SurfingDocument2 pagesDifference Between Browsing and SurfingMinal FegadeNo ratings yet
- NOC ModbusTcp SlaveDocument17 pagesNOC ModbusTcp Slavegroup nishNo ratings yet
- Linux File System StructureDocument14 pagesLinux File System Structurejeromet681No ratings yet
- CM Adapter SDK GuideDocument9 pagesCM Adapter SDK GuideJanos KovacsNo ratings yet
- Implementing a Service ProviderDocument25 pagesImplementing a Service ProviderJoe MalemaNo ratings yet
- Introduction To High Performance Scientific ComputingDocument464 pagesIntroduction To High Performance Scientific ComputingSaraDimitrijevicNo ratings yet
- HoneypotsDocument27 pagesHoneypotsDeval GaudaniNo ratings yet
- CS 1102 Unit 2 Programming AssignmentDocument2 pagesCS 1102 Unit 2 Programming AssignmentKareem Nabil29% (7)
- 3.1.1.5 - Dario Relatic - Packet Tracer - Who Hears The Broadcast InstructionsDocument2 pages3.1.1.5 - Dario Relatic - Packet Tracer - Who Hears The Broadcast InstructionsDario Relatic100% (2)
- WellBG 5800 User Guide V1.3Document50 pagesWellBG 5800 User Guide V1.3Phan van TuanNo ratings yet
- Technical QuestionsDocument59 pagesTechnical QuestionsVinen TomarNo ratings yet
- OSPF PresentationDocument43 pagesOSPF PresentationBehzad ZahidNo ratings yet
- SonicWALL Application Risk Management Report Implementation GuideDocument21 pagesSonicWALL Application Risk Management Report Implementation GuideHab BoNo ratings yet
- 2015 Hack in Paris Oracle PeopleSoft Applications Are Under AttacksDocument79 pages2015 Hack in Paris Oracle PeopleSoft Applications Are Under AttacksNadezhdaNo ratings yet
- System Requirements Specification ExampleDocument2 pagesSystem Requirements Specification ExampleChan Pei XinNo ratings yet
- Object Oriented Software Engineering ManualDocument41 pagesObject Oriented Software Engineering ManualDevyani PatilNo ratings yet
- GCV405-RCII-Chapter 12 - Introduction To Seismic Design - Norms and StandardsDocument3 pagesGCV405-RCII-Chapter 12 - Introduction To Seismic Design - Norms and StandardsOec EngNo ratings yet
- (CITATION Cod16 /L 1033) (CITATION H3V19 /L 1033)Document4 pages(CITATION Cod16 /L 1033) (CITATION H3V19 /L 1033)PATRICIA SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Automatic Timetable GeneratorDocument4 pagesAutomatic Timetable GeneratorArohi LigdeNo ratings yet
- ns-3 Development Overview and CapabilitiesDocument27 pagesns-3 Development Overview and CapabilitiesAriawan D RachmantoNo ratings yet
- Python ProgramsDocument5 pagesPython Programskapil kumarNo ratings yet