Professional Documents
Culture Documents
1718 QS015 - 1 Solution PDF
Uploaded by
aliaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
1718 QS015 - 1 Solution PDF
Uploaded by
aliaCopyright:
Available Formats
QS 015/1
Matriculation Programme
Examination
Semester I
Session 2017/2018
Chow Choon Wooi
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
2 3
1. Given matrix 𝐴 = ( ) such that 𝐴2 + 𝛼𝐴 + 𝛽𝐼 = 0, 𝛼 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝛽 are constants, where 𝐼
−2 5
and 𝑂 are identity matrix and zero matrix of 2 𝑥 2 respectively. Determine the value of
𝛼 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝛽.
2. Solve the equation 32𝑥+1 − (16)3𝑥 + 5 = 0.
3. The first and three more successive terms in a geometric progression are given as follows:
7, …, 189, y, 1701, …
Obtain the common ratio r. Hence, find the smallest integer n such that the n-th term
exceeds 10,000.
1
𝑥 2
4. a) Expand (1 − ) in ascending power of 𝑥 up to the term in 𝑥 3 and state the interval
3
of 𝑥 for which the expansion is valid.
1
𝑥 2
b) From part 4(a), express √9 − 3𝑥 in the form of 𝑎 (1 − ), where 𝑎 is an integer.
3
c) Hence, by substituting the suitable value of 𝑥, approximate √8.70 correct to two
decimal places.
5. Solve the equation 3 𝑙𝑜𝑔9 𝑥 = (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2 .
6. Given a complex number 𝑧 = 2 + 𝑖.
1
a. Express 𝑧̅ − in the form 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖, where 𝑎 and 𝑏 are real numbers.
𝑧̅
1
b. Obtain |𝑧̅ − |. Hence, determine the values of real numbers 𝛼 and 𝛽 if 𝛼 +
𝑧̅
1 1 2
𝛽𝑖 = |𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ | (𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ ) .
7. Find the interval of 𝑥 for which the following inequalities are true.
5
a. 𝑥+3
− 1 ≤ 0.
3𝑥−2
b. |2𝑥+3| > 2.
8. Consider functions of 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 2)2 + 1, 𝑥 > 2 and 𝑔(𝑥) = ln(𝑥 + 1), 𝑥 > 0.
a. Find 𝑓 −1 (𝑥) and 𝑔−1 (𝑥), and state the domain and range for each of the
inverse function.
b. Obtain (𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(𝑥). Hence, evaluate (𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(2).
1
9. Given the function 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥−5.
a. Find the domain and range of 𝑔(𝑥).
b. Show that 𝑔(𝑥) is a one-to-one function. Hence, find 𝑔−1 (𝑥).
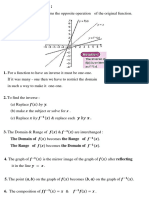
c. On the same axis, sketch the graph of 𝑔(𝑥) and 𝑔−1 (𝑥).
d. Show that 𝑔 𝑜 𝑔−1 (𝑥) = 𝑥.
10. Given the system of linear equations as follow:
Chow Choon Wooi Page 2
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
2𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 𝑧 = 77
4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 7𝑧 = 114
2𝑥 + 𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 48
a. Express the system of equations in the form of matrix equation 𝐴𝑋 = 𝐵 where
𝑥
𝑥 = (𝑦). Hence, determine matrix 𝐴 and matrix 𝐵.
𝑧
b. Based on part 10(a), obtain |𝐴|.
Hence, find
i. |𝑃| if 𝑃𝐴 = 𝐼, where 𝐼 is an identity matrix 3 𝑥 3.
ii. |𝑄| if 𝑄 = (2𝐴)𝑇 .
iii. 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 𝐴.
Hence, obtain 𝐴−1 and find the values of 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑧.
END OF QUESTION PAPER
Chow Choon Wooi Page 3
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
2 3
1. Given matrix 𝐴 = ( ) such that 𝐴2 + 𝛼𝐴 + 𝛽𝐼 = 0, 𝛼 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝛽 are constants, where 𝐼
−2 5
and 𝑂 are identity matrix and zero matrix of 2 𝑥 2 respectively. Determine the value of
𝛼 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝛽.
SOLUTION
2 3
𝐴=( )
−2 5
𝐴2 + 𝛼𝐴 + 𝛽𝐼 = 0
2 3 2 3 2 3 1 0 0 0
( )( )+𝛼( )+𝛽( )=( )
−2 5 −2 5 −2 5 0 1 0 0
4−6 6 + 15 2𝛼 3𝛼 𝛽 0 0 0
( )+( )+( )=( )
−4 − 10 −6 + 25 −2𝛼 5𝛼 0 𝛽 0 0
−2 21 2𝛼 3𝛼 𝛽 0 0 0
( )+( )+( )=( )
−14 19 −2𝛼 5𝛼 0 𝛽 0 0
−2 + 2𝛼 + 𝛽 21 + 3𝛼 0 0
( )=( )
−14 − 2𝛼 19 + 5𝛼 + 𝛽 0 0
21 + 3𝛼 = 0
𝛼 = −7
−2 + 2𝛼 + 𝛽 = 0
−2 + 2(−7) + 𝛽 = 0
𝛽 = 16
∴ 𝛼 = −7, 𝛽 = 16
Chow Choon Wooi Page 4
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
2. Solve the equation 32𝑥+1 − (16)3𝑥 + 5 = 0.
SOLUTION
32𝑥+1 − (16)3𝑥 + 5 = 0
32𝑥 31 − (16)3𝑥 + 5 = 0
3. (3𝑥 )2 − (16)3𝑥 + 5 = 0
Let 𝑦 = 3𝑥
3𝑦 2 − 16𝑦 + 5 = 0
(3𝑦 − 1)(𝑦 − 5) = 0
(3𝑦 − 1) = 0 (𝑦 − 5) = 0
1
𝑦=3 𝑦=5
1
3𝑥 = 3 3𝑥 = 5
3𝑥 = 3−1 ln 3𝑥 = ln 5
𝑥 = −1 𝑥 ln 3 = ln 5
𝑥 = 1.465
∴ 𝑥 = −1 𝑜𝑟 𝑥 = 1.465
Chow Choon Wooi Page 5
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
3. The first and three more successive terms in a geometric progression are given as follows:
7, … , 189, 𝑦, 1701, …
Obtain the common ratio r. Hence, find the smallest integer n such that the n-th term
exceeds 10,000.
SOLUTION
7, … , 189, 𝑦, 1701, …
𝑎=7
𝑦 1701
=
189 𝑦
𝑦 2 = 321489
𝑦 = 567
567
𝑟=
189
𝑟=3
𝑇𝑛 > 10000
𝑎𝑟 𝑛−1 > 10000
(7)3𝑛−1 > 10000
3𝑛−1 > 1428.57
ln 3𝑛−1 > ln 1428.57
(𝑛 − 1) ln 3 > ln 1428.57
(𝑛 − 1) > 6.61
𝑛 > 6.61 + 1
𝑛 > 7.61
𝑛=8
Chow Choon Wooi Page 6
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
1
𝑥 2
4. a) Expand (1 − ) in ascending power of 𝑥 up to the term in 𝑥 3 and state the interval
3
of 𝑥 for which the expansion is valid.
1
𝑥 2
b) From part 4(a), express √9 − 3𝑥 in the form of 𝑎 (1 − 3
), where 𝑎 is an integer.
c) Hence, by substituting the suitable value of 𝑥, approximate √8.70 correct to two
decimal places.
SOLUTION
1 1 1 1 1 1 3
𝑥 2 ( )
2 𝑥 1 ( )(− )
2 2 𝑥 2 ( )(− )(− )
2 2 2 𝑥 3
a. (1 − 3) = 1 + 1!
(− 3) + 2!
(− 3) + 3!
(− 3)
𝑥 1 𝑥2 3 𝑥3
=1− − ( )− ( )
6 8 9 48 27
𝑥 𝑥2 3 𝑥3
=1− − − ( )
6 72 48 27
1 1 1 3
= 1 − 𝑥 − 𝑥2 − 𝑥
6 72 432
The interval of 𝑥 for which the expansion is valid:
𝑥
| |<1
3
𝑥
−1 < <1
3
−3 < 𝑥 < 3
1
b. √9 − 3𝑥 = (9 − 3𝑥)2
1
1 3𝑥 2
= 92 (1 − )
9
1
𝑥 2
= 3 (1 − )
3
c. √8.70 = √9 − 3(0.01)
Chow Choon Wooi Page 7
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
𝑥 = 0.01
1
𝑥 2
√9 − 3𝑥 = 3 (1 − )
3
1 1 1 3
√9 − 3𝑥 = 3 [1 − 𝑥 − 𝑥 2 − 𝑥 ]
6 72 432
1 1 1
√9 − 3(0.01) = 3 [1 − (0.01) − (0.01)2 − (0.01)3 ]
6 72 432
√8.7 = 2.95
Chow Choon Wooi Page 8
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
5. Solve the equation 3 𝑙𝑜𝑔9 𝑥 = (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2 .
SOLUTION
3 𝑙𝑜𝑔9 𝑥 = (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
3𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥
= (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
𝑙𝑜𝑔3 9
3𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥
= (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
𝑙𝑜𝑔3 32
3𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥
= (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
2𝑙𝑜𝑔3 3
3𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥
= (𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
2
3𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥 = 2(𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥)2
𝐿𝑒𝑡 𝑦 = 𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥
3𝑦 = 2𝑦 2
2𝑦 2 − 3𝑦 = 0
𝑦(2𝑦 − 3) = 0
𝑦=0 2𝑦 − 3 = 0
3
𝑦=0 𝑦=2
3
𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥 = 0 𝑙𝑜𝑔3 𝑥 = 2
3
𝑥 = 30 𝑥 = 32
𝑥=1 𝑥 = 5.196
Chow Choon Wooi Page 9
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
6. Given a complex number 𝑧 = 2 + 𝑖.
1
a. Express 𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ in the form 𝑎 + 𝑏𝑖, where 𝑎 and 𝑏 are real numbers.
1
b. Obtain |𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ |. Hence, determine the values of real numbers 𝛼 and 𝛽 if
1 1 2
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = |𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ | (𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ ) .
SOLUTION
(a) 𝑧 = 2 + 𝑖
1 1
𝑧̅ − = (2 − 𝑖) −
𝑧̅ 2−𝑖
1 (2 + 𝑖)
= (2 − 𝑖) −
(2 − 𝑖) (2 + 𝑖)
(2 + 𝑖)
= (2 − 𝑖) −
4 + 2𝑖 − 2𝑖 − 𝑖 2
(2 + 𝑖)
= (2 − 𝑖) −
5
2 1
=2−𝑖− − 𝑖
5 5
8 6
= − 𝑖
5 5
1 8 6
(b) |𝑧̅ − 𝑧̅ | = |5 − 5 𝑖|
8 2 6 2
= √( ) + ( )
5 5
64 36
=√ +
25 25
100
=√
25
= √4
=2
1 1 2
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = |𝑧̅ − | (𝑧̅ − )
𝑧̅ 𝑧̅
Chow Choon Wooi Page 10
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
8 6 2
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = 2 ( − 𝑖)
5 5
8 2 8 6 6 2
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = 2 [( ) − 2 ( ) ( ) 𝑖 + ( 𝑖) ]
5 5 5 5
64 96 36
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = 2 [ − 𝑖− ]
25 25 25
28 96
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = 2 [ − 𝑖]
25 25
56 192
𝛼 + 𝛽𝑖 = − 𝑖
25 25
56 192
𝛼 = 25 𝛽=− 25
Chow Choon Wooi Page 11
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
7. Find the interval of 𝑥 for which the following inequalities are true.
5
a. −1 ≤ 0
𝑥+3
3𝑥−2
b. |
2𝑥+3
|>2
SOLUTION
5
a) 𝑥+3
−1 ≤ 0
5 − (𝑥 + 3)
≤0
𝑥+3
5−𝑥−3
≤0
𝑥+3
2−𝑥
≤0
𝑥+3
2−𝑥 =0 𝑥+3=0
𝑥=2 𝑥 = −3
(−∞, −3) (−3, 2) (2, ∞)
2−𝑥 + + -
𝑥+3 - + +
2−𝑥
- + -
𝑥+3
{𝑥: 𝑥 < −3 ∪ 𝑥 ≥ 2}
3𝑥−2 |𝑥| > 𝑎 ⟺ 𝑥 > 𝑎 𝑜𝑟 𝑥 < −𝑎
b) |2𝑥+3| > 2
3𝑥 − 2 𝑜𝑟 3𝑥 − 2
>2 < −2
2𝑥 + 3 2𝑥 + 3
3𝑥 − 2 3𝑥 − 2
−2>0 +2<0
2𝑥 + 3 2𝑥 + 3
(3𝑥 − 2) − 2(2𝑥 + 3) (3𝑥 − 2) + 2(2𝑥 + 3)
>0 <0
2𝑥 + 3 2𝑥 + 3
3𝑥 − 2 − 4𝑥 − 6 3𝑥 − 2 + 4𝑥 + 6
>0 <0
2𝑥 + 3 2𝑥 + 3
−𝑥 − 8 7𝑥 + 4
>0 <0
2𝑥 + 3 2𝑥 + 3
Chow Choon Wooi Page 12
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
−𝑥 − 8 = 0 2𝑥 + 3 = 0 7𝑥 + 4 = 0 2𝑥 + 3 = 0
3 4 3
𝑥 = −8 𝑥 = −2 𝑥 = −7 𝑥 = −2
3 3 3 3 4 4
(−∞, −8) (−8, − ) (− , ∞) (−∞, − ) (− , − ) (− , ∞)
2 2 2 2 7 7
−𝑥 − 8 + - - 7𝑥 + 4 - - +
2𝑥 + 3 - - + 2𝑥 + 3 - + +
−𝑥 − 8
2𝑥 + 3
- + -
7𝑥 + 4
2𝑥 + 3
+ - +
3 3 4
(−8, − ) or (− , − )
2 2 7
3 4
−8 − −
2 7
3 3 4
(−8, − ) ∪ (− , − )
2 2 7
Chow Choon Wooi Page 13
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
8. Consider functions of 𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 2)2 + 1, 𝑥 > 2 and 𝑔(𝑥) = ln(𝑥 + 1), 𝑥 > 0.
a. Find 𝑓 −1 (𝑥) and 𝑔−1 (𝑥), and state the domain and range for each of the
inverse function.
b. Obtain (𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(𝑥). Hence, evaluate (𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(2).
SOLUTION
𝑓(𝑥) = (𝑥 − 2)2 + 1, 𝑥>2
𝑔(𝑥) = ln(𝑥 + 1), 𝑥 > 0.
(a) Let 𝑦 = 𝑓 −1 (𝑥)
𝑓(𝑦) = 𝑥
(𝑦 − 2)2 + 1 = 𝑥
(𝑦 − 2)2 = 𝑥 − 1
𝑦 − 2 = √𝑥 − 1
𝑦 = √𝑥 − 1 + 2
𝑓 −1 (𝑥) = √𝑥 − 1 + 2
Let 𝑦 = 𝑔−1 (𝑥)
𝑔(𝑦) = 𝑥
ln(𝑦 + 1) = 𝑥
𝑦 + 1 = 𝑒𝑥
𝑦 = 𝑒𝑥 − 1
𝑔−1 (𝑥) = 𝑒 𝑥 − 1
𝐷𝑓−1 : (1, ∞)
𝑅𝑓−1 : (2, ∞)
𝐷𝑔−1 : (0, ∞)
𝑅𝑔−1 : (0, ∞)
(b) (𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(𝑥)
𝑔[𝑓(𝑥)] = 𝑔[(𝑥 − 2)2 + 1]
= ln[[(𝑥 − 2)2 + 1] + 1]
= ln[(𝑥 − 2)2 + 2]
(𝑔 𝑜 𝑓)(2) = ln[(2 − 2)2 + 2]
= ln[2]
Chow Choon Wooi Page 14
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
1
9. Given the function 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥−5.
a. Find the domain and range of 𝑔(𝑥).
b. Show that 𝑔(𝑥) is a one-to-one function. Hence, find 𝑔−1 (𝑥).
c. On the same axis, sketch the graph of 𝑔(𝑥) and 𝑔−1 (𝑥).
d. Show that 𝑔 𝑜 𝑔−1 (𝑥) = 𝑥.
SOLUTION
1
𝑔(𝑥) =
2𝑥 − 5
(a) 𝐷𝑔 : 2𝑥 − 5 ≠ 0
5
𝑥≠
2
5 5
𝐷𝑔 : (−∞, ) ∪ ( , ∞)
2 2
𝑅𝑔 : (−∞, 0) ∪ (0, ∞)
1
(b) 𝑔(𝑥) = 2𝑥−5
1
𝑔(𝑥1 ) =
2𝑥1 − 5
1
𝑔(𝑥2 ) =
2𝑥2 − 5
Let 𝑔(𝑥1 ) = 𝑔(𝑥2 )
1 1
=
2𝑥1 − 5 2𝑥2 − 5
2𝑥1 − 5 = 2𝑥2 − 5
2𝑥1 = 2𝑥2
𝑥1 = 𝑥2
𝑆𝑖𝑛𝑐𝑒 𝑥1 = 𝑥2 𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝑔(𝑥1 ) = 𝑔(𝑥2 ), 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒𝑓𝑜𝑟𝑒 𝑔(𝑥) 𝑖𝑠 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑡𝑜 𝑜𝑛𝑒 𝑓𝑢𝑛𝑐𝑡𝑖𝑜𝑛.
Let 𝑦 = 𝑔−1 (𝑥)
𝑔(𝑦) = 𝑥
1
=𝑥
2𝑦 − 5
1
2𝑦 − 5 =
𝑥
1
2𝑦 = +5
𝑥
Chow Choon Wooi Page 15
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
1 + 5𝑥
2𝑦 =
𝑥
1 + 5𝑥
𝑦=
2𝑥
1 + 5𝑥
𝑔−1 (𝑥) =
2𝑥
(c)
𝑦=𝑥
𝑔−1 (𝑥)
𝑔(𝑥)
(d) 𝑔 𝑜 𝑔−1 (𝑥) = 𝑔[𝑔−1 (𝑥)]
1 + 5𝑥
= 𝑔[ ]
2𝑥
1
=
1 + 5𝑥
2 [ 2𝑥 ] − 5
1
=
1 + 5𝑥
[ 𝑥 ]−5
1
=
1 + 5𝑥 − 5𝑥
[ 𝑥 ]
1
=
1
[𝑥 ]
=𝑥
Chow Choon Wooi Page 16
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
10. Given the system of linear equations as follow:
2𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 𝑧 = 77
4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 7𝑧 = 114
2𝑥 + 𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 48
a. Express the system of equations in the form of matrix equation 𝐴𝑋 = 𝐵 where
𝑥
𝑥 = (𝑦). Hence, determine matrix 𝐴 and matrix 𝐵.
𝑧
b. Based on part 10(a), obtain |𝐴|.
Hence, find
i. |𝑃| if 𝑃𝐴 = 𝐼, where 𝐼 is an identity matrix 3 𝑥 3.
ii. |𝑄| if 𝑄 = (2𝐴)𝑇 .
iii. 𝐹𝑖𝑛𝑑 𝑎𝑑𝑗𝑜𝑖𝑛𝑡 𝐴.
Hence, obtain 𝐴−1 and find the values of 𝑥, 𝑦 𝑎𝑛𝑑 𝑧.
SOLUTION
2𝑥 + 4𝑦 + 𝑧 = 77
4𝑥 + 3𝑦 + 7𝑧 = 114
2𝑥 + 𝑦 + 3𝑧 = 48
(a)
2 4 1 𝑥 77
(4 3 𝑦
7) ( ) = (114)
2 1 3 𝑧 48
𝐴𝑋 = 𝐵
2 4 1 77
𝐴 = (4 3 7); 𝐵 = (114)
2 1 3 48
(b)
4 7
|𝐴| = +(2) |3 7
| − (4) | | + (1) |
4 3
|
1 3 2 3 2 1
= 2(9 − 7) − 4(12 − 14) + (4 − 6)
= 2(2) − 4(−2) + (−2)
= 10
Chow Choon Wooi Page 17
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
(i) 𝑃𝐴 = 𝐼
𝑃 = 𝐴−1 𝐼𝑓 𝐴𝐵 = 𝐼 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 𝐴 = 𝐵−1
|𝑃| = |𝐴−1 |
1 1
= |𝐴−1 | =
|𝐴| |𝐴|
1
=
10
(ii) 𝑄 = (2𝐴)𝑇 (𝑘𝐴)𝑇 = 𝑘𝐴𝑇
|𝑄| = |(2𝐴)𝑇 |
= 23 |𝐴𝑇 | 𝐼𝑓 𝐴 𝑖𝑠 𝑛 𝑥 𝑛 𝑚𝑎𝑡𝑟𝑖𝑥, 𝑡ℎ𝑒𝑛 |𝑘𝐴| = 𝑘 𝑛 |𝐴|
= 8|𝐴|
|𝐴|𝑇 = |𝐴|
= 8(10)
= 80
(iii) 𝑎𝑑𝑗 (𝐴) = 𝐶 𝑇
2 4 1
𝐴 = (4 3 7)
2 1 3
3 7 4 7 4 3
+| | −| | +| |
1 3 2 3 2 1
4 1 2 1 2 4
𝐶𝑜𝑓𝑎𝑐𝑡𝑜𝑟, 𝐶 = − | | +| | −| |
1 3 2 3 2 1
4 1 2 1 2 4
(+ |3 7
| −|
4 7
| +|
4 3)
|
2 2 −2
= (−11 4 6 )
25 −10 −10
𝑎𝑑𝑗 (𝐴) = 𝐶 𝑇
2 2 −2 𝑇
= (−11 4 6 )
25 −10 −10
2 −11 25
=( 2 4 −10)
−2 6 −10
1
𝐴−1 = 𝑎𝑑𝑗(𝐴)
|𝐴|
1 2 −11 25
= (2 4 −10)
10
−2 6 −10
Chow Choon Wooi Page 18
PSPM I QS015/1 Session 2017/2018
2 −11 25
10 10 10
2 4 −10
=
10 10 10
−2 6 −10
( 10 10 10 )
1 −11 5
5 10 2
1 2
= −1
5 5
−1 3
(5 −1)
5
𝐴𝑋 = 𝐵
𝐴−1 𝐴𝑋 = 𝐴−1 𝐵
𝐼𝑋 = 𝐴−1 𝐵
𝑋 = 𝐴−1 𝐵
1 −11 5
𝑥 5 10 2
1 2 77
(𝑦) = −1 (114 )
𝑧 5 5 48
−1 3
(5 −1 )
5
10
= (13)
5
∴ 𝑥 = 10, 𝑦 = 13, 𝑧 = 5
Chow Choon Wooi Page 19
You might also like
- QS 015/2 Matriculation Programme Examination Semester I Session 2016/2017Document28 pagesQS 015/2 Matriculation Programme Examination Semester I Session 2016/2017Attika zahira100% (1)
- 1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionDocument22 pages1718 QS015 - 2 SolutionVeshal RameshNo ratings yet
- National 2017 - SolutionsDocument5 pagesNational 2017 - SolutionsOfelia Aljade RamosNo ratings yet
- MATRICULATION PROGRAMME EXAMDocument22 pagesMATRICULATION PROGRAMME EXAMMuhd Azri SufiNo ratings yet
- Class 12 Modern, BK Question BankDocument2 pagesClass 12 Modern, BK Question Bankfilm boss ronitchawlaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsDocument89 pagesAnswer Key: All Problems (Q1-Q66) Except DerivationsAnish Anand kumar100% (1)
- Al 21 p2 RevisionDocument6 pagesAl 21 p2 RevisionSenuja ChammithaNo ratings yet
- P3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersDocument3 pagesP3 JAN 21 Revision Worksheet All ChaptersSheikh HassanNo ratings yet
- Paper I - EnglishDocument3 pagesPaper I - EnglishHarshanaNuwanNo ratings yet
- 2007 H2 MathsDocument33 pages2007 H2 MathsNicholas Teh100% (1)
- Class XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With SolutionDocument128 pagesClass XII Top 10 Sample Papers Mathematics With Solutionanushkabisht2006No ratings yet
- Algebra For Statistics ASSIGNMENT 1Document8 pagesAlgebra For Statistics ASSIGNMENT 1John ChiwaiNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Lesson 7 WorksheetDocument2 pagesUnit 1 Lesson 7 WorksheetIshai TepperNo ratings yet
- Corona Break Advanced p1 Exam 's-8011-1Document4 pagesCorona Break Advanced p1 Exam 's-8011-1nassorussi9No ratings yet
- 1516 QS015 - 1 SolutionDocument25 pages1516 QS015 - 1 SolutionVeshal RameshNo ratings yet
- Maths Mid Term MQP2-SolutionDocument14 pagesMaths Mid Term MQP2-Solutionvaishnav girish100% (6)
- II PU MATHS Three MARK QUESTIONS...Document5 pagesII PU MATHS Three MARK QUESTIONS...anjum6608No ratings yet
- Linear RegressionDocument4 pagesLinear RegressionDeadly ChillerNo ratings yet
- ACET December 2023 SolutionDocument10 pagesACET December 2023 Solutionomkarsutar9440No ratings yet
- MAT1100 Tutorial Sheet 4 - 2022Document3 pagesMAT1100 Tutorial Sheet 4 - 2022Nathan MulunguNo ratings yet
- AI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsDocument26 pagesAI AA SL Core Diagnostic Test Ch. 1 3-5 Suggested SolutionsAlexandr BostanNo ratings yet
- Challenging Questions v2 QDocument20 pagesChallenging Questions v2 QAdwin JY LowNo ratings yet
- s.5 Mid-Term 2 PureDocument3 pagess.5 Mid-Term 2 PurekelvinhunghanaNo ratings yet
- Chapter Two NewDocument56 pagesChapter Two NewDana S. Hama AminNo ratings yet
- Phase II Basic MathematicsDocument31 pagesPhase II Basic MathematicsSid PascuaNo ratings yet
- Paper III - EnglishDocument4 pagesPaper III - EnglishHarshanaNuwanNo ratings yet
- II Sem B.Sc. (NEP) Mathematics Lab Manual UOMDocument48 pagesII Sem B.Sc. (NEP) Mathematics Lab Manual UOMrakshajain287No ratings yet
- Topical Guidance of SPM MathematicsDocument39 pagesTopical Guidance of SPM MathematicsSEOW INN LEENo ratings yet
- General Instructions:: Part-A Has Objective Type Questions and Part - B Has Descriptive Type QuestionsDocument6 pagesGeneral Instructions:: Part-A Has Objective Type Questions and Part - B Has Descriptive Type QuestionsBhawesh Kumar SoniNo ratings yet
- Maths Mid Term MQP3-SolutionDocument14 pagesMaths Mid Term MQP3-Solutionvaishnav girish100% (1)
- W4 CH 1-4 Mixed QuestionsDocument6 pagesW4 CH 1-4 Mixed QuestionsJessicaNo ratings yet
- Preparation Paper 1 (X Maths)Document2 pagesPreparation Paper 1 (X Maths)Quirat RanaNo ratings yet
- 2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsDocument5 pages2018 Metrobank-MTAP-DepEd Math Challenge National Finals Grade 10 Individual Oral Competition QuestionsHarris Lee50% (2)
- Senior Secondary Set 4: Solved Problems in Logarithms, Functions and SeriesDocument14 pagesSenior Secondary Set 4: Solved Problems in Logarithms, Functions and Seriesf l u f f yNo ratings yet
- Adv Ex 16 InequalitiesDocument4 pagesAdv Ex 16 InequalitiesLeroy ChengNo ratings yet
- Quiz3 SolutionDocument3 pagesQuiz3 Solution張育安No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight LinesDocument17 pagesChapter 1 Linear Equations and Straight LinesGlendaNo ratings yet
- 2019-2-NS- ST. PAUL, SEREMBANDocument6 pages2019-2-NS- ST. PAUL, SEREMBANBryanLeeChienYungNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 12 Mathematics Sample Paper 1 0Document23 pagesCBSE Class 12 Mathematics Sample Paper 1 0vinay sharmaNo ratings yet
- Relations and Functions Power Point-1Document102 pagesRelations and Functions Power Point-1fmukuka12No ratings yet
- Matriculation Programme Examination Session 2018/2019Document21 pagesMatriculation Programme Examination Session 2018/2019.....No ratings yet
- Day-11: Section 13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal VectorsDocument13 pagesDay-11: Section 13.7 Tangent Planes and Normal VectorsFaizaNo ratings yet
- ACET January 2021 - SolutionDocument11 pagesACET January 2021 - SolutionMeghna GuptaNo ratings yet
- ACHIEVE 1 SolutionsDocument2 pagesACHIEVE 1 SolutionsLeviNo ratings yet
- cs23m511 Gur Prasad Srivastava Discrete Mathematics Assignment 8Document7 pagescs23m511 Gur Prasad Srivastava Discrete Mathematics Assignment 8Gur PrasadNo ratings yet
- 2016 Mmcgrade 10Document8 pages2016 Mmcgrade 10api-339611548100% (17)
- 2.4 Inverse of A FunctionDocument19 pages2.4 Inverse of A FunctionNot.DXcr GaMeRNo ratings yet
- HHWXII 202223 CommerceDocument9 pagesHHWXII 202223 CommerceParth BeriNo ratings yet
- 2020 Tutorial 3 MAT3611Document1 page2020 Tutorial 3 MAT3611Manex ManNo ratings yet
- 10 Set SQP Maths Puc I YearDocument33 pages10 Set SQP Maths Puc I YearSUSHAN POOJARY100% (1)
- 3.1 The Double Integral and Rectangular RegionsDocument8 pages3.1 The Double Integral and Rectangular Regionsshamarplummer0923No ratings yet
- Target-40 Maths XiiDocument9 pagesTarget-40 Maths XiiRohith SNo ratings yet
- Pre-University STPM Semester Two Trial Year 2019 Mathematics T (954/2Document8 pagesPre-University STPM Semester Two Trial Year 2019 Mathematics T (954/2Jean TanNo ratings yet
- Mathematics-I, SEM-I PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON ALL MODULES-3-4Document2 pagesMathematics-I, SEM-I PRACTICE QUESTIONS ON ALL MODULES-3-4aditya2189rdNo ratings yet
- Maths PUC I Year 3 Set Mid Term QPDocument6 pagesMaths PUC I Year 3 Set Mid Term QProblility23No ratings yet
- CBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Straight LinesDocument6 pagesCBSE Class 11 Mathematics Worksheet - Straight LinesEshita AgarwalNo ratings yet
- De Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankFrom EverandDe Moiver's Theorem (Trigonometry) Mathematics Question BankNo ratings yet
- Trigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsFrom EverandTrigonometric Ratios to Transformations (Trigonometry) Mathematics E-Book For Public ExamsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Philosophies of Education That Is Learner CenteredDocument5 pagesPhilosophies of Education That Is Learner CenteredPrincess zamora100% (1)
- Learning Activity Sheet 1Document1 pageLearning Activity Sheet 1Bernadeth Dusal GuiasilonNo ratings yet
- GembelDocument63 pagesGembelRobith MunadiNo ratings yet
- Business Communication Study MaterialDocument36 pagesBusiness Communication Study MaterialDr. Deepti SharmaNo ratings yet
- Adsorption Tank Specification SheetDocument16 pagesAdsorption Tank Specification SheetKristine AmbasNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Siap CetakDocument90 pagesAcademic Writing Siap CetakRetno OktavianiNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan Science 5Document9 pagesLesson Plan Science 5Marj Reña LunaNo ratings yet
- How To Make Jupiter StrongDocument6 pagesHow To Make Jupiter StrongSreenivasulu E NNo ratings yet
- Building Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project HopeDocument18 pagesBuilding Learning Commitment - Perdalin-Project Hopesusy kusumawardaniNo ratings yet
- Cualesreginaldray 12881 322722 CE52FB1-Group-7-2 PDFDocument408 pagesCualesreginaldray 12881 322722 CE52FB1-Group-7-2 PDFMæbēTh CuarterosNo ratings yet
- Hilario-Marvin S - FS1 - E-PortfolioDocument5 pagesHilario-Marvin S - FS1 - E-PortfolioMARVIN HILARIONo ratings yet
- Emma Warren-8Document6 pagesEmma Warren-8api-533666360No ratings yet
- CHAPTER 1 - Giving SuggestionDocument2 pagesCHAPTER 1 - Giving SuggestionRika Rahayu Ningsih100% (1)
- Data Science: What Is Data Science and Who Is Data ScientistDocument26 pagesData Science: What Is Data Science and Who Is Data ScientistZaib KhanNo ratings yet
- IELTStask1 LineDocument3 pagesIELTStask1 LineTrần Nguyễn Thủy Chi (FGW DN)No ratings yet
- CV Suvam 13 05 2023 PDFDocument2 pagesCV Suvam 13 05 2023 PDFSuvam SwainNo ratings yet
- Europass Curriculum Vitae: Updated January 4, 2021Document4 pagesEuropass Curriculum Vitae: Updated January 4, 2021Сарангэрэл БNo ratings yet
- The Self and Its Brain: University of California, Santa BarbaraDocument45 pagesThe Self and Its Brain: University of California, Santa BarbaraAlexander S. Aliaga TarazonaNo ratings yet
- Point/Liquid Level Switch Measurement SystemsDocument6 pagesPoint/Liquid Level Switch Measurement SystemsJustin Paul CongeNo ratings yet
- Essay Animalsrights Books&musicDocument3 pagesEssay Animalsrights Books&musicQuick FactsNo ratings yet
- Charts The Chart WizardDocument7 pagesCharts The Chart WizardFaishal HummamNo ratings yet
- The 8 Models of CommunicationDocument4 pagesThe 8 Models of CommunicationEd Ali L. Magondacan100% (1)
- Chemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14Document13 pagesChemfile Mini-Guide To Problem Solving Chapter 14MANDARAW100% (1)
- Differences Between Solids and FluidsDocument4 pagesDifferences Between Solids and FluidsgknindrasenanNo ratings yet
- Seismic Hazard Modelling For Malaysia 2017Document24 pagesSeismic Hazard Modelling For Malaysia 2017Zeric TengNo ratings yet
- B Som and FM Lab ManualDocument101 pagesB Som and FM Lab ManualGANESH GOMATHINo ratings yet
- TRIALOG 106 FreeDownloadDocument64 pagesTRIALOG 106 FreeDownloadAmos Pangihutan SNo ratings yet
- 1801-Article Text-7307-1-10-20220201Document10 pages1801-Article Text-7307-1-10-20220201LEO LESTERE TAO TAONo ratings yet
- Sweden's Leadership on Climate ActionDocument9 pagesSweden's Leadership on Climate ActionSandra ZeidanNo ratings yet
- g11 PSC p2 Jun 2019 and MemoDocument20 pagesg11 PSC p2 Jun 2019 and MemoKholofelo SebakeNo ratings yet