Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Basic Life Support (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) : Respiratory Cardiac Arrest
Uploaded by
steve jaymeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Basic Life Support (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation) : Respiratory Cardiac Arrest
Uploaded by
steve jaymeCopyright:
Available Formats
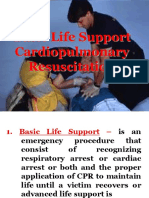
BASIC LIFE SUPPORT (CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION)
Basic Life Support - an emergency procedure that consists of recognizing respiratory or cardiac arrest or both Formatted: Font color: Yellow
and the proper application of CPR to maintain life until a victim recovers or advanced life support is available. Formatted: Font color: Yellow
Sudden Cardiac Arrest
o Can happen at any time, to anyone, anywhere without warning;
o Most common mode of death in patients with coronary artery disease;
o Although pre-existing heart disease is a common cause, it may strike people with no history of cardiac
disease or cardiac symptoms;
o In sudden cardiac arrest or sudden cardiac death, the heart usually goes into a fatal arrhythmia called
“Ventricular Fibrillation”
Objectives:
● Preserve Life
● Prevent Further harm and Complications
● Seek Immediate Medical Help
● Provide Reassurance
Heart attack - occurs when the blood and oxygen supply to the heart is reduced causing damage to the
heart muscle and preventing blood from circulating effectively.
First Aid Management
✓ Call the local emergency number immediately.
✓ Have the person stop what he or she is doing and rest comfortably.
✓ Loosen any tight or uncomfortable clothing.
✓ Closely watch the person until advanced medical personnel take over.
✓ Be prepared to perform CPR and use an AED, if available, once the person loses consciousness and
stops breathing.
✓ Ask the person if he or she has a history of heart disease.
✓ Offer aspirin if it is prescribed by his/her physician for his/her condition and only if he patient can
swallow.
✓ Be calm and reassuring.
✓ Talk to bystanders and if to possible the person to get more information.
✓ Do not try to drive the person to the hospital yourself.
Cardiac arrest
Occurs when the heart stops beating or beats too ineffectively to circulate blood to the brain and other vital
organs.
CPR- is a combination of chest compressions and rescue breaths.
Chest Compression Only (Hands-Only CPR)
Continue giving chest compressions until EMS personnel take over or you notice an obvious sign of life, such
as breathing.
When to Stop CPR
Spontaneous signs of breathing and circulation
Turned over to professional provider
Operator is exhausted
Physician assumes responsibility
Basic Life Support (CPR) Table of Comparison
Action Adult (13 yrs & above Child (1-12 yrs old) Infant (under 1 yrs old)
Compression Area Center of the chest
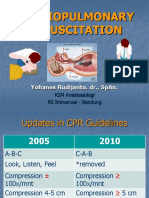
Depth At least 2 inches 5 cm At least 2 inches 5 cm 1 ½ inches 4 cm
How to compress Heels of 2 hands Heel of 1 or 2 hands 2 fingertips
Compression to 30:2 (1 or 2 rescuers) 30:2 (for 1 rescuer)
Ventilation Ratio 15:2 (for 2 rescuers)
Ventilation Until the chest clearly rise
Number of Cycle 5 Cycles (1 or 2 5 Cycles for 1 rescuer
per 2 minutes rescuers) 10 Cycles for 2 rescuers
Opening of Airway Maximum head tilt- Neutral plus position Neutral position
chin-lift
Ways to Ventilate Mouth to Mouth or Mouth to Mouth or Mouth to Mouth and
the lungs Mouth to Nose Mouth to Nose Nose
Protective equipment to ventilate:
Face Shield; Face Mask and Bag Valve Mask (BVM)
Breaths Normal breath (1 second per breath) enough to make the patient’s chest rise
Rate 24 breaths for 4o breaths for 2 minutes
2 minutes (1 breath every 3 seconds)
(1 breath every 5
seconds)
FOREIGN BODY AIRWAY OBSTRUCTION MANAGEMENT
Emergency Care for Conscious Adult/Child
➢ 5 Back blows (Back slap) and 5 Abdominal Thrust (Chest Thrust)
➢ 5 Back blows and 5 chest thrust (Infant)
Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)
➢ Check the Scene (Determine if it’s a witnessed cardiac arrest)
➢ Check Responsiveness (Tap and Shout, “Are you Okay?”)
➢ If no response, have someone Activate Medical Assistance or the Local Emergency Number and get an
AED
➢ Responding with Normal Breathing Monitor and Place to Recovery Position
➢ If no breathing & pulse, perform 30 Compressions and 2 Rescue Breaths
➢ (1 or 2 rescuer CPR) for 5 cycles (2mins) and
➢ Attach AED once available
➢ Re-assess for breathing no more than 10secs. If still no breathing, continue CPR. If AED is used follow
AED prompt. If revive place on recovery position or endorsed patient when professional responders arrive
Foreign Body Airway Obstruction Management (FBAO) Conscious Victim
➢ Universal Sign of Choking
o Ask are you “OK?”
o “Can you cough?”
o “Can you speak?”
o Can you breathe?”
➢ If can cough; speak; or breathe: Encourage coughing forcefully
➢ Confirm if person is choking
➢ Note: If obvious pregnant or known to be pregnant; or an infant (under age of 1) or obese, give chest
thrust.
➢ Have someone Activate Medical Assistance or the Local Emergency Number and get an AED
➢ Obtain consent
➢ Airway clear: monitor until HELP arrives
➢ Give 5 back blows
➢ If still choking
➢ Airway clear: monitor until HELP arrives
➢ Give 5 abdominal/chest thrust
➢ Still choking repeat process 5 back blows & abdominal/chest thrust
➢ If unconscious perform a modified CPR (follow CPR Algorithm)
➢ Until object is expelled or become unconscious
Rescue Breathing
➢ Check the Scene (Determine if it’s a respiratory arrest)
➢ Check Responsiveness (Tap and Shout, “Are you Okay?”)
➢ Responding with Normal Breathing
➢ Monitor and Place to Recovery Position
➢ If no response, have someone Activate Medical Help or the Local Emergency Number and get an AED
➢ Quick check for airway (head tilt-chin lift), normal breathing or no breathing (look, listen & feel) and
Pulse (carotid or brachial) no more than 10secs.
➢ If no breathing but with pulse, perform 24 breaths for adult/child and 40 breaths for infant in
2minutes
➢ Re-assess for breathing and pulse no more than 10secs. If still no breathing, continue CPR. If AED is
used follow AED prompt. If revive place on recovery position or endorsed patient when professional
responders arrives
You might also like
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandPediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- BASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPRDocument28 pagesBASIC LIFE SUPPORT CPRaefgNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- CPR For ChildDocument19 pagesCPR For Childicuanak anakicuNo ratings yet
- BLSDocument45 pagesBLSgemergencycareNo ratings yet
- BlsDocument75 pagesBlsgemergencycareNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument38 pagesCardiopulmonary ResuscitationAgus SyaifudinNo ratings yet
- Bls - Fbao - First AidDocument172 pagesBls - Fbao - First AidMaria Regina Castro Gabriel100% (1)
- Basic Life SuppDocument46 pagesBasic Life SuppDiana Garcia SaclutiNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support - American Heart Association: WilliamDocument6 pagesBasic Life Support - American Heart Association: WilliamAbel C. Idusma Jr.No ratings yet
- Basic Life Support For Healthcare Providers (BLS) : Presented By: Youssef Youssef RT Respiratory Therapy DepartementDocument43 pagesBasic Life Support For Healthcare Providers (BLS) : Presented By: Youssef Youssef RT Respiratory Therapy Departementkurt94764No ratings yet
- BLS Kursus KguDocument82 pagesBLS Kursus KgujohnachyeonNo ratings yet
- CPR For AdultsDocument1 pageCPR For Adultsevelyn kNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Basic and Advanced Cardiac Life SupportDocument26 pagesPediatric Basic and Advanced Cardiac Life SupportZoe Jeanne GarcianoNo ratings yet
- BLS Algorithms and Training 2020Document22 pagesBLS Algorithms and Training 2020Ronald Aranha100% (1)
- Basic Life Support CPRDocument44 pagesBasic Life Support CPRJasmin KulanićNo ratings yet
- BLS Algorithms and Training 2019: (Basic Life Support)Document21 pagesBLS Algorithms and Training 2019: (Basic Life Support)Haidir MuhammadNo ratings yet
- PROTOCOLS For MANAGEMENT OF MEDICAL AND SURGICAL EMERGENCIES For WORKSHOP HOSPITALDocument7 pagesPROTOCOLS For MANAGEMENT OF MEDICAL AND SURGICAL EMERGENCIES For WORKSHOP HOSPITALSubhashish DasNo ratings yet
- First Aid Essentials for Life Saving (39Document64 pagesFirst Aid Essentials for Life Saving (39KBDNo ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument25 pagesBasic Life Supportguido pirelaNo ratings yet
- Dart BLS CPR With AEDDocument27 pagesDart BLS CPR With AEDLucas WangNo ratings yet
- C.P.R. (1)Document19 pagesC.P.R. (1)sxm2901No ratings yet
- Dart Bls CPR With Aed 2018 1Document33 pagesDart Bls CPR With Aed 2018 1NivekNo ratings yet
- CPR Guide for Adults, Children & BabiesDocument6 pagesCPR Guide for Adults, Children & Babiesrupali gahalian100% (2)
- Hands Only CPRDocument17 pagesHands Only CPRLee Arven DiwaNo ratings yet
- CPR Consist of 4 Main Parts Which AreDocument6 pagesCPR Consist of 4 Main Parts Which Arematgar100% (3)
- Basic Life Support Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument37 pagesBasic Life Support Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationRoma Vey LaagNo ratings yet
- CPR ReportingDocument39 pagesCPR ReportingNheler SonNo ratings yet
- BLS Algorithms and Training 2018Document14 pagesBLS Algorithms and Training 2018AndyNo ratings yet
- 1 Principles of First Aid and Its PracticeDocument118 pages1 Principles of First Aid and Its PracticeMohamed SamyNo ratings yet
- Cardio resuscitationDocument38 pagesCardio resuscitationBhakti WashilkarNo ratings yet
- Basic Life Support Lecture PresentationDocument38 pagesBasic Life Support Lecture PresentationAlsaud BansilNo ratings yet
- Dr. Kunal Jhaveri (MD)Document42 pagesDr. Kunal Jhaveri (MD)Bhaskar Äðítýæ Phatak100% (1)
- CPR and First Aid Guidelines: Presentation Prepared By: Randy G. Tabaog, LPT AMA Computer College Santiago CampusDocument24 pagesCPR and First Aid Guidelines: Presentation Prepared By: Randy G. Tabaog, LPT AMA Computer College Santiago CampussunshineNo ratings yet
- BLS2 ConferenceDocument39 pagesBLS2 Conferencekurt94764No ratings yet
- Basic Life SupportDocument27 pagesBasic Life SupportPisay Shehannah Grail Medina100% (1)
- Emed - BLS - FBAO - First Aid Part 1Document85 pagesEmed - BLS - FBAO - First Aid Part 1Princess Cate MercadoNo ratings yet
- Basic LifeDocument33 pagesBasic LifetmschppmNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 8.2-3 Making Decisions Under Pressure - Part 3Document79 pagesInformation Sheet 8.2-3 Making Decisions Under Pressure - Part 3Angel VillaruelNo ratings yet
- Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Yohanes Rudijanto, DR., SpanDocument63 pagesCardiopulmonary Resuscitation: Yohanes Rudijanto, DR., SpanPadrepio R RahadiNo ratings yet
- CPR Presentation - EnglishDocument31 pagesCPR Presentation - EnglishveroNo ratings yet
- CPR PresentationDocument22 pagesCPR PresentationAlan HabalNo ratings yet
- Learn Basic Life Support with this BLS Course OverviewDocument33 pagesLearn Basic Life Support with this BLS Course OverviewJoshi Thomas John JikkuNo ratings yet
- Importance of CPRDocument6 pagesImportance of CPRKatherine Canisguin AlvarecoNo ratings yet
- Cardio Pulmonary ResuscitationDocument42 pagesCardio Pulmonary ResuscitationDennis Nabor Muñoz, RN,RMNo ratings yet
- BLS Skills Lab For SimulationDocument116 pagesBLS Skills Lab For Simulationczeremar chan100% (1)
- Cardio Pulmonary ResuscitationDocument34 pagesCardio Pulmonary Resuscitationanimesh pandaNo ratings yet
- Prof - Dr. Ruswan Dachlan, SP An KIC Dept - of Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care FKUIDocument71 pagesProf - Dr. Ruswan Dachlan, SP An KIC Dept - of Anaesthesiology & Intensive Care FKUIFerdy ErawanNo ratings yet
- First Aid (CPR AND CHOKING)Document29 pagesFirst Aid (CPR AND CHOKING)kula diamondNo ratings yet
- CPR Hey Sir Hey SirDocument9 pagesCPR Hey Sir Hey SirMiguel AbaradoNo ratings yet
- BLS Ahmad Hafiz 01Document31 pagesBLS Ahmad Hafiz 01Fahad MahmoodNo ratings yet
- Introduction To First Aid & Basic Life SupportDocument34 pagesIntroduction To First Aid & Basic Life SupportRO Chiel Kjskjs100% (1)
- CPRDocument23 pagesCPRJoanne CareahNo ratings yet
- BLS BasicsDocument24 pagesBLS BasicsaruNo ratings yet
- BLS FinalDocument47 pagesBLS Finalshouvik chowdhury100% (1)
- Cardiac Arrest & Cardiopulmonary ResuscitationDocument40 pagesCardiac Arrest & Cardiopulmonary Resuscitationjoms_pasanoNo ratings yet
- CPR ALS ProcedureDocument10 pagesCPR ALS ProcedureTanmoyNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Document18 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation (CPR)Savita HanamsagarNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Sebastian ValceaDocument16 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: Dr. Sebastian ValceaAna MariaNo ratings yet
- Iap Cprday PptDocument33 pagesIap Cprday PptRabi KumarNo ratings yet
- Republic Act 9184 Government Procurement Act Article I General ProvisionsDocument21 pagesRepublic Act 9184 Government Procurement Act Article I General Provisionssteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- Column No.1 Design Results GearDocument3 pagesColumn No.1 Design Results Gearsteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- Chapter IDocument8 pagesChapter Isteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- Flood Control Using Floodgate and Reservoir at Tipolo Creek in Mandaue CityDocument5 pagesFlood Control Using Floodgate and Reservoir at Tipolo Creek in Mandaue Citysteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- Column No.1 Design Results GearDocument3 pagesColumn No.1 Design Results Gearsteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- Seismic Design ConsiderationsDocument5 pagesSeismic Design ConsiderationserleosNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument2 pagesEarthquakesteve jaymeNo ratings yet
- ETHICSDocument18 pagesETHICSMichelle MunozNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety ManagementDocument2 pagesNEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety ManagementHashem RezayiNo ratings yet
- COVID-19 Vaccine Arrives in IndonesiaDocument3 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Arrives in Indonesiawawan budiantoNo ratings yet
- What Is AmpalayaDocument5 pagesWhat Is Ampalayarugu0% (1)
- Vaishali Bujad Project..2Document54 pagesVaishali Bujad Project..2Mitesh Prajapati 7765No ratings yet
- Pathology MBBSDocument12 pagesPathology MBBSDinah Penserga100% (1)
- Approaches To The Diagnosis of Portal HipertensionDocument12 pagesApproaches To The Diagnosis of Portal HipertensionValentina IorgaNo ratings yet
- NO Nama Pasien Tanggal Rujukan/Tujuan RsDocument44 pagesNO Nama Pasien Tanggal Rujukan/Tujuan RsfennyNo ratings yet
- 23 Nov 2022Document1 page23 Nov 2022Tahir ShahNo ratings yet
- 4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CareDocument8 pages4 Coercion in Mental Healthcare The Principle of Least Coercive CarePedro Y. LuyoNo ratings yet
- Indian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuDocument4 pagesIndian Herbs For Healthy Body - Healing Properties of Adalodakam, Arogya Pacha, Ashokam, IrattimadhuNEELNo ratings yet
- Pre-Test Hope 2Document4 pagesPre-Test Hope 2Jodel GombaNo ratings yet
- PHARMACOLOGY PrelimDocument26 pagesPHARMACOLOGY PrelimCrystal MiranaNo ratings yet
- Please Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceDocument2 pagesPlease Quote This Reference Number in All Future CorrespondenceSaipraveen PerumallaNo ratings yet
- CureDocument338 pagesCureThiago Cavalli Azambuja100% (1)
- NCM104-FNCP ColladoDocument3 pagesNCM104-FNCP ColladoProplays ytNo ratings yet
- Republika NG PilipinasDocument2 pagesRepublika NG PilipinasAcii monseNo ratings yet
- Mammograms and Other Breast Imaging Procedures: What Is A Mammogram?Document25 pagesMammograms and Other Breast Imaging Procedures: What Is A Mammogram?Marina StosicNo ratings yet
- Maternity and Newborn MedicationDocument34 pagesMaternity and Newborn MedicationNicholas ClaytonNo ratings yet
- Body Mass IndexDocument3 pagesBody Mass IndexSunnyVermaNo ratings yet
- Iringan (1st Activity PHED 112)Document2 pagesIringan (1st Activity PHED 112)Juliezel IringanNo ratings yet
- Letter of Intent (LOI) TemplateDocument1 pageLetter of Intent (LOI) Templatesmvhora100% (1)
- Neurorobotics Presentation 3Document8 pagesNeurorobotics Presentation 3Hamza MinhasNo ratings yet
- Food PoisoningDocument24 pagesFood PoisoningSena AjahNo ratings yet
- What Is Healing?Document33 pagesWhat Is Healing?Chef Jem100% (1)
- BSBWHS401 - Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative RequirementsDocument11 pagesBSBWHS401 - Implement and Monitor WHS Policies, Procedures and Programs To Meet Legislative RequirementsPattaniya KosayothinNo ratings yet
- Nursing Licensure Exam Compilation of TipsDocument3 pagesNursing Licensure Exam Compilation of TipsIkarishinNo ratings yet
- Pamti Who Wipo WtoDocument262 pagesPamti Who Wipo WtoJorge Antonio CENo ratings yet
- Misty Williams How Are You Wired To Sleep UpdatedDocument21 pagesMisty Williams How Are You Wired To Sleep UpdatedCarolyn McClendonNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (GBS)Document16 pagesDrug Study (GBS)Mary Rose Verzosa LuisNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (402)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (13)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- Roxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingFrom EverandRoxane Gay & Everand Originals: My Year of Psychedelics: Lessons on Better LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (33)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: It Didn't Start with You: How Inherited Family Trauma Shapes Who We Are and How to End the Cycle By Mark Wolynn: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (3)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)
- The Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsFrom EverandThe Garden Within: Where the War with Your Emotions Ends and Your Most Powerful Life BeginsNo ratings yet
- The Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossFrom EverandThe Tennis Partner: A Doctor's Story of Friendship and LossRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)