Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Analysis and Design of Flat Slabs
Uploaded by
fish0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views49 pagesThe document discusses the analysis and design of flat slab structures. It begins with an introduction to flat slabs, which are slabs supported directly by columns without beams. The main methods of analysis covered are the simplified direct method and equivalent frame method. The simplified direct method divides the slab into column and middle strips. Design considerations include bending moments, shear forces, punching shear capacity and reinforcement details. An example problem demonstrates the full design process.
Original Description:
class note for structural design
Original Title
RCII CH2 PPT
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document discusses the analysis and design of flat slab structures. It begins with an introduction to flat slabs, which are slabs supported directly by columns without beams. The main methods of analysis covered are the simplified direct method and equivalent frame method. The simplified direct method divides the slab into column and middle strips. Design considerations include bending moments, shear forces, punching shear capacity and reinforcement details. An example problem demonstrates the full design process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
18 views49 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flat Slabs
Uploaded by
fishThe document discusses the analysis and design of flat slab structures. It begins with an introduction to flat slabs, which are slabs supported directly by columns without beams. The main methods of analysis covered are the simplified direct method and equivalent frame method. The simplified direct method divides the slab into column and middle strips. Design considerations include bending moments, shear forces, punching shear capacity and reinforcement details. An example problem demonstrates the full design process.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 49
REINFOERCED CONCRETE
STRUCTURES II (Ceng 3112)
Lecture II
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g)
1
Chapter Two
Analysis & Design of Flat Slab
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 2
1.Introduction
Types of slab:
One way Slab Two way slab
Ribbed slab Waffle Type
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 3
Introduction,…,Cont’d
What is Flat slab ?
Slab supported directly by concrete columns without
the use of beams.
Thickness is less than thickness of one way slab but
greater than that of two way slab
To increase the shear strength of the slab around the
column supports
The slab thickness in the area of the column may be
thickened as a drop panel
The column may also be flared to form a column head
or capital.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 4
Introduction,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 5
Introduction,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 6
Introduction,…,Cont’d
Flat slabs with drop panel and column head are suitable for
spans up to 9 m and LL > 5.0 KN/m2
Advantage of flat slab
Simplified form work
Reduced story height
No obstruction of light & circulation of air due to beams.
Shorter construction time
Dis-advantage of flat slab
Reinforcement arrangement is complex
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 7
Introduction,…,Cont’d
Effective diameter of a column on a column head (hc) is
defined as the diameter of a circle whose area equals
the cross-sectional area of the column:
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 8
Introduction,…,Cont’d
Statical moment Mo:
Sum of positive and average negative moments
wL2 2h
Mo [ L1 c ]2
8 3
Where, w - Design load (gd+qd)
L1 - length of slab b/n centers of columns.
L2 – width of slab b/n centers of columns.
hc – effective diameter of column or column head.
hc < Lx/4 , where Lx - shorter span of slab
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 9
Method of analysis:
1) Finite element analysis( by SAFE, ADAPT, etc.)
2) Simplified direct method
3) Equivalent frame method
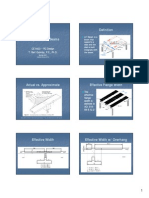
1.Simplified direct method
The panel in flat slab is divided into column strip and middle strip
as shown below.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 10
Simplified direct Method
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 11
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
A column strip
Serves the purpose of a beam spanning between columns
and deflects as continuous beam
Width on each side of a column centerline=0.25Lx
If drops with dimensions not less than LX/3 are
used, a width equal to the drop dimension
Middle strip
Strip bounded by two column strips
Drop panels :rectangular, square or circular
The smaller dimension of the drop is LX/3
The drop may be 25 to 50% more thicker than
the rest of the slab i.e. (td =1.25 ts to 1.5 ts )
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 12
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
Limitations:
Design is based on the single load case of all spans loaded with
the maximum design ultimate load.
There are at least three rows of panels of approximately equal
span in the direction being considered.
Successive span length in each direction shall not differ by more
than one-third of the longer span.
Maximum offsets of columns from either axis between center
lines of successive columns shall not exceed 10% of the span (in
the direction of the offset).
Panels should be rectangular and the ratio of the longer span to
shorter span should not be greater than 2.0
The design live load should not exceed two times the design
dead load.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 13
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
Bending Moment and Shear Force Coefficients
Outer support Near First Center of Interior
Center of Interior interior support
first span support span
Column Wall
Moment -0.040FL -0.020FL 0.083FL -0.063FL 0.071FL -0.055FL
Shear 0.45F 0.40F - 0.60F - 0.50F
Total 0.040FL - - 0.022FL - 0.022FL
column
moments
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 14
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
Division of Moments between Strips
Distribution between column and middle strip
Column strip (%) Middle strip (%)
Negative 75 25
Positive 55 45
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 15
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
Example: Moment division
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 16
Simplified direct Method,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 17
Equivalent frame (Approximate) Method
The bending moments and shear forces may be
determined by dividing the structure longitudinally and
transversely into frames consisting of column and strips
of slabs.
The frames of slab used to define the effective
stiffness of the slab.
For vertical loading assume full width of panel between
columns for frame analysis.
For lateral loading, as a frame of half width of panel
Loading Ratio of LL/DL < 1.25
LL ≤ 5 kN/m2
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 18
Equivalent frame Method,…,Cont’d
During analysis maximum
design load on all spans
may be only considered
Each frame is analyzed using
any elastic method.
Moment distribution
Kani’s method,
Matrix method etc.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 19
Design of flat slab for punching shear
Occur due to large concentrated loads around column-slab
interface.
Thus, for punching shear, the average shear stress
becomes:
υ = V/udav
Where u = length of the critical perimeter
dav = average of the two effective depths.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 20
Punching shear,…,Cont’d
Critical shear perimeter
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 21
Punching shear,…,Cont’d
The shear strength, υc, for members subjected to
punching, is calculated differently
υc = 0.25fctdk1k2udav
Where k1 1 50 e 2.0
k 2 1.6 d 1.0
d av d x d y 2
e ey 0.015
1
2
ex
When applied punching shear force is eccentric to loaded
area multiplication of the applied force, Vsd , by a factor β
is taken. When no eccentricity of loading is possible, β =1.
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 22
Punching shear,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 23
Detail of reinforcement
2/3Ast required to resist Mneg in the column strip
shall be placed in a width equal to half that of the
column strip.
Column Strip
Half Column strip
1/6 Ast 2/3 Ast 1/6 Ast
Center line of column
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 24
Bend and extension for reinforcement
ln: clear span
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 25
Flat slab reinforcement under construction
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 26
Design example
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 27
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 28
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 29
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 30
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 31
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 32
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 33
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 34
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 35
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 36
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 37
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 38
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 39
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 40
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 41
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 42
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 43
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 44
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 45
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 46
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 47
Design example,…,Cont’d
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 48
The End
By: Chimdi G.(M.Sc in Structural. Eng.g) 49
You might also like
- Analysis and Design of Flat Slab and Grid Slab and Their Cost ComparisonDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flat Slab and Grid Slab and Their Cost ComparisonjonnypremNo ratings yet
- RC2 MeDocument11 pagesRC2 MeZelalem AberaNo ratings yet
- 4.3 Moment Magnification PDFDocument13 pages4.3 Moment Magnification PDFChetan ChaudhariNo ratings yet
- 5 6332349680705339984Document124 pages5 6332349680705339984gaurav mandkeNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of Flat Slab and Grid Slab and Their Cost ComparisonDocument5 pagesAnalysis and Design of Flat Slab and Grid Slab and Their Cost ComparisonNAUTILUS87No ratings yet
- 01.structural Analysis Question (Qwah)Document26 pages01.structural Analysis Question (Qwah)linkesh balajeeNo ratings yet
- PPSC Test Questions - Civil Engineers PKDocument5 pagesPPSC Test Questions - Civil Engineers PKali akmalNo ratings yet
- Direct Design MethodDocument90 pagesDirect Design Methodborja familyNo ratings yet
- Tensile Strength of Good Quality BricksDocument21 pagesTensile Strength of Good Quality BricksFiaz Gujjar100% (1)
- Lecture 4 (EC4 Version)Document67 pagesLecture 4 (EC4 Version)ikanyu79100% (1)
- ACI 318M-11 Training by Prof. David Darwin PDFDocument371 pagesACI 318M-11 Training by Prof. David Darwin PDFwisnusantari100% (1)
- Q.no 1. The Maximum Ratio of Span To Depth of A Slab Simply Supported and Spanning in Two Directions, IsDocument145 pagesQ.no 1. The Maximum Ratio of Span To Depth of A Slab Simply Supported and Spanning in Two Directions, IsNitin kolheNo ratings yet
- Balanced Cantilever BridgeDocument4 pagesBalanced Cantilever Bridgesushant metriNo ratings yet
- Bracing of Steel-Concrete Composite Bridges During Deck CastingDocument12 pagesBracing of Steel-Concrete Composite Bridges During Deck Castingparvaneh.eNo ratings yet
- RCC Structures Design 8lcb64Document47 pagesRCC Structures Design 8lcb64Paul Jefferson PamaniNo ratings yet
- Design of Triangular Reinforced Concrete Beam in Usd: March 2011Document10 pagesDesign of Triangular Reinforced Concrete Beam in Usd: March 2011Husen GhoriNo ratings yet
- Concrete Column PresentationDocument14 pagesConcrete Column PresentationkabirNo ratings yet
- Shear Area of Reinforced Circular Concrete MembersDocument7 pagesShear Area of Reinforced Circular Concrete MemberstrabajosicNo ratings yet
- One Way Slab DesignDocument19 pagesOne Way Slab DesignMandar NadgaundiNo ratings yet
- Design Example of Reinforce Concrete BeamsDocument60 pagesDesign Example of Reinforce Concrete BeamsMario FrankistaNo ratings yet
- Tension Member 19.3.2023Document85 pagesTension Member 19.3.2023Akib IslamNo ratings yet
- OPSC 2015 Civil Engineering Paper 1 Answer KeyDocument17 pagesOPSC 2015 Civil Engineering Paper 1 Answer Keysmishra2222100% (1)
- Flat Slab GuideDocument3 pagesFlat Slab GuideAMAN FREDYNo ratings yet
- Analysis and Design of A Multi-Storey Reinforced ConcreteDocument61 pagesAnalysis and Design of A Multi-Storey Reinforced Concretenour94% (18)
- Shear Design of RC SectionsDocument18 pagesShear Design of RC SectionsMeor Asyraf Rostam AffandiNo ratings yet
- Steel - 04-Prof. Zahid Siddiqi PDFDocument57 pagesSteel - 04-Prof. Zahid Siddiqi PDFMuhammad AhmedNo ratings yet
- WSM PDFDocument17 pagesWSM PDFSathish SelvaNo ratings yet
- Reinforced Cement Concrete QuestionsDocument6 pagesReinforced Cement Concrete QuestionsArmaan Gupta89% (9)
- ME364 Forming SheetDocument11 pagesME364 Forming SheetVed Prakash ChoudharyNo ratings yet
- CE 4014 Design of Concrete Structures (Bond, Anchorage and Development Length) Part (IDocument31 pagesCE 4014 Design of Concrete Structures (Bond, Anchorage and Development Length) Part (IAbu ZaforNo ratings yet
- Shear Strength Model of Reinforced Concrete Circular Cross-Section MembersDocument6 pagesShear Strength Model of Reinforced Concrete Circular Cross-Section Membersswathi1717No ratings yet
- CE A433 CE A433 - RC Design RC Design T. Bart Quimby, P.E., Ph.D. T. Bart Quimby, P.E., PH.DDocument3 pagesCE A433 CE A433 - RC Design RC Design T. Bart Quimby, P.E., Ph.D. T. Bart Quimby, P.E., PH.DSeifeldin Ali MarzoukNo ratings yet
- (Mate) DCS-2 MCQ W AnsDocument53 pages(Mate) DCS-2 MCQ W AnsAhmad QureshiNo ratings yet
- RC 1 MeDocument20 pagesRC 1 MeZelalem AberaNo ratings yet
- IIT Hyderabad Faculty Housing Design CalculationsDocument33 pagesIIT Hyderabad Faculty Housing Design CalculationssmijusNo ratings yet
- Design of Reinforced Concrete ColumnsDocument25 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Columnsmedodo100% (1)
- Chapter 2: Design For Shear and TorsionDocument51 pagesChapter 2: Design For Shear and TorsionMunther MohdNo ratings yet
- Design of RCC T - Girder Deck Using Morice & Little MethodDocument33 pagesDesign of RCC T - Girder Deck Using Morice & Little Methodvasu7900100% (4)
- Flat Slabs - Analysis, Design and 2003Document45 pagesFlat Slabs - Analysis, Design and 2003kiran mNo ratings yet
- AP PGECET Civil Engg 2015 Question Paper & Answer Key DownloadDocument16 pagesAP PGECET Civil Engg 2015 Question Paper & Answer Key Downloadpavani83% (6)
- Reinforced concrete design of two-way slabsDocument8 pagesReinforced concrete design of two-way slabsBehairy AhmedNo ratings yet
- Design Load Combinations for Eurocode 2Document24 pagesDesign Load Combinations for Eurocode 2Tai Pham100% (1)
- Design of Reinforced Concrete Columns PDFDocument26 pagesDesign of Reinforced Concrete Columns PDFMa Gh100% (1)
- Formulae: Two-Way Shear With Negligible Moment TransferDocument7 pagesFormulae: Two-Way Shear With Negligible Moment TransferKory EstesNo ratings yet
- RCC Structures DesignDocument10 pagesRCC Structures DesignmsafdarNo ratings yet
- RCCDocument46 pagesRCCNareshNo ratings yet
- Methodology: Soil Lateral LoadDocument10 pagesMethodology: Soil Lateral LoadAllyssa OpantoNo ratings yet
- Etapa IIGrinda PrincipalaDocument7 pagesEtapa IIGrinda PrincipalaMacovei AlinNo ratings yet
- Lateral Support For Tier Building FramesDocument4 pagesLateral Support For Tier Building Framesuhu_plus6482No ratings yet
- RBC Note New ReducedDocument43 pagesRBC Note New Reducedindraupa94No ratings yet
- MCQ Interview Questions On Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesMCQ Interview Questions On Strength of MaterialsBaydaa QaidyNo ratings yet
- Shallow Crack Fracture Mechanics Toughness Tests and Applications: First International ConferenceFrom EverandShallow Crack Fracture Mechanics Toughness Tests and Applications: First International ConferenceNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- Composite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsFrom EverandComposite Structures of Steel and Concrete: Beams, Slabs, Columns and Frames for BuildingsNo ratings yet
- G+3 Solid Slab Design & Cost Estmation Modified KabtamuDocument156 pagesG+3 Solid Slab Design & Cost Estmation Modified Kabtamuyene0% (1)
- Environmental AssignmentDocument16 pagesEnvironmental AssignmentfishNo ratings yet
- Environmental Impact AssessmentDocument19 pagesEnvironmental Impact AssessmentfishNo ratings yet
- Key Nursing SkillsDocument359 pagesKey Nursing Skillsmordanga100% (6)
- Theory of Structures-II (Course Outline)Document2 pagesTheory of Structures-II (Course Outline)fish100% (1)
- Joints in Monolithic Reinforced Concrete Structures: Recommendations For Design of Beam-ColumnDocument29 pagesJoints in Monolithic Reinforced Concrete Structures: Recommendations For Design of Beam-ColumnJishad NalakathNo ratings yet
- Structural, Optical and Electrical Studies of Nickel FerriteDocument39 pagesStructural, Optical and Electrical Studies of Nickel FerriteDNST CUJNo ratings yet
- Rockwell Hardness of MaterialsDocument118 pagesRockwell Hardness of MaterialsBalakumarNo ratings yet
- Nano MaterialsDocument38 pagesNano Materialsaedi0611100% (2)
- Concrete Mechanics and Design - Solution ManualDocument277 pagesConcrete Mechanics and Design - Solution Manualramya_an241167% (3)
- NA To Sls en 1993-1-1Document16 pagesNA To Sls en 1993-1-1Shan Sandaruwan AbeywardeneNo ratings yet
- Punching of Prestressed Flat Slabs - Experimental Analysis - António M. P. Ramos, Válter J.G. LúcioDocument8 pagesPunching of Prestressed Flat Slabs - Experimental Analysis - António M. P. Ramos, Válter J.G. LúcioVálter LúcioNo ratings yet
- Pcd-Basic, C-Line-Load Balancing MethodsDocument29 pagesPcd-Basic, C-Line-Load Balancing Methodsfrancis baldonadoNo ratings yet
- 7 Christian Gaier Multi Axial Fatigue Analysis With The Fe Post Processor Femfat Utmis 2010Document50 pages7 Christian Gaier Multi Axial Fatigue Analysis With The Fe Post Processor Femfat Utmis 2010ashish38799100% (2)
- 2003 N. Kharouf G. McClure I. Smith - Elasto-Plastic Modeling of Wood Bolted ConnectionsDocument8 pages2003 N. Kharouf G. McClure I. Smith - Elasto-Plastic Modeling of Wood Bolted ConnectionsBatuhan DerNo ratings yet
- CHW Pipe Support SampleDocument19 pagesCHW Pipe Support SamplesyedmuzafferNo ratings yet
- BPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceDocument4 pagesBPUT Question Bank For Material ScienceMr.S UpenderNo ratings yet
- Sample Question Paper: (Strength of Materials-I) Maximum Marks: 75 Time Allowed: 3 HoursDocument4 pagesSample Question Paper: (Strength of Materials-I) Maximum Marks: 75 Time Allowed: 3 HoursYagnik BandyopadhyayNo ratings yet
- MGB 2Document9 pagesMGB 2afacanevrimNo ratings yet
- Stress Check For E.J PierDocument29 pagesStress Check For E.J PierVasu Deva Rao ChilukuriNo ratings yet
- Boundary Vlaue Problem Module 4 With Solutions Page 1-20Document20 pagesBoundary Vlaue Problem Module 4 With Solutions Page 1-20maran.suguNo ratings yet
- LRFD Compression Member DesignDocument267 pagesLRFD Compression Member DesignAnonymous 7MdZQn1No ratings yet
- Defects and Transport in Crystalline SolidsDocument209 pagesDefects and Transport in Crystalline SolidsKhánhNo ratings yet
- HDPE 4710 FM Pipe SpecificationDocument2 pagesHDPE 4710 FM Pipe SpecificationJulio CongonaNo ratings yet
- FLAC2 DDocument180 pagesFLAC2 DMohamed A. El-BadawiNo ratings yet
- Unit5 Deflection of Beam Som1 Mu201Document9 pagesUnit5 Deflection of Beam Som1 Mu201Ave de GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Fiber Test2 1Document9 pagesFiber Test2 1Mohamed Gamal100% (1)
- Me 544 Course OutlineDocument2 pagesMe 544 Course OutlineMohamed H. ShedidNo ratings yet
- StructAeroBeamsPart2 PDFDocument93 pagesStructAeroBeamsPart2 PDFAlem LoajnerNo ratings yet
- Tensile and Chemical Analyses of Selected Steel Bars Produced in NigeriaDocument6 pagesTensile and Chemical Analyses of Selected Steel Bars Produced in NigeriaSalih MohayaddinNo ratings yet
- Spe 171590 MSDocument14 pagesSpe 171590 MSDaniele OliveiraNo ratings yet
- Structural DesignDocument33 pagesStructural DesignMelaku Seyoum100% (3)
- Hastelloy C-22HS Alloy: Oil & Gas ApplicationsDocument12 pagesHastelloy C-22HS Alloy: Oil & Gas ApplicationsYudha SatriaNo ratings yet
- FRP STRUCTURAL GUIDELINES, ACI 440.1 r06Document1 pageFRP STRUCTURAL GUIDELINES, ACI 440.1 r06Gohar ZamanNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 Notes-1 - Magnetic & DielectricsDocument23 pagesUnit 2 Notes-1 - Magnetic & Dielectricsaman bhatiaNo ratings yet