Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Age Pile Capacity
Uploaded by
mrmerajOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Age Pile Capacity
Uploaded by
mrmerajCopyright:
Available Formats
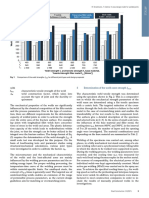
are similar, ageing effects can be quite variable.
For
where: Qt is the capacity at time t, Q0 is the reference example the nine day capacity of concrete piles re-
capacity at time t0 (which is equal to 1 day for Figure ported by Tavenas and Audy had QT/Q0 ratios be-
1), and A is a constant (dimensionless set-up factor). tween 1.1 and 1.85.
Based on a database study, Chow et al. (1998)
suggested an average increase in shaft capacity of
50% per log cycle of time, whilst Axellson (2000) 2.2 Pile Tests at Dunkirk
suggested a somewhat lower percentage of 40 ± Chow et al. (1998) describe a case history for a 324
25%. The data in Figure 1 demonstrate the variabil- mm diameter, 11 m long pipe pile installed into
ity often seen in these database studies. Although dense sand at Dunkirk, France. Brucy et al. (1991)
most piles exhibited some increase in capacity, the reported data relating to the installation of the pile
increase for the H Piles described by Shek et al. and the results of four static load tests (two tension
(2006) were small, whilst that for the concrete and two compression) performed on the pile follow-
closed-ended piles (Tavenas & Audy 1972 and Ax- ing its installation in 1989. The six-month load test
ellson 2000) was relatively large, with piles capaci- was performed with the soil core intact with tension
ties doubling over the time period considered. De- loading followed by compression loading. After
spite the large increases evident at some sites, the completion of the first load test, the soil core was
gains in pile capacity at a given time were highly drilled out and the pile was reloaded nine months af-
variable. This results in a wide range for the set-up ter installation. The purpose of this test was to assess
factor A, even for a given site. It is noted that Lim & the effect of the pile plug on the pile performance.
Lehane (2015) show that the value of A is critically
dependent on the reference time and that the quanti-
fication of set-up is better achieved by normalising
capacity with respect to a reference capacity such as
given by any particular design method.
Figure 2. Evidence of changes in capacity of open-ended pile in
Dunkirk over a five year set-up period (tests on pile CS after
Chow et al. 1998)
Figure 1. Case histories of pile set-up in sandy soil (after Zhang
and Wang 2014)
The results from this series of tests are plotted on
Figure 2 with the pile head displacement set to zero
Bowman & Soga (2005) and Lim & Lehane at the start of each tension load test. The tension ca-
(2014) identify a number of limitations which may pacity of the pile with the core removed was slightly
affect database studies on pile ageing. These include; higher than that measured in the six-month load test.
(i) uncertainty in comparing pile capacity measured The capacity measured in two compression tests (the
in dynamic and static load tests, (ii) the effects of data from which are not included in Figure 2) was
multiple pile testing on set-up, (iii) under mobilisa- quite similar, although it was noted that the removal
tion of pile capacity (particularly in compression of the complete plug proved quite difficult and a por-
load tests), (iv) uncertainty is separating shaft and tion of the lower plug remained in the pile. When the
base resistance for compression load tests, (v) the pile was reloaded in 1994 (T94) a tension resistance
adoption of variable reference times, t0 and (vi) of 810 kN was mobilised, representing an 85% in-
choosing reference times such as the end of installa- crease in shaft resistance over a five year period. The
tion (EOI) resistance which might include short-term initial stiffness response was surprisingly similar
effects associated with excess pore pressures devel- during all the load tests.
oped during driving. However, Figure 1 demon- Chow (1997) considered a number of potential
strates that even when considering a single site mechanisms to explain the ageing trend. These in-
where the pile type, soil conditions and loading type cluded corrosion of the steel pipe pile and physio-
You might also like
- Electrical Units of MeasureDocument36 pagesElectrical Units of MeasureHyung BaeNo ratings yet
- Spud CanDocument16 pagesSpud CanDyah Arintha DewiNo ratings yet
- Friction Fatigue and Drivability Analysis of Open Ended Pipe Piles Based On Cone Penetration Testing Results Maghaddam Et Al. 2017Document13 pagesFriction Fatigue and Drivability Analysis of Open Ended Pipe Piles Based On Cone Penetration Testing Results Maghaddam Et Al. 2017nsaifulNo ratings yet
- Surgical InstrumentsDocument4 pagesSurgical InstrumentsWafa L. AbdulrahmanNo ratings yet
- The Structural Design of Light Gauge Silo HoppersDocument26 pagesThe Structural Design of Light Gauge Silo Hoppersmrnaeem50% (2)
- Ultimate Capacity of Pile FoundationsDocument26 pagesUltimate Capacity of Pile Foundationsriz2010No ratings yet
- PileTestingSettlementPrediction Poulos 2013Document21 pagesPileTestingSettlementPrediction Poulos 2013PranavaDartNo ratings yet
- Interpretations of Instrumented Bored Piles in Kenny Hill FormationDocument8 pagesInterpretations of Instrumented Bored Piles in Kenny Hill Formationtangkokhong100% (1)
- Physical Modelling of The Behaviour of Helical AnchorsDocument19 pagesPhysical Modelling of The Behaviour of Helical AnchorsCristina De Hollanda Cavalcanti TsuhaNo ratings yet
- Case History Evaluation of Axial Behaviour of Bored Pile from SPTDocument110 pagesCase History Evaluation of Axial Behaviour of Bored Pile from SPTKS ChongNo ratings yet
- Induction Hardening - Interpretation of Drawing & Testing PDFDocument4 pagesInduction Hardening - Interpretation of Drawing & Testing PDFrajesh DESHMUKHNo ratings yet
- Driven Pipe Piles in Dense Sand Field TestsDocument11 pagesDriven Pipe Piles in Dense Sand Field TestsmarcvenzNo ratings yet
- Piles and Piling FormulaDocument10 pagesPiles and Piling FormulaSamia H. BhuiyanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 214. The Use of Osterberg Cell Load Tests To Predict Piles ResistanceDocument6 pagesChapter 214. The Use of Osterberg Cell Load Tests To Predict Piles ResistanceTony ChanNo ratings yet
- The Study of 220 KV Power Substation Equipment DetailsDocument90 pagesThe Study of 220 KV Power Substation Equipment DetailsAman GauravNo ratings yet
- Upheaval Buckling Resistance of Pipelines Buried in Clayey BackfillDocument7 pagesUpheaval Buckling Resistance of Pipelines Buried in Clayey BackfillDr I Thusyanthan100% (6)
- Set-Up Effect of Cohesive Soils in Pile Capacity - SvinkinDocument7 pagesSet-Up Effect of Cohesive Soils in Pile Capacity - SvinkinkyrheeNo ratings yet
- Application of bidirectional static loading tests to evaluate deep foundationsDocument7 pagesApplication of bidirectional static loading tests to evaluate deep foundationshugojameswoodNo ratings yet
- EYGEC Paper - Time Effects On Pile Capacity - EKWDocument8 pagesEYGEC Paper - Time Effects On Pile Capacity - EKWBülent SarıalioğluNo ratings yet
- Influence of Uplift On Liquid Storage TaDocument14 pagesInfluence of Uplift On Liquid Storage TaFerdolin EbikNo ratings yet
- Gavin and Igoe - Final PublishedDocument12 pagesGavin and Igoe - Final PublisheddigoeNo ratings yet
- Physical Modelling of The Behaviour of Helical Anchors: June 2016Document20 pagesPhysical Modelling of The Behaviour of Helical Anchors: June 2016Oxiris QuitianNo ratings yet
- Estimating Two-Way Slab Deflections: Spreadsheet Includes Construction Load EffectsDocument6 pagesEstimating Two-Way Slab Deflections: Spreadsheet Includes Construction Load EffectsKojo AsareNo ratings yet
- DynaDocument19 pagesDynaSafalsha BabuNo ratings yet
- Advances in full-flow penetrometer testing quantify soil strengthDocument13 pagesAdvances in full-flow penetrometer testing quantify soil strengthZhenhe SongNo ratings yet
- Setupmechanismsofdrivenpilesinsand ZZ YHW Revised 4Document49 pagesSetupmechanismsofdrivenpilesinsand ZZ YHW Revised 4zahra yousefiNo ratings yet
- G&P-Design and Construction of Driven Piles Over Soft Marine Clay 2019Document4 pagesG&P-Design and Construction of Driven Piles Over Soft Marine Clay 2019BinSayeedNo ratings yet
- 2013 - Mohammed Sakr Comparison Between High Strain Dynamic and Static Load TestsDocument11 pages2013 - Mohammed Sakr Comparison Between High Strain Dynamic and Static Load TestslbiNo ratings yet
- Field Investigation of The Effect of Installation Method On The Shaft Resistance On Piles in ClayDocument13 pagesField Investigation of The Effect of Installation Method On The Shaft Resistance On Piles in Clayamin sharafianNo ratings yet
- Incorporating Long-Term Pile Set-up into LRFD DesignDocument16 pagesIncorporating Long-Term Pile Set-up into LRFD DesignmarcvenzNo ratings yet
- Study t-z and q-z Curves on Bored PileDocument6 pagesStudy t-z and q-z Curves on Bored PileHong Viet NguyenNo ratings yet
- Sitar and Wagner 6ICEGE Christchurch 2015Document13 pagesSitar and Wagner 6ICEGE Christchurch 2015Alexandros ValsamisNo ratings yet
- Field Axial Cyclic Loading Experiments On Piles Driven in Sand PDFDocument14 pagesField Axial Cyclic Loading Experiments On Piles Driven in Sand PDFyousifNo ratings yet
- 14 - 04 02 0061 PDFDocument8 pages14 - 04 02 0061 PDFAngga Fajar SetiawanNo ratings yet
- Snap-Back Testing For Estimation of Nonlinear Behaviour of Shallow and Pile FoundationsDocument8 pagesSnap-Back Testing For Estimation of Nonlinear Behaviour of Shallow and Pile FoundationsRavi SalimathNo ratings yet
- The Use of Osterberg Cell Load Tests To Predict Piles ResistanceDocument6 pagesThe Use of Osterberg Cell Load Tests To Predict Piles Resistancedidiet noer affendiNo ratings yet
- 2010 Villalobos - Model Testing of Suction Caissons in Clay Subjected To Vertical LoadingDocument11 pages2010 Villalobos - Model Testing of Suction Caissons in Clay Subjected To Vertical Loadingvananhlt18No ratings yet
- 395 Common-Mistakes in Static Loading-Test Procedures and Result AnalysesDocument13 pages395 Common-Mistakes in Static Loading-Test Procedures and Result AnalysesmanachemiaaNo ratings yet
- Suction Caisson Foundations For Offshore Wind TurbinesDocument10 pagesSuction Caisson Foundations For Offshore Wind TurbinespontiacceNo ratings yet
- Comparing In-Situ Cone Resistance and Pile Jacking Force: M. Marchi, L. Balbarini & G. Gottardi L. ZambianchiDocument8 pagesComparing In-Situ Cone Resistance and Pile Jacking Force: M. Marchi, L. Balbarini & G. Gottardi L. ZambianchiPrunici IonNo ratings yet
- Interlocking BlockDocument6 pagesInterlocking BlockhamzeNo ratings yet
- Briaud Etal 2000 StatnamicDocument10 pagesBriaud Etal 2000 StatnamicDavid WhiteNo ratings yet
- Testing Deep FoundationsDocument9 pagesTesting Deep FoundationsDRocha1No ratings yet
- Pile Foundation Design in Soft Soils For The World'S Largest Drainage Pumping StationDocument12 pagesPile Foundation Design in Soft Soils For The World'S Largest Drainage Pumping StationSoumya GuptaNo ratings yet
- Akl-Mossaad2021 Article DetectingPistonEffectOnDrilledDocument11 pagesAkl-Mossaad2021 Article DetectingPistonEffectOnDrilledMohamed KadryNo ratings yet
- Compressive Behavior of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Columns Subjected To Long-Term Loading PDFDocument7 pagesCompressive Behavior of Concrete Filled Steel Tubular Columns Subjected To Long-Term Loading PDFzakai zakiNo ratings yet
- Leonards e Loveel-Interpretation of Load Tests On High-Capacity Driven PilesDocument28 pagesLeonards e Loveel-Interpretation of Load Tests On High-Capacity Driven PilesElisângela AlmeidaNo ratings yet
- 98s11 PDFDocument11 pages98s11 PDFpaulkohanNo ratings yet
- Pile driveability in low-to-medium density chalk: A new predictive methodDocument43 pagesPile driveability in low-to-medium density chalk: A new predictive methodingchiara85No ratings yet
- Lateral Resistance of Helical Monopole Bases - SakrDocument8 pagesLateral Resistance of Helical Monopole Bases - SakrvilaneneNo ratings yet
- Behaviour of Open and Closed End Pile Groups Subjected To Vertical Loading A Comparative StudyDocument11 pagesBehaviour of Open and Closed End Pile Groups Subjected To Vertical Loading A Comparative StudynsaifulNo ratings yet
- Magazine of Concrete Research - 61!6!2009-Slab DeflectionDocument42 pagesMagazine of Concrete Research - 61!6!2009-Slab DeflectionSyed RaziuddinNo ratings yet
- Comparison of pile design standards: EC7 vs AS2159Document12 pagesComparison of pile design standards: EC7 vs AS2159Stephen ButtlingNo ratings yet
- Chr. Moorman - Simulation of Soil Plug Effects in Open Steel Pipe PilesDocument15 pagesChr. Moorman - Simulation of Soil Plug Effects in Open Steel Pipe PilesAnonymous PibYPghNo ratings yet
- Field Trials of Suction Caissons in Clay For Offshore Wind Turbine FoundationsDocument10 pagesField Trials of Suction Caissons in Clay For Offshore Wind Turbine FoundationsRajaa KodadNo ratings yet
- A Dosumu Et Al Jan2012 BUCKLINGDocument10 pagesA Dosumu Et Al Jan2012 BUCKLINGJiu JitsanNo ratings yet
- Shear Behavior of Headed Anchors With Large Diameters and Deep Embedments - Discussion Title 107-S14 - Mar-Apr 2010Document6 pagesShear Behavior of Headed Anchors With Large Diameters and Deep Embedments - Discussion Title 107-S14 - Mar-Apr 2010ehab.attalaNo ratings yet
- US-Japan 2000Document15 pagesUS-Japan 2000Mustafa KutanisNo ratings yet
- Loads On Barricades in Hydraulically Backfilled Underground Mine StopesDocument12 pagesLoads On Barricades in Hydraulically Backfilled Underground Mine StopesAlagu RamNo ratings yet
- Control secondary creep in soft soil with surchargeDocument9 pagesControl secondary creep in soft soil with surchargeZhiren ZhuNo ratings yet
- References: Footing PlateDocument1 pageReferences: Footing PlateThoong Yew ChanNo ratings yet
- A Fatigue Endurance Limit For Highway and Airport Pavements TRB 2003-001428Document17 pagesA Fatigue Endurance Limit For Highway and Airport Pavements TRB 2003-001428bkollarou9632No ratings yet
- Chapter6 PDFDocument59 pagesChapter6 PDFGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Bolted Beam ConnectionDocument1 pageBolted Beam ConnectionmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Bolted Beam ConnectionDocument1 pageBolted Beam ConnectionmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 16 CompoComposite Structures of Steel and ConcreDocument7 pages16 CompoComposite Structures of Steel and ConcremrmerajNo ratings yet
- Lateral TorsionDocument3 pagesLateral TorsionmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Welded DesignDocument1 pageWelded DesignmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 9 Check of Torque and Re-Calibration: Number of Available Places Accept or Reject CommentDocument1 page9 Check of Torque and Re-Calibration: Number of Available Places Accept or Reject CommentmrmerajNo ratings yet
- R. Stroetmann, T. Kästner: A New Design Model For Welded JointsDocument1 pageR. Stroetmann, T. Kästner: A New Design Model For Welded JointsmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Welded DesignDocument1 pageWelded DesignmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 13 PDFsam TN62Part1Document1 page13 PDFsam TN62Part1mrmerajNo ratings yet
- 16 CompoComposite Structures of Steel and ConcreDocument7 pages16 CompoComposite Structures of Steel and ConcremrmerajNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Acceptance Criteria For Bolt Tensioning - Load Indicating WashersDocument1 page8.1 Acceptance Criteria For Bolt Tensioning - Load Indicating WashersmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Figure 7.2 (D) - View of The Torque Wrench On The True CheckerDocument1 pageFigure 7.2 (D) - View of The Torque Wrench On The True CheckermrmerajNo ratings yet
- 2 Str016Document1 page2 Str016mrmerajNo ratings yet
- 2 Str01222 STRDocument1 page2 Str01222 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 3 Str01222 STRDocument1 page3 Str01222 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 1 Str01222 STRDocument1 page1 Str01222 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Option 1: 7.2 Calibrated Impact WrenchDocument1 pageOption 1: 7.2 Calibrated Impact WrenchmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 3 Str016Document1 page3 Str016mrmerajNo ratings yet
- Option 2: TN62 Assembly and Tensioning of High Strength Bolts and Nuts - Part 1: Class 8.8Document1 pageOption 2: TN62 Assembly and Tensioning of High Strength Bolts and Nuts - Part 1: Class 8.8mrmerajNo ratings yet
- 3 Str223 STRDocument1 page3 Str223 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 2 Str223 STRDocument1 page2 Str223 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 4.2 8.8/TF and 8.8/TB (Or 8.8/T When Referring To Both Types)Document1 page4.2 8.8/TF and 8.8/TB (Or 8.8/T When Referring To Both Types)mrmerajNo ratings yet
- 8.1 Acceptance Criteria For Bolt Tensioning - Load Indicating WashersDocument1 page8.1 Acceptance Criteria For Bolt Tensioning - Load Indicating WashersmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 1 Str223 STRDocument1 page1 Str223 STRmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 7.1 Types of Tensioning Equipment Figure 7.1 (A) - Electric Torque Wrench - Accuracy of +/-4%Document1 page7.1 Types of Tensioning Equipment Figure 7.1 (A) - Electric Torque Wrench - Accuracy of +/-4%mrmerajNo ratings yet
- Figure 7.1 (C) - Pneumatic Torque Wrench: TN62 Assembly and Tensioning of High Strength Bolts and Nuts - Part 1: Class 8.8Document1 pageFigure 7.1 (C) - Pneumatic Torque Wrench: TN62 Assembly and Tensioning of High Strength Bolts and Nuts - Part 1: Class 8.8mrmerajNo ratings yet
- 1 Clarification of Bolt Tensioning: SteelworkDocument1 page1 Clarification of Bolt Tensioning: SteelworkmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Figure 7.2 (D) - View of The Torque Wrench On The True CheckerDocument1 pageFigure 7.2 (D) - View of The Torque Wrench On The True CheckermrmerajNo ratings yet
- Single Sections in BendingDocument1 pageSingle Sections in BendingmrmerajNo ratings yet
- 6 Acceptable Method For Tensioning Bolts: 6.1 Load Indicating WashersDocument1 page6 Acceptable Method For Tensioning Bolts: 6.1 Load Indicating WashersmrmerajNo ratings yet
- Year 5:: NUMBERS TO 1 000 000Document47 pagesYear 5:: NUMBERS TO 1 000 000Rusehaiza Bin Md DarusNo ratings yet
- Workload Assessment in Railway ControlDocument8 pagesWorkload Assessment in Railway ControlbbeeNo ratings yet
- Surface Hardening enDocument20 pagesSurface Hardening engtm1207No ratings yet
- NASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78Document17 pagesNASA Technical Mem Randum: E-Flutter N78gfsdg dfgNo ratings yet
- Guidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagDocument10 pagesGuidelines On Dissolution Profile Comparison: Udrun ReitagRaju GawadeNo ratings yet
- Cdd153167-Samsung Un32d6500vf Un32 40 46 55d6400uf 6420uf 6450uf 6500vf 6900wf Chassis U63a SM PDFDocument87 pagesCdd153167-Samsung Un32d6500vf Un32 40 46 55d6400uf 6420uf 6450uf 6500vf 6900wf Chassis U63a SM PDFMilciades MurilloNo ratings yet
- The Baptismal Liturgy in The Easter Vigil According To The Sacramentary of Fulda (10th Century)Document7 pagesThe Baptismal Liturgy in The Easter Vigil According To The Sacramentary of Fulda (10th Century)Henry DonascoNo ratings yet
- The Quill Vol. LVIII Issue 1 1-12Document12 pagesThe Quill Vol. LVIII Issue 1 1-12Yves Lawrence Ivan OardeNo ratings yet
- Desiderata: by Max EhrmannDocument6 pagesDesiderata: by Max EhrmannTanay AshwathNo ratings yet
- Datasheet Optris XI 410Document2 pagesDatasheet Optris XI 410davidaldamaNo ratings yet
- Edexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)Document16 pagesEdexcel A-Level Biology Experimental Design Marks Scheme (1) (Full Permission)FardeenKhanNo ratings yet
- QUESTION A2 and A3 Examples PDFDocument24 pagesQUESTION A2 and A3 Examples PDFDemian VeNo ratings yet
- Contact GRRSB Team for InquiriesDocument2 pagesContact GRRSB Team for Inquiriesmsis81No ratings yet
- Project Data Collection & Risk ReportingDocument2 pagesProject Data Collection & Risk Reportinggambler yeagerNo ratings yet
- 4thinternationalconferencetheimportanceofplace Proceedings 2017 PDFDocument428 pages4thinternationalconferencetheimportanceofplace Proceedings 2017 PDFnerko86No ratings yet
- Jual Sokkia SET 350X Total Station - Harga, Spesifikasi Dan ReviewDocument5 pagesJual Sokkia SET 350X Total Station - Harga, Spesifikasi Dan Reviewbramsalwa2676No ratings yet
- SmartRunway SmartLandingDocument39 pagesSmartRunway SmartLandingMikeNo ratings yet
- Sony HCD-GTX999 PDFDocument86 pagesSony HCD-GTX999 PDFMarcosAlves100% (1)
- Schaeffler - Account Insights - Mar 2020Document13 pagesSchaeffler - Account Insights - Mar 2020mohit negiNo ratings yet
- Whatever Happens, Happens For Something Good by MR SmileyDocument133 pagesWhatever Happens, Happens For Something Good by MR SmileyPrateek100% (3)
- LOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorDocument1 pageLOGARITHMS, Exponentials & Logarithms From A-Level Maths TutorHorizon 99No ratings yet
- Vrio Analysis Slide Template 16x9 1Document8 pagesVrio Analysis Slide Template 16x9 1Alt HrishiNo ratings yet
- Basler Electric 87T - Great InfoDocument3 pagesBasler Electric 87T - Great InfoMrNo ratings yet
- Mfz-Odv065r15j DS 1-0-0 PDFDocument1 pageMfz-Odv065r15j DS 1-0-0 PDFelxsoonNo ratings yet
- Request Letter Group 7Document1 pageRequest Letter Group 7Brent PatarasNo ratings yet
- IIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestDocument15 pagesIIT2019 RIT-1-CPM Chemistry TestPRAKHAR GUPTANo ratings yet