Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What is an earthquake? Causes and effects in 40 chars
Uploaded by
mary cris tubalOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What is an earthquake? Causes and effects in 40 chars
Uploaded by
mary cris tubalCopyright:
Available Formats
What is earthquake?
An earthquake is the shaking of the surface of the Earth, resulting from the
sudden release of energy in the Earth’s lithosphere that creates seismic waves.
Earthquakes can range in size from those that are so weak that they cannot be
felt to those violent enough to toss people around and destroy whole cities. The
seismicity or seismic activity of an area refers to the frequency, type and size of
earthquakes experienced over a period of time.
At the Earth’s surface, earthquakes manifest themselves by shaking and
sometimes displacement of the ground. When the epicenter of a large
earthquake is located offshore, the seabed may be displaced sufficiently to
cause a tsunami. Earthquakes can also trigger landslides, and occasionally
volcanic activity.
In its most general sense, the word earthquake is used to describe any seismic
event — whether natural or caused by humans — that generates seismic waves.
Earthquakes are caused mostly by rupture of geological faults, but also by other
events such as volcanic activity, landslides, mine blasts, and nuclear tests. An
earthquake’s point of initial rupture is called its focus or hypocenter. The
epicenter is the point at ground level directly above the hypocenter.
What causes earthquakes and where do
they happen?
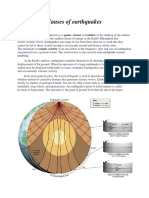
The earth has four major layers: the inner core, outer core, mantle and crust.
The crust and the top of the mantle make up a thin skin on the surface of our
planet. But this skin is not all in one piece – it is made up of many pieces like a
puzzle covering the surface of the earth. Not only that, but these puzzle pieces
keep slowly moving around, sliding past one another and bumping into each
other. We call these puzzle pieces tectonic plates, and the edges of the plates
are called the plate boundaries. The plate boundaries are made up of many
faults, and most of the earthquakes around the world occur on these faults.
Since the edges of the plates are rough, they get stuck while the rest of the
plate keeps moving. Finally, when the plate has moved far enough, the edges
unstick on one of the faults and there is an earthquake.
Why does the earth shake when there is an
earthquake?
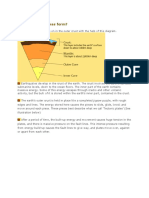
While the edges of faults are stuck together, and the rest of the block is
moving, the energy that would normally cause the blocks to slide past one
another is being stored up. When the force of the moving blocks finally
overcomes the friction of the jagged edges of the fault and it unsticks, all that
stored up energy is released. The energy radiates outward from the fault in all
directions in the form of seismic waves like ripples on a pond. The seismic
waves shake the earth as they move through it, and when the waves reach the
earth’s surface, they shake the ground and anything on it, like our houses and
us! (see P&S Wave inset)
These seven plates make up most of the seven continents and the Pacific Ocean.
African Plate.
Antarctic plate.
Australian Plate.
North American Plate.
Pacific Plate.
South American Plate.
Eurasian plate.
Triangulation is a method used by qualitative researchers to check and establish validity
in their studies by analysing a research question from multiple perspectives is to arrive at
consistency across data sources or approaches, in fact, such inconsistencies should not be
seen as weakening the evidence, but should be
You might also like
- The Earthquake 2aDocument5 pagesThe Earthquake 2aAdrián Lume HuayllaniNo ratings yet
- The Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceFrom EverandThe Earth-Shaking Facts about Earthquakes with Max Axiom, Super Scientist: 4D An Augmented Reading Science ExperienceNo ratings yet
- Why Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksFrom EverandWhy Do Tectonic Plates Crash and Slip? Geology Book for Kids | Children's Earth Sciences BooksNo ratings yet
- Geological Information - ShashankDocument4 pagesGeological Information - Shashankapi-242780017No ratings yet
- UntitledDocument43 pagesUntitledbaylon joeann nicoleNo ratings yet
- Causes of EarthquakesDocument8 pagesCauses of Earthquakesdumea paulNo ratings yet
- Definition of EarthquakeDocument12 pagesDefinition of Earthquakeroyani1965No ratings yet
- Understanding Earthquakes: Causes, Effects and TerminologyDocument22 pagesUnderstanding Earthquakes: Causes, Effects and TerminologyRahul SharmaNo ratings yet
- Presentation On EarthquakeDocument7 pagesPresentation On Earthquakesofia khanumNo ratings yet
- The Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksFrom EverandThe Ground Is Shaking! What Happens During An Earthquake? Geology for Beginners| Children's Geology BooksNo ratings yet
- Shake, Rattle, and Roll: Exploring the Science of EarthquakesFrom EverandShake, Rattle, and Roll: Exploring the Science of EarthquakesNo ratings yet
- Phy PW Xii p3Document13 pagesPhy PW Xii p3omprakash sahNo ratings yet
- L4 - EarthquakesDocument9 pagesL4 - EarthquakesTaylah ClarkNo ratings yet
- Elements of Sisomology: Understanding EarthquakesDocument11 pagesElements of Sisomology: Understanding EarthquakesRohan ShreshthiNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics 122447Document12 pagesPlate Tectonics 122447mkwa811No ratings yet
- Earthquakes and FaultsDocument16 pagesEarthquakes and FaultsJoeseph CoNo ratings yet
- Earthquake LessonDocument46 pagesEarthquake LessonAvis pittNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument69 pagesEarthquakesunil yadavNo ratings yet
- How Do Earthquakes FormDocument4 pagesHow Do Earthquakes FormMonaoray BalowaNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument41 pagesEarthquakeASNINo ratings yet
- Earthquakes and Faults ModuleDocument8 pagesEarthquakes and Faults ModuleJoeseph CoNo ratings yet
- Introduction To EarthquakesDocument3 pagesIntroduction To EarthquakesMonaoray BalowaNo ratings yet
- ALI AHMED AWAN EqSe1Document13 pagesALI AHMED AWAN EqSe1Zeeshan ahmedNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes, Volcanoes, and Tsunamis: Projects and Principles for Beginning GeologistsFrom EverandEarthquakes, Volcanoes, and Tsunamis: Projects and Principles for Beginning GeologistsNo ratings yet
- Quarter 2 and 3 Sicence NotesDocument19 pagesQuarter 2 and 3 Sicence NotesMaria Ysabel Forneste SuniNo ratings yet
- Measuring EarthquakesDocument6 pagesMeasuring EarthquakesregilynNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument177 pagesEarthquakebharasha mahantaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Different Types of Plate BoundariesDocument19 pagesLesson 2 - Different Types of Plate Boundariesken arellanoNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering: Bulacan State UniversityDocument10 pagesCollege of Engineering: Bulacan State UniversityRenz Olex M. CanlasNo ratings yet
- The Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetDocument32 pagesThe Turbulent Earth I. Questions To Pose: An Uneasy PlanetsshoeburrahmanNo ratings yet
- Origin and Types of EarthquakesDocument3 pagesOrigin and Types of EarthquakesLyn OzitlamNo ratings yet
- Lecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Earthquakes and VolcanoesDocument7 pagesLecture Note Topic 4 Endogenous Process-Earthquakes and VolcanoesQP0125 Vu Song HaNo ratings yet
- EarthquakesDocument33 pagesEarthquakesPetar PavlovNo ratings yet
- Science ReviewerDocument4 pagesScience ReviewerMarinelle Joy PALADANo ratings yet
- Explanation Text: Andi Adhyaksa Gilang Afif M Daffa Nur M Rayhan Teuku AuliDocument7 pagesExplanation Text: Andi Adhyaksa Gilang Afif M Daffa Nur M Rayhan Teuku AulirayhanNo ratings yet
- Grade 10 Lesson 3 Earthquake Seismic WaveDocument34 pagesGrade 10 Lesson 3 Earthquake Seismic Wavemae ann perochoNo ratings yet
- What Is EarthquakeDocument4 pagesWhat Is EarthquakeCresanta BuyanNo ratings yet
- The Quake StartsDocument8 pagesThe Quake StartsJessa Gualberto-Gimena PabiaNo ratings yet
- Earthquakes ExplainedDocument7 pagesEarthquakes ExplainedNishant ThakurNo ratings yet
- Interior of The EarthDocument2 pagesInterior of The EarthWaskitaMurtyNo ratings yet
- Dr. A. B. Danie Roy: Faculty of Civil Engineering Thapar University, PatialaDocument33 pagesDr. A. B. Danie Roy: Faculty of Civil Engineering Thapar University, Patialaprateek buddyNo ratings yet
- Fun Facts About Tectonic Plates For KDocument8 pagesFun Facts About Tectonic Plates For KViorel MaresNo ratings yet
- What Is Plate TectonicsDocument5 pagesWhat Is Plate TectonicskemcanaboNo ratings yet
- Unit 2. Lesson 3Document16 pagesUnit 2. Lesson 312 STEM 2CNo ratings yet
- Pointers in ScienceDocument4 pagesPointers in ScienceRhana ClaireNo ratings yet
- EarthquakeDocument97 pagesEarthquakeJocelyn MatigaNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 dmDocument14 pagesUnit 4 dmAman SinghNo ratings yet
- 9 Interior of The EarthDocument50 pages9 Interior of The EarthNaga Lakshmi100% (1)
- Earthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006Document17 pagesEarthquakes: Ive Polanco 14-1006LossyTNo ratings yet
- Science 8 4Document17 pagesScience 8 4Hannah Leigh CoronelNo ratings yet
- Eart 2Document14 pagesEart 29897856218No ratings yet
- Lecture Guide in Science 10Document5 pagesLecture Guide in Science 10reynaldo banaria jrNo ratings yet
- Dissertation On Effects of Earthquake, Volcano & TsunamiDocument217 pagesDissertation On Effects of Earthquake, Volcano & TsunamiumzzNo ratings yet
- Faults and EarthquakesDocument7 pagesFaults and EarthquakesAngela AlexandraNo ratings yet
- Plate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Document27 pagesPlate Tectonics and Seismography Class 7.5Monica SreeNo ratings yet
- Environmental Management - Plate TectonicsDocument17 pagesEnvironmental Management - Plate TectonicsNikhil YadavNo ratings yet
- Engineering Geology Assignment No. 2: How Disasters Are Caused by Earthquake?Document2 pagesEngineering Geology Assignment No. 2: How Disasters Are Caused by Earthquake?Sheikh MuneebNo ratings yet
- Geography IndiaDocument173 pagesGeography IndiaArvind KumarNo ratings yet
- Wegener Was Convinced That All of EarthDocument2 pagesWegener Was Convinced That All of Earthmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Alnie Kun KyootDocument1 pageAlnie Kun Kyootmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Research Paper MLDocument1 pageResearch Paper MLmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Alnie Kun KyootDocument1 pageAlnie Kun Kyootmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Accent' Matters: Philippines Acquiring 70% of India Call CentersDocument1 pageAccent' Matters: Philippines Acquiring 70% of India Call Centersmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Continenta L Drift: Alfred WegenerDocument7 pagesContinenta L Drift: Alfred Wegenermary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Accent' Matters: Philippines Acquiring 70% of India Call CentersDocument1 pageAccent' Matters: Philippines Acquiring 70% of India Call Centersmary cris tubalNo ratings yet
- Physics O LevelDocument32 pagesPhysics O LevelCollins JimNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable Energies-A Suitable and Cost-Competitive Solution For Rural Electrification PDFDocument7 pagesHybrid Power Systems Based On Renewable Energies-A Suitable and Cost-Competitive Solution For Rural Electrification PDFbdsrlNo ratings yet
- SCES1094 Tutorial 2Document21 pagesSCES1094 Tutorial 2SN2-0622 NURUL ADLYNA BINTI LOKMANNo ratings yet
- 124HarnessingThePower HarnessingThePowerDocument5 pages124HarnessingThePower HarnessingThePower.No ratings yet
- Topic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter NotesDocument7 pagesTopic 1 The Particulate Nature of Matter Notessteve KingNo ratings yet
- Challenges and Opportunities of Sustainable UrbanizationDocument18 pagesChallenges and Opportunities of Sustainable UrbanizationAniket gajanan shinde shindeNo ratings yet
- R - Selected Species, K - Selected Speices, ESS (In T&T)Document2 pagesR - Selected Species, K - Selected Speices, ESS (In T&T)Tsh RNo ratings yet
- Earth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceDocument4 pagesEarth's Timeline (Earth & Life ScienceRUTH DEBORAH PECIONo ratings yet
- Earth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test BankDocument10 pagesEarth System History 4th Edition Stanley Test Bankpanabase.trevat.puhh6e100% (19)
- Diesel Combustion Model Using Tabulated Chemistry Wit PDFDocument11 pagesDiesel Combustion Model Using Tabulated Chemistry Wit PDFNguyen ChungNo ratings yet
- Previous Year Question Papers (Evs) 2014-2016Document25 pagesPrevious Year Question Papers (Evs) 2014-2016kashishsirohi051No ratings yet
- Energy ResourceDocument37 pagesEnergy ResourcewtkovtuprNo ratings yet
- Bearing Capacity - WikipediaDocument4 pagesBearing Capacity - WikipediaAlkindi YahyaNo ratings yet
- Web+info. LOT21 Multi+V+indoor+unitDocument15 pagesWeb+info. LOT21 Multi+V+indoor+unitJohny WooNo ratings yet
- Classification of Matter: Material Pure Substance or Mixture Element, Compound, Homogeneous, HeterogeneousDocument2 pagesClassification of Matter: Material Pure Substance or Mixture Element, Compound, Homogeneous, HeterogeneousKira YoshikageNo ratings yet
- Thermodynamics Exam Questions Focus on Cycles, Processes, and Efficiency CalculationsDocument26 pagesThermodynamics Exam Questions Focus on Cycles, Processes, and Efficiency CalculationsSuhas G MNo ratings yet
- PXC XCXDocument23 pagesPXC XCXKashif LiaqatNo ratings yet
- Rock Classification and Formation ProcessesDocument6 pagesRock Classification and Formation ProcessesYogendra PatilNo ratings yet
- Physical ScienceDocument3 pagesPhysical ScienceShin NeulNo ratings yet
- Hansan Regulator 2015Document16 pagesHansan Regulator 2015arminNo ratings yet
- Sustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyDocument9 pagesSustainability - The Role of Mineral Processing and Extractive MetallurgyakshukNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines Department of Education Deped Complex, Pasig City Science Iii K To 12 Curriculum Guide Planner / Budget of WorkDocument3 pagesRepublic of The Philippines Department of Education Deped Complex, Pasig City Science Iii K To 12 Curriculum Guide Planner / Budget of WorkLedie Lou Cetoy SuperalesNo ratings yet
- Transpiration: Prepared By: Concepcion, Ada - Trinidad, Lester - Tolon, ChristianDocument17 pagesTranspiration: Prepared By: Concepcion, Ada - Trinidad, Lester - Tolon, ChristiannimhaNo ratings yet
- RE-REFINING OF USED LUBRICATING OILSDocument23 pagesRE-REFINING OF USED LUBRICATING OILSJaydeep TayadeNo ratings yet
- 00Document40 pages00ShōyōHinataNo ratings yet
- Modern Electronic Theory of Atoms UploadedDocument86 pagesModern Electronic Theory of Atoms UploadedRaluchukwu ChukwurahNo ratings yet
- Scilab - Thermodynamics - An Engineering Approach (SI Units) - Y. A. Cengel, M. A. BolesDocument157 pagesScilab - Thermodynamics - An Engineering Approach (SI Units) - Y. A. Cengel, M. A. BolesMoyses Naves de MoraesNo ratings yet
- Drying Applications: CHE 408: Heat and Mass TransferDocument15 pagesDrying Applications: CHE 408: Heat and Mass TransferYasmin KayeNo ratings yet
- What Is A Gram Atom? Why Is The Concept of Gram Atoms Useful in Chemistry? AnswerDocument75 pagesWhat Is A Gram Atom? Why Is The Concept of Gram Atoms Useful in Chemistry? Answeryaseen shahNo ratings yet
- Nexans - SIWO KUL B10 13 8 15 KVDocument3 pagesNexans - SIWO KUL B10 13 8 15 KVMohamed SaberNo ratings yet