Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Orca Share Media1561345296214
Uploaded by
Solomon Risty CahuloganOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Orca Share Media1561345296214
Uploaded by
Solomon Risty CahuloganCopyright:
Available Formats
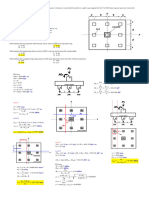
GERTC – November 2019 Review HYDRAULICS – Buoyancy & Stability on Floating Bodies
BUOYANCY
Buoyancy (also known as the buoyant force) is the force exerted on an
object that is wholly or partly immersed in a fluid.
- The symbol for the magnitude of buoyancy is BF or FB
- As a vector it must be stated with both magnitude and direction.
• Buoyancy acts upward for the kind of situations encountered
in everyday experience.
- As with other forces, the SI unit of buoyancy is the newton [N].
Archimedes' Principle
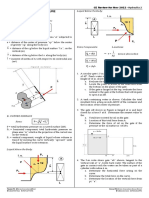
The magnitude of the buoyant force on an object is equal to the weight Figure 3: Unstable Position
of the fluid it displaces.
Righting Moment and Overturning Moment
BF = liqVdisplaced RM = W ( x )
OM = W ( x )
The factors that affect buoyancy are:
a. the density of the fluid,
b. the volume of the fluid displaced, and Metacentric Height
c. the local acceleration due to gravity. MG = MBo GBo
The buoyant force is not affected by:
a. the mass of the immersed object or Use (-) if G is above Bo
b. the density of the immersed object. Use (+) if G is below Bo
Buoyancy vs. Density Value of MBo
B2 tan2
Densities BF > Wobject BF = Wobject BF < Wobject MBo = 1 +
object rises float on surface
12D 2
ρobject < ρfluid (wholly (partly
immersed) immersed)
neutral
Sample Problems:
buoyancy
ρobject = ρfluid (wholly
1. An iceberg having specific gravity of 0.92 is floating on salt water of
sp. gr. 1.03. If the volume of ice above the water surface is 1000m3,
immersed)
what is the total volume of the ice?
ρobject > ρfluid object sinks
2. A block of wood 0.60m by 0.60m by h meters in dimension was
Stability of floating bodies thrown into the water and floats with 0.18m projecting above the
water surface. The same block was thrown into a container of a liquid
having a specific gravity of 0.90 and it floats with 0.14m projecting
above the surface. Determine the following:
a. the value of h
b. the specific gravity of the block
c. the weight of the block
3. A piece of irregularly shaped metal weighs 300.0 N in air. When the
metal is completely submerged in water, it weighs 232.5 N. Find the
volume of the metal.
Figure 1: Upright position
4. Determine the magnitude and direction of the force necessary to hold
Initial value of MBo a concrete cube, 0.300 m on each side, in equilibrium and completely
I submerged (a) in mercury (Hg) and (b) in water. Use s.g. = 2.40.
MBo =
Vdisplaced 5. Determine the submerged depth of a cube of steel 0.30 m on each side
floating in mercury. The specific gravities of steel and mercury are 7.8
and 13.6, respectively.
6. A hollow cube 1.0 m on each side weighs 2.4 kN. The cube is tied to a
solid concrete block weighing 10.0 kN. Will these two objects tied
together float or sink in water? The specific gravity of the concrete is
2.40.
7. A concrete cube 0.5 m on each side is to be held in equilibrium under
water by attaching a light foam buoy to it. What minimum volume of
foam is required? The specific weights of concrete and foam are 23.58
kN/m^3 and 0.79 kN/m^3, respectively.
Figure 2: Stable Position 8. What fraction of the volume of a solid piece of metal of s.g. 7.25 floats
above the surface of a container of mercury?
9. A hydrometer weighs of 0.17 N and has a stem diameter of 11 mm.
What is the distance between scale markings for s.g. = 1.0 and s.g. =
1.1? Between 1.1 and 1.2?
10. A square pole (s.g. = 0.68), 80 mm by 80 mm by 6 m long, is suspended
by a wire so that 4 m is submerged in water and 2 m is above the
surface. What is the tension in the wire?
1|Engr. C.G. D ua so, CE, RMP
GERTC – November 2019 Review HYDRAULICS – Buoyancy & Stability on Floating Bodies
11. A right circular cone is 50 mm in radius and 170 mm high and weighs
1.5 N in air. How much force is required to push this cone vertex-
downward into ethanol so that its base is exactly at the surface? How
much additional force will push the base 6.5 mm below the surface?
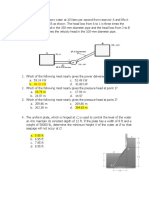
12. The block shown in the figure weighs 21,000 kN. Find the value of h.
13. A cube 0.7m on an edge has its lower half of s.g. = 1.6 and upper half
of s.g. = 0.7. It rests in a two – layer fluid, with lower s.g. = 1.4 and
upper s.g. = 0.8. Determine the h of the top of the cube above the
interface.
Situation 1 – A ship having a displacement of 23,416 metric tons and a
draft of 10.552 m in ocean (sp. gr. = 1.025) enters a harbor of fresh
water (sp. gr. = 1). The horizontal section of the ship at the waterline
is 2,750 m2.
14. What is the displacement (in m3) of the ship in salt water?
A. 22845 B. 23918 C. 23657 D. 24500
15. What depth of fresh water is required to float the ship?
A. 11.7m B. 10.8m C. 10.7m D. 11.5m
16. A rectangular scow 9m wide, 15m long, and 3.6m high has a draft in
sea water 2.4m. Its center of gravity is 2.7m above the bottom of the
scow.
a. Determine the initial metacentric height.
b. Determine the righting or overturning moment when the scow
tilts until one side is just at the point of submergence.
17. A barge floating in fresh water has the form of a parallelepiped having
dimensions 10m by 30m by 3m. It weighs 4,500 kN when loaded with
center of gravity along its vertical axis 4m from the bottom.
a. Find the metacentric height about its longest centerline (Rolling
action).
b. Find the metacentric height about its shortest centerline
(Pitching action).
2|Engr. C.G. D ua so, CE, RMP
GERTC – November 2019 Review HYDRAULICS – Buoyancy & Stability on Floating Bodies
3|Engr. C.G. D ua so, CE, RMP
You might also like
- Irrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsDocument6 pagesIrrigation Problems: Properties of Fluids, Pressures & DamsJeiel ValenciaNo ratings yet
- November 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesNovember 2021 Ce Board Exam Tuzon 6: Eview NnovationsamberNo ratings yet
- Exam in Fluids1Document4 pagesExam in Fluids1Prince Winderic Gaza AclanNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Document2 pagesCE Board Nov 2021 - Geotechnical Engineering - Set 5Lemuel TeopeNo ratings yet
- CE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Document1 pageCE Board Nov 2020 - Hydraulics - Set 13Justine Ejay MoscosaNo ratings yet
- Plate No.6 - SolutionDocument6 pagesPlate No.6 - SolutionBillie Ian. Salamante JrNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoDocument5 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Engr. Jonathan C. BulagaoMichael James ll BanawisNo ratings yet
- Special Group Study 1: Inhinyero Review CenterDocument2 pagesSpecial Group Study 1: Inhinyero Review CenterAngelo John R. JavinezNo ratings yet
- 100 MSTE Problems Prepared by CEneerDocument21 pages100 MSTE Problems Prepared by CEneerfrancis bautistaNo ratings yet
- Hge Mid PreboardDocument7 pagesHge Mid PreboardChrisneil Delosreyes0% (1)
- Tye ENGG. REFRESHER (SEPT. 28,2021)Document2 pagesTye ENGG. REFRESHER (SEPT. 28,2021)ELMERNo ratings yet
- BESA Mathematics Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Document50 pagesBESA Mathematics Preboard Solutions 18 Feb. 2022Chaythina CortezaNo ratings yet
- Consolidated Drained Tri AxialDocument15 pagesConsolidated Drained Tri AxialJemuel FloresNo ratings yet
- Two Open TanksDocument10 pagesTwo Open TanksMaverick TimbolNo ratings yet
- Final Preboard Exam - MSTE - SolutionDocument7 pagesFinal Preboard Exam - MSTE - SolutionKathryne BernardoNo ratings yet
- CE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Document3 pagesCE Module 25 - Soil Testing (Answer Key)Angelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Probability: Number of Favorable Outcomes Number of All Possible of OutcomesDocument2 pagesProbability: Number of Favorable Outcomes Number of All Possible of OutcomesFrederick Perez IINo ratings yet
- PREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set ADocument2 pagesPREBOARD GEO HYDRA WITH ANSWERS NOV 2017 - Set AEngr. HLDCNo ratings yet
- CE Board May 2014Document41 pagesCE Board May 2014Ayen100% (1)
- Tos1 MidtermDocument2 pagesTos1 MidtermMa.Zyra M. DascoNo ratings yet
- Kippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Document9 pagesKippap Diagnostic Exam May 2022Maryrose Aguirre SerranoNo ratings yet
- 2019 Hyd MayDocument13 pages2019 Hyd MayChantal Faye GacusanNo ratings yet
- Mata Deseree Plate 7Document9 pagesMata Deseree Plate 7Diecon Irish ArboledaNo ratings yet
- Geotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Document87 pagesGeotechnical Engineering and Hydraulics Final Coaching Nov 2018Jeremy Mark SorianoNo ratings yet
- Quiz 12Document6 pagesQuiz 12John Taylor BernasNo ratings yet
- Final Quiz Problems To Be MadeDocument16 pagesFinal Quiz Problems To Be MadeRyan ReyesNo ratings yet
- CE Board May 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 4Document2 pagesCE Board May 2021 - Hydraulics - Set 4Kiesha SantosNo ratings yet
- Camarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummDocument3 pagesCamarines Norte State College: College of Engineering SummjefreyNo ratings yet
- Second Preboard Exam - MsteDocument8 pagesSecond Preboard Exam - MsteCzatrina QuintasNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics (4th Year)Document2 pagesFluid Mechanics (4th Year)Jaypee Calamba100% (1)
- Refresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemDocument1 pageRefresher Module 04 - M6 - Intermodal Transportation SystemKiki Do youNo ratings yet
- Set BDocument12 pagesSet BDan CasuraoNo ratings yet
- Training 1.2.0Document121 pagesTraining 1.2.0Sigue Ramel HinayasNo ratings yet
- Refresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringDocument1 pageRefresher Module 20 - (S6) - Basic-Structural-EngineeringMadelyn Oronos100% (1)
- Total Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyDocument2 pagesTotal Hydrostatic Pressure: P Ha I e AyJocelyn CabarlesNo ratings yet
- RCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersDocument1 pageRCE2018 math and geometry problems solutions under 40 charactersArwin VillegasNo ratings yet
- Quiz No. 3 – CE4 - 01 Surveying LevelsDocument5 pagesQuiz No. 3 – CE4 - 01 Surveying LevelsGanigan GajoNo ratings yet
- Conc 1 - Nov 2020Document2 pagesConc 1 - Nov 2020Glenn CalingasanNo ratings yet
- Refresher MODULE – Construction Estimate and Planning (Part 1Document1 pageRefresher MODULE – Construction Estimate and Planning (Part 1Mohammad Hussein Masiu BacaramanNo ratings yet
- No Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set ADocument4 pagesNo Answer Eval Hydraulics Nov 2018 Set AAlthara BaldagoNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsDocument1 pageHydraulics review module on relative equilibrium of fluidsYeddaMIlaganNo ratings yet
- Fluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingDocument36 pagesFluid Mechanics & Hydraulics Civil Engineering - PRACTICE PROBLEMS - 2017 INSTRUCTION: Select The Correct Answer For Each of The FollowingFrancis Philippe CariñoNo ratings yet
- CE Board 2010 2023 Definition of TermsDocument37 pagesCE Board 2010 2023 Definition of TermsRichard ParedesNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics10 Neric10Document12 pagesHydraulics10 Neric10jrmmansayonNo ratings yet
- Soil Mechanics Problems on Compressibility and Shear StrengthDocument4 pagesSoil Mechanics Problems on Compressibility and Shear Strengthrmle100% (1)
- Auxiliary Lesson - Water HammerDocument6 pagesAuxiliary Lesson - Water HammerEmmanuel MaalaNo ratings yet
- XVI To XVII PDFDocument28 pagesXVI To XVII PDFAmira Ramlee0% (1)
- November 2021 Ce Board Exam Santos 1: Eview NnovationsDocument3 pagesNovember 2021 Ce Board Exam Santos 1: Eview NnovationsamberNo ratings yet
- Preboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingDocument1 pagePreboard2 Psad Situation 2 Pile FootingAngelice Alliah De la CruzNo ratings yet
- Hydraulics Problems and SolutionsDocument8 pagesHydraulics Problems and SolutionsJebone Stein Web JuarbalNo ratings yet
- CE Refresher Course Review: Math and Mechanics ProblemsDocument3 pagesCE Refresher Course Review: Math and Mechanics ProblemsGary BagoNo ratings yet
- Kippap-Handout-MSTE (05 Probability and Statistics)Document2 pagesKippap-Handout-MSTE (05 Probability and Statistics)NaniNo ratings yet
- Pump transfers water between reservoirs: Power, heads, seepage problemsDocument7 pagesPump transfers water between reservoirs: Power, heads, seepage problemsAL YanGaNo ratings yet
- CE199 2L 1Q1819 DC 1st TakeDocument10 pagesCE199 2L 1Q1819 DC 1st TakeJohn Michael Ramos100% (1)
- Activity 2Document2 pagesActivity 2Marben Leynes-Cereno Agustin-ViernesNo ratings yet
- Inhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersDocument1 pageInhouse Practice Problems - RCD-Column - Without AnswersAndrea Sochayseng SolijonNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 - SEPT 2018Document32 pagesTopic 2.2 - SEPT 2018Andrew SebastianNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2 PDFDocument21 pagesTopic 2.2 PDFZadariana JamilNo ratings yet
- Topic 2.2Document35 pagesTopic 2.2Naqib KamarozamanNo ratings yet
- 2017 National Building Cost ManualDocument52 pages2017 National Building Cost ManualNaveen Bansal0% (1)
- Plumbing Material Prices Philippines - PHILCON PRICESDocument33 pagesPlumbing Material Prices Philippines - PHILCON PRICESSolomon Risty Cahulogan0% (1)
- 1096 PDFDocument10 pages1096 PDFSolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Chapter 10 - Depreciation: EGR 403 Capital Allocation TheoryDocument30 pagesChapter 10 - Depreciation: EGR 403 Capital Allocation TheorySolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- 570024Document5 pages570024Solomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Helical spring stress and elongation calculationsDocument4 pagesHelical spring stress and elongation calculationsMavrix AgustinNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions: Definition. If The Random VariableDocument9 pagesChapter 5 Discrete Probability Distributions: Definition. If The Random VariableSolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Yeh - Google Search PDFDocument4 pagesYeh - Google Search PDFSolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Orca Share Media1561345296282Document7 pagesOrca Share Media1561345296282Solomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- How To Find The Equation of A Circle - ACT MathDocument14 pagesHow To Find The Equation of A Circle - ACT MathSolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Moments, Couples, Forces Systems & Force ResolutionDocument28 pagesMoments, Couples, Forces Systems & Force Resolutionvectra7No ratings yet
- Minor Test Sep 2018 Q. Papers MeDocument51 pagesMinor Test Sep 2018 Q. Papers MeSolomon Risty CahuloganNo ratings yet
- Numericals on Interference and DiffractionDocument15 pagesNumericals on Interference and DiffractionPratik WalimbeNo ratings yet
- CH 1. Structure of Atom (Chem +1)Document80 pagesCH 1. Structure of Atom (Chem +1)Rehan AnjashahNo ratings yet
- Installation Manual: Model APS 400Document24 pagesInstallation Manual: Model APS 400Willy DacoNo ratings yet
- Volumes by Shell MethodDocument16 pagesVolumes by Shell Methodayesha noorNo ratings yet
- CalibrationDocument25 pagesCalibrationEka SulistyaningsihNo ratings yet
- CSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMODocument33 pagesCSP Exam Equation Fully Explained DEMOFff63% (8)
- ADV-1 Phase-2 ITR B-Lot T-171473Document15 pagesADV-1 Phase-2 ITR B-Lot T-171473Ashish SharmaNo ratings yet
- SsssDocument17 pagesSsssPhysicsNo ratings yet
- Heisenberg Uncertainty Principle WorksheetDocument4 pagesHeisenberg Uncertainty Principle WorksheetFrank CamachoNo ratings yet
- Aqa 84031 W MS Jun13 PDFDocument18 pagesAqa 84031 W MS Jun13 PDFdadajee420No ratings yet
- Ideal Gas CyclesDocument8 pagesIdeal Gas CyclesMLNDG boysNo ratings yet
- Full Download General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Denniston Test BankDocument35 pagesFull Download General Organic and Biochemistry 8th Edition Denniston Test Bankwaylayfilsaxaq100% (39)
- ElectricityDocument25 pagesElectricityWeb BooksNo ratings yet
- 25 Clicker QuestionsDocument20 pages25 Clicker QuestionsFuentesBrisbaneNo ratings yet
- Viscous ForceDocument20 pagesViscous ForceMostafaNo ratings yet
- Air Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewDocument8 pagesAir Crew Radiation Exposure - An OverviewStarxteelNo ratings yet
- Three-Phase Circuit FundamentalsDocument32 pagesThree-Phase Circuit FundamentalsSathia RajNo ratings yet
- Wellbore Stability AnalysisDocument148 pagesWellbore Stability Analysishagh1234No ratings yet
- RDII - Chapter 5 HandoutDocument8 pagesRDII - Chapter 5 HandoutIlamurianNo ratings yet
- 2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTDocument6 pages2003 Nissan Altima 2.5 Serivce Manual WTAndy DellingerNo ratings yet
- ChemistryDocument5 pagesChemistryTirupal PuliNo ratings yet
- AP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDocument13 pagesAP Chemistry 2010 Free-Response Questions Form B: The College BoardDharul Handri PranawaNo ratings yet
- S-Series Single Stage Gear MotorsDocument138 pagesS-Series Single Stage Gear MotorssirabhijeetNo ratings yet
- Part - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift MathongoDocument37 pagesPart - A (Physics) : Jee Main 2019 - 10 April - Morning Shift Mathongorohit574No ratings yet
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AME, MSNT)Document2 pagesWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: (Common To ME, AME, MSNT)Asheesh KumarNo ratings yet
- EECE 522 Notes - 08 CH - 3 CRLB Examples in BookDocument19 pagesEECE 522 Notes - 08 CH - 3 CRLB Examples in Bookkarim2005No ratings yet
- Chapter 12: Vibrations and Waves: 12.1 Simple Harmonic MotionDocument5 pagesChapter 12: Vibrations and Waves: 12.1 Simple Harmonic MotionSteven SuNo ratings yet
- Capacitors PDFDocument84 pagesCapacitors PDFNaseerUddin100% (1)
- Unit 2Document3 pagesUnit 2V V Satyanarayana PasupuletiNo ratings yet
- BMS481 3.0Document45 pagesBMS481 3.0syuhadahNo ratings yet