Professional Documents
Culture Documents
TECHNICAL DATA ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS AND TEXTURE INDICATION
Uploaded by
dmayhillOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
TECHNICAL DATA ON SURFACE ROUGHNESS AND TEXTURE INDICATION
Uploaded by
dmayhillCopyright:
Available Formats
PD-4 1st
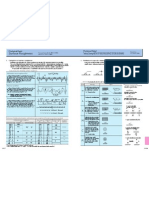
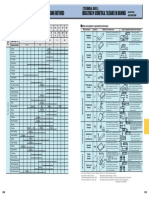
TECHNICAL DATA TECHNICAL DATA
SURFACE ROUGHNESS Excerpt from JIS B 0601(1994)and
JIS B 0031(1994) TECHNICAL DRAWINGS METHOD OF INDICATING SURFACE
TEXTURE ON DRAWINGS
Excerpt from
JIS Z B 0031(1994)
Categories of surface roughness Positions of respective indicating symbols relative to indicating symbol of surface
Definitions and indications for surface roughness parameters(for industrial products)are specified. They are arithmetical mean roughness(Ra), Each grain surface position is indicated as shown in Fig. 1.This includes surface roughness,
maximum height(Ry), ten-point mean roughness(Rz), mean spacing of profile irregularities(Sm), mean spacing of local peaks of the profile(S) cut-off value or reference length, processing method, symbol of direction of lay, surface waviness, etc.
and profile bearing length ratio(tp). Surface roughness is given as the arithmetical mean value for a randomly sampled area. [Mean center line
Fig. 1 Legend
roughness(Ra 75)is defined in the annexes of JIS B 0031 and JIS B 0061].
a :Value of Ra
b :Processing method
Typical ways for obtaining surface roughness b
f c :Cutoff value. Evaluation length
1 r a c
Arithmetical mean roughness(Ra) Ra= r f( x ) d x
c c :Reference length. Evaluation length
Y 0 e d g e d g
m d :Symbol of direction of lay
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on the
roughness chart. The mean line is laid on a Cartesian coordinate f :Parameter other than Ra(With tp, parameter/cutoff level)
system wherein the mean line runs in the direction of the x-axis and g :Surface waviness(according to JIS B 0610)
Ra
magnification is the y-axis.The value obtained with the formula on 0 X Note: Items other than a and f are added as necessary.
the right is expressed in micrometer Reference:The location of lay of e in Fig. 1.is given as the finish allowance in ISO 1302.
r
(Om)when y=f(a) .
Symbol Meaning Figure
IExamples indicating surface texture on drawing
Maximum peak(Ry) r
Indicating symbol of surface
m Parallel to the projected surface on
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on the
which the direction of lay of the
roughness chart. The distance between the peaks and valleys of the
Rp
Ry
cutting blade is indicated.
sampled line is measured in the y direction. The value is expressed
(ex) Shaped surface Direction of lay
in micrometer(Om) .
Rv
of cutting blade Indicating symbol of surface requiring removal press
Note:To obtain Ry, sample only the standard length. The part, where peaks and
valleys are wide enough to be interpreted as scratches, should be avoided. Ry=Rp+Rv
Perpendicular to the projected surfa-
Ten-point mean roughness(Rz) m ce on which the direction of lay of the Indicating symbol of surface on which no removal process is permitted
Yp 1
Yp4
cutting blade is indicated.
Yp 2
A section of standard length is sampled from the mean line on the
Yp 5
roughness chart. The distance between the peaks and valleys of the Yp 3 (ex)Shaped surface( when viewed Direction of lay
Y V3
of cutting blade
Y V2
from the side), machined or cyli-
Y V1
Y V4
Y V5
sampled line is measured in the y direction.
r ndrical ground surface.
Then, the average peak is obtained among 5 tallest peaks(Yp) , as
is the average valley between 5 lowest valleys(Yv). Examples indicating the upper limits of Ra
Yp1+Yp2+Yp3+Yp4+Yp 5 + Yv1+Yv 2+Yv 3+Yv 4+Yv 5
The sum of these two values is expressed in micrometer(Om). Rz= Intersection of two diagonal lines on the
5 (a) (b) (c)
projected surface on which the direction of
Yp1, Yp2, Yp3, Yp4, Yp5: Tallest 5 peaks within sample lay of the cutting blade is indicated. 25 6.3 25
Honing finished surface
(ex) Direction of lay
Yv1, Yv2, Yv3, Yv4, Yv5: Lowest 5 peaks within sample of cutting blade
25 6.3 25
Multidirectional intersection or non-
directional point on the projected surface
Reference:Relationship between arithmetical mean roughness(Ra)and conventional symbols on which the direction of lay of the
Standard length cutting blade is indicated. Examples indicating direction of lay
Arithmetical mean roughness Max. height Ten-point mean roughness
Triangular
Ra Ry Rz of RyCRz (ex)Rapping finished surface, super
indication
Preferred number series Cut-off value
Indication of surface texture on drawings Preferred number series r (mm) finished surface, face milled or end
c(mm)
milled surface in surfacing feed
0.012 a 0.08 0.05 s 0.05 z
0.08 direction
0.025 a 0.1 s 0.1 z
0.25 0.012 ~ 0.2
0.05 a 0.2 s 0.2 z Concentric circles roughly centered
0.25 Examples indicating the upper limit and lower limit of Ra
0.1 a 0.4 s 0.4 z on the same on the surface on which
0.2 a 0.8 s 0.8 z (a) (b)
the direction of lay of the cutting
0.4 a 0.8 1.6 s 1.6 z blade is indicated. 6.3
0.8 a 0.4 ~ 1.6 3.2 s 3.2 z 0.8 1.6
(ex) Facing surface
1.6 a 6.3 s 6.3 z 6.3
1.6
3.2 a 12.5 s 12.5 z
0.25 3.2 ~ 6.3
6.3 a 25 s 25 z 0.25 Radiating shape roughly centered
Examples indicating processing method
12.5 a 50 s 50 z on the same point on the surface
12.5 ~ 25 (a) (b)
25 a 8 100 s 100 z on which the direction of lay of the
8 cutting blade is indicated.
Front milled M
50 a 200 s 200 z 3.2 3.2
50 ~ 100 ~
100 a - 400 s 400 z -
GThe interdependence for 3 classes is not strictly enforced.
GThe evaluation length of Ra, Ry and Rz:Five times the cut-off value standard length respectively.
1167 1168
You might also like
- Domex Welding PDFDocument16 pagesDomex Welding PDFAgourame Abderrahmane100% (1)
- Standard GB - T1804-m & ISO 2768-1 - 2 - Advanced CeramicsDocument5 pagesStandard GB - T1804-m & ISO 2768-1 - 2 - Advanced CeramicsMohd DanishNo ratings yet
- SAE J1926, MS 16142 - CuttersDocument11 pagesSAE J1926, MS 16142 - CutterspbsurfNo ratings yet
- DIN en 462-1 Image Quality of Radiographs (Wire Type)Document10 pagesDIN en 462-1 Image Quality of Radiographs (Wire Type)QA QC100% (2)
- En Iso 15609-1-2004Document10 pagesEn Iso 15609-1-2004Marija IvanovskaNo ratings yet
- Aisi 1018Document1 pageAisi 10188085roNo ratings yet
- Supraform S315-700 MC / EN10149-2 S315-700 MC: Hot Rolled High Strength Low Alloy Structural Steel CoilDocument2 pagesSupraform S315-700 MC / EN10149-2 S315-700 MC: Hot Rolled High Strength Low Alloy Structural Steel CoilHugo RodriguezNo ratings yet
- ISO-10664Document10 pagesISO-10664Daniel Quijada LucarioNo ratings yet
- Ford Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledDocument7 pagesFord Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are Uncontrolledferhat aydoganNo ratings yet
- DIN ISO Equivalent FastenersDocument12 pagesDIN ISO Equivalent FastenersGunnie PandherNo ratings yet
- Worldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledDocument2 pagesWorldwide Fastener Standard: Printed Copies Are UncontrolledRasatja Yongskulrote100% (1)
- Surface Comparator Chart Sa 2 5Document5 pagesSurface Comparator Chart Sa 2 5Vebryan SyahNo ratings yet
- Standards Din HANDBOOKDocument7 pagesStandards Din HANDBOOKbhartiNo ratings yet
- Din en Iso 1302Document51 pagesDin en Iso 1302vijayanth gNo ratings yet
- Astm A31 (1995)Document4 pagesAstm A31 (1995)gsb2100% (1)
- Din 76-1Document5 pagesDin 76-1mesa142No ratings yet
- EN10034 Beams Rolling TolerancesDocument2 pagesEN10034 Beams Rolling Tolerancesrameshdatta100% (1)
- EN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steel.Document6 pagesEN 10025: 2004 Is The New European Standard For Structural Steel.Alin DavidNo ratings yet
- SAE 1018 - Data Sheet PDFDocument1 pageSAE 1018 - Data Sheet PDFHari SuthanNo ratings yet
- ISO 1302 DIN 4768 Comparison of Surface Roughness Values Stainless Steel T PDFDocument2 pagesISO 1302 DIN 4768 Comparison of Surface Roughness Values Stainless Steel T PDFYohanes Wahyu TdNo ratings yet
- Thread Gauge ISO1502 PDFDocument5 pagesThread Gauge ISO1502 PDFBaldev SinghNo ratings yet
- ASME B1.13M - 2005 (Reaffirmed 2010) PDFDocument84 pagesASME B1.13M - 2005 (Reaffirmed 2010) PDFKristin JonesNo ratings yet
- Din 3760 KeçeDocument13 pagesDin 3760 KeçeUfuk YürekNo ratings yet
- VW 13750Document16 pagesVW 13750Reginaldo Santos100% (1)
- Surface RoughnessDocument35 pagesSurface Roughnessds_srinivasNo ratings yet
- Vdocuments - MX Din 405 Universo For Knuckle Thread Din 405Document7 pagesVdocuments - MX Din 405 Universo For Knuckle Thread Din 405wauwio1906No ratings yet
- Is 11166 PDFDocument13 pagesIs 11166 PDFAnonymous NRlowQUcn100% (1)
- GB T 1804 200Document7 pagesGB T 1804 200dreamingscientist3393No ratings yet
- Foreword: ISO 7044:2012 (En) Prevailing Torque Type All-Metal Hexagon Nuts With Flange, Style 2 - Product Grades A and BDocument4 pagesForeword: ISO 7044:2012 (En) Prevailing Torque Type All-Metal Hexagon Nuts With Flange, Style 2 - Product Grades A and BMarcelo KleinNo ratings yet
- Astm A312 PDFDocument12 pagesAstm A312 PDFStephen TilleyNo ratings yet
- AISI 1015: Digest DDocument2 pagesAISI 1015: Digest DGovinda RajNo ratings yet
- Din1688 1 PDFDocument4 pagesDin1688 1 PDFFelipe FernandesNo ratings yet
- Welding StandardsDocument31 pagesWelding StandardsRakeshNo ratings yet
- Sfa-5 8 PDFDocument24 pagesSfa-5 8 PDFgst ajahNo ratings yet
- As 1897-1976 Electroplated Coatings On Threaded Components (Metric Coarse Series)Document11 pagesAs 1897-1976 Electroplated Coatings On Threaded Components (Metric Coarse Series)SAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Iso 15330 en PDFDocument6 pagesIso 15330 en PDFScube engineersNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Steel Standards - VoestalpineDocument14 pagesComparison of Steel Standards - VoestalpineAnonymous 6aGAvbN100% (1)
- En 10051 PDFDocument2 pagesEn 10051 PDFSrikanth Reddy0% (1)
- Saej 356 V 002Document7 pagesSaej 356 V 002Evandro Luis GomesNo ratings yet
- Asme B1.13M-2005Document84 pagesAsme B1.13M-2005Anuj Garg100% (1)
- EN 10025 S275 Steel (S275JR, S275J0 & S275J2)Document3 pagesEN 10025 S275 Steel (S275JR, S275J0 & S275J2)MohamedNo ratings yet
- Mil H 25579Document22 pagesMil H 25579Senthil KumarNo ratings yet
- ISO 8062 3 2007 Casting Tolerance PDFDocument1 pageISO 8062 3 2007 Casting Tolerance PDFPankajMakwanaNo ratings yet
- Astm B446 - 2003 - 2008Document5 pagesAstm B446 - 2003 - 2008isaque300984No ratings yet
- International Standard: Stainless Steels For Springs - WireDocument8 pagesInternational Standard: Stainless Steels For Springs - WireAfzal ImamNo ratings yet
- WPS Format For ISO 15614-1 WPSDocument1 pageWPS Format For ISO 15614-1 WPSThe Welding Inspections CommunityNo ratings yet
- GuidanceNotes EN131 Version2Document10 pagesGuidanceNotes EN131 Version2Javier Quintero SaavedraNo ratings yet
- Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials: Standard Test Method ForDocument33 pagesBrinell Hardness of Metallic Materials: Standard Test Method ForRichard AlcaldeNo ratings yet
- Iso 2768Document5 pagesIso 2768thanhhai130No ratings yet
- 7 1-2008Document8 pages7 1-2008SAI Global - APACNo ratings yet
- Projection Welding NutDocument1 pageProjection Welding NutMadhav RajpurohitNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness Drawing Indications of Surface TextureDocument1 pageSurface Roughness Drawing Indications of Surface TextureSIVA 1010No ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 pageSurface RoughnesswholenumberNo ratings yet
- Surface Texture SymbolDocument1 pageSurface Texture SymbolSrinivas RaoNo ratings yet
- Surface RoughnessDocument1 pageSurface Roughnessapi-3848892100% (2)
- Measuring Surface Roughness: Drawing Symbols (DIN EN ISO 1302:2002)Document1 pageMeasuring Surface Roughness: Drawing Symbols (DIN EN ISO 1302:2002)SudhagarNo ratings yet
- Surface Roughness JIS B 0601 (1994)Document1 pageSurface Roughness JIS B 0601 (1994)Tú Nguyễn MinhNo ratings yet
- pr1169 1170 PDFDocument1 pagepr1169 1170 PDFrahulmuleNo ratings yet
- 1 ECI 2015 Final ProgramDocument122 pages1 ECI 2015 Final ProgramDenada Florencia LeonaNo ratings yet
- grr5504 1e Emeraldcity Playersguidev11Document94 pagesgrr5504 1e Emeraldcity Playersguidev11Kánya Zoltán100% (1)
- Theories and Models of Organizational DevelopmentDocument4 pagesTheories and Models of Organizational DevelopmentHappy Singh88% (8)
- Cover Page ( (DLW 5013) ) 11 April 2020 - .222 PDFDocument4 pagesCover Page ( (DLW 5013) ) 11 April 2020 - .222 PDFElamaaran AlaggarNo ratings yet
- Study PlanDocument1 pageStudy PlanMTINo ratings yet
- IRL - Information Request List For Performance DiagnosticsDocument3 pagesIRL - Information Request List For Performance Diagnosticsd280299No ratings yet
- CGC Construction Handbook Ch9 Acoustical Ceiling Design and Application Can en PDFDocument26 pagesCGC Construction Handbook Ch9 Acoustical Ceiling Design and Application Can en PDFKeri Gobin SamarooNo ratings yet
- Video WorksheetDocument9 pagesVideo Worksheetapi-316047658100% (1)
- Detection of Structural Damage in Building Using Changes in Modal Damping Mechanism (2012) - Paper PDFDocument6 pagesDetection of Structural Damage in Building Using Changes in Modal Damping Mechanism (2012) - Paper PDFJulio Humberto Díaz RondánNo ratings yet
- RS: Railway reservation systemDocument6 pagesRS: Railway reservation systemSaravana KumarNo ratings yet
- Understanding A Brain Based Approach To Learning PDFDocument6 pagesUnderstanding A Brain Based Approach To Learning PDFChandrika SimadereyNo ratings yet
- QC Story TRAINING SLIDEDocument47 pagesQC Story TRAINING SLIDEDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE83% (6)
- Recruitment Needs Are of Three Types: PlannedDocument7 pagesRecruitment Needs Are of Three Types: PlannedShraddha MomayaNo ratings yet
- Tips for Kerala PSC Exam on Office ToolsDocument3 pagesTips for Kerala PSC Exam on Office ToolsSameer MaheNo ratings yet
- College New Prospectus PDFDocument32 pagesCollege New Prospectus PDFJawad ArifNo ratings yet
- Astro-Vision Pancha-Pakshi Shastra ExplainedDocument17 pagesAstro-Vision Pancha-Pakshi Shastra ExplainedVensun Reddy100% (5)
- Gas Dynamic Resonance Ignition For Repetitive StartsDocument8 pagesGas Dynamic Resonance Ignition For Repetitive StartsBrunno VasquesNo ratings yet
- 1Document37 pages1Phuong MaiNo ratings yet
- Computer Science Important Question For Class 12 C++Document24 pagesComputer Science Important Question For Class 12 C++Ravi singhNo ratings yet
- Database AdministrationDocument12 pagesDatabase AdministrationjayNo ratings yet
- Cyril Acott - Occultism - An Alternative To Scientific HumanismDocument20 pagesCyril Acott - Occultism - An Alternative To Scientific Humanismparadigmshifter6360100% (2)
- C QuestionsDocument6 pagesC QuestionsRanjith RanjithNo ratings yet
- THEORY Transformation Question BankDocument7 pagesTHEORY Transformation Question Bankpankaj12345katreNo ratings yet
- Snorks Udl Lesson Plan-1Document4 pagesSnorks Udl Lesson Plan-1api-253110466No ratings yet
- Essay One Othering and Rhetorical AnalysisDocument7 pagesEssay One Othering and Rhetorical Analysisapi-324018733No ratings yet
- Homeopathy BrochureDocument2 pagesHomeopathy Brochuresrwelling67% (3)
- G10 Q3 PPT3Document20 pagesG10 Q3 PPT3Ma. Shiela Mira NarceNo ratings yet
- Etienne Gilson - The Christian Philosophy of St. Augustine PDFDocument418 pagesEtienne Gilson - The Christian Philosophy of St. Augustine PDFMihai Sarbu95% (21)
- 01 AP1 Graphical Analysis Motion SDocument6 pages01 AP1 Graphical Analysis Motion SGevans GabeauNo ratings yet