Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Integrated Gaps Model of Service Quality: MKTG/HTM 386
Uploaded by
jaiswalpraveeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The Integrated Gaps Model of Service Quality: MKTG/HTM 386
Uploaded by
jaiswalpraveeCopyright:
Available Formats
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
The Integrated Gaps Model of
Service Quality
MKTG/HTM 386
Why is the Gaps Model of
Service Quality Important?
Customer Gap
n Chp 2 – Consumer Behavior in Services
n Chp 3 – Customer Expectations of Service
n Chp 4 – Consumer Perceptions of Service
Gap 1 – Not Knowing What the Customer
Expects
n Chp 5 – Understanding Customer Expectations
Through Marketing Research
n Chp 6 – Building Customer Relationships
n Chp 7 – Service Recovery
James Madison University - College of
Business 1
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
Why is the Gaps Model of
Service Quality Important?
Gap 2 – Not Having the Right Service
Quality Designs and Standards
n Chp 8 – Service Development and Design
n Chp 9 – Customer-Defined Service
Standards
n Chp 10 – Physical Evidence and the
Servicescape
Why is the Gaps Model of
Service Quality Important?
Gap 3 – Not Delivering to Service Standards
n Chp 11 – Employee’s Roles in Service Delivery
n Chp 12 – Customer’s Roles in Service Delivery
n Chp 13 – Delivering Services Through
Intermediaries and Electronic Channels
n Chp 14 – Managing Demand and Capacity
Gap 4 – Not Matching Performance to
Promises
n Chp 15 – Integrating Services Marketing
Communications
n Chp 16 – Pricing of Services
James Madison University - College of
Business 2
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
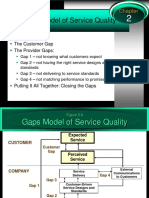
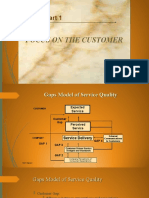
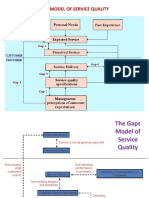
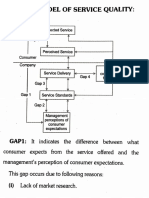
Figure 18-1
Gaps Model of Service Quality
Expected
Service
CUSTOMER
Customer
Gap
Perceived
Service
External
COMPANY Service Delivery Communications
GAP 4 to Customers
GAP 1 GAP 3
Customer -Driven Service
Designs and Standards
GAP 2
Company Perceptions of
Consumer Expectations
Figure 18-2
Key Factors Leading to
the Customer Gap
Customer
Expectations
Customer
Gap
l Provider Gap 1: Not knowing what customers expect
l Provider Gap 2: Not selecting the right service designs and standards
l Provider Gap 3: Not delivering to service standards
l Provider Gap 4: Not matching performance to promises
Customer
Perceptions
James Madison University - College of
Business 3
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
Figure 18-3
Key Factors Leading to Provider Gap 1
Customer
Expectations
GAP q Inadequate Marketing Research Orientation
Insufficient marketing research
1 Research not focused on service quality
Inadequate use of market research
q Lack of Upward Communication
Lack of interaction between management and customers
Insufficient communication between contact employees
and managers
Too many layers between contact personnel and top
management
q Insufficient Relationship Focus
Lack of market segmentation
Focus on transactions rather than relationships
Focus on new customers rather than relationship
customers
q Inadequate Service Recovery
Company Perceptions of
Customer Expectations
Figure 18-4
Key Factors Leading to Provider Gap 2
Customer-Driven Service
Designs and Standards
q Poor Service Design
Unsystematic new service development process
GAP Vague, undefined service designs
Failure ot connect service design to service
2 positioning
q Absence of Customer-Driven Standards
Lack of customer-driven service standards
Absence of process management to focus on
customer requirements
Absence of formal process for setting service
quality goals
q Inappropriate Physical Evidence and Servicescape
Management Perceptions
of Customer
Expectations
James Madison University - College of
Business 4
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
Figure 18-5
Key Factors Leading to Provider GAP 3
Customer-Driven Service
Designs and Standards
q Deficiencies in Human Resource Policies
GAP Ineffective recruitment
Role ambiguity and role conflict
3 Poor employee-technology job fit
Inappropriate evaluation and compensation systems
Lack of empowerment, perceived control and teamwork
q Failure to Match Supply and Demand
Failure to smooth peaks and valleys of demand
Inappropriate customer mix
Over-reliance on price to smooth demand
q Customers Not Fulfilling Roles
Customers lack knowledge of their roles and responsibilities
Customers negatively impact each other
q Problems with Service Intermediaries
Channel conflict over objectives and performance
Channel conflict over costs and rewards
Difficulty controlling quality and consistency
Tension between empowerment and control
Service Delivery
Figure 18-6
Key Factors Leading to Provider GAP 4
Service Delivery
q Lack of Integrated Services Marketing Communications
Tendency to view each external communication as
independent
GAP Not including interactive marketing in communications plan
Absence of strong internal marketing program
4 q Ineffective Management of Customer Expectations
Not managing customer expectations through all forms of
communication
Not adequately educating customers
q Overpromising
Overpromising in advertising
Overpromising in personal selling
Overpromising through physical evidence cues
q Inadequate Horizontal Communications
Insufficient communication between sales and operations
Insufficient communication between advertising and operations
Differences in policies and procedures across branches or units
External Communications to
Customers
James Madison University - College of
Business 5
MKTG/HTM 386 -- Hospitality Services Spring 2001
Marketing
Team Discussion Questions
If you were a manager of a service
organization and wanted to apply the gaps
model to improve service, which gap would
you start with? Why? In what order would
you proceed to close the gaps?
Can provider gap 4 be closed prior to closing
any of the other three provider gaps? How?
Which of the four provider gaps do you
believe is the hardest to close? Why?
James Madison University - College of
Business 6
You might also like
- IMC, The Next Generation: Five Steps for Delivering Value and Measuring Returns Using Marketing CommunicationFrom EverandIMC, The Next Generation: Five Steps for Delivering Value and Measuring Returns Using Marketing CommunicationRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (4)
- Poverty and Crime PDFDocument17 pagesPoverty and Crime PDFLudwigNo ratings yet
- Life Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFDocument132 pagesLife Sciences Part 1 CSIR JRF NET GATE DBT PDFPavani Reddy68% (22)
- Unit 3 Gap Model of Service QualityDocument58 pagesUnit 3 Gap Model of Service QualityRuchika JainNo ratings yet
- Haematology Notes - 3rd EdDocument100 pagesHaematology Notes - 3rd EdSally Brit100% (1)
- GTT Module 5Document156 pagesGTT Module 5ABDULRAHIMAN RAJEKHANNo ratings yet
- MKTG 386 Hospitality Services Gaps ModelDocument6 pagesMKTG 386 Hospitality Services Gaps ModelEmad Al-AmadNo ratings yet
- The Big Picture: Closing All The Gaps: Mcgraw-Hill © 2000 The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniesDocument8 pagesThe Big Picture: Closing All The Gaps: Mcgraw-Hill © 2000 The Mcgraw-Hill CompaniessangitaNo ratings yet
- Service Marketing - Lesson 02 - Gap Theory - Modified 13.05.2019Document20 pagesService Marketing - Lesson 02 - Gap Theory - Modified 13.05.2019Santosh KarakNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument10 pagesGaps Model of Service Qualitymubarak@No ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument11 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityNidhi SomaniNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument10 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityAPOORVA GUPTANo ratings yet
- Serqual ModelDocument19 pagesSerqual ModelSuraj OVNo ratings yet
- The Gap Model of Service QualityDocument16 pagesThe Gap Model of Service QualityVettri MaranNo ratings yet
- SM-7-Service Quality GAPS ModelDocument42 pagesSM-7-Service Quality GAPS ModelHimansu S M100% (1)
- Gap Model of Service Quality: Group1 Manuara Chisty Mayur Parvani Farah Deepa Jince AbrahamDocument14 pagesGap Model of Service Quality: Group1 Manuara Chisty Mayur Parvani Farah Deepa Jince AbrahamMayur ParvaniNo ratings yet
- Bridging the GapsDocument56 pagesBridging the GapsKazi Rabbi Al AzizNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument11 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityPrashant PathakNo ratings yet
- Role of Service Quality in Providing Customer ValueDocument15 pagesRole of Service Quality in Providing Customer ValueKittu KewlaniNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service Quality Part 1Document4 pagesGaps Model of Service Quality Part 1DrSachin SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- Services Marketing: Presentation By, Dr. Basavaraj S.KudachimathDocument51 pagesServices Marketing: Presentation By, Dr. Basavaraj S.KudachimathBasavaraj KudachimathNo ratings yet
- CH 02Document18 pagesCH 02Afjal HossainNo ratings yet
- Service Marketing - Chapter 2 - The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument24 pagesService Marketing - Chapter 2 - The Gaps Model of Service QualityAtique FaisalNo ratings yet
- Service Productivity and Quality ControlDocument22 pagesService Productivity and Quality ControlaparnaskiniNo ratings yet
- Service QualityDocument23 pagesService QualityrutujazworldNo ratings yet
- GAP Model of Service QualityDocument21 pagesGAP Model of Service QualityDeeps KaleNo ratings yet
- S MKT 02Document17 pagesS MKT 02Afjal HossainNo ratings yet
- Icici Bank FinalDocument25 pagesIcici Bank Finaldinesh mehlawatNo ratings yet
- Customer Satisfaction and Service Quality in Four Wheeler Automobile Service Industry: A ReviewDocument4 pagesCustomer Satisfaction and Service Quality in Four Wheeler Automobile Service Industry: A ReviewShiyaNo ratings yet
- Gaps Analysis For Customer Service MeasurementcDocument4 pagesGaps Analysis For Customer Service MeasurementcsoniankitaNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document10 pagesChap 002onlyforcat4735No ratings yet
- Gaps Model in Service QualityDocument24 pagesGaps Model in Service Qualitykiruba kiruNo ratings yet
- Lit Revw Shah SirDocument3 pagesLit Revw Shah SirShuvo ChowdhuryNo ratings yet
- Consumer ExpectationDocument9 pagesConsumer ExpectationKamaldeep Singh OberoiNo ratings yet
- Service Design and DevelopmentDocument21 pagesService Design and DevelopmentkovendhNo ratings yet
- Integrated Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument8 pagesIntegrated Gaps Model of Service QualitykritikandhariNo ratings yet
- Marketing Services Using the Gaps ModelDocument10 pagesMarketing Services Using the Gaps ModelArpita BajajNo ratings yet
- bus 5062-topic 4Document25 pagesbus 5062-topic 4drzubeir8No ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service Quality: "Service Marketing", Valarie A. Zeithaml & Mary Jo BitnerDocument16 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service Quality: "Service Marketing", Valarie A. Zeithaml & Mary Jo BitnerMohammed ObaidNo ratings yet
- Customer Expectations of ServicesDocument6 pagesCustomer Expectations of ServicessakibNo ratings yet
- Gap ModelDocument5 pagesGap ModelArushiNo ratings yet
- Gap ModelDocument17 pagesGap Modelsadaf_gul_7No ratings yet
- 22 Laws of BrandingDocument7 pages22 Laws of BrandingGten UNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument17 pagesGaps Model of Service QualitySadman EvanNo ratings yet
- Gap Analysis of Banking ServiceDocument29 pagesGap Analysis of Banking ServiceMahbubul Islam KoushickNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service Quality ExplainedDocument11 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service Quality ExplainedChandan MallikNo ratings yet
- Gap ModelDocument16 pagesGap ModelSagar PaulNo ratings yet
- Service Quality Issues in Financial ServicesDocument14 pagesService Quality Issues in Financial ServicesVardhan SinghNo ratings yet
- Chap 002Document16 pagesChap 002samee khanNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service Quality ExplainedDocument10 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service Quality ExplainedDebadarshi RoyNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument20 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityMoneimul IslamNo ratings yet
- Services MarketingDocument21 pagesServices Marketingpawan_talwareNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument9 pagesGaps Model of Service QualityTanusha LakshmananNo ratings yet
- Marketing Services - Chap002Document16 pagesMarketing Services - Chap002Renjumul MofidNo ratings yet
- Service Marketing Chapter 2Document17 pagesService Marketing Chapter 2laimeysanNo ratings yet
- The Basis of The Servqual Model: The Gaps The Key Service Dimensions Causes & Solutions To GapsDocument18 pagesThe Basis of The Servqual Model: The Gaps The Key Service Dimensions Causes & Solutions To GapsTanmayNo ratings yet
- Module 16 - Exercise 2- Applying the SERVQUAL GAPS ModelDocument5 pagesModule 16 - Exercise 2- Applying the SERVQUAL GAPS ModelJay DaveNo ratings yet
- ServqualDocument8 pagesServqualNandini KumarNo ratings yet
- The Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument16 pagesThe Gaps Model of Service QualityNidhi Ratna JaiswalNo ratings yet
- The Gap Model: Service QualityDocument15 pagesThe Gap Model: Service QualitythanhnganzuizeNo ratings yet
- Marketing Services - Chap002Document16 pagesMarketing Services - Chap002FazleRabbiNo ratings yet
- Gaps Model of Service QualityDocument32 pagesGaps Model of Service QualityjaitleyarushiNo ratings yet
- 8m_MDSBANKDocument18 pages8m_MDSBANKĐinh Hồng AnhNo ratings yet
- Quality ImprovementDocument3 pagesQuality ImprovementViky SinghNo ratings yet
- Kertas Trial English Smka & Sabk K1 Set 2 2021Document17 pagesKertas Trial English Smka & Sabk K1 Set 2 2021Genius UnikNo ratings yet
- Schneider Electric PowerPact H-, J-, and L-Frame Circuit Breakers PDFDocument3 pagesSchneider Electric PowerPact H-, J-, and L-Frame Circuit Breakers PDFAnonymous dH3DIEtzNo ratings yet
- Mufon Ufo JournalDocument21 pagesMufon Ufo JournalSAB78No ratings yet
- Completed Manuscript 1 5Document52 pagesCompleted Manuscript 1 5SAMANTHA LACABANo ratings yet
- Aplikasi Berbagai Jenis Media Dan ZPT Terhadap Aklimatisasi Anggrek VandaDocument15 pagesAplikasi Berbagai Jenis Media Dan ZPT Terhadap Aklimatisasi Anggrek VandaSihonoNo ratings yet
- Quality Nutrition and Dietetics PracticeDocument3 pagesQuality Nutrition and Dietetics PracticeNurlienda HasanahNo ratings yet
- Erapol EHP95ADocument2 pagesErapol EHP95AMohammad Doost MohammadiNo ratings yet
- Stress and FilipinosDocument28 pagesStress and FilipinosDaniel John Arboleda100% (2)
- Annex 8 Qualification of BalancesDocument11 pagesAnnex 8 Qualification of BalancesMassimiliano PorcelliNo ratings yet
- Board Review Endocrinology A. ApiradeeDocument47 pagesBoard Review Endocrinology A. ApiradeePiyasak NaumnaNo ratings yet
- Speaking Coursebook C1.1Document80 pagesSpeaking Coursebook C1.1Yến VõNo ratings yet
- Spec BoilerDocument9 pagesSpec BoilerAchmad MakmuriNo ratings yet
- Abstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFDocument634 pagesAbstract - Tropen Tag 2011 PDFzmoghesNo ratings yet
- Clinical Case Report No 2Document11 pagesClinical Case Report No 2ملک محمد صابرشہزاد50% (2)
- PHAR342 Answer Key 5Document4 pagesPHAR342 Answer Key 5hanif pangestuNo ratings yet
- Job Satisfaction RRLDocument39 pagesJob Satisfaction RRLMarie Tiffany100% (1)
- GSIS vs. de LeonDocument9 pagesGSIS vs. de Leonalwayskeepthefaith8No ratings yet
- Funds Flow Statement ExplainedDocument76 pagesFunds Flow Statement Explainedthella deva prasad0% (1)
- Wastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFDocument68 pagesWastewater Treatment Plant Design PDFmostafa1alaahobaNo ratings yet
- Executive Order 000Document2 pagesExecutive Order 000Randell ManjarresNo ratings yet
- Jairo Garzon 1016001932 G900003 1580 Task4Document12 pagesJairo Garzon 1016001932 G900003 1580 Task4Jairo Garzon santanaNo ratings yet
- OC - PlumberDocument6 pagesOC - Plumbertakuva03No ratings yet
- BS 5911-120Document33 pagesBS 5911-120Niranjan GargNo ratings yet
- Cot 1 Vital SignsDocument22 pagesCot 1 Vital Signscristine g. magatNo ratings yet
- TS4-F - Fire SafetyDocument2 pagesTS4-F - Fire SafetyDominic SantiagoNo ratings yet